The Impact of Severe COVID-19 on Plasma Antioxidants
et al., Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27165323, Aug 2022
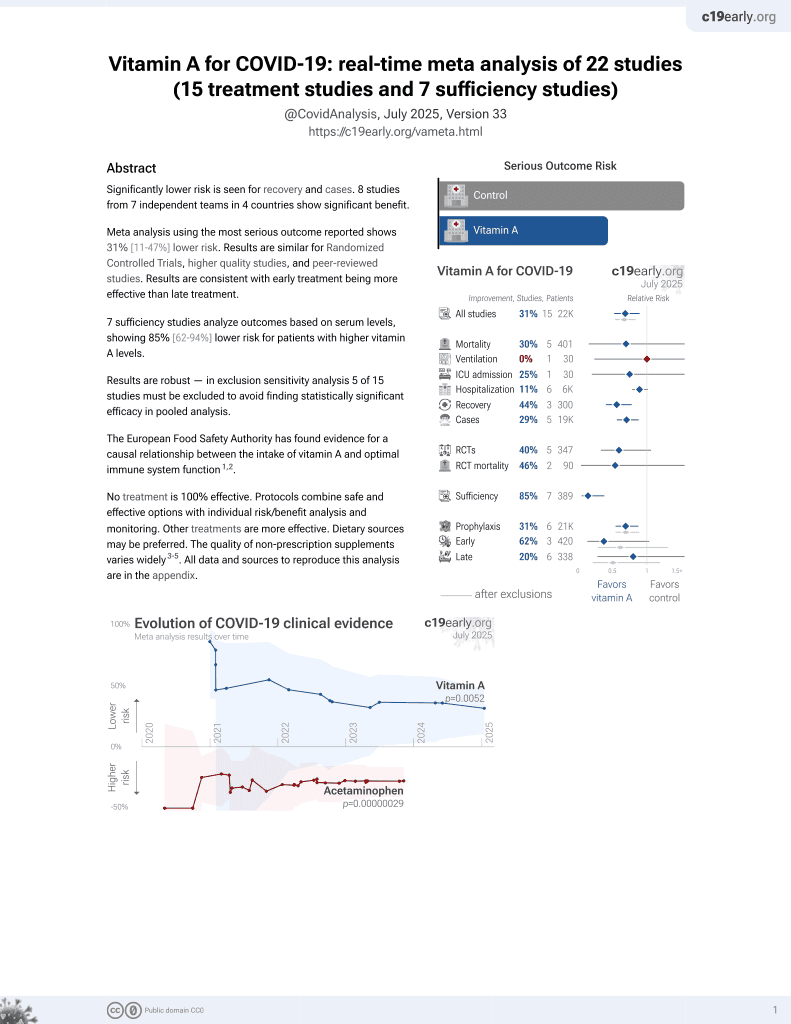
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
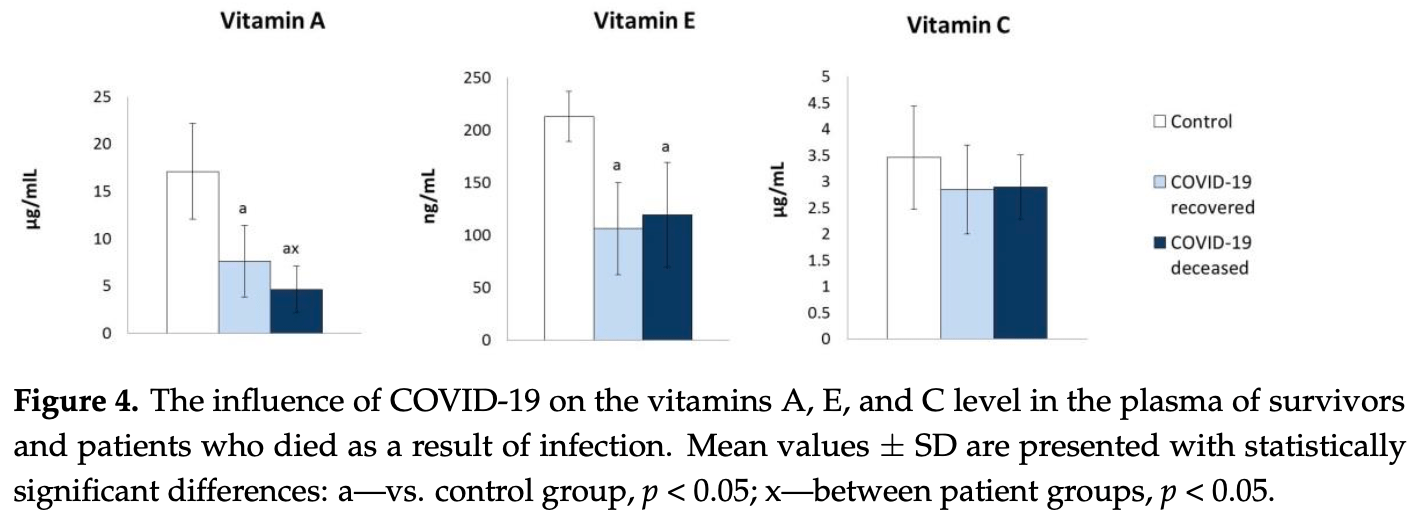
Retrospective 88 COVID-19 patients and 33 healthy controls, showing significantly lower vitamin A levels in COVID-19 patients vs. healthy controls, and in patients that did not survive vs. survivors. Patient ages were significantly different between groups.
Žarković et al., 21 Aug 2022, Croatia, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: zarkovic@irb.hr (corresponding author).
The Impact of Severe COVID-19 on Plasma Antioxidants
Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27165323
Several studies suggested the association of COVID-19 with systemic oxidative stress, in particular with lipid peroxidation and vascular stress. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant signaling in the plasma of eighty-eight patients upon admission to the Clinical Hospital Dubrava in Zagreb, of which twenty-two died within a week, while the other recovered. The differences between the deceased and the survivors were found, especially in the reduction of superoxide dismutases (SOD-1 and SOD-2) activity, which was accompanied by the alteration in glutathione-dependent system and the intensification of the thioredoxin-dependent system. Reduced levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants, especially tocopherol, were also observed, which correlated with enhanced lipid peroxidation (determined by 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and neuroprostane levels) and oxidative modifications of proteins assessed as 4-HNE-protein adducts and carbonyl groups. These findings confirm the onset of systemic oxidative stress in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2, especially those who died from COVID-19, as manifested by strongly reduced tocopherol level and SOD activity associated with lipid peroxidation. Therefore, we propose that preventive and/or supplementary use of antioxidants, especially of lipophilic nature, could be beneficial for the treatment of COVID-19 patients.
