Aspirin reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes associated with COVID-19
et al., npj Metabolic Health and Disease, doi:10.1038/s44324-025-00072-3, Jun 2025
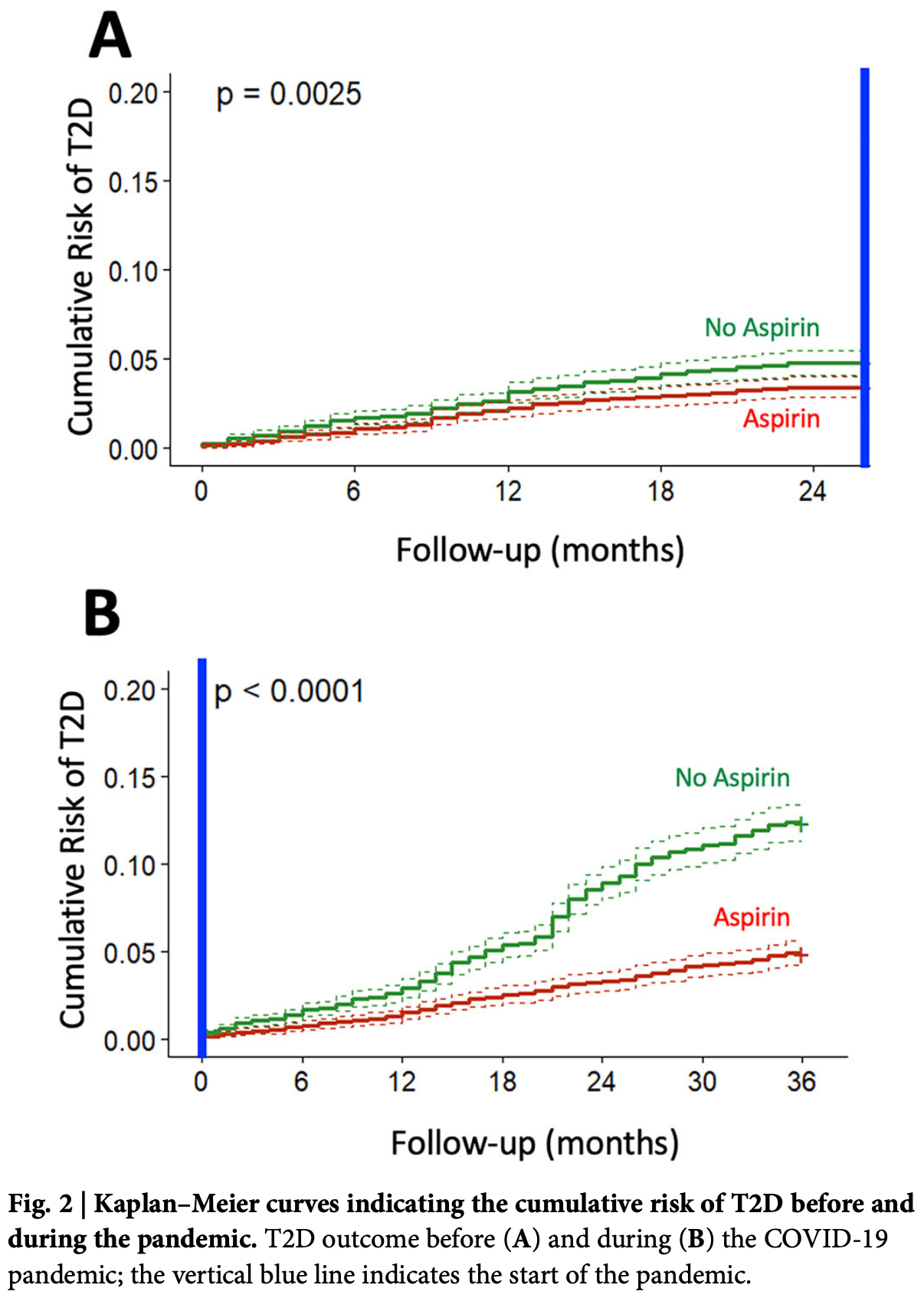
Retrospective 35,525 adults followed from 2018 to 2022, showing that daily low-dose aspirin (100 mg) significantly reduced the risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D). After propensity score matching, aspirin users had a 52% overall reduction in T2D risk compared to non-users, with a stronger protective effect during the pandemic period than before. Authors suggest inflammation plays a key role in COVID-19-associated diabetes development. However, aspirin treatment was associated with increased bleeding risk.
Trimarco et al., 18 Jun 2025, Italy, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
Contact: gsantulli001@gmail.com.
