Associations of vitamin D levels and clinical parameters with COVID‐19 infection, severity and mortality in hemodialysis patients: A cohort study
et al., Hemodialysis International, doi:10.1111/hdi.13194, Dec 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
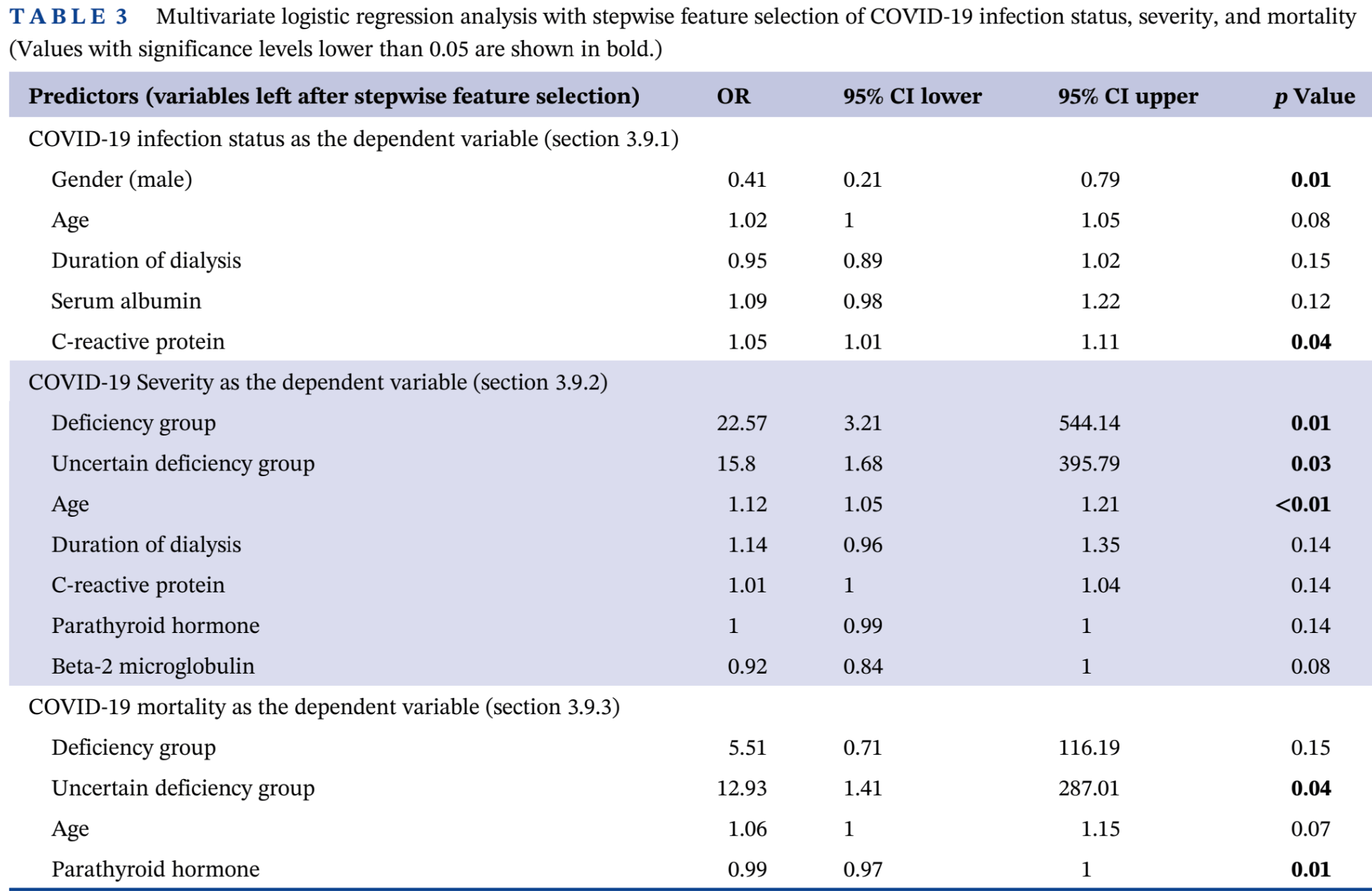
Retrospective 198 hemodialysis patients in China showing vitamin D deficiency associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 severity.
