COVID-19 in individuals adapted to aerobic exercise
et al., Pulmonologiya, doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2020-30-5-553-560, Oct 2020
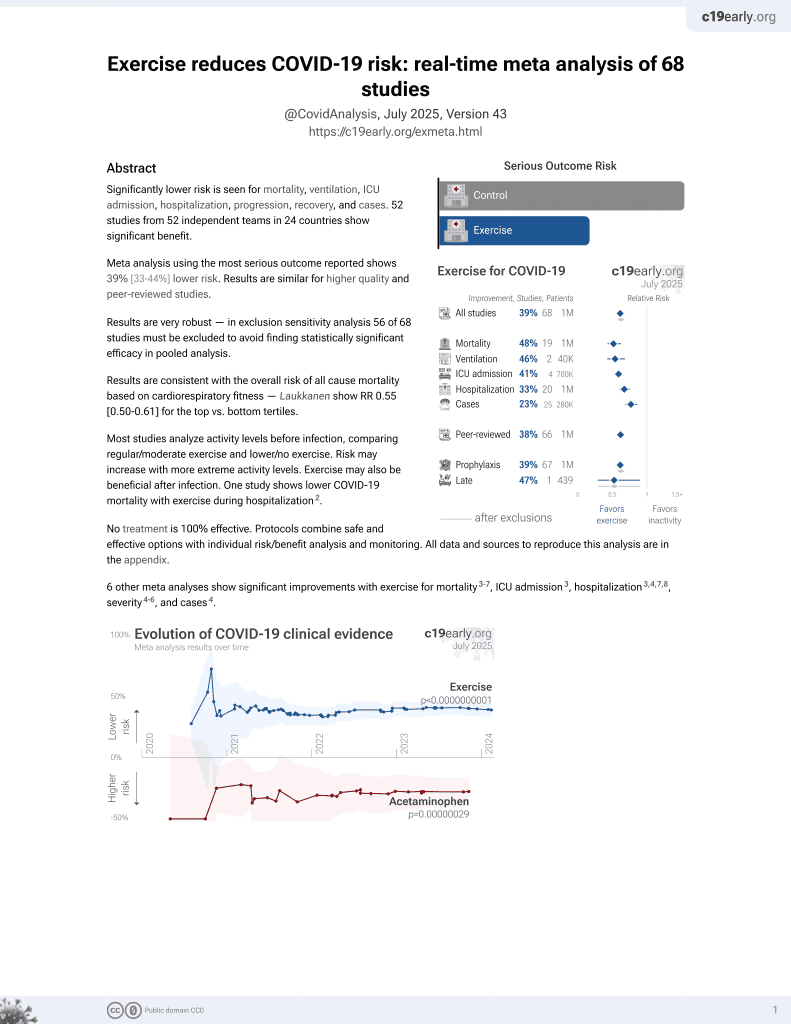
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
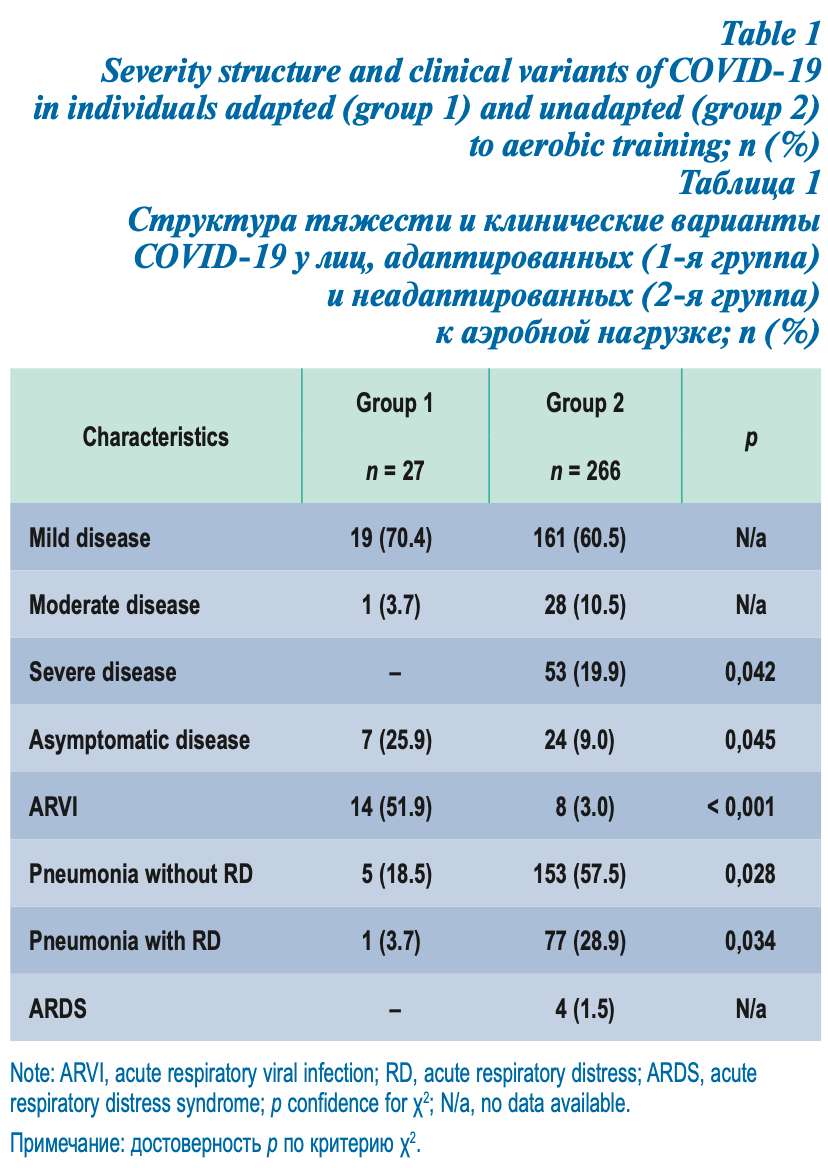
Retrospective 293 COVID+ patients in Russia, showing lower risk of severe COVID-19 for individuals who regularly practice aerobic training in unadjusted results.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of severe case, 98.3% lower, RR 0.02, p = 0.007, high activity levels 0 of 27 (0.0%), low activity levels 53 of 266 (19.9%), NNT 5.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tret'yakov et al., 26 Oct 2020, retrospective, Russia, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
COVID-19 in individuals adapted to aerobic exercise
PULMONOLOGIYA, doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2020-30-5-553-560
Analysis of COVID-19 features in individuals who regularly practice aerobic training. Methods. Asymptomatic persons and patients with COVID-19 older than 30 years, 293 people (180 men and 113 women), 214 of them -inhabitants of the Moscow region (the beginning of the sampling -2 nd decade of April 2020) and 79 -inhabitants of the Belgorod region (the beginning of the sampling -2 nd decade of May 2020), adapted (27 people -1 st group) and unadapted (266 -control group) to aerobic training (AT). Computer tomography of the chest, RNA test for SARS-CoV-2 in smears from the nasopharynx-oropharynx, the clinical blood sample and level of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 were studied. The criterion for adaptation to aerobic loads was considered compliance with the rules of the American Heart Association, 2008. Results. Adapted to AT individuals, in contrast to the control group, characterized with the prevalence of asymptomatic (p = 0.045) and absence of severe forms of COVID-19, limited cataral simptoms of the disease (p < 0.001), rare pneumonia with absence (1) or presence (2) of acute respiratory failure (p 1 = 0,028; p 2 = 0,034), along with lower prevalence of diseases, potentiating this infection (p = 0.03). Conclusion. Patients adapted to AT have less severe course of COVID-19.