Aspirin reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes associated with COVID-19
npj Metabolic Health and Disease, doi:10.1038/s44324-025-00072-3
This study aimed to determine whether daily low-dose aspirin reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) associated with COVID-19. A longitudinal cohort of 200,000 adults followed from 2018 to 2022 was analyzed, comparing T2D incidence between aspirin users and non-users. Propensity score matching was used to balance the groups. The incidence of T2D was substantially lower in the aspirin group, with Cox regression showing a 52% risk reduction. Kaplan-Meier analysis confirmed a significant divergence in cumulative T2D risk after two years. This protective effect was observed both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a stronger association during the pandemic period. These findings indicate that daily low-dose aspirin significantly reduces the risk of COVID-19-associated new-onset T2D, highlighting the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of T2D triggered or unmasked by COVID-19. Substantial evidence has shown that the incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) increased during the acute phase of COVID-19 pandemic [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] . Initial reports compared groups of patients who certainly had a positive SARS-CoV-2 test vs individuals with similar demographic characteristics who did not have COVID-19, showing the effect of the long-term individual COVID-19 infection (post-acute sequelae) on the incidence of diabetes [reviewed in ref. 3]. Recently, we analyzed a large real-world dataset of adults and demonstrated that the incidence of newly diagnosed T2D in the general population was 4.85 per 1000 person-years before the COVID-19 pandemic, vs 12.21 per 1000 person-years during the pandemic 14 . However, these findings do not allow any conclusion on the pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying the increased incidence of T2D in the pandemic period, which could be ascribed to direct effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and indirect effects like stress, changes in diet/exercise and in cardiovascular prevention strategies, as well as reduced access to healthcare [15] [16] [17] [18] . The observation that fully vaccinated individuals might be protected from the risk of incident diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection 19 seems to support a functional role of inflammation, autoimmune dysregulation, and endothelial dysfunction in the regulation of this process [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] . Indeed, experimental and epidemiological data have suggested that subclinical inflammation might contribute to metabolic diseases, insulin resistance, and T2D 29, 30 . Specifically, analyzing the comprehensive data collected in the ASPREE trial 31 , Zoungas and coworkers 32 have tested the hypothesis that treatment of healthy elder adults with 100 mg daily of enteric-coated oral aspirin would reduce incident diabetes or slow the increase in fasting glucose plasma concentration over time when compared with treatment with placebo. This post hoc analysis 32 revealed that, during a median follow-up of 4,7 years, the..
Author contributions G.S. and B.T. conceived the idea; V.T., R.I., M.V.M., and B.T. wrote the first draft of the paper; D.P. performed statistical analysis; S.S.J., P.G., F.R., G.G., A.S., G.E., R.P., G.P., C.M., and M.L. helped in collecting and analyzing data; G.S. revised critically the paper. V.T., R.I., D.P., and M.V.M. are co-first authors; G.S. and B.T. are co-last authors.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s44324-025-00072-3 . Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Gaetano Santulli. Reprints and permissions information is available at http://www.nature.com/reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article..
References
Accili, Can COVID-19 cause diabetes?, Nat. Metab
Ahlqvist, Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables, Lancet Diab. Endocrinol
Arda, Age-dependent pancreatic gene regulation reveals mechanisms governing human beta cell function, Cell Metab
Atkinson, Powers, Distinguishing the real from the hyperglycaemia: does COVID-19 induce diabetes?, Lancet Diab. Endocrinol
Bansal, Gubbi, Muniyappa, Metabolic syndrome and COVID 19: endocrine-immune-vascular interactions shapes clinical course, Endocrinology
Baron, A single-cell transcriptomic map of the human and mouse pancreas reveals inter-and intra-cell population structure, Cell Syst
Bellia, Prevalence and risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Endocrinol
Birabaharan, Kaelber, Pettus, Smith, Risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes in 600 055 people after COVID-19: a cohort study, Diab. Obes. Metab
Blodgett, Novel observations from next-generation RNA sequencing of highly purified human adult and fetal islet cell subsets, Diabetes
Cefalu, COVID-19 and rising incidence of diabetes: despite evolving data, an enigma still to be solved, Diab. Care
Choi, Kim, Song, Seo, Risk for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean adults: a Nationwide Matched Cohort Study, Endocrinol. Metab
Clark, Mirmira, SARS-CoV-2 infection of islet beta cells: evidence and implications, Cell Rep. Med
Coate, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are expressed in the microvasculature and ducts of human pancreas but are not enriched in beta cells, Cell Metab
D'ardes, Metabolic changes in SARS-CoV-2 infection: clinical data and molecular hypothesis to explain alterations of lipid profile and thyroid function observed in COVID-19 patients, Life (Basel)
Di Pietro, Plasma miR-1-3p levels predict severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Br. J. Pharm
Drucker, Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning, Cell Metab
El-Huneidi, Hamad, Taneera, Expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor "ACE2" in human pancreatic beta cells: to be or not to be!, Islets
El-Naas, New onset of type 1 and type 2 diabetes post-COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2492211
Erthal, Lifestyle pattern changes, eating disorders, and sleep quality in diabetes: how are the effects of 18 months of COVID-19 pandemic being felt?, Acta Diabetol
Faghihimani, Reduction of insulin resistance and plasma glucose level by salsalate treatment in persons with prediabetes, Endocr. Pract
