The safety and efficacy of oral antiviral drug VV116 for treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000034105, PROSPERO CRD42023391130, Jul 2023
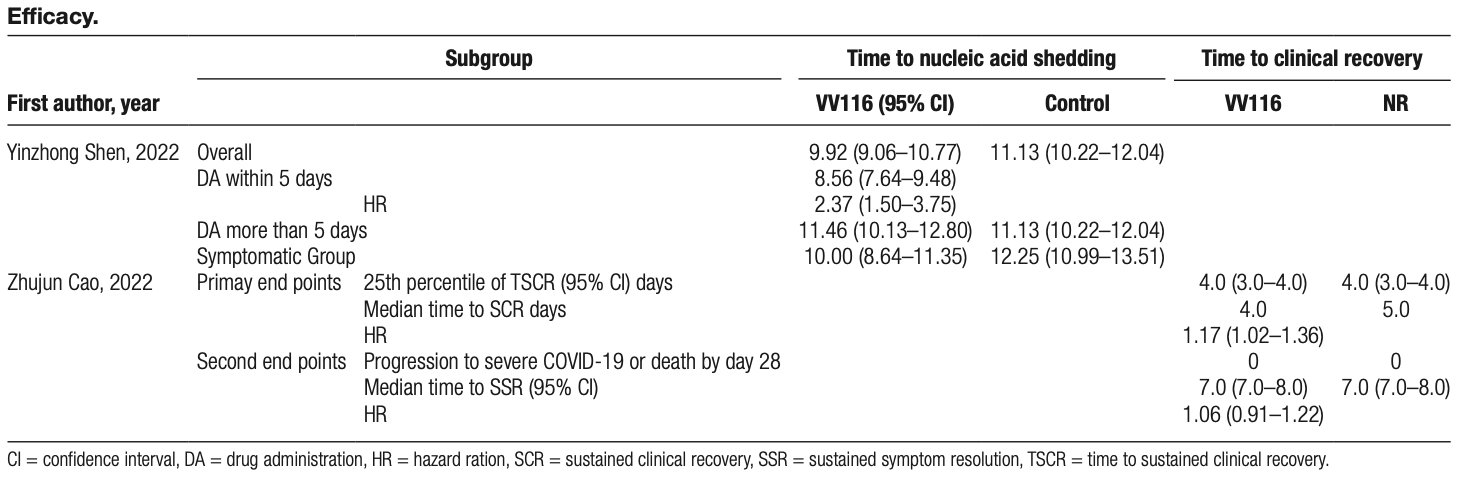
Systematic review of 3 VV116 studies with 1,044 participants. Authors conclude that VV116 had minimal adverse events and was not inferior in symptomatic alleviation when compared with paxlovid. Authors note that more research into the safety and efficacy of VV116 is needed, and more elderly and critically ill patients with COVID-19 should be included.
See Ma et al. for another review covering deuremidevir for COVID-19.
Xiao et al., 7 Jul 2023, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023391130.
Contact: fellones.zero@gmail.com.
Abstract: Medicine
®
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
The safety and efficacy of oral antiviral drug
VV116 for treatment of COVID-19
wCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3i3D0OdRyi7TvSFl4Cf3VC1y0abggQZXdgGj2MwlZLeI= on 01/29/2024
A systematic review
Ningkun Xiao, MDa,* , Xinlin Huang, MDa, Xiaotian Kang, Bachelorb, Wanli Zang, MDc, Bo Li, MDd,
Sergey Kiselev, PhDa
Abstract
Background: Recent trials have highlighted the potential of oral antiviral VV116 in the treatment of patients with mild COVID-
19. However, no comprehensive studies have assessed the safety and efficacy of VV116. Therefore, we conducted a systematic
review to assess the safety and efficacy of VV116.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted on PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar websites, with a cutoff date of
March 23, to identify pertinent studies.
Results: The results from the 3 included studies indicated that no serious adverse events were reported in the VV116 experimental
groups, which exhibited a 2.57-day faster time to viral shedding than the control group and demonstrated non-inferiority to the
nirmatrelvir-ritonavir control group in alleviating major symptoms.