References
Agarwal, Welsch, Keller, Francis, Chronic exercise modulates RAS components and improves balance between pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the brain of SHR, Basic Res. Cardiol, doi:10.1007/s00395-011-0231-7
Agarwal, Welsch, Keller, Francis, Chronic exercise modulates RAS components and improves balance between pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the brain of SHR, Basic Res. Cardiol, doi:10.1007/s00395-011-0231-7
Campbell, Infekt nach Marathon? Mythos widerlegt!, Dtsch. Med. Wochensch, doi:10.1055/a-0598-1219
Campbell, Infekt nach Marathon? Mythos widerlegt!, Dtsch. Med. Wochensch, doi:10.1055/a-0598-1219
Campbell, Turner, There is limited existing evidence to support the common assumption that strenuous endurance exercise bouts impair immune competency, Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1080/1744666
Campbell, Turner, There is limited existing evidence to support the common assumption that strenuous endurance exercise bouts impair immune competency, Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1080/1744666X.2019.1548933
Combes, Dekerle, Dumont, Continuous exercise induces airway epithelium damage while a matched-intensity and volume intermittent exercise does not, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-019-0978-1
Combes, Dekerle, Dumont, Continuous exercise induces airway epithelium damage while a matched-intensity and volume intermittent exercise does not, Respir. Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-019-0978-1.Поступила25.07.20
Dizon, Seo, Kim, Exercise perspective on common cardiac medications, Integr. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.imr.2013.04.006
Dizon, Seo, Kim, Exercise perspective on common cardiac medications, Integr. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.imr.2013.04.006
Dmitricu, .ru Ченцова Дарья Дмитриевна -врач-терапевт клинико-диагностического центра Федерального государственного автономного образовательного учреждения высшего образования
Estruel-Amades, Camps-Bossacoma, Massot-Cladera, Alterations in the innate immune system due to exhausting exercise in intensively trained rats, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-57783-4
Estruel-Amades, Camps-Bossacoma, Massot-Cladera, Alterations in the innate immune system due to exhausting exercise in intensively trained rats, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-57783-4
Foster, Ravikumar, Bellotto, Fatty diabetic lung: altered alveolar structure and surfactant protein expression, Am. J. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00041.2009
Foster, Ravikumar, Bellotto, Fatty diabetic lung: altered alveolar structure and surfactant protein expression, Am. J. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00041.2009
Gazenko, Meerson, Pshennikova, Physiology of adaptation processes
Gleeson, Pyne, Austin, Epstein-Barr virus reactivation and upper-respiratory illness in elite swimmers, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc, doi:10.1097/00005768-200203000-00005
Gleeson, Pyne, Austin, Epstein-Barr virus reactivation and upper-respiratory illness in elite swimmers, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc, doi:10.1097/00005768-200203000-00005
Halabchi, Ahmadinejad, Selk-Ghaffari, COVID-19 Epidemic: exercise or not to exercise; that is the question! Asian, J. Sports. Med, doi:10.5812/asjsm.102630
Halabchi, Ahmadinejad, Selk-Ghaffari, COVID-19 Epidemic: exercise or not to exercise; that is the question! Asian, J. Sports. Med, doi:10.5812/asjsm.102630
Kai, Kai, Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors -lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19, Hypertens. Res, doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8
Kai, Kai, Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors -lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19, Hypertens. Res, doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8
Magalhães, Nunes-Silva, Rocha, Two protocols of aerobic exercise modulate the counter-regulatory axis of the renin-angiotensin system, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03208
Magalhães, Nunes-Silva, Rocha, Two protocols of aerobic exercise modulate the counterregulatory axis of the renin-angiotensin system, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03208
Meerson, Pshennikova, Adaptation to stressful situations and physical exertion
Nieman, Exercise, upper respiratory tract infection, and the immune system, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/00005768-199402000-00002
Nieman, Exercise, upper respiratory tract infection, and the immune system, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/00005768-199402000-00002
Nieman, Wentz, The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system, J. Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009