Fignani, SARS-CoV-2 receptor angiotensin I-converting enzyme type 2 (ACE2) is expressed in human pancreatic beta-cells and in the human pancreas microvasculature, Front. Endocrinol
Fiorentino, Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis, EClinicalMedicine
Fleischman, Shoelson, Bernier, Goldfine, Salsalate improves glycemia and inflammatory parameters in obese young adults, Diab. Care
Gambardella, Role of endothelial miR-24 in COVID-19 cerebrovascular events, Crit. Care
Gaziano, Use of aspirin to reduce risk of initial vascular events in patients at moderate risk of cardiovascular disease (ARRIVE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet
Greenfield, Campbell, Relationship between inflammation, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: 'cause or effect'?, Curr. Diab. Rev
Group, Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in persons with diabetes mellitus, N. Engl. J. Med
Grubisic, Molecular mechanisms responsible for diabetogenic effects of COVID-19 infection-induction of autoimmune dysregulation and metabolic disturbances, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Holshue, Washington state -nCo VCIT: first case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N. Engl. J. Med
Izzo, Incidence of type 2 diabetes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Naples, Italy: a longitudinal cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Jankauskas, COVID-19 causes ferroptosis and oxidative stress in human endothelial cells, Antioxidants (Basel)
Johnson, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) coronary vascular thrombosis: correlation with neutrophil but not endothelial activation, Am. J. Pathol
Joseph, Comprehensive management of cardiovascular risk factors for adults with type 2 diabetes: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, Circulation
Kazakou, Diabetes and COVID-19: a bidirectional interplay, Front. Endocrinol
Khunti, COVID-19, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes, Diab. Care
Kim, New-Onset Diabetes After COVID-19, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Kusmartseva, Expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors in the pancreas of normal organ donors and individuals with COVID-19, Cell Metab
Lai, Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism
Landstra, De Koning, COVID-19 and diabetes: understanding the interrelationship and risks for a severe course, Front. Endocrinol
Lastra, Whaley-Connell, Diabetes: aspirin and prevention of diabetes still a topic of debate, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol
Lee, Halter, The pathophysiology of hyperglycemia in older adults: clinical considerations, Diab. Care
Lembo, Daily low dose aspirin halves incident type 2 diabetes in elderly subjects with prediabetes. A five-year longitudinal cohort study in a real-word population, Cardiovasc Diabetol
Lembo, Statin-induced risk of diabetes does not reduce cardiovascular benefits in primary prevention: a 6-year propensity-score matched study in a large population, Cardiovasc Diabetol
Li, Increased risk of new-onset diabetes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Public Health
Manrique, Lastra, Palmer, Gardner, Sowers, Aspirin and diabetes mellitus: revisiting an old player, Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc Dis
Mcneil, Effect of aspirin on all-cause mortality in the healthy elderly, N. Engl. J. Med
Mehran, Standardized bleeding definitions for cardiovascular clinical trials: a consensus report from the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium, Circulation
Miller, Terebuh, Kaelber, Xu, Davis, SARS-CoV-2 Infection and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Among Pediatric Patients, 2020 to 2022, JAMA Netw Open
Mone, Cognitive impairment in frail hypertensive elderly patients: role of hyperglycemia, Cells
Mone, Endothelial extracellular vesicles enriched in microRNA-34a predict new-onset diabetes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: novel insights for long COVID metabolic sequelae, J. Pharm. Exp. Ther
Mone, Stress hyperglycemia drives the risk of hospitalization for chest pain in patients with ischemia and nonobstructive coronary arteries (INOCA), Diab. Care
Morris, Effects of low-dose aspirin on acute inflammatory responses in humans, J. Immunol
Morris, Effects of pancreatic SARS-CoV-2 infection identified, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol
Muller, SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas, Nat. Metab
Notarte, Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: a systematic review, EClinicalMedicine
O'mahoney, The prevalence and long-term health effects of Long Covid among hospitalised and non-hospitalised populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis, EClinicalMedicine
O'mahoney, The risk of Long Covid symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies, Nat. Commun
Oguntibeju, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: examining the links, Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharm
Pantea Stoian, Cardiometabolic panel of international experts on syndemic C: new-onset diabetes mellitus in COVID-19: a scoping review, Diab. Ther
Pellegrini, Inflammatory trajectory of type 2 diabetes: novel opportunities for early and late treatment, Cells
Pradhan, Cook, Manson, Ridker, Buring, A randomized trial of low-dose aspirin in the prevention of clinical type 2 diabetes in women, Diab. Care
Qadir, SARS-CoV-2 infection of the pancreas promotes thrombofibrosis and is associated with new-onset diabetes, JCI Insight
Rubino, New-onset diabetes in Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Rumore, Kim, Potential role of salicylates in type 2 diabetes, Ann. Pharmacother
Sardu, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence, J Clin Med
Segerstolpe, Single-cell transcriptome profiling of human pancreatic islets in health and type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Shirakawa, Pancreatic beta-cell fate in subjects with COVID-19, J. Diab. Investig
Shoelson, Lee, Yuan, Inflammation and the IKK beta/I kappa B/NF-kappa B axis in obesity-and diet-induced insulin resistance, Int J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord
Steenblock, Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19, Nat. Commun