Discussion: Collectively, available studies suggest a reliable safety and efficacy profile for VV116. However, the limited number
of trials was insufficient for meta-analysis, and the included population consisted of younger individuals with mild and moderate
symptoms, not encompassing the elderly who are severely affected by COVID-19. We hope that more studies will be conducted
in the future to ensure that VV116 has a more reliable safety and efficacy profile in the clinical setting, especially in severe or critical
patients.
Abbreviations: AEs = adverse events, AUC = concentration-time curve, Cmax = the maximum measured plasma concentration,
COVID-19 = corona virus disease 2019, NR = nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, PEDro = Physiotherapy Evidence Database scale, SARSCoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Keywords: COVID-19, oral antiviral drug, public health, vaccines, VV116
have high spike protein mutation rates. There is a higher probability of vaccine breakthrough rates and widespread escape
from existing neutralizing antibodies,[8,9] more specifically, The
BQ and XBB subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron are currently
expanding rapidly, and BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 are the
most resistant SARS-CoV-2 variations to date,[10] which poses
a huge challenge to the immune protection of the majority of
the population and a threat to worldwide health endeavors.
Consequently, adjunct medications have become increasingly
important for safeguarding global health.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved 2 oral
antiviral drugs for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19
outpatients at risk of progression to severe COVID-19: Pfizer’s
PF-07321332 (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, paxlovid)[11,12] and Merck’s
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000034105",
"ISSN": [
"0025-7974"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000034105",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background:</jats:title><jats:p>Recent trials have highlighted the potential of oral antiviral VV116 in the treatment of patients with mild COVID-19. However, no comprehensive studies have assessed the safety and efficacy of VV116. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to assess the safety and efficacy of VV116.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods:</jats:title><jats:p>A comprehensive search was conducted on PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar websites, with a cutoff date of March 23, to identify pertinent studies.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results:</jats:title><jats:p>The results from the 3 included studies indicated that no serious adverse events were reported in the VV116 experimental groups, which exhibited a 2.57-day faster time to viral shedding than the control group and demonstrated non-inferiority to the nirmatrelvir-ritonavir control group in alleviating major symptoms.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Discussion:</jats:title><jats:p>Collectively, available studies suggest a reliable safety and efficacy profile for VV116. However, the limited number of trials was insufficient for meta-analysis, and the included population consisted of younger individuals with mild and moderate symptoms, not encompassing the elderly who are severely affected by COVID-19. We hope that more studies will be conducted in the future to ensure that VV116 has a more reliable safety and efficacy profile in the clinical setting, especially in severe or critical patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0615-3222",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory for Brain and Neurocognitive Development, Department of Psychology, Institution of Humanities, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Ningkun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory for Brain and Neurocognitive Development, Department of Psychology, Institution of Humanities, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Xinlin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of General Medicine, Ural State Medical University, Yekaterinburg, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Kang",
"given": "Xiaotian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Postgraduate School, University of Harbin Sport, Harbin, China"
}
],
"family": "Zang",
"given": "Wanli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institution of Humanities, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, Russia."
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory for Brain and Neurocognitive Development, Department of Psychology, Institution of Humanities, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, Russia"
}
],
"family": "Kiselev",
"given": "Sergey",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-07T12:06:09Z",
"timestamp": 1688731569000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-16T16:42:59Z",
"timestamp": 1702744979000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-16T17:15:19Z",
"timestamp": 1702746919724
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "27",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "27",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688688000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000034105",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e34105",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015355",
"article-title": "Oral GS-441524 derivatives: next-generation inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015355",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "R1-20230802",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.8565",
"article-title": "Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Al Kaabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R2-20230802",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116063",
"article-title": "Covid-19 Vaccine effectiveness in New York State.",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R3-20230802",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-022-00890-1",
"article-title": "Neutralizing antibodies and their cocktails against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other circulating variants.",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "962",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol",
"key": "R4-20230802",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scib.2022.02.011",
"article-title": "COVID-19 can be called a treatable disease only after we have antivirals.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "999",
"journal-title": "Sci Bull (Beijing)",
"key": "R5-20230802",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2078230",
"article-title": "An open, prospective cohort study of VV116 in Chinese participants infected with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants.",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1518",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "R6-20230802",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.733",
"article-title": "Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and strategies for tackling the infection.",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e733",
"journal-title": "Immun Inflammation Dis",
"key": "R7-20230802",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses.",
"author": "Dejnirattisai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "R8-20230802",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"article-title": "Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies.",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "R9-20230802",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.018",
"article-title": "Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "R10-20230802",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "R11-20230802",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00618-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "R12-20230802",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus.",