Nieman, Wentz, The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system, J. Sport Health Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009
Pashukova, Dopira, D'yakonov, Psychological research: a workshop on general psychology for students of pedagogical universities
Paterlini, On the front lines of coronavirus: the Italian response to covid-19, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1065
Paterlini, On the front lines of coronavirus: the Italian response to covid-19, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1065
Poos, Costello, Carlson-Newberry, Military strategies for sustainment of nutrition and immune function in the field, doi:10.17226/6450
Poos, Costello, Carlson-Newberry, Military strategies for sustainment of nutrition and immune function in the field, doi:10.17226/6450
Pulmonologist, None
Svetlana, Белгородский государственный национальный исследовательский университет» Министерства науки и высшего образования Российской Федерации, врач-рентгенолог Областного государственного бюджетного учреждения здравоохранения «Городская больница № 2 г
Tedjasaputra, Bouwsema, Stickland, Effect of aerobic fitness on capillary blood volume and diffusing membrane capacity responses to exercise, J. Physiol, doi:10.1113/JP272037
Tedjasaputra, Bouwsema, Stickland, Effect of aerobic fitness on capillary blood volume and diffusing membrane capacity responses to exercise, J. Physiol, doi:10.1113/JP272037
Timmons, Cieslak, Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review, Exerc. Immunol. Rev
Timmons, Cieslak, Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review, Exerc. Immunol. Rev
Toledo, Magalhaes, Hizume, Aerobic exercise attenuates pulmonary injury induced by exposure to cigarette smoke, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.00003411
Toledo, Magalhaes, Hizume, Aerobic exercise attenuates pulmonary injury induced by exposure to cigarette smoke, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.00003411
Tret, Yu, COVID-19 in individuals adapted to aerobic exercise
Tret, Медицинского института Федерального государственного автономного образовательного учреждения высшего образования «Белгородский государственный национальный исследовательский университет
Wackerhage, Everett, Krüger, Sport, exercise and COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, Dtsch. Z. Sportmed, doi:10.5960/dzsm.2020.441
Wackerhage, Everett, Krüger, Sport, exercise and COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, Dtsch. Z. Sportmed, doi:10.5960/dzsm.2020.441
Yakov, Yu, Ермилов Олег Владимирович -ассистент Медицинского института Федерального государственного автономного образовательного учреждения высшего образования «Белгородский государственный национальный исследовательский университет» Министерства науки и высшего образования Российской Федерации, врач-пульмонолог пульмонологического отделения Областного государственного Tret
Yan, Xiao, Lin, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword?, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202000782
Yan, Xiao, Lin, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword?, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202000782
Yilmaz, Ravikumar, Gyawali, Alveolarcapillary adaptation to chronic hypoxia in the fatty lung, Acta Physiol, doi:10.1111/apha.12419
Yilmaz, Ravikumar, Gyawali, Alveolarcapillary adaptation to chronic hypoxia in the fatty lung, Acta Physiol, doi:10.1111/apha.12419
Zhang, Zhu, Cai, Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134
Zhang, Zhu, Cai, Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134
Газенко, Меерсон, Пшенникова М. Физиология адаптационных процессов
Меерсон, Пшенникова, Г. Адаптация к стрессорным ситуациям и физическим нагрузкам
Пашукова, Допира, Дьяконов, .В. Психологические исследования: Практикум по общей психологии для студентов педагогических вузов
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18093/0869-0189-2020-30-5-553-560",
"ISSN": [
"2541-9617",
"0869-0189"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-2020-30-5-553-560",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Analysis of COVID-19 features in individuals who regularly practice aerobic training. <jats:bold>Methods</jats:bold>. Asymptomatic persons and patients with COVID-19 older than 30 years, 293 people (180 men and 113 women), 214 of them – inhabitants of the Moscow region (the beginning of the sampling – 2<jats:sup>nd</jats:sup> decade of April 2020) and 79 – inhabitants of the Belgorod region (the beginning of the sampling – 2<jats:sup>nd</jats:sup> decade of May 2020), adapted (27 people 1<jats:sup>st</jats:sup> group) and unadapted (266 – control group) to aerobic training (AT). Computer tomography of the chest, RNA test for SARS-CoV-2 in smears from the nasopharynx-oropharynx, the clinical blood sample and level of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 