Stiegmann, Payne, Kiel, Stahlman, Increased prevalence of overweight and obesity and incidence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Active Component Service Members, U.S. Armed Forces
Tran, Perrodeau, Saldanha, Pane, Ravaud, Efficacy of first dose of COVID-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort, BMJ Med
Trimarco, A six-year study in a real-world population reveals an increased incidence of dyslipidemia during COVID-19, J. Clin. Invest
Trimarco, Increased prevalence of cardiovascular-kidneymetabolic syndrome during COVID-19: a propensity score-matched study, Diab. Res. Clin. Pract
Vas, Hopkins, Feher, Rubino, Whyte, Diabetes, obesity and COVID-19: a complex interplay, Diab. Obes. Metab
Weinberg Sibony, Segev, Dor, Raz, Overview of oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes, J. Diab
Wu, SARS-CoV-2 infects human pancreatic beta cells and elicits beta cell impairment, Cell Metab
Xie, Al-Aly, Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study, Lancet Diab. Endocrinol
Xiong, Incidence of diabetes following COVID-19 vaccination and SARS-CoV-2 infection in Hong Kong: a population-based cohort study, PLoS Med
Zeyfang, Wernecke, Bahrmann, Diabetes mellitus at an elderly age, Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes
Zoungas, Daily low-dose aspirin and incident type 2 diabetes in community-dwelling healthy older adults: a post-hoc analysis of efficacy and safety in the ASPREE randomised placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Diab. Endocrinol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s44324-025-00072-3",
"ISSN": [
"2948-2828"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s44324-025-00072-3",
"alternative-id": [
"72"
],
"article-number": "27",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "28 May 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "18 June 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trimarco",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Izzo",
"given": "Raffaele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pacella",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manzi",
"given": "Maria Virginia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jankauskas",
"given": "Stanislovas S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallo",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rozza",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giugliano",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spinelli",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esposito",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piccinocchi",
"given": "Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piccinocchi",
"given": "Gaetano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morisco",
"given": "Carmine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lembo",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santulli",
"given": "Gaetano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trimarco",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "npj Metabolic Health and Disease",
"container-title-short": "npj Metab Health Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-18T10:09:55Z",
"timestamp": 1750241395000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-18T11:03:27Z",
"timestamp": 1750244607000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000062",
"award": [
"R01-DK123259"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000062",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-19T04:28:33Z",
"timestamp": 1750307313265,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1750204800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1750204800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44324-025-00072-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44324-025-00072-3",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44324-025-00072-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "RA Stiegmann",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "MSMR",
"key": "72_CR1",
"unstructured": "Stiegmann, R. A., Payne, C. B., Kiel, M. A. & Stahlman, S. L. Increased prevalence of overweight and obesity and incidence of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Active Component Service Members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2018 to 2021. MSMR 30, 11–18 (2023).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2023.1170156",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "72_CR2",
"unstructured": "Li, J. et al. Increased risk of new-onset diabetes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 11, 1170156 (2023).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dci22-0067",
"author": "WT Cefalu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "913",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR3",
"unstructured": "Cefalu, W. T. COVID-19 and rising incidence of diabetes: despite evolving data, an enigma still to be solved. Diab. Care 46, 913–915 (2023).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2023.1215879",
"author": "C Bellia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol. ((Lausanne))",
"key": "72_CR4",
"unstructured": "Bellia, C. et al. Prevalence and risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. ((Lausanne)) 14, 1215879 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39444",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR5",
"unstructured": "Miller, M. G., Terebuh, P., Kaelber, D. C., Xu, R. & Davis, P. B. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Among Pediatric Patients, 2020 to 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 7, e2439444 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-020-00339-7",
"author": "D Accili",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Nat. Metab.",
"key": "72_CR6",
"unstructured": "Accili, D. Can COVID-19 cause diabetes?. Nat. Metab. 3, 123–125 (2021).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2018688",
"author": "F Rubino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "789",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "72_CR7",
"unstructured": "Rubino, F. et al. New-onset diabetes in Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 789–790 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3803/EnM.2023.1662",
"author": "JH Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol. Metab. ((Seoul.))",
"key": "72_CR8",