References
Amatore, Sgarbanti, Aquilano, Baldelli, Limongi et al., Influenza Virus Replication in Lung Epithelial Cells Depends on Redox-Sensitive Pathways Activated by NOX4-Derived ROS, Cell. Microbiol, doi:10.1111/cmi.12343
Anca, Toth, Kempler, Rizzo, Gender Differences in the Battle against COVID-19: Impact of Genetics, Comorbidities, Inflammation and Lifestyle on Differences in Outcomes, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13666
Ayala, Muñoz, Argüelles, Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2014/360438
Bekyarova, Tzaneva, Bratoeva, Ivanova, Kotzev et al., 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) and Hepatic Injury Related to Chronic Oxidative Stress, Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip
Belikov, Schraven, Simeoni, Cells and Reactive Oxygen Species, J. Biomed Sci, doi:10.1186/s12929-015-0194-3
Busnadiego, Kane, Rihn, Preugschas, Hughes et al., Host and Viral Determinants of Mx2 Antiretroviral Activity, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00214-14
Chen, Tian, She, Cai, Li, Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.025
Chung, Zhang, Wooten, Borrelia Burgdorferi Elicited-IL-10 Suppresses the Production of Inflammatory Mediators, Phagocytosis, and Expression of Co-Stimulatory Receptors by Murine Macrophages and/or Dendritic Cells, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084980
Contoli, Papi, Tomassetti, Rizzo, Vieceli Dalla Sega et al., Blood Interferon-α Levels and Severity, Outcomes, and Inflammatory Profiles in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.648004
Coolen, Van Buuren, Duchateau, Upritchard, Verhagen, Kinetics of Biomarkers: Biological and Technical Validity of Isoprostanes in Plasma, Amino Acids, doi:10.1007/s00726-005-0229-2
Cuadrado, Rojo, Wells, Hayes, Cousin et al., Therapeutic Targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 Partnership in Chronic Diseases, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/s41573-018-0008-x
Darenskaya, Kolesnikova, Kolesnikov, Free Radical Reactions in Socially Significant Infectious Diseases: HIV Infection, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis, Ann. Russ. Acad. Med. Sci, doi:10.15690/vramn1328
Derouiche, Oxidative Stress Associated with SARS-Cov-2 (COVID-19) Increases the Severity of the Lung Disease-A Systematic Review, J. Infect. Dis. Epidemiol, doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510121
Dupuy, Le Faouder, Vigor, Oger, Galano et al., Simultaneous Quantitative Profiling of 20 Isoprostanoids from Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by LC-MS/MS in Various Biological Samples, Anal. Chim. Acta, doi:10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.024
Ebrahimi, Norouzi, Aazami, Moosavi-Movahedi, Review on Oxidative Stress Relation on COVID-19: Biomolecular and Bioanalytical Approach, Int. J. Biol. Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.095
Fernandes, De Brito, Dos Reis, Sato, Pereira, SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: What Does Oxidative Stress Have to Do with It?, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2020/8844280
Fraternale, Zara, De Angelis, Nencioni, Palamara et al., Intracellular Redox-Modulated Pathways as Targets for Effective Approaches in the Treatment of Viral Infection, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22073603
Geller, Winge, A Method for Distinguishing Cu,Zn-and Mn-Containing Superoxide Dismutases, Anal. Biochem, doi:10.1016/0003-2697(83)90348-2
Griffiths, Gao, Pararasa, Redox Regulation in Metabolic Programming and Inflammation, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.023
Holmgren, Björnstedt, Thioredoxin and Thioredoxin Reductase, doi:10.1016/0076-6879(95)52023-6
Ivanov, Bartosch, Isaguliants, Oxidative Stress in Infection and Consequent Disease, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2017/3496043
Ivanović, Popović, Radulović, Medenica, Reversed-Phase Ion-Pair HPLC Determination of Some Water-Soluble Vitamins in Pharmaceuticals, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal, doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(98)00109-5
Jastrz Ąb, Skrzydlewska, Thioredoxin-Dependent System. Application of Inhibitors, J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem, doi:10.1080/14756366.2020.1867121
Jevtic, Nazy, The COVID Complex: A Review of Platelet Activation and Immune Complexes in COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.807934
Karkhanei, Talebi Ghane, Mehri, Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Level: Total Antioxidant Capacity, Total Oxidant Status and Glutathione Activity in Patients with COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897
Kelleher, Sha, Foster, Foster, Forrester et al., Thioredoxin-Mediated Denitrosylation Regulates Cytokine-Induced Nuclear Factor KB (NF-KB) Activation, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.503938
Khomich, Kochetkov, Bartosch, Ivanov, Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v10080392
Komaravelli, Casola, Respiratory Viral Infections and Subversion of Cellular Antioxidant Defenses, J. Pharm. Pharm, doi:10.4172/2153-0645.1000141
Koo, Garg, Metabolic Programming of Macrophage Functions and Pathogens Control, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101198
Laforge, Elbim, Frère, Hémadi, Massaad et al., Tissue Damage from Neutrophil-Induced Oxidative Stress in COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1
Lee, Ghode, Ong, Redox Regulation of Cell State and Fate, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.014