This is the 210th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of death, 81.9% lower, OR 0.18, p = 0.15, high D levels 96, low D levels 73, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor high D levels, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 95.6% lower, OR 0.04, p = 0.01, high D levels 96, low D levels 73, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor high D levels, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
You et al., 22 Dec 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/hdi.13194",
"ISSN": [
"1492-7535",
"1542-4758"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/hdi.13194",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent among patients undergoing hemodialysis. This study aimed to investigate the associations between vitamin D levels and clinical parameters with the risk of COVID‐19 infection, severity, and mortality in hemodialysis patients with end‐stage kidney disease (ESKD).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This retrospective cohort study included 198 hemodialysis patients from a single center. Vitamin D deficiency was defined by the last measurement of 25‐hydroxycholecalciferol less than 20 ng/mL. Vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D supplements were combined to categorize patients into three groups: deficiency, uncertain deficiency, and likely sufficient. COVID‐19 infection status, severity, and outcomes were recorded. Statistical analyses were performed to assess the associations between vitamin D levels and COVID‐19 severity and mortality.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Findings</jats:title><jats:p>Among the 198 patients, 73 patients (37%) were in the deficiency group, 29 patients (15%) had uncertain deficiency, and 96 patients (48%) were likely sufficient. The overall COVID‐19 infection rate was 59%. The deficiency group had a similar infection rate (60.3%) compared to those with likely sufficient levels (54.2%). However, the severity and mortality rates of vitamin D deficiency group had a significantly higher rate than those with likely sufficient levels. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that vitamin D deficiency and uncertain deficiency group were significantly associated with an increased risk of COVID‐19 severity (OR = 22.57, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.01 and OR = 15.8, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03, respectively). Uncertain deficiency group was significantly associated with an increased risk of COVID‐19 mortality (OR = 12.93, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.04), while the deficiency group should similarly trend but did not reach statistical significance.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Discussion</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of COVID‐19 severity in hemodialysis patients with ESKD. These findings suggest that monitoring and managing vitamin D levels may be important in reducing the risk of COVID‐19 severity in this vulnerable population.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/hdi.13194"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-06-12"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-12-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2024-12-22"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0001-4924-0078",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology West China Xiamen Hospital of Sichuan University Xiamen China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology Army 73rd Group Military Hospital Xiamen China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "You",
"given": "Yanhua",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology Army 73rd Group Military Hospital Xiamen China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Chun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology Army 73rd Group Military Hospital Xiamen China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Yuqing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology Army 73rd Group Military Hospital Xiamen China"
}
],
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Meng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology Army 73rd Group Military Hospital Xiamen China"
}
],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Hemodialysis International",
"container-title-short": "Hemodialysis International",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-23T07:41:58Z",
"timestamp": 1734939718000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-23T07:42:06Z",
"timestamp": 1734939726000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-23T08:10:10Z",
"timestamp": 1734941410883,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1734825600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/hdi.13194",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline",
"author": "Holick MF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ki.5002009",
"article-title": "Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease",
"author": "Levin A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000081023",
"article-title": "Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in chronic kidney disease",
"author": "González EA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Nephrol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ki.5002451",
"article-title": "Vitamin D levels and early mortality among incident hemodialysis patients",
"author": "Wolf M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1004",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ki.2008.501",
"article-title": "Vitamin D levels and patient outcome in chronic kidney disease",
"author": "Ravani P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "88",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the immune system",
"author": "Aranow C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Investig Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function",
"author": "Prietl B",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2502",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta‐analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau AR",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2008.560",
"article-title": "Association between serum 25‐hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the third National Health and nutrition examination survey",
"author": "Ginde AA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"article-title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"author": "Cannell JJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.29094",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to prevent seasonal influenza a in schoolchildren",
"author": "Urashima M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1255",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11255-020-02451-9",
"article-title": "Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) infection",
"author": "Henry BM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1193",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int Urol Nephrol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.005",
"article-title": "Kidney disease is associated with in‐hospital death of patients with COVID‐19",
"author": "Cheng Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "829",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID‐19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer DO",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061620",
"article-title": "Reply: “Vitamin D supplementation in influenza and COVID‐19 infections. Comment on: Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID‐19 infections and deaths nutrients 2020, 12 (4), 988”",
"author": "Grant WB",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie PC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgac719",
"article-title": "Consensus and controversial aspects of vitamin D and COVID‐19",
"author": "Bilezikian JP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1034",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"article-title": "Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Daneshkhah A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2141",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID‐19 infection: an Israeli population‐based study",
"author": "Merzon E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2021.2012419",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D status and risk of covid‐19 in‐hospital mortality: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Ebrahimzadeh A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5033",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nep.14071",
"article-title": "The effect of prescribing vitamin D analogues and serum vitamin D status on both contracting COVID‐19 and clinical outcomes in kidney dialysis patients'",
"author": "Tangwonglert T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "815",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nephrology (Carlton)",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101400",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D status and lifestyle factors in Brazilian women: implications of sun exposure levels, Diet, and Health",
"author": "Santana KVDSD",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980024000934",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID‐19 patients: evidence from an umbrella meta‐analysis of interventional and observational studies",
"author": "Jamilian A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-023-03331-9",
"article-title": "Low vitamin D levels predict outcomes of COVID‐19 in patients with both severe and non‐severe disease at hospitalization",
"author": "Filippo L",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15051234",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in severe COVID‐19 patients—randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Bugarin JD",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2023.1131103",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID‐19 patients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Zhang Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "e_1_2_8_28_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/hdi.13194"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Associations of vitamin D levels and clinical parameters with <scp>COVID</scp>‐19 infection, severity and mortality in hemodialysis patients: A cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}
