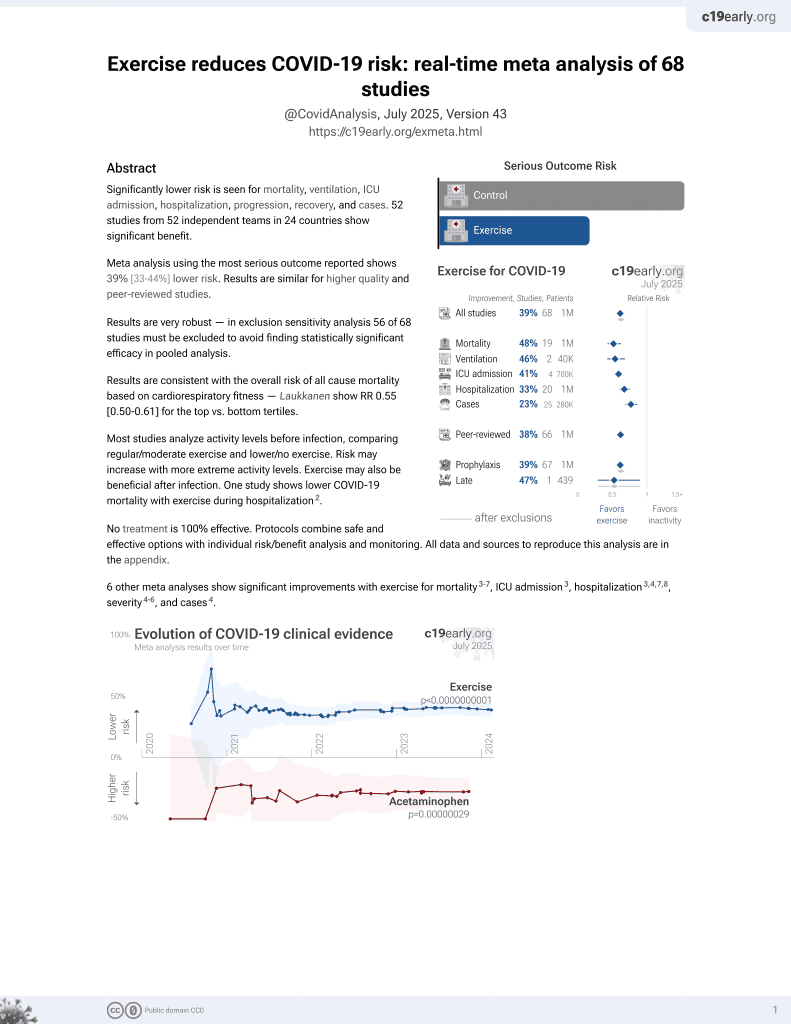
Worldwide physical activity trends since COVID-19 onset
et al., The Lancet Global Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8, Oct 2022
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
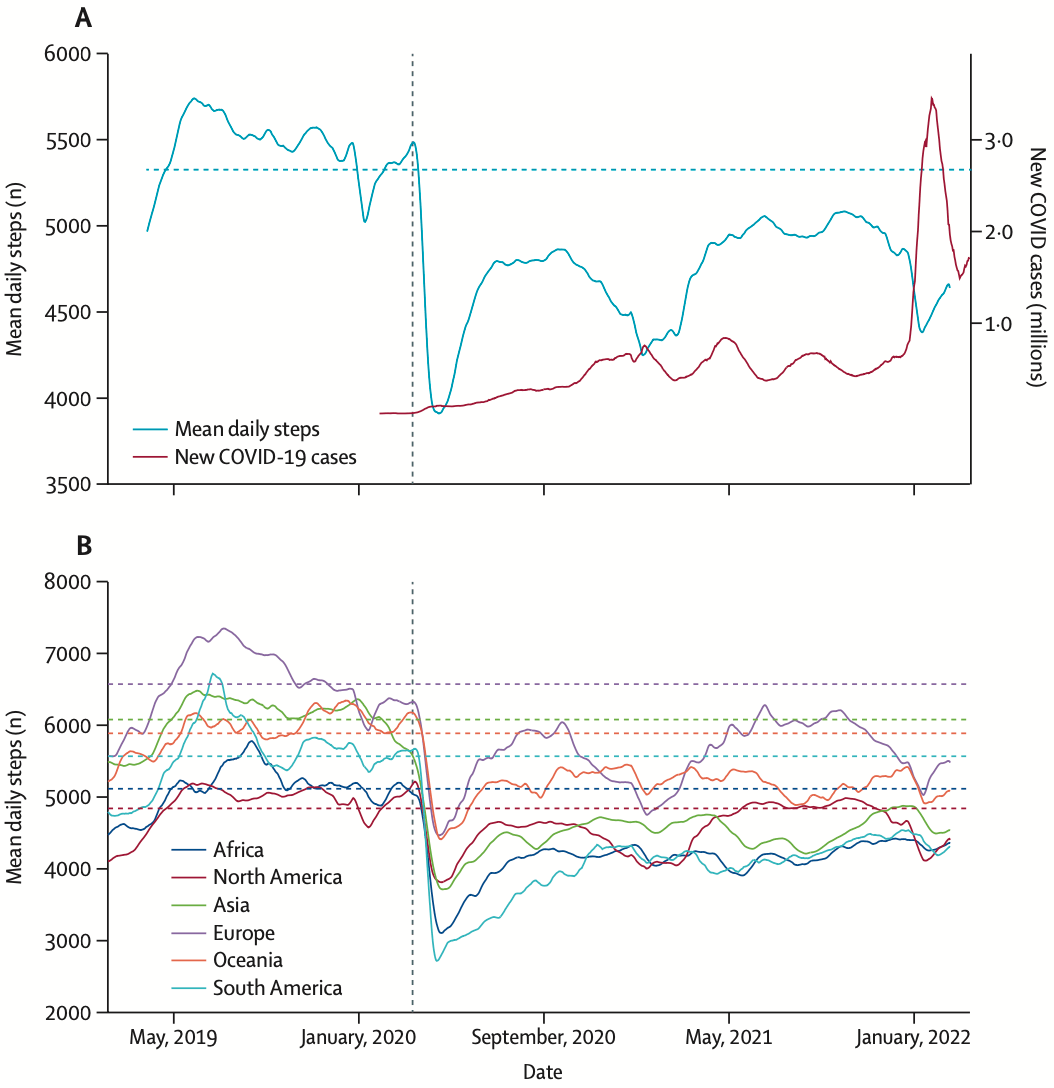
Analysis of 1.2 million global users showing a significant decline in physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic, which remained below the pre-pandemic baseline as of February 2022.