Levine, Garland, Oliver, Amici, Climent et al., Determination of Carbonyl Content in Oxidatively Modified Proteins, Methods Enzymol, doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86141-h
Libby, Lüscher, COVID-19 Is, in the End, an Endothelial Disease, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa623
Lim, Leprivier, The Impact of Oncogenic RAS on Redox Balance and Implications for Cancer Development, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2192-y
Lingappan, NF-KB in Oxidative Stress, Curr. Opin. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.cotox.2017.11.002
Lovell, Xie, Gabbita, Markesbery, Decreased Thioredoxin and Increased Thioredoxin Reductase Levels in Alzheimer's Disease Brain, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00258-0
Maeso, García-Martínez, Rupérez, Cifuentes, Barbas, Capillary Electrophoresis of Glutathione to Monitor Oxidative Stress and Response to Antioxidant Treatments in an Animal Model, J. Chromatogr. B, doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.05.015
Martín-Fernández, Aller, Heredia-Rodríguez, Gómez-Sánchez, Martínez-Paz et al., Lipid Peroxidation as a Hallmark of Severity in COVID-19 Patients, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102181
Miyazawa, Burdeos, Itaya, Nakagawa, Miyazawa et al., Regulatory Redox Interactions, IUBMB Life, doi:10.1002/iub.2008
Mize, Langdon, Hepatic Glutathione Reductase. I. Purification and General Kinetic Properties, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)83745-6
Muhammad, Aminu, Ahmad, Iliya, Muhd et al., An Elevated 8-Isoprostaglandin F2 Alpha (8-Iso-PGF2α) in COVID-19 Subjects Co-Infected with Malaria, Pan. Afr. Med. J, doi:10.11604/pamj.2020.37.78.25100
Mullen, Mengozzi, Hanschmann, Alberts, Ghezzi, How the Redox State Regulates Immunity, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.022
Murata, Ohteki, Koyasu, Hamuro, IFN-Gamma and pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production by Antigen-Presenting Cells Is Dictated by Intracellular Thiol Redox Status Regulated by Oxygen Tension, Eur. J. Immunol
Murata, Shimamura, Tagami, Takatsuki, Hamuro, The Skewing to Th1 Induced by Lentinan Is Directed through the Distinctive Cytokine Production by Macrophages with Elevated Intracellular Glutathione Content, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/S1567-5769(01)00212-0
Novaes, Teixeira, De Miranda, Oxidative Stress in Microbial Diseases: Pathogen, Host, and Therapeutics, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2019/8159562
Paglia, Valentine, Studies on the Quantitative and Qualitative Characterization of Erythrocyte Glutathione Peroxidase, J. Lab Clin. Med
Pang, Zhou, Ewald, Chang, Hacariz et al., Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC-HRMS Spectra Processing, Multi-Omics Integration and Covariate Adjustment of Global Metabolomics Data, Nat. Protoc, doi:10.1038/s41596-022-00710-w
Pennathur, Heinecke, Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction in Vascular Disease, Curr. Diabetes Rep, doi:10.1007/s11892-007-0041-3
Pincemail, Cavalier, Charlier, Cheramy-Bien, Brevers et al., Oxidative Stress Status in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit for Severe Pneumonia. A Pilot Study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10020257
Pohanka, Role of Oxidative Stress in Infectious Diseases. A Review, Folia Microbiol, doi:10.1007/s12223-013-0239-5
Polonikov, Endogenous Deficiency of Glutathione as the Most Likely Cause of Serious Manifestations and Death in COVID-19 Patients, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288
Schwartz, Conn, RNA Regulation of the Antiviral Protein 2 -5 -Oligoadenylate Synthetase, WIREs RNA, doi:10.1002/wrna.1534
Shastri, Shukla, Chong, Dua, Peterson et al., Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathology and Management of Human Tuberculosis, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2018/7695364
Solis-Paredes, Montoya-Estrada, Cruz-Rico, Reyes-Muñoz, Perez-Duran et al., Plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity and Carbonylated Proteins Are Increased in Pregnant Women with Severe COVID-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040723
Spadaro, Fogagnolo, Campo, Zucchetti, Verri et al., Markers of Endothelial and Epithelial Pulmonary Injury in Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 ICU Patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03499-4
Stoian, Banerjee, Rizvi, Rizzo, Diabetes and the COVID-19 Pandemic: How Insights from Recent Experience Might Guide Future Management, Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord, doi:10.1089/met.2020.0037
Sykes, Mccormack, O'brien, A Preliminary Study of the Superoxide Dismutase Content of Some Human Tumors, Cancer Res
Trachootham, Lu, Ogasawara, Nilsa, Huang, Redox Regulation of Cell Survival, Antioxid. Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1957
Tsikas, Rothmann, Schneider, Gutzki, Beckmann et al., Simultaneous GC-MS/MS Measurement of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal in Human Plasma: Effects of Long-Term L-Arginine Administration, Anal. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.ab.2016.08.009
Van Den Brand, Haagmans, Van Riel, Osterhaus, Kuiken, The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Experimental Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome and Influenza in Animal Models, J. Comp. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.01.004
Vatassery, Brin, Fahn, Kayden, Traber, Effect of High Doses of Dietary Vitamin E on the Concentrations of Vitamin E in Several Brain Regions, Plasma, Liver, and Adipose Tissue of Rats, J. Neurochem, doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01083.x