were studied. The criterion for adaptation to aerobic loads was considered compliance with the rules of the American Heart Association, 2008. <jats:bold>Results</jats:bold>. Adapted to AT individuals, in contrast to the control group, characterized with the prevalence of asymptomatic (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.045) and absence of severe forms of COVID-19, limited cataral simptoms of the disease (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001), rare pneumonia with absence (1) or presence (2) of acute respiratory failure (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic><jats:sub>1</jats:sub> = 0,028; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic><jats:sub>2</jats:sub> = 0,034), along with lower prevalence of diseases, potentiating this infection (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03). <jats:bold>Conclusion</jats:bold>. Patients adapted to AT have less severe course of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal Belgorod National Research University, Ministry of Education and Science of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Tret'yakov",
"given": "A. Yu.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal Belgorod National Research University, Ministry of Education and Science of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Zakharchenko",
"given": "S. P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "V.P.Serbskiy National Medical Research Center оf Psychiatry аnd Narcology, Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Romasenko",
"given": "L. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Institution “City Сlinic No.212”, Moscow Healthcare Department"
}
],
"family": "Dyatlova",
"given": "A. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal Belgorod National Research University, Ministry of Education and Science of Russia; Belgorod Сity Municipal Нospital No.2"
}
],
"family": "Zhabskaya",
"given": "A. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8489-3851",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal Belgorod National Research University, Ministry of Education and Science of Russia; Saint Ioasaf Belgorod Region Clinical Hospital"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ermilov",
"given": "O. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal Belgorod National Research University, Ministry of Education and Science of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Tret'yakov",
"given": "M. A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Chentsova",
"given": "D. D.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PULMONOLOGIYA",
"container-title-short": "Pulʹmonologiâ (Mosk.)",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journal.pulmonology.ru"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-26T14:30:56Z",
"timestamp": 1603722656000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-26T14:36:41Z",
"timestamp": 1603723001000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T07:50:23Z",
"timestamp": 1667893823559
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://journal.pulmonology.ru/pulm/about/editorialPolicies#openAccessPolicy",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1603670400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journal.pulmonology.ru/pulm/article/viewFile/1376/1753",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "7431",
"original-title": [],
"page": "553-560",
"prefix": "10.18093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Scientific and Practical Reviewed Journal Pulmonology",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Gazenko O., Meerson F., Pshennikova M. [Physiology of adaptation processes]. Moscow: Nauka; 1986 (in Russian)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/asjsm.102630",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Halabchi F., Ahmadinejad Z., Selk-Ghaffari M. COVID-19 Epidemic: exercise or not to exercise; that is the question! Asian. J. Sports. Med. 2020; 11 (1): e102630. DOI: 10.5812/asjsm.102630."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5960/dzsm.2020.441",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Wackerhage H., Everett R., Krüger K. et al. Sport, exercise and COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed. 2020; 71 (5): e1–12. DOI: 10.5960/dzsm.2020.441."
},
{
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Pashukova T.I., Dopira A.I., D’yakonov G.V. [Psychological research: a workshop on general psychology for students of pedagogical universities]. Moscow: Institut prakticheskoy psikhologii; 1996 (in Russian)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1065",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Paterlini M. On the front lines of coronavirus: the Italian response to covid-19. Br. Med. J. 2020; 368: m1065. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.m1065."
