Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia
et al., Hellenic Journal of Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011, Dec 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
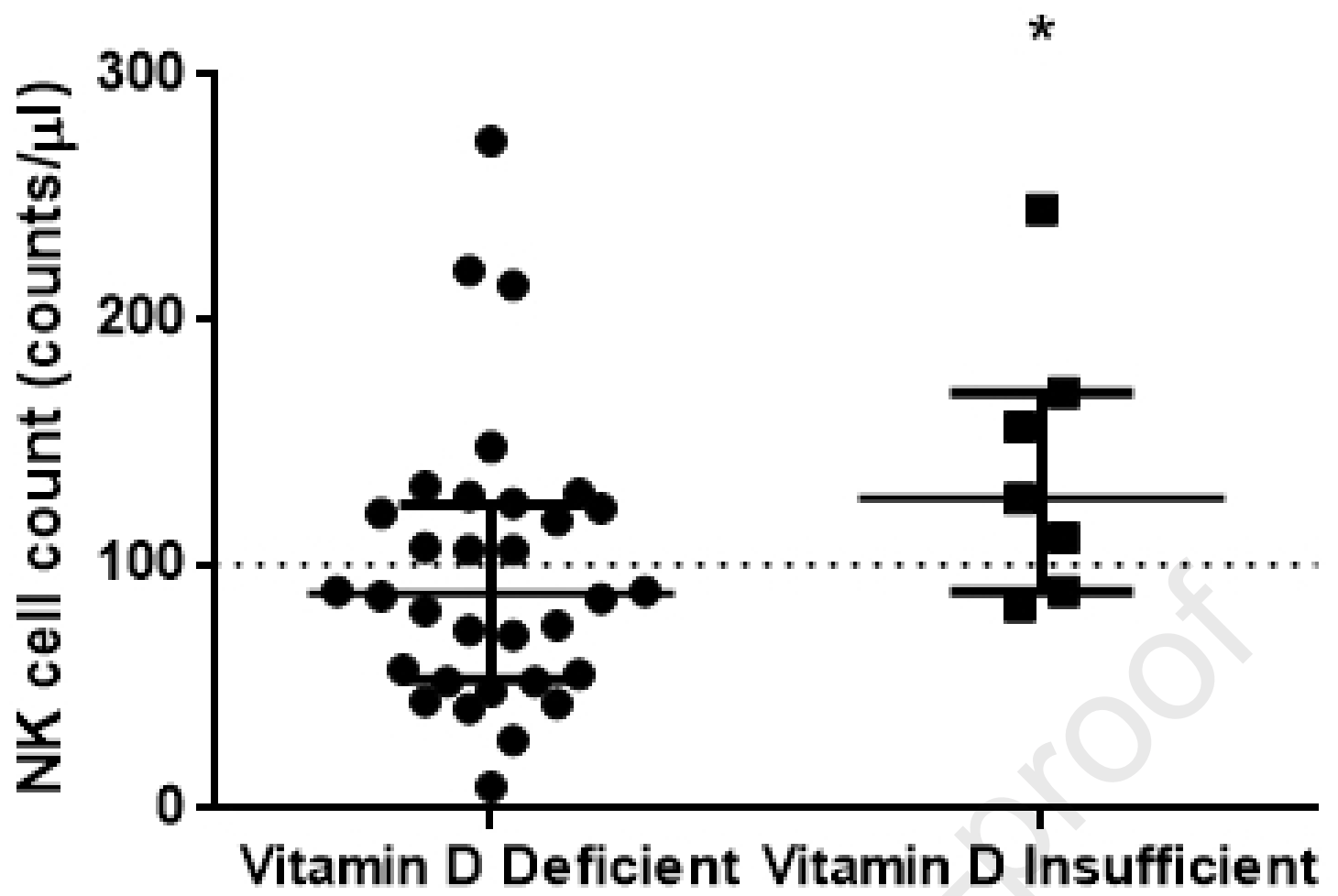
Observational study of 29 ICU patients and 10 non-ICU patients showing vitamin D levels positively correlated with cytotoxic T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, NK-T cells, and regulatory T cells.
Vassiliou et al., 9 Dec 2020, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Abstract: Hellenic Journal of Cardiology 62 (2021) 381e383
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Hellenic Journal of Cardiology
journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/
hellenic-journal-of-cardiology/
Correspondence
Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural
killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with
COVID-19 pneumonia
Keywords:
COVID-19
Vitamin D
Natural killer cells
Regulation of immune function continues to be one of the most
well-recognised extra-skeletal actions of vitamin D. In vitro data
have shown that vitamin D modulates immune cells and induces
immune tolerance, while in vivo data from animal studies and
from vitamin D supplementation human studies have shown beneficial effects of vitamin D on immune function, particularly in the
context of autoimmunity.1 In the present study, we examined
whether vitamin D deficiency modulates the number of immune
cells in COVID-19 patients.