Vieceli Dalla Sega, Fortini, Spadaro, Ronzoni, Zucchetti et al., Time Course of Endothelial Dysfunction Markers and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study, Clin. Transl. Med, doi:10.1002/ctm2.283
Violi, Pastori, Pignatelli, Cangemi, SARS-CoV-2 and Myocardial Injury: A Role for Nox2?, Intern. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02348-6
Völlmy, Van Den Toorn, Zenezini Chiozzi, Zucchetti, Papi et al., A Serum Proteome Signature to Predict Mortality in Severe COVID-19 Patients, Life Sci. Alliance, doi:10.26508/lsa.202101099
Weber, Milkovic, Bennett, Griffiths, Zarkovic et al., Measurement of HNE-Protein Adducts in Human Plasma and Serum by ELISA-Comparison of Two Primary Antibodies, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.012
Wu, Wang, Zhang, Xu, Chen et al., Breaking the Vicious Loop between Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Coagulation, a Novel Anti-Thrombus Insight of Nattokinase by Inhibiting LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101500
Yaghoubi, Youssefi, Hashemy, Rafat Panah, Mashkani et al., Thioredoxin Reductase Gene Expression and Activity among Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1-Infected Patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25371
Ye, Zhang, Townsend, Tew, Oxidative Stress, Redox Regulation and Diseases of Cellular Differentiation, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.010
Zarkovic, Jakovcevic, Mataic, Jaganjac, Vukovic et al., Post-Mortem Findings of Inflammatory Cells and the Association of 4-Hydroxynonenal with Systemic Vascular and Oxidative Stress in Lethal COVID-19, Cells
Zhang, Li, Wu, Nice, Huang et al., Oxidative Stress and Diabetes: Antioxidative Strategies, Front. Med, doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0729-1
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Lancet
Çakırca, Çakırca, Üstünel, Torun, Koyuncu et al., Thiol Level and Total Oxidant/Antioxidant Status in Patients with COVID-19 Infection, Ir. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-021-02743-8
Łuczaj, Gęgotek, Skrzydlewska, Antioxidants and HNE in Redox Homeostasis, Free Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.033
Žarković, Orehovec, Milković, Baršić, Tatzber et al., Preliminary Findings on the Association of the Lipid Peroxidation Product 4-Hydroxynonenal with the Lethal Outcome of Aggressive COVID-19, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10091341
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27165323",
"ISSN": [
"1420-3049"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165323",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Several studies suggested the association of COVID-19 with systemic oxidative stress, in particular with lipid peroxidation and vascular stress. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant signaling in the plasma of eighty-eight patients upon admission to the Clinical Hospital Dubrava in Zagreb, of which twenty-two died within a week, while the other recovered. The differences between the deceased and the survivors were found, especially in the reduction of superoxide dismutases (SOD-1 and SOD-2) activity, which was accompanied by the alteration in glutathione-dependent system and the intensification of the thioredoxin-dependent system. Reduced levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants, especially tocopherol, were also observed, which correlated with enhanced lipid peroxidation (determined by 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and neuroprostane levels) and oxidative modifications of proteins assessed as 4-HNE-protein adducts and carbonyl groups. These findings confirm the onset of systemic oxidative stress in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2, especially those who died from COVID-19, as manifested by strongly reduced tocopherol level and SOD activity associated with lipid peroxidation. Therefore, we propose that preventive and/or supplementary use of antioxidants, especially of lipophilic nature, could be beneficial for the treatment of COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"molecules27165323"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5032-0369",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Žarković",
"given": "Neven",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5766-6271",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jastrząb",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8923-3529",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jarocka-Karpowicz",
"given": "Iwona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orehovec",
"given": "Biserka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baršić",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4173-1278",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tarle",
"given": "Marko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kmet",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9138-2037",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lukšić",
"given": "Ivica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3992-1910",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Łuczaj",
"given": "Wojciech",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5397-7139",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Skrzydlewska",
"given": "Elżbieta",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Molecules",
"container-title-short": "Molecules",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T03:51:01Z",