Tison et al., 31 Oct 2022, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: geoff.tison@ucsf.edu.
Worldwide physical activity trends since COVID-19 onset The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted nearly all aspects of daily life worldwide. Public health interventions necessary to curb disease spread could have unintended consequences that adversely influence long-term health outcomes beyond near-term mortality. 1 For example, step counts-a proxy for physical activity 2 -were markedly lower early in the COVID-19 pandemic than pre-pandemic. 3 As the global pandemic persists despite vaccines, understanding its long-term ramifications on physical activity-an important determinant of health 4is crucial, and might help to inform public health and regional policy decisions. We examined worldwide trends in physical activity, measured by step counts, 2 years since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. We hypothesised that worldwide physical activity remains lower than pre-COVID-19. We used deidentified individual-level data from Jan 1, 2019, to Feb 17, 2022, collected from the freely available Azumio Argus smartphone app, a popular health-wellness app. Daily step counts are determined using smartphone accelerometers and Apple or Android algorithms for step counting. 5 User location was determined by smartphone IP address. Pre-pandemic baseline mean steps were calculated per region using data from Jan 1, 2019, to Dec 31, 2019. COVID-19 regional case counts were obtained from publicly available sources. Significant differences in mean step counts for various time windows were examined using the Kruskal-Wallis and Conover's tests with Bonferroni correction at p<0•001. This study was reviewed and exempted by the University of California, San Francisco Institutional Review Board (20-30 539). A total of 140 424 429 daily step count measurements were provided by 1 255 811 unique users from more than 200 countries and territories during the study period; 92% of smartphones were iOS, 8% were Android. Worldwide, physical activity has somewhat recovered but remains depressed compared with the pre-pandemic baseline of 5323 steps per day during the 2019 calendar year (figure). The mean step count in the 90 days preceding the end of the study period (November 2021-February 2022) was significantly lower for all continents compared with the same 90-day, 2019-2020 prepandemic period (p<0•001). The same 2020-2021 midpandemic 90-day period was also significantly lower
References
Althoff, Sosič, Hicks, King, Delp et al., Large-scale physical activity data reveal worldwide activity inequality, Nature
Azumio, Pk, Bb, None
Case, Burwick, Volpp, Patel, Accuracy of smartphone applications and wearable devices for tracking physical activity data, JAMA
Lee, Shiroma, Lobelo, Puska, Blair et al., Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy, Lancet
Saint-Maurice, Troiano, Bassett Drj Jr, Association of daily step count and step intensity with mortality among US adults, JAMA
Tison, Avram, Kuhar, Worldwide effect of COVID-19 on physical activity: a descriptive study, Ann Intern Med
Wang, Paulson, Pease, Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020-21, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2214-109x(22)00361-8",
"ISSN": [
"2214-109X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8",
"alternative-id": [
"S2214109X22003618"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Worldwide physical activity trends since COVID-19 onset"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Global Health"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tison",
"given": "Geoffrey H",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrios",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avram",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuhar",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bostjancic",
"given": "Bojan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marcus",
"given": "Gregory M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pletcher",
"given": "Mark J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olgin",
"given": "Jeffrey E",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Global Health",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Global Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-31T22:29:32Z",
"timestamp": 1661984972000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-18T19:15:28Z",
"timestamp": 1679166928000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"K23HL135274"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "NHLBI"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000156",
"award": [
"312758"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-27T15:28:45Z",
"timestamp": 1679930925448
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1664582400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1660003200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2214109X22003618?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2214109X22003618?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e1381-e1382",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020–21",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib1",
"volume": "6736",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1382",
"article-title": "Association of daily step count and step intensity with mortality among US adults",
"author": "Saint-Maurice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1151",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib2",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-2665",
"article-title": "Worldwide effect of COVID-19 on physical activity: a descriptive study",
"author": "Tison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "767",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib3",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61031-9",
"article-title": "Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib4",
"volume": "380",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature23018",
"article-title": "Large-scale physical activity data reveal worldwide activity inequality",
"author": "Althoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "336",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib5",
"volume": "547",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.17841",
"article-title": "Accuracy of smartphone applications and wearable devices for tracking physical activity data",
"author": "Case",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "625",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00361-8_bib6",
"volume": "313",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2214109X22003618"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Worldwide physical activity trends since COVID-19 onset",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "10"
}