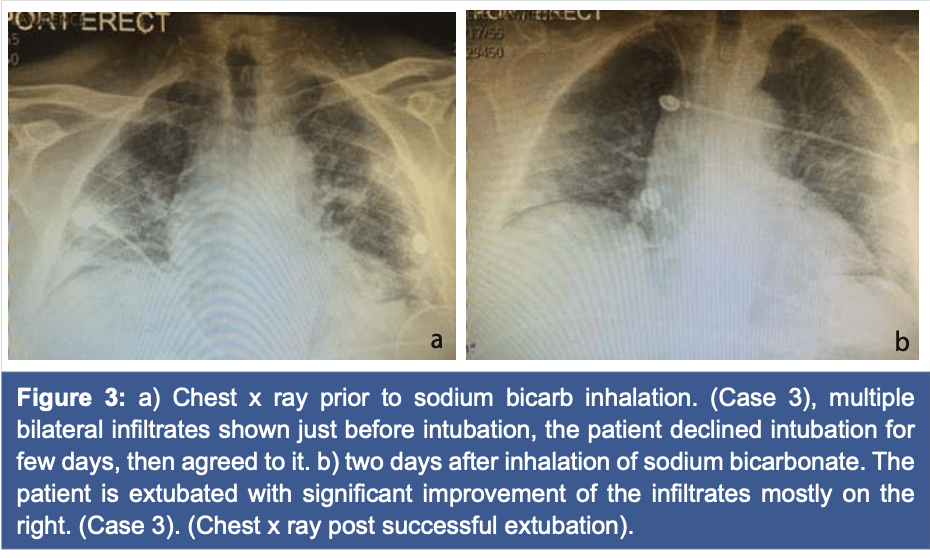
Case reports of observed significant improvement in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 and maximum ventilatory support after inhalation of sodium bicarbonate
et al., Journal of Clinical Intensive Care and Medicine, doi:10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029, May 2020
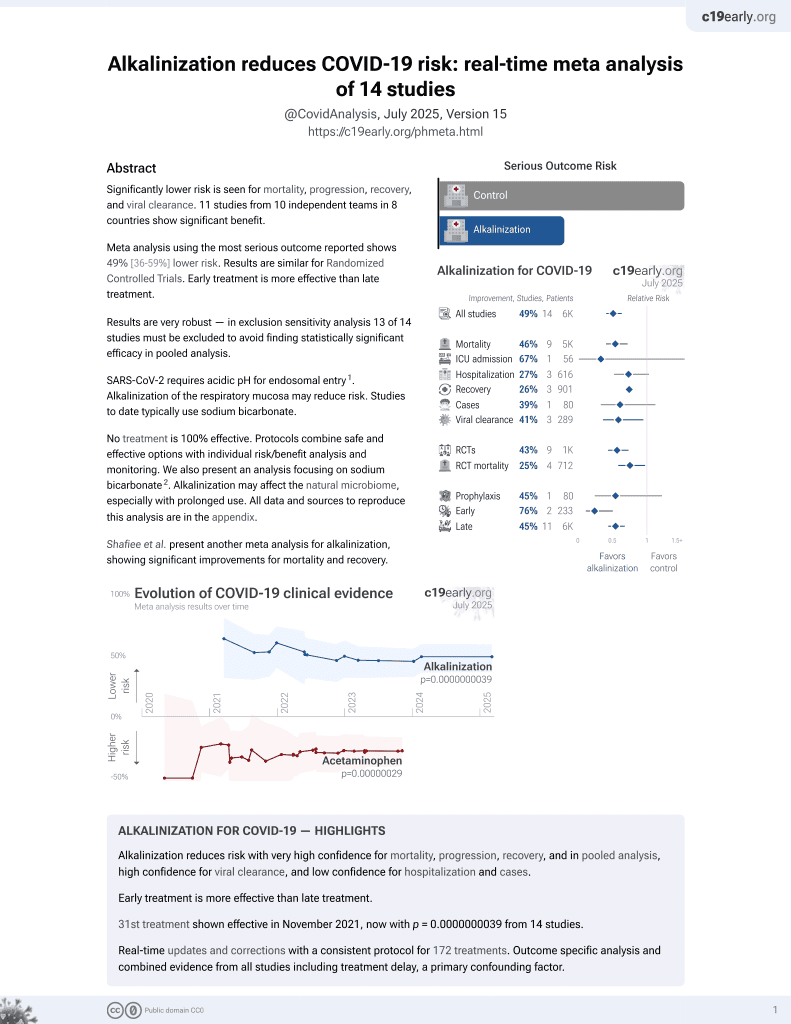
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0000000039 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Case series of four ventilated COVID-19 patients treated with sodium bicarbonate inhalation, all showing clinical and radiological improvement, with 2 patients extubated within 24-72 hours.
Wardeh et al., 19 May 2020, China, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: awardeh1@aol.com, awardeh1@icloud.com.