"timestamp": 1661140261000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T04:45:07Z",
"timestamp": 1661143507000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T05:12:52Z",
"timestamp": 1661145172025
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "16",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "16",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661040000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/16/5323/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5323",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2007.1957",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-019-2192-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iub.2008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cotox.2017.11.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/3496043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12223-013-0239-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/8159562",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12929-015-0194-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/2153-0645.1000141",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/7695364",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15690/vramn1328",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11030444",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14040723",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/360438",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10091341",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202101099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8844280",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2019.101198",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02348-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13666",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.807934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11892-007-0041-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03499-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.283",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14756366.2020.1867121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23937/2474-3658/1510121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-021-02743-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1521-4141(2002010)32:10<2866::AID-IMMU2866>3.0.CO;2-V",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.648004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cmi.12343",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/wrna.1534",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00214-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1567-5769(01)00212-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22073603",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v10080392",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11604/pamj.2020.37.78.25100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10020257",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.102181",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13102818.2019.1674690",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.01.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M113.503938",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-018-0008-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0084980",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/met.2020.0037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-019-0729-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref59"
},
{
"article-title": "Studies on the Quantitative and Qualitative Characterization of Erythrocyte Glutathione Peroxidase",
"author": "Paglia",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "J. Lab Clin. Med.",
"key": "ref60",
"volume": "70",
"year": "1967"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(19)83745-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00258-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0076-6879(95)52023-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref63"
},
{
"article-title": "A Preliminary Study of the Superoxide Dismutase Content of Some Human Tumors",
"author": "Sykes",
"first-page": "2759",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "ref64",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0003-2697(83)90348-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref65"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.05.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref66"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01083.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref67"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0731-7085(98)00109-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ab.2016.08.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-005-0229-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref70"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref72"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0076-6879(90)86141-h",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref73"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41596-022-00710-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref74"
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/16/5323"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Chemistry (miscellaneous)",
"Analytical Chemistry",
"Organic Chemistry",
"Physical and Theoretical Chemistry",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmaceutical Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Impact of Severe COVID-19 on Plasma Antioxidants",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "27"
}