Plasma zinc status and hyperinflammatory syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: an observational study
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271, Jun 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
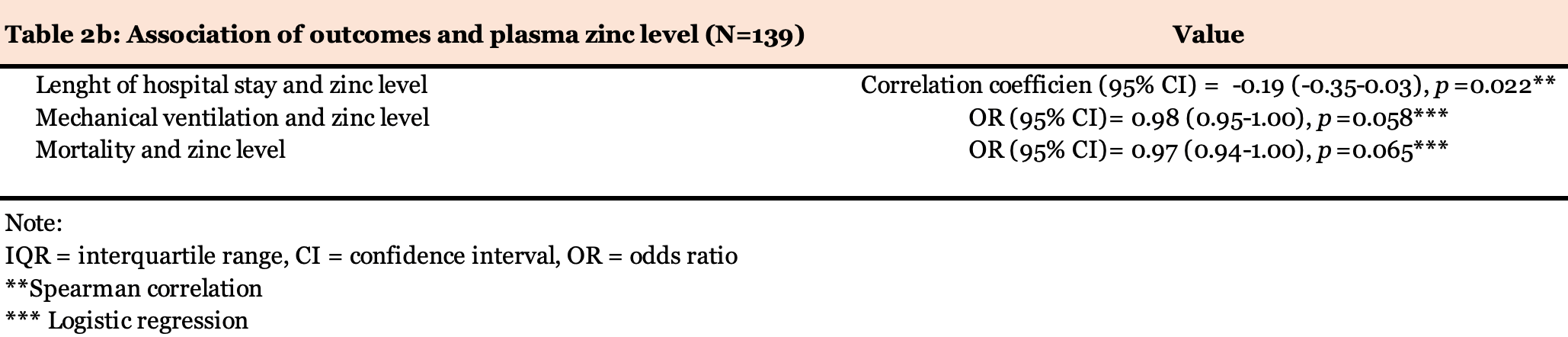
Prospective study of 139 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, showing 96% had zinc deficiency. Higher zinc levels were associated with a shorter length of hospitalization. Mortality and ventilation was lower with higher zinc levels, but not reaching statistical significance.
Verschelden et al., 12 Jun 2021, preprint, 8 authors.
Plasma zinc status and hyperinflammatory syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: an observational study
doi:10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271
Deficiency of the element zinc is associated with cytokine releasing syndrome (CRS) and the related acute respiratory distress syndrome as well as impaired antiviral response. Similar complications associate with severe SARS-CoV-2. We conducted a prospective, single-center, observational study in a tertiary university hospital (CUB-Hopital Erasme, Brussels) to address the zinc status, the association between the plasma zinc concentration, development of CRS, and the clinical outcomes in PCR-confirmed and hospitalized COVID-19 patients. One hundred and thirty-nine eligible patients were included between May 2020 and November 2020 (median age of 65 years [IQR, 54 to 77]). Our cohort's mean plasma zinc concentration was 56.2 µg/dL (standard deviation [SD], 14.8) compared to 75.7 µg/dL (SD = 18.9 µg/dL) in the retrospective non-COVID-19 control group (N = 1513; P <.001). Markedly, the absolute majority of patients (96%) were zinc deficient (<80 µg/dL).
Ethics approval and consent to participate Informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Erasme Hospital, EC identifier P2020/261. Conflict of interest and funding: We hereby confirm that there is no conflict of interest associated with this publication and that this work did not receive any financial support that could have influenced its outcome.