"author": "Fischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabl7430",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "R13-20230802",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients.",
"author": "Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R14-20230802",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern.",
"author": "Vangeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105252",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "R15-20230802",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2.",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R16-20230802",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/Spectrum.01537-21",
"article-title": "Broad-spectrum in vitro antiviral Activity of ODBG-P-RVn: an orally-available, lipid-modified monophosphate prodrug of remdesivir parent nucleoside (GS-441524).",
"author": "Lo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01537",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Spectr",
"key": "R17-20230802",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117",
"article-title": "Discovery of S-217622, a Noncovalent Oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for Treating COVID-19.",
"author": "Unoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6499",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "R18-20230802",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 rebound after Paxlovid and Molnupiravir during January-June 2022.",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "R19-20230802",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o926",
"article-title": "Covid-19: what is the evidence for the antiviral molnupiravir?",
"author": "Extance",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o926",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "R20-20230802",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0",
"article-title": "Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis.",
"author": "Kabinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Nat Struct Mol Biol",
"key": "R21-20230802",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26760-4",
"article-title": "Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets.",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6415",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "R22-20230802",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bdr2.2111",
"article-title": "Developmental toxicity of remdesivir, an anti-COVID-19 drug, is implicated by in vitro assays using morphogenetic embryoid bodies of mouse and human pluripotent stem cells.",
"author": "Kirkwood-Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"journal-title": "Birth Defects Res",
"key": "R23-20230802",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106201",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the promise of small molecule therapeutics: are there lessons to be learnt?",
"author": "Ho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106201",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "R24-20230802",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00192-8",
"article-title": "The future of Paxlovid for COVID-19.",
"author": "Burki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e68",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "R25-20230802",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00119-0",
"article-title": "Availability of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and the requirement for an ethical prescribing approach.",
"author": "Dal-Ré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e231",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "R26-20230802",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2208822",
"article-title": "VV116 versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for oral treatment of Covid-19.",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "406",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R27-20230802",
"volume": "388",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01855-7",
"article-title": "Modeling transmission of SARS-CoV-2 omicron in China.",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1468",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "R28-20230802",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00795",
"article-title": "Recent developments for the deuterium and tritium labeling of organic molecules.",
"author": "Kopf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6634",
"journal-title": "Chem Rev",
"key": "R29-20230802",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00048",
"article-title": "Insights into PPARγ phosphorylation and its inhibition mechanism.",
"author": "Montanari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4811",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "R30-20230802",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00570-1",
"article-title": "Design and development of an oral remdesivir derivative VV116 against SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1212",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "R31-20230802",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40262-021-00984-5",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and drug-interaction profile of remdesivir, a SARS-CoV-2 Replication Inhibitor.",
"author": "Humeniuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "569",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacokinet",
"key": "R32-20230802",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115340",
"article-title": "Characterization of in-vivo human metabolites of the oral nucleoside anti-COVID-19 drug VV116 using UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115340",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Biomed Anal",
"key": "R33-20230802",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-022-00895-6",
"article-title": "Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of VV116, an oral nucleoside analog against SARS-CoV-2, in Chinese healthy subjects.",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3130",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "R34-20230802",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0004-9514(14)60281-6",
"article-title": "Evidence for physiotherapy practice: a survey of the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro).",
"author": "Moseley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Aust J Physiother",
"key": "R35-20230802",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph20032630",
"article-title": "Effects of equine-assisted activities and therapies for individuals with autism spectrum disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2630",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "R36-20230802",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40489-018-0130-z",
"article-title": "Effects of equine therapy on individuals with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review.",
"author": "Srinivasan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "156",
"journal-title": "Rev J Autism Dev Disord",
"key": "R37-20230802",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2012.02.010",
"article-title": "Grading dermatologic adverse events of cancer treatments: the common terminology criteria for adverse events Version 4.0.",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "J Am Acad Dermatol",
"key": "R38-20230802",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsomega.2c04160",
"article-title": "Deuterated drugs and biomarkers in the COVID-19 Pandemic.",
"author": "Jansen-van Vuuren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41840",
"journal-title": "ACS Omega",
"key": "R39-20230802",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000034105"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The safety and efficacy of oral antiviral drug VV116 for treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "102"
}