Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054, NCT04625114, Sep 2022
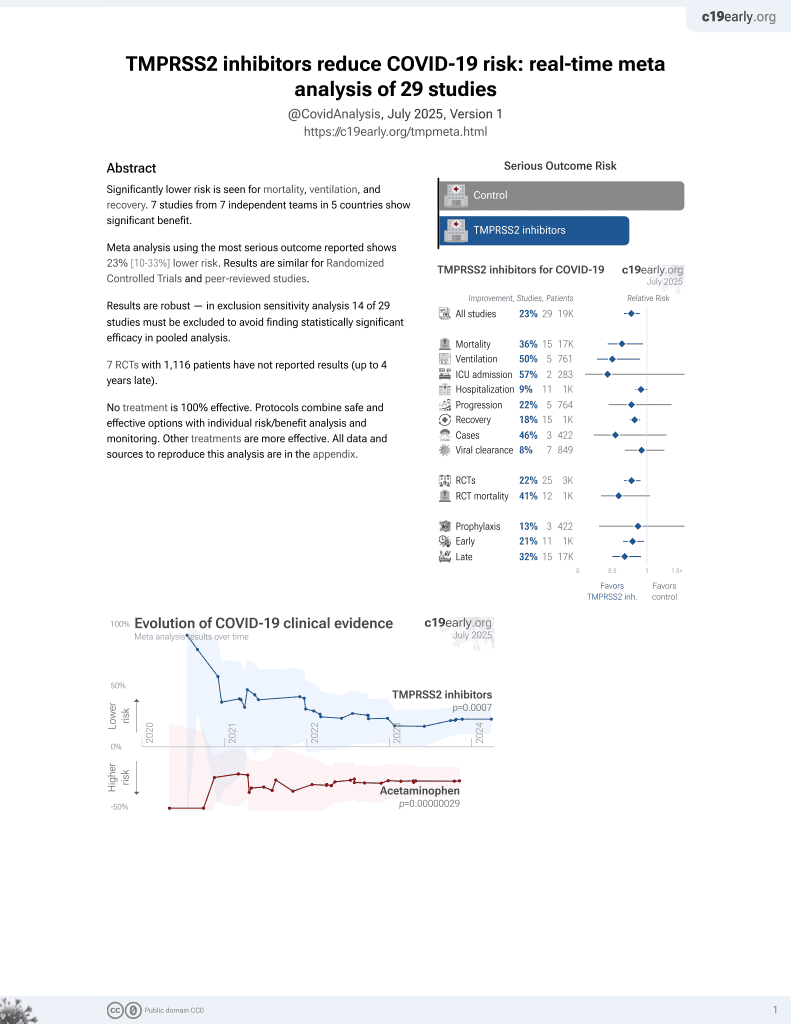
22nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.00063 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
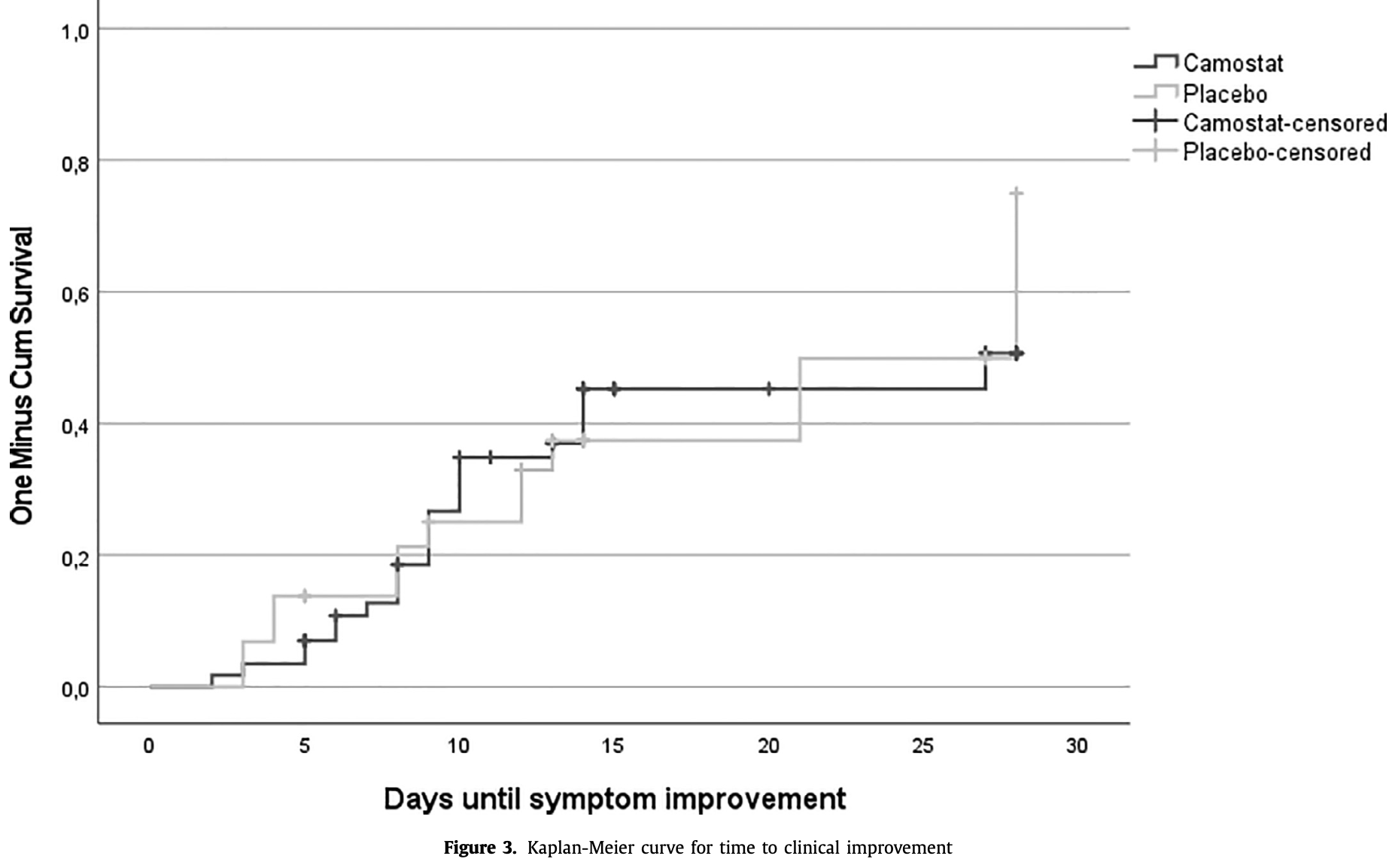
RCT 90 outpatients showing no significant difference in viral load or time to clinical improvement with camostat mesylate. The trial was discontinued early and did not reach the intended sample size. Authors note that combining camostat with a cathepsin inhibitor may improve efficacy.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and camostat.
|
risk of hospitalization, 36.4% higher, RR 1.36, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 66 (4.5%), control 1 of 30 (3.3%).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 7.7% lower, HR 0.92, p = 0.84, treatment 61, control 29, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tobback et al., 30 Sep 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Belgium, peer-reviewed, median age 40.0, 13 authors, study period November 2020 - June 2021, average treatment delay 3.0 days, trial NCT04625114 (history).
Contact: els.tobback@uzgent.be, sabine.buysse2@uzgent.be, lucas.vandooren@uzgent.be, vanherrewege@uzgent.be, cyril.barbezange@sciensano.be, veronik.hutse@sciensano.be, marta.romano@sciensano.be, isabelle.thomas.xyz@gmail.com, elizaveta.padalko@uzgent.be, steven.callens@uzgent.be.
Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of 300 mg camostat mesylate three times daily in a fasted state to treat early phase COVID-19 in an ambulatory setting. Methods: We conducted a phase II randomized controlled trial in symptomatic (maximum 5 days) and asymptomatic patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either camostat mesylate or a placebo. Outcomes included change in nasopharyngeal viral load, time to clinical improvement, the presence of neutralizing antibodies, and safety. Results: Of 96 participants randomized between November 2020 and June 2021, analyses were performed on the data of 90 participants who completed treatment (N = 61 camostat mesylate, N = 29 placebo). The estimated mean change in cycle threshold between day 1 and day 5 between the camostat and placebo group was 1.183 ( P = 0.511). The unadjusted hazard ratio for clinical improvement in the camostat group was 0.965 (95% confidence interval, 0.480-1.942, P = 0.921 by Cox regression). The percentage distribution of the 50% neutralizing antibody titer at day 28 visit and frequency of adverse events were similar between the two groups. Conclusion: Under this protocol, camostat mesylate was not found to be effective as an antiviral drug against SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author contributions MADS conceived and designed the analysis, contributed to data collectiona and analysis and review, ET wrote the paper and contributed to data collection and analysis; LD, SB, SVH and LVD contributed to data collection; SDG, VH, MR, IT, EP contributed to data analysis; SC contributed to the protocol and review.