"unstructured": "Choi, J. H., Kim, K. M., Song, K. & Seo, G. H. Risk for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean adults: a Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. Endocrinol. Metab. ((Seoul.)) 38, 245–252 (2023).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155330",
"author": "H Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "72_CR9",
"unstructured": "Lai, H. et al. Risk of incident diabetes after COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 137, 155330 (2022).",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14659",
"author": "M Birabaharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1176",
"journal-title": "Diab. Obes. Metab.",
"key": "72_CR10",
"unstructured": "Birabaharan, M., Kaelber, D. C., Pettus, J. H. & Smith, D. M. Risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes in 600 055 people after COVID-19: a cohort study. Diab. Obes. Metab. 24, 1176–1179 (2022).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14134",
"author": "P Vas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1892",
"journal-title": "Diab. Obes. Metab.",
"key": "72_CR11",
"unstructured": "Vas, P., Hopkins, D., Feher, M., Rubino, F. & B Whyte, M. Diabetes, obesity and COVID-19: a complex interplay. Diab. Obes. Metab. 22, 1892–1896 (2020).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101762",
"author": "LL O’Mahoney",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "72_CR12",
"unstructured": "O’Mahoney, L. L. et al. The prevalence and long-term health effects of Long Covid among hospitalised and non-hospitalised populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 55, 101762 (2023).",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgad284",
"author": "SH Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1164",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "72_CR13",
"unstructured": "Kim, S. H. et al. New-Onset Diabetes After COVID-19. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 108, e1164–e1174 (2023).",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102345",
"author": "R Izzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "72_CR14",
"unstructured": "Izzo, R. et al. Incidence of type 2 diabetes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Naples, Italy: a longitudinal cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 66, 102345 (2023).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13300-023-01465-7",
"author": "A Pantea Stoian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Diab. Ther.",
"key": "72_CR15",
"unstructured": "Pantea Stoian, A. et al. Cardiometabolic panel of international experts on syndemic C: new-onset diabetes mellitus in COVID-19: a scoping review. Diab. Ther. 15, 33–60 (2024).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.01.016",
"author": "DJ Drucker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR16",
"unstructured": "Drucker, D. J. Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning. Cell Metab. 33, 479–498 (2021).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1318",
"author": "K Khunti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2645",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR17",
"unstructured": "Khunti, K. et al. COVID-19, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes. Diab. Care 44, 2645–2655 (2021).",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.649525",
"author": "CP Landstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Endocrinol. ((Lausanne))",
"key": "72_CR18",
"unstructured": "Landstra, C. P. & de Koning, E. J. P. COVID-19 and diabetes: understanding the interrelationship and risks for a severe course. Front. Endocrinol. ((Lausanne)) 12, 649525 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1004274",
"author": "X Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1004274",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med.",
"key": "72_CR19",
"unstructured": "Xiong, X. et al. Incidence of diabetes following COVID-19 vaccination and SARS-CoV-2 infection in Hong Kong: a population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 20, e1004274 (2023).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2022.780663",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR20",
"unstructured": "Kazakou, P. et al. Diabetes and COVID-19: a bidirectional interplay. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 780663 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endocr/bqaa112",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR21",
"unstructured": "Bansal, R., Gubbi, S. & Muniyappa, R. Metabolic syndrome and COVID 19: endocrine-immune-vascular interactions shapes clinical course. Endocrinology 161, bqaa112 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.09.004",
"author": "JE Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "72_CR22",
"unstructured": "Johnson, J. E. et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) coronary vascular thrombosis: correlation with neutrophil but not endothelial activation. Am. J. Pathol. 192, 112–120 (2022).",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9051417",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR23",
"unstructured": "Sardu, C. et al. Hypertension, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence. J Clin Med 9, 1417 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox12020326",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR24",
"unstructured": "Jankauskas, S. S. et al. COVID-19 causes ferroptosis and oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. Antioxidants (Basel) 12, 326 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241411576",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR25",
"unstructured": "Grubisic, B. et al. Molecular mechanisms responsible for diabetogenic effects of COVID-19 infection-induction of autoimmune dysregulation and metabolic disturbances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11576 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.17392",
"author": "P Di Pietro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharm.",
"key": "72_CR26",
"unstructured": "Di Pietro, P. et al. Plasma miR-1-3p levels predict severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Br. J. Pharm. 182, 451–467 (2025).",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2025.2492211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "72_CR27",
"unstructured": "El-Naas, A. et al. New onset of type 1 and type 2 diabetes post-COVID-19 infection: a systematic review. Emerg. Microbes Infect. https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2025.2492211 (2025)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-025-59012-w",