This observational, single-centre study included consecutive
COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU) patients (N ¼ 29) and consecutive patients hospitalised in a specialised non-ICU COVID-19 ward
(N ¼ 10) who were discharged from the hospital without being
transferred to the ICU, from March 18th 2020 to May 25th 2020.
The study was approved by the Hospital's Research Ethics Committee (129/19-3-2020), and all procedures carried out on patients
were in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Informed written consent was obtained from all patients or patients' next-ofkin. Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D was measured on hospital admission using the electrochemiluminescence immunoassay method
(Cobas E602, Roche Diagnostics International Ltd). Immune phenotyping was performed by flow cytometric analysis (Navios EX flow
cytometer, Beckman Coulter).
Vitamin D levels positively correlated with subpopulations of
immune cells, namely, cytotoxic T cells (rs ¼ 0.344, p ¼ 0.032), natural killer (NK) cells (rs ¼ 0.496, p ¼ 0.001), NK-T cells (rs ¼ 0.325,
p ¼ 0.044) and regulatory T cells (rs ¼ 0.333, p ¼ 0.038). With
respect to all other clinical and laboratory parameters, vitamin D
levels correlated only with albumin (rs ¼ 0.387, p ¼ 0.018). To
further explore these associations, we divided our cohort into
two groups based on their vitamin D levels; we classified them as
vitamin D deficient (19.9 ng/ml, N ¼ 32) and vitamin D insufficient (20-29.9 ng/ml, N ¼ 7). Demographics, clinical and biochemical characteristics on hospital admission and important outcomes
Peer review under responsibility of Hellenic Society of Cardiology.
of the two patient groups are listed in Table 1. As expected, hypertension was the most common comorbidity.2 The two groups
differed only in the number of NK cells (Table 1 and Figure 1). Cytotoxic T cells, NK-T cells and regulatory T cells did not differ in the
two groups. It should also be noted that the two patient groups
did not differ with respect to hospital mortality or disease severity.
The beneficial effects of vitamin D on protective immunity are
due in part to its effects on the innate immune system. In vitro
studies have reported contradictory results on the role of vitamin
D on NK cell function, but whether vitamin D induces or inhibits
NK cell function in vivo remains unclear.3 NK cells are a type of
cytotoxic lymphocytes that are critical to the innate immune system and secrete many cytokines and chemokines. Despite their vital role in viral infections, the contribution of NK cells in..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011",
"ISSN": [
"1109-9666"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011",
"alternative-id": [
"S1109966620302840"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Hellenic Journal of Cardiology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Hellenic Society of Cardiology. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4984-0476",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vassiliou",
"given": "Alice G.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7306-713X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jahaj",
"given": "Edison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pratikaki",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keskinidou",
"given": "Chrysi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4425-235X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Detsika",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grigoriou",
"given": "Eirini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Psarra",
"given": "Katherina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orfanos",
"given": "Stylianos E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsirogianni",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dimopoulou",
"given": "Ioanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kotanidou",
"given": "Anastasia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Hellenic Journal of Cardiology",
"container-title-short": "Hellenic Journal of Cardiology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-09T22:10:19Z",
"timestamp": 1607551819000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T08:22:19Z",
"timestamp": 1715415739000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-12T00:09:15Z",
"timestamp": 1715472555543
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 19,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630454400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630454400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1607126400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1109966620302840?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1109966620302840?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "381-383",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory",
"author": "Bishop",
"journal-title": "JBMR plus",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.04.001",
"article-title": "Current data on the cardiovascular effects of COVID-19",
"author": "Vlachakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Hellenic J Cardiol HJC : HJC = Hellenike kardiologike epitheorese",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib2",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.01.004",
"article-title": "Differential effect of dietary vitamin D supplementation on natural killer cell activity in lean and obese mice",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "178",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib3",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.009",
"article-title": "Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure",
"author": "Giamarellos-Bourboulis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "992",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib4",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.001",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Unanswered questions on immune response and pathogenesis",
"author": "Maggi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib5",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01512",
"article-title": "Flattening the COVID-19 Curve With Natural Killer Cell Based Immunotherapies",
"author": "Market",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib6",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abd6832",
"article-title": "Natural killer cell immunotypes related to COVID-19 disease severity",
"author": "Maucourant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "50",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib7",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib8",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113512",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 as Potential Treatment Adjuncts for COVID-19",
"author": "Malaguarnera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in pathogenesis and severity of COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Honardoost",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Physiol Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105771",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and survival in COVID-19 patients: A quasi-experimental study",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105771",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib11",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hjc.2018.06.014",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular disease: Fact or fiction?",
"author": "Tousoulis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Hellenic J Cardiol HJC : HJC = Hellenike kardiologike epitheorese",
"key": "10.1016/j.hjc.2020.11.011_bib12",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1109966620302840"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "62"
}
vassiliou