},
{
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Meerson F.Z., Pshennikova M.G. [Adaptation to stressful situations and physical exertion]. M.: Meditsina; 1988 (in Russian)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00003411",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Toledo A.C., Magalhaes R.M., Hizume D.C. et al. Aerobic exercise attenuates pulmonary injury induced by exposure to cigarette smoke. Eur. Respir. J. 2012; 39 (2): 254–264. DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00003411."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202000782",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Yan T., Xiao R., Lin G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARSCoV-2: A double-edged sword? FASEB J. 2020; 34 (5): 6017–6026. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202000782."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1113/JP272037",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Tedjasaputra V., Bouwsema M.M., Stickland M.K. Effect of aerobic fitness on capillary blood volume and diffusing membrane capacity responses to exercise. J. Physiol. 2016; 594 (15): 4359–4370. DOI: 10.1113/JP272037."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00041.2009",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Foster D.J., Ravikumar P., Bellotto D.J. et al. Fatty diabetic lung: altered alveolar structure and surfactant protein expression. Am. J. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010; 298 (3): L392–403. DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00041.2009."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apha.12419",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Yilmaz C., Ravikumar P., Gyawali D. et al. Alveolarcapillary adaptation to chronic hypoxia in the fatty lung. Acta Physiol. 2015; 213 (4): 933–946. DOI: 10.1111/apha.12419."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imr.2013.04.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Dizon L.A., Seo D.Y., Kim H.K. et al. Exercise perspective on common cardiac medications. Integr. Med. Res. 2013; 2 (2): 49–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2013.04.006."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00395-011-0231-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Agarwal D., Welsch M.A., Keller J.N., Francis J. Chronic exercise modulates RAS components and improves balance between pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the brain of SHR. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011; 106 (6): 1069–1085. DOI: 10.1007/s00395-011-0231-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Zhang P., Zhu L., Cai J. Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020; 126 (12): 1671–1681. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Kai H., Kai M. Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors – lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19. Hypertens. Res. 2020; 43 (7): 648–654. DOI: 10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03208",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Magalhães D.M., Nunes-Silva A., Rocha G.C. et al. Two protocols of aerobic exercise modulate the counter-regulatory axis of the renin-angiotensin system. Heliyon. 2020; 6 (1): e03208. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03208."
},
{
"DOI": "10.17226/6450",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Poos M.I., Costello R., Carlson-Newberry S.J. Military strategies for sustainment of nutrition and immune function in the field. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, Institute of Medicine; 1999. DOI: 10.17226/6450."
},
{
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Timmons B.W., Cieslak T. Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2008; 14: 8–23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Nieman D.C., Wentz L.M. The compelling link between physical activity and the body’s defense system. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019; 8 (3): 201–217. DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2018.09.009."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-0598-1219",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Campbell J.P. Infekt nach Marathon? Mythos widerlegt! Dtsch. Med. Wochensch. 2018; 143 (12): 853–853. DOI: 10.1055/a-0598-1219."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005768-200203000-00005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Gleeson M., Pyne D.B., Austin J.P. et al. Epstein–Barr virus reactivation and upper-respiratory illness in elite swimmers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002; 34 (3): 411–417. DOI: 10.1097/00005768-200203000-00005."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/00005768-199402000-00002",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Nieman D.C. Exercise, upper respiratory tract infection, and the immune system. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994; 26 (2): 128–139. DOI: 10.1249/00005768-199402000-00002."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2019.1548933",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Campbell J.P., Turner J.E. There is limited existing evidence to support the common assumption that strenuous endurance exercise bouts impair immune competency. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019; 15 (2): 105–109. DOI: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1548933."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-57783-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Estruel-Amades S., Camps-Bossacoma M., Massot-Cladera M. et al. Alterations in the innate immune system due to exhausting exercise in intensively trained rats. Sci. Rep. 2020; 10 (1): 967. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-57783-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-019-0978-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Combes A., Dekerle J., Dumont X. et al. Continuous exercise induces airway epithelium damage while a matched-intensity and volume intermittent exercise does not. Respir. Res. 2019; 20 (1): 12. DOI: 10.1186/s12931-019-0978-1."
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journal.pulmonology.ru/pulm/article/view/1376"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 in individuals adapted to aerobic exercise",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-crossmark",
"volume": "30"
}