"author": "LL O’Mahoney",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "72_CR28",
"unstructured": "O’Mahoney, L. L. et al. The risk of Long Covid symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Nat. Commun. 16, 4249 (2025).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"author": "OO Oguntibeju",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharm.",
"key": "72_CR29",
"unstructured": "Oguntibeju, O. O. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: examining the links. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharm. 11, 45–63 (2019).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.70014",
"author": "R Weinberg Sibony",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Diab.",
"key": "72_CR30",
"unstructured": "Weinberg Sibony, R., Segev, O., Dor, S. & Raz, I. Overview of oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes. J. Diab. 16, e70014 (2024).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1803955",
"author": "JJ McNeil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1519",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "72_CR31",
"unstructured": "McNeil, J. J. et al. Effect of aspirin on all-cause mortality in the healthy elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 1519–1528 (2018).",
"volume": "379",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00327-3",
"author": "S Zoungas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "98",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diab. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR32",
"unstructured": "Zoungas, S. et al. Daily low-dose aspirin and incident type 2 diabetes in community-dwelling healthy older adults: a post-hoc analysis of efficacy and safety in the ASPREE randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 12, 98–106 (2024).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157339906776818532",
"author": "JR Greenfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Curr. Diab. Rev.",
"key": "72_CR33",
"unstructured": "Greenfield, J. R. & Campbell, L. V. Relationship between inflammation, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: ‘cause or effect’?. Curr. Diab. Rev. 2, 195–211 (2006).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-2500-0428",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR34",
"unstructured": "Zeyfang, A., Wernecke, J. & Bahrmann, A. Diabetes mellitus at an elderly age. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 133, 168–176 (2025)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc16-1732",
"author": "PG Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "444",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR35",
"unstructured": "Lee, P. G. & Halter, J. B. The pathophysiology of hyperglycemia in older adults: clinical considerations. Diab. Care 40, 444–452 (2017).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10082115",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR36",
"unstructured": "Mone, P. et al. Cognitive impairment in frail hypertensive elderly patients: role of hyperglycemia. Cells 10, 2115 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI183777",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR37",
"unstructured": "Trimarco, V. et al. A six-year study in a real-world population reveals an increased incidence of dyslipidemia during COVID-19. J. Clin. Invest. 134, e183777 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111926",
"author": "V Trimarco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diab. Res. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "72_CR38",
"unstructured": "Trimarco, V. et al. Increased prevalence of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome during COVID-19: a propensity score-matched study. Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 218, 111926 (2024).",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.596898",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR39",
"unstructured": "Fignani, D. et al. SARS-CoV-2 receptor angiotensin I-converting enzyme type 2 (ACE2) is expressed in human pancreatic beta-cells and in the human pancreas microvasculature. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11, 596898 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.005",
"author": "I Kusmartseva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1041",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR40",
"unstructured": "Kusmartseva, I. et al. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors in the pancreas of normal organ donors and individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab. 32, 1041–1051.e1046 (2020).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.151551",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR41",
"unstructured": "Qadir, M. M. F. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the pancreas promotes thrombofibrosis and is associated with new-onset diabetes. JCI Insight 6, e151551 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100380",
"author": "AL Clark",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "72_CR42",
"unstructured": "Clark, A. L. & Mirmira, R. G. SARS-CoV-2 infection of islet beta cells: evidence and implications. Cell Rep. Med. 2, 100380 (2021).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00087-5",
"author": "MA Atkinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "328",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diab. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR43",
"unstructured": "Atkinson, M. A. & Powers, A. C. Distinguishing the real from the hyperglycaemia: does COVID-19 induce diabetes?. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 9, 328–329 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23886-3",
"author": "C Steenblock",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "72_CR44",
"unstructured": "Steenblock, C. et al. Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 12, 3534 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdi.13671",
"author": "J Shirakawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2126",
"journal-title": "J. Diab. Investig.",
"key": "72_CR45",
"unstructured": "Shirakawa, J. Pancreatic beta-cell fate in subjects with COVID-19. J. Diab. Investig. 12, 2126–2128 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19382014.2021.1954458",