Abstract: Case Report
More Information
Case reports of observed significant
improvement in patients with ARDS
due to COVID-19 and maximum
ventilatory support after inhalation
of sodium bicarbonate
*Address for Correspondence: Anas Wardeh,
Department of Critical Care Medicine, Uniontown
Hospital, Uniontown, PA, USA,
Tel: 508-479-4213; Email: awardeh1@aol.com;
awardeh1@icloud.com
Wardeh A*, Conklin J and Ko M
The emergence of COVID-19 worldwide in an unprecedented
pandemic. COVID-19 has a signi icant mortality, mostly from
acute lung injury. We reviewed the available literature from
China and Europe in regard to the behavior of SARS-Cov2 and
ability to adhere to the cell wall [1,2]. The evidence based
literature describes three component for the virus to grant
entry to the target cells including Cathepsin B/L (the viral cap
protein needed for initial connectivity to the cell wall), the
angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and a low PH environment
to allow the irst connectivity of the virus to the cell wall [3].
The goal of our Case study was to prevent SARS- SARS-Cov2
from entering target cells by raising the airways PH using
sodium bicarbonate inhalation. The sodium Bicarbonate
inhalation (4.2% concentration) has been used safely in Cystic
ibrosis (CF) patients with inspissated mucoid impaction [3,4]
and in chloride inhalation toxicity by opposing the effect of the
low PH induced by the insulting agent [4,5]. It has not been
administered for COVID -19 patients particularly prior to this
study.
Methods
Four patients required mechanical ventilation due to
COVID-19 pneumonia. All patients have proven positive
COVID-19 RNA collected from the airway’s secretions. Each
one of the patients received inhaled 4.2% sodium bicarbonate
as a salvage therapy. All four patients had severe adult
respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and required 100 %
Fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO2). Due to severe hypoxia
despite 100% FIO2, these patients were placed on Positive
end expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 15 to maintain their Oxygen
saturation at 87% at minimum. Also, a standard PEEP of 15
was used throughout the process to keep the alveoli patent to
https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029
How to cite this article: Wardeh A, Conklin
J, Ko M. Case reports of observed significant
improvement in patients with ARDS due to
COVID-19 and maximum ventilatory support
after inhalation of sodium bicarbonate. J Clin
Intensive Care Med. 2020; 5: 016-019.
DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029
Department of Critical Care Medicine, Uniontown Hospital, Uniontown, PA, USA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029",
"ISSN": [
"2639-6653"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wardeh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conklin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ko",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Clinical Intensive Care and Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Clin Intensive Care Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.heighpubs.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-26T05:40:16Z",
"timestamp": 1590471616000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T06:00:34Z",
"timestamp": 1632981634000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-29T12:11:14Z",
"timestamp": 1674994274802
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2013,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2013-11-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1385337600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.intensivecaremedjournal.com/licensing-policy",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2016,
4,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2016-04-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1460937600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.intensivecaremedjournal.com/articles/jcicm-aid1029.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "11877",
"original-title": [],
"page": "015-019",
"prefix": "10.29328",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Heighten Science Publications Corporation",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.80.7.3180-3188.2006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref0",
"unstructured": "1. Chu, V. McElroy, L. Chu, V. Bauman, B. Whittaker, G. The Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis undergoes direct low PH dependent Fusion activation during entry into the host cells. J Virol. 2006; 80: 3180-3188. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16537586"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.78.11.5642-5650.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "2. Yong ZY, Huang Y, Ganesh L, Leung K, Kong wp. et al. pH-Dependent Entry of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Is Mediated by the Spike Glycoprotein and Enhanced by Dendritic Cell Transfer through DC-SIGN. J Virol. 2004; 78: 5642-5650. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC415834/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.03.00027603",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "3. McShane D, Davies JC, Davies MG, Bush A, Geddes DM, et al. Airway surface PH in subjects with cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2003; 21: 37-42. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12570106"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-019-00861-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "4. Gomez CCS, Parazzi PLF, Clinckspoor KJ, Mauch RM, Pessine FBT, et al, safety, tolerability and effectes of sodium bicarbonate inhalation in cystic fibrosis. Clin Drug Investig. 2019; 40: 105-117. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31721070"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08958370600822615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "5. Aslan S, Kandiş H, Akgun M, Cakir Z, Inandi T, et al. The effect of nebulized sodium bicarbonate treatment on RADS patients due to chlorine gas inhalation. Inhal. Tox. 2006; 18: 895-900. PubMed. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16864407"
},
{
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "6. NIH NHLBI ARDS clinical network, mechanical ventilation protocol summary, 2017."
},
{
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "7. Kis A. Toth L, Kunos L, Gyorgy L, Wanner A. The effect of airway alkalinization by nebulized sodium bicarbonate on airway blood flow. European Res. Journal. 2012; 40: P2143."
},
{
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "8. Chinese SARS Molecular Consortium. Science 10.1126/science.1092002."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0400576101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "9. Bosch BJ, Martina BE, Van Der Zee R, Lepault J, Haijema BJ, et al. Severe ARDS due to SARS CoV infection inhibition using spike protein heptad repeated-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101: 8455-8460. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15150417"
}
],
"reference-count": 9,
"references-count": 9,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.heighpubs.org/jcicm/jcicm-aid1029.php"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Environmental Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Case reports of observed significant improvement in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 and maximum ventilatory support after inhalation of sodium bicarbonate",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.29328/journal",
"update-to": [
{
"DOI": "10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001029",
"label": "New edition",
"type": "new_edition",
"updated": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1589846400000
}
}
],
"volume": "5"
}