Author contributions G.V and M.Noep: conceived the idea, co-authored the research proposal, designed the study, analyzed the data, interpreted the results, generated the tables, and coauthored the manuscript. G.V: medical consultation and handling the patients' material. M.Nop: supervised the study design and the statistical analyses and critically revised and contributed to drafting the manuscript. M.L, C.M, F.C: handled the patients' material and performed the laboratory assessments. C.G: contributed to . Note: IQR = interquartile range, CI = confidence interval, OR = odds ratio
References
Asl, Nikfarjam, Majidi Zolbanin, Nassiri, Jafari, Immunopharmacological perspective on zinc in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int. Immunopharmacol
Boudreault, Zinc deficiency primes the lung for ventilator-induced injury, JCI insight
Chen, Hoiland, Stukas, Wellington, Sekhon, Confronting the controversy: interleukin-6 and the COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome, Eur. Respir. J
Davies, Musa, Dormandy, Measurements of plasma zinc. I. In health and disease, J. Clin. Pathol
Horby, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Hosmer, Lemeshow, Applied Logistic Regression Second Edition, Applied Logistic Regression
Leisman, Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes, Lancet. Respir. Med
Mehta, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Noeparast, Verschelden, Degeyter, Marco, Goyvaerts et al., None
Prasad, Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells, Mol. Med
Prasad, Zinc supplementation decreases incidence of infections in the elderly: effect of zinc on generation of cytokines and oxidative stress, Am. J. Clin. Nutr
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity, Adv. Nutr
Webb, Clinical criteria for COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: a cohort study, Lancet. Rheumatol
Wessels, Zinc supplementation ameliorates lung injury by reducing neutrophil recruitment and activity, Thorax
Youden, Index for rating diagnostic tests, Cancer
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Deficiency of the element zinc is associated with cytokine releasing syndrome (CRS) and the related acute respiratory distress syndrome as well as impaired antiviral response. Similar complications associate with severe SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p><jats:p>We conducted a prospective, single-center, observational study in a tertiary university hospital (CUB-Hopital Erasme, Brussels) to address the zinc status, the association between the plasma zinc concentration, development of CRS, and the clinical outcomes in PCR-confirmed and hospitalized COVID-19 patients. One hundred and thirty-nine eligible patients were included between May 2020 and November 2020 (median age of 65 years [IQR, 54 to 77]).</jats:p><jats:p>Our cohort’s mean plasma zinc concentration was 56.2 µg/dL (standard deviation [SD], 14.8) compared to 75.7 µg/dL (SD = 18.9 µg/dL) in the retrospective non-COVID-19 control group (N = 1513;<jats:italic>P</jats:italic><.001). Markedly, the absolute majority of patients (96%) were zinc deficient (<80 µg/dL).</jats:p><jats:p>The mean zinc concentration was lower in patients with CRS compared to those without CRS (−5 µg/dL; 95% CI, -10.5 to 0.051;<jats:italic>P</jats:italic>= 0.048).</jats:p><jats:p>Among the tested outcomes, zinc concentration is significantly correlated with only the length of hospital stay (rho = -0.19;<jats:italic>P</jats:italic>= 0.022), but not with mortality or morbidity. As such, our findings do not support the role of zinc as a robust prognostic marker among hospitalized COVID-19 patients who in our cohort presented high prevalence of zinc deficiency. It might be more beneficial to explore the role of zinc as a biomarker for assessing the risk of developing a tissue-damaging CRS and predicting outcomes in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 at the early stage of the disease.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
26
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5856-3143",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Verschelden",
"given": "Gil",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3216-5630",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Noeparast",
"given": "Maxim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9052-0979",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Noparast",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3267-6606",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lauwers",
"given": "Maïlis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michel",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7356-7417",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cotton",
"given": "Frédéric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1725-7772",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Goyvaerts",
"given": "Cleo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6961-6039",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hites",
"given": "Maya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-13T00:00:24Z",
"timestamp": 1623542424000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-04T21:06:32Z",
"timestamp": 1699131992000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T23:48:42Z",
"timestamp": 1709336922816
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
12
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
12
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30404-5",
"article-title": "Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: a rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "Lancet. Respir. Med",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03006-2020",
"article-title": "Confronting the controversy: interleukin-6 and the COVID-19 cytokine storm syndrome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2003006",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.2",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz0135476413",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.86507",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.4",
"unstructured": "Boudreault, F. et al. Zinc deficiency primes the lung for ventilator-induced injury. JCI insight 2, (2017)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213357",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107630",
"article-title": "Immunopharmacological perspective on zinc in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107630",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.6",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.7",
"unstructured": "Noeparast, A. ; Verschelden, G. ; Degeyter, D. ; Marco, M. ; Goyvaerts, C. ; Hites, M. In Light of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Revisit of the Evidence Associating Zinc and Anti-viral Response. Preprints 2020, 2020040094. In Light of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Revisit of the Evidence Associating Zinc and Anti-viral Response. Preprints 2020040094, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00894-008-0277-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/85.3.837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jcp.21.3.359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30343-X",
"article-title": "Clinical criteria for COVID-19-associated hyperinflammatory syndrome: a cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e754",
"journal-title": "Lancet. Rheumatol",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.13",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/0470011815.b2a10029",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.14",
"unstructured": "Hosmer, D. W. & Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression Second Edition. Applied Logistic Regression (2004)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<32::AID-CNCR2820030106>3.0.CO;2-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021072705550508000_2021.06.09.21258271v2.16"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {
"is-preprint-of": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108163",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.06.09.21258271"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Plasma zinc status and hyperinflammatory syndrome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: an observational study",
"type": "posted-content"
}