"author": "W El-Huneidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Islets",
"key": "72_CR46",
"unstructured": "El-Huneidi, W., Hamad, M. & Taneera, J. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor “ACE2” in human pancreatic beta cells: to be or not to be!. Islets 13, 106–114 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00481-6",
"author": "A Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR47",
"unstructured": "Morris, A. Effects of pancreatic SARS-CoV-2 infection identified. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 17, 192 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00347-1",
"author": "JA Muller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Nat. Metab.",
"key": "72_CR48",
"unstructured": "Muller, J. A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Nat. Metab. 3, 149–165 (2021).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.013",
"author": "CT Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1565",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR49",
"unstructured": "Wu, C. T. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects human pancreatic beta cells and elicits beta cell impairment. Cell Metab. 33, 1565–1576.e1565 (2021).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.006",
"author": "KC Coate",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1028",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR50",
"unstructured": "Coate, K. C. et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are expressed in the microvasculature and ducts of human pancreas but are not enriched in beta cells. Cell Metab. 32, 1028–1040.e1024 (2020).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.020",
"author": "A Segerstolpe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR51",
"unstructured": "Segerstolpe, A. et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of human pancreatic islets in health and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 24, 593–607 (2016).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db15-0039",
"author": "DM Blodgett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3172",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "72_CR52",
"unstructured": "Blodgett, D. M. et al. Novel observations from next-generation RNA sequencing of highly purified human adult and fetal islet cell subsets. Diabetes 64, 3172–3181 (2015).",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cels.2016.08.011",
"author": "M Baron",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "346",
"journal-title": "Cell Syst.",
"key": "72_CR53",
"unstructured": "Baron, M. et al. A single-cell transcriptomic map of the human and mouse pancreas reveals inter- and intra-cell population structure. Cell Syst. 3, 346–360.e344 (2016).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.002",
"author": "HE Arda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "909",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab.",
"key": "72_CR54",
"unstructured": "Arda, H. E. et al. Age-dependent pancreatic gene regulation reveals mechanisms governing human beta cell function. Cell Metab. 23, 909–920 (2016).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life11080860",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR55",
"unstructured": "D’Ardes, D. et al. Metabolic changes in SARS-CoV-2 infection: clinical data and molecular hypothesis to explain alterations of lipid profile and thyroid function observed in COVID-19 patients. Life (Basel) 11, 860 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30051-2",
"author": "E Ahlqvist",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "361",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diab. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR56",
"unstructured": "Ahlqvist, E. et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 6, 361–369 (2018).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"author": "ML Holshue",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "72_CR57",
"unstructured": "Holshue, M. L. et al. Washington state -nCo VCIT: first case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 929–936 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "72_CR58",
"unstructured": "Lembo, M. et al. Daily low dose aspirin halves incident type 2 diabetes in elderly subjects with prediabetes. A five-year longitudinal cohort study in a real-word population. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025; in press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells13191662",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR59",
"unstructured": "Pellegrini, V. et al. Inflammatory trajectory of type 2 diabetes: novel opportunities for early and late treatment. Cells 13, 1662 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1345/aph.1M483",
"author": "MM Rumore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1207",
"journal-title": "Ann. Pharmacother.",
"key": "72_CR60",
"unstructured": "Rumore, M. M. & Kim, K. S. Potential role of salicylates in type 2 diabetes. Ann. Pharmacother. 44, 1207–1221 (2010).",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0900477",
"author": "T Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2089",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "72_CR61",
"unstructured": "Morris, T. et al. Effects of low-dose aspirin on acute inflammatory responses in humans. J. Immunol. 183, 2089–2096 (2009).",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ijo.0802501",
"author": "SE Shoelson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S49",
"journal-title": "Int J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "72_CR62",
"unstructured": "Shoelson, S. E., Lee, J. & Yuan, M. Inflammation and the IKK beta/I kappa B/NF-kappa B axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 27, S49–S52 (2003).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753944707088185",
"author": "C Manrique",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc Dis.",
"key": "72_CR63",
"unstructured": "Manrique, C., Lastra, G., Palmer, J., Gardner, M. & Sowers, J. R. Aspirin and diabetes mellitus: revisiting an old player. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc Dis. 2, 37–42 (2008).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2009.109",
"author": "G Lastra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR64",