References
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill
Devos, Van Thillo, Compernolle, Najdovski, Romano et al., Early high antibody titre convalescent plasma for hospitalised COVID-19 patients: DAWn-plasma, Eur Respir J
Gunst, Staerke, Pahus, Kristensen, Bodilsen et al., Efficacy of the TMPRSS2 inhibitor camostat mesilate in patients hospitalized with COVID-19-a double-blind randomized controlled trial, EClinicalmedicine
Harris, Taylor, Minor, Elliott, Fernandez et al., The RED-Cap consortium: building an international community of software partners, J Biomed Inform
Harris, Taylor, Thielke, Payne, Gonzalez et al., Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) -a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J Biomed Inform
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Kitagawa, Arai, Iida, Mukai, Furukawa et al., A phase I study of high dose camostat mesylate in healthy adults provides a rationale to re-purpose the TMPRSS2 inhibitor for the treatment of COVID-19, Clin Transl Sci
Kreutzberger, Sanyal, Ojha, Pyle, Vapalahti et al., Synergistic block of SARS-CoV-2 infection by combined drug inhibition of the host entry factors PIKfyve kinase and TMPRSS2 protease, J Virol
Midgley, Hood, Proctor, Chasseaud, Irons et al., Metabolic fate of 14C-camostat mesylate in man, rat and dog after intravenous administration, Xenobiotica
Sakr, Bensasi, Taha, Bauer, Kthe et al., Camostat mesylate therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Intensive Care Med
Uno, Camostat mesilate therapy for COVID-19, Intern Emerg Med
Willett, Grove, Maclean, Wilkie, Logan et al., The hypertransmissible SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant exhibits significant antigenic change, vaccine escape and a switch in cell entry mechanism, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111
Zhou, Vedantham, Lu, Agudelo, Jr et al., Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry, Antiviral Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971222003885"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8852-8373",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tobback",
"given": "Els",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5482-0926",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Degroote",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buysse",
"given": "Sabine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0022-1212",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Delesie",
"given": "Liesbeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2650-3928",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Van Dooren",
"given": "Lucas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0942-1106",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vanherrewege",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9606-2983",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Barbezange",
"given": "Cyril",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutse",
"given": "Veronik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8996-7899",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Romano",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padalko",
"given": "Elizaveta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7245-527X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Callens",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Scheerder",
"given": "Marie-Angélique",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"ijidonline.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-05T15:33:47Z",
"timestamp": 1657035227000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T14:34:31Z",
"timestamp": 1715438071000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ono Pharmaceutical Co Ltd"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T15:10:10Z",
"timestamp": 1715440210501
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661990400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1661990400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656547200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222003885?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222003885?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "628-635",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0002",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01724-2021",
"article-title": "Early high antibody titre convalescent plasma for hospitalised COVID-19 patients: DAWn-plasma",
"author": "Devos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0003",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100849",
"article-title": "Efficacy of the TMPRSS2 inhibitor camostat mesilate in patients hospitalized with COVID-19-a double-blind randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Gunst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalmedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0004",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208",
"article-title": "The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software partners",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0005",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"article-title": "Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) – a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0006",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0007",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0008",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.13052",
"article-title": "A phase I study of high dose camostat mesylate in healthy adults provides a rationale to repurpose the TMPRSS2 inhibitor for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Kitagawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1967",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0009",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00975-21",
"article-title": "Synergistic block of SARS-CoV-2 infection by combined drug inhibition of the host entry factors PIKfyve kinase and TMPRSS2 protease",
"author": "Kreutzberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0010",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00498259409043223",
"article-title": "Metabolic fate of 14C-camostat mesylate in man, rat and dog after intravenous administration",
"author": "Midgley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0011",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-021-06395-1",
"article-title": "Camostat mesylate therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Sakr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "707",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0013",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02345-9",
"article-title": "Camostat mesilate therapy for COVID-19",
"author": "Uno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1577",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0014",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0015",
"unstructured": "Willett B, Grove J, MacLean O, Wilkie C, Logan N, Lorenzo G, et al. The hyper-transmissible SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant exhibits significant antigenic change, vaccine escape and a switch in cell entry mechanism. medRxiv 26 January 2022. doi:10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011",
"article-title": "Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.054_bib0016",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971222003885"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of camostat mesylate in early COVID-19 disease in an ambulatory setting: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "122"
}