"unstructured": "Lastra, G. & Whaley-Connell, A. Diabetes: aspirin and prevention of diabetes still a topic of debate. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 5, 365–366 (2009).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP12064.OR",
"author": "E Faghihimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "826",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Pract.",
"key": "72_CR65",
"unstructured": "Faghihimani, E. et al. Reduction of insulin resistance and plasma glucose level by salsalate treatment in persons with prediabetes. Endocr. Pract. 18, 826–833 (2012).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc07-1338",
"author": "A Fleischman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR66",
"unstructured": "Fleischman, A., Shoelson, S. E., Bernier, R. & Goldfine, A. B. Salsalate improves glycemia and inflammatory parameters in obese young adults. Diab. Care 31, 289–294 (2008).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc08-1206",
"author": "AD Pradhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR67",
"unstructured": "Pradhan, A. D., Cook, N. R., Manson, J. E., Ridker, P. M. & Buring, J. E. A randomized trial of low-dose aspirin in the prevention of clinical type 2 diabetes in women. Diab. Care 32, 3–8 (2009).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1804988",
"author": "ASC Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1529",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "72_CR68",
"unstructured": "Group, A. S. C. et al. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in persons with diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 1529–1539 (2018).",
"volume": "379",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31924-X",
"author": "JM Gaziano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1036",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "72_CR69",
"unstructured": "Gaziano, J. M. et al. Use of aspirin to reduce risk of initial vascular events in patients at moderate risk of cardiovascular disease (ARRIVE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 392, 1036–1046 (2018).",
"volume": "392",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-022-01927-7",
"author": "IN Erthal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1265",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol.",
"key": "72_CR70",
"unstructured": "Erthal, I. N. et al. Lifestyle pattern changes, eating disorders, and sleep quality in diabetes: how are the effects of 18 months of COVID-19 pandemic being felt?. Acta Diabetol. 59, 1265–1274 (2022).",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjmed-2022-000229",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "72_CR71",
"unstructured": "Tran, V. T., Perrodeau, E., Saldanha, J., Pane, I. & Ravaud, P. Efficacy of first dose of COVID-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort. BMJ Med. 2, e000229 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624",
"author": "KI Notarte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "72_CR72",
"unstructured": "Notarte, K. I. et al. Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: a systematic review. EClinicalMedicine 53, 101624 (2022).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.122.001253",
"author": "P Mone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Exp. Ther.",
"key": "72_CR73",
"unstructured": "Mone, P. et al. Endothelial extracellular vesicles enriched in microRNA-34a predict new-onset diabetes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: novel insights for long COVID metabolic sequelae. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 389, 34–39 (2024).",
"volume": "389",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125",
"author": "G Fiorentino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "72_CR74",
"unstructured": "Fiorentino, G. et al. Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis. EClinicalMedicine 40, 101125 (2021).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03731-1",
"author": "J Gambardella",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "72_CR75",
"unstructured": "Gambardella, J. et al. Role of endothelial miR-24 in COVID-19 cerebrovascular events. Crit. Care 25, 306 (2021).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00044-4",
"author": "Y Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diab. Endocrinol.",
"key": "72_CR76",
"unstructured": "Xie, Y. & Al-Aly, Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 10, 311–321 (2022).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIR.0000000000001040",
"author": "JJ Joseph",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e722",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "72_CR77",
"unstructured": "Joseph, J. J. et al. Comprehensive management of cardiovascular risk factors for adults with type 2 diabetes: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 145, e722–e759 (2022).",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.009449",
"author": "R Mehran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2736",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "72_CR78",
"unstructured": "Mehran, R. et al. Standardized bleeding definitions for cardiovascular clinical trials: a consensus report from the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium. Circulation 123, 2736–2747 (2011).",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc22-0783",
"author": "P Mone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Diab. Care",
"key": "72_CR79",
"unstructured": "Mone, P. et al. Stress hyperglycemia drives the risk of hospitalization for chest pain in patients with ischemia and nonobstructive coronary arteries (INOCA). Diab. Care 46, 450–454 (2023).",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-025-02798-2",
"author": "M Lembo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Diabetol",
"key": "72_CR80",
"unstructured": "Lembo, M. et al. Statin-induced risk of diabetes does not reduce cardiovascular benefits in primary prevention: a 6-year propensity-score matched study in a large population. Cardiovasc Diabetol 24, 233 (2025).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2025"
}
],
"reference-count": 80,
"references-count": 80,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44324-025-00072-3"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Aspirin reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes associated with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "3"
}