Drug-induced liver injury associated with lopinavir-ritonavir in patients with COVID-19: a disproportionality analysis of U.S. food and drug administration adverse event reporting system (FAERS) data
et al., International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, doi:10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5, Jul 2021
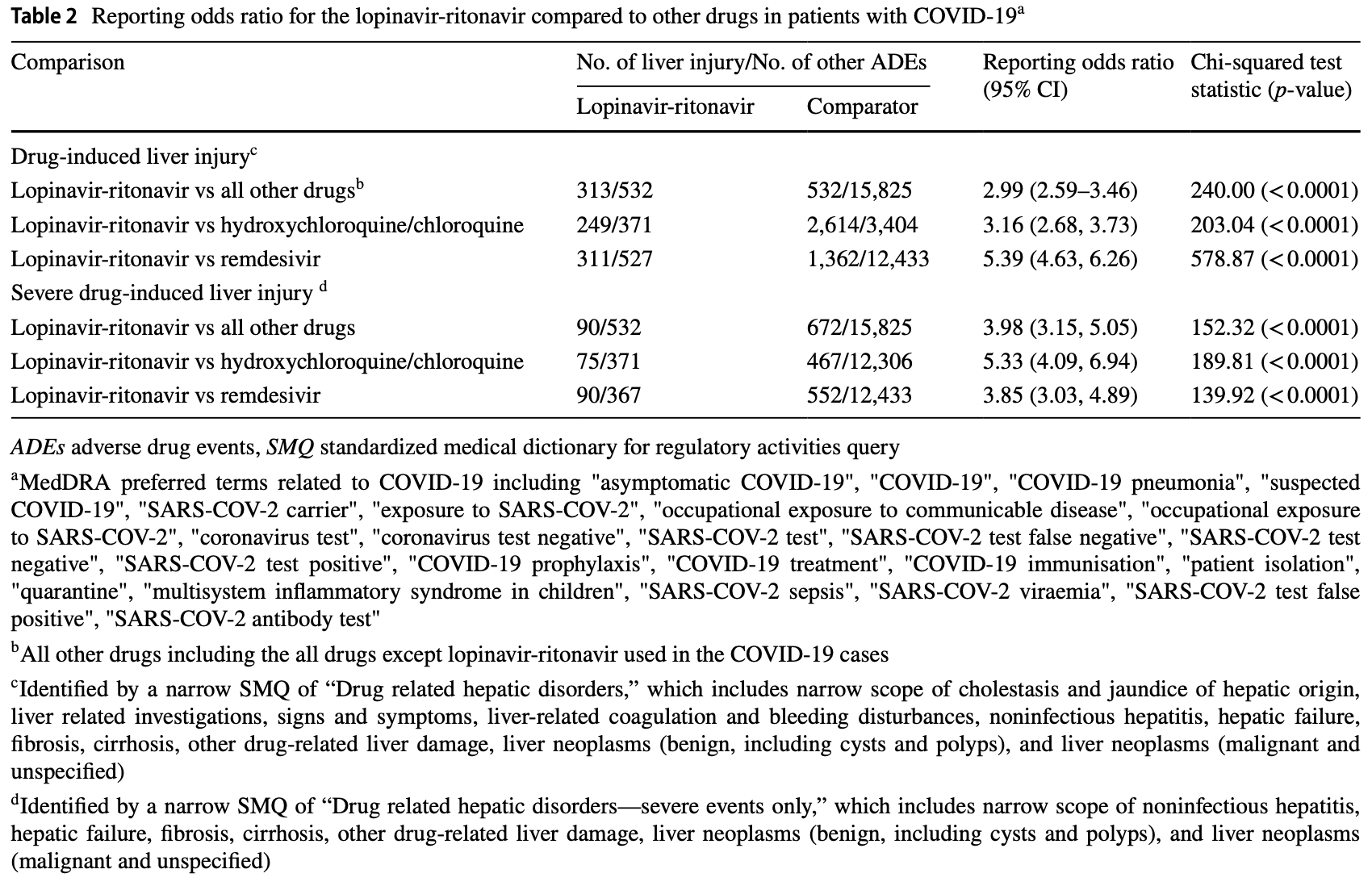
Disproportionality analysis showing higher risk of liver injury with lopinavir/ritonavir for COVID-19 patients. Paxlovid combines nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.
Tang et al., 30 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: tang.huilin@ufl.edu.
Drug-induced liver injury associated with lopinavir-ritonavir in patients with COVID-19: a disproportionality analysis of U.S. food and drug administration adverse event reporting system (FAERS) data
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, doi:10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5
Background Liver injury has been documented independently in novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients and patients treated with lopinavir-ritonavir. Objective to investigate the drug-induced liver injury associated with lopinavirritonavir among the patients with COVID-19. Methods We conducted a disproportionality analysis of US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) between 2020Q1 and 2021Q1 to evaluate the association between lopinavir-ritonavir and risk of drug-induced liver injury (or severe drug-induced liver injury) and calculated their reporting odds ratios (RORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results A total of 3,425 cases of drug-induced liver injury were reported in 19,782 patients with COVID-19. The ROR for drug-induced liver injury was 2.99 (2.59-3.46), 3.16 (2.68-3.73), and 5.39 (4.63-6.26) when comparing lopinavir-ritonavir with all other drugs, hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine only, and remdesivir, respectively. For severe drug-induced liver injury, RORs for lopinavir-ritonavir provided evidence of an association compared with all other drugs (3.98; 3.15-5.05), compared with hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine only (5.33; 4.09-6.94), and compared with remdesivir (3.85; 3.03-4.89). Conclusions In the FAERS, we observed a disproportional signal for druginduced liver injury associated with lopinavir-ritonavir in patients with COVID-19.
Declarations Conflicts of interest HT is a consultant for Evidpro, LLC. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare. Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Almenoff, Pattishall, Gibbs, Dumouchel, Evans et al., Novel statistical tools for monitoring the safety of marketed drugs, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Cai, Huang, Yu, Zhu, Xia et al., COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests, J Hepatol
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Fan, Chen, Li, Cheng, Yang et al., Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Gahr, Zeiss, Lang, Connemann, Hiemke et al., Drug-induced liver injury associated with antidepressive psychopharmacotherapy: an explorative assessment based on quantitative signal detection using different MedDRA terms, J Clin Pharmacol
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Nunez, Hepatotoxicity of antiretrovirals: incidence, mechanisms and management, J Hepatol
Olry, Meunier, Delire, Larrey, Horsmans et al., Drug-Induced Liver Injury and COVID-19 Infection: The Rules Remain the Same, Drug Saf
Osborne, Davies, Lane, Evans, Denyer et al., Lopinavir-ritonavir in the treatment of COVID-19: a dynamic systematic benefit-risk assessment, Drug Saf
Rochwerg, Agarwal, Siemieniuk, Agoritsas, Lamontagne et al., A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Rothman, Lanes, Sacks, The reporting odds ratio and its advantages over the proportional reporting ratio. Pharmacoepidemiol, Drug Saf
Schrezenmeier, Dorner, Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: implications for rheumatology, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Sherman, Shire, Cernohous, Rouster, Omachi et al., Liver injury and changes in hepatitis C Virus (HCV) RNA load associated with protease inhibitor-based antiretroviral therapy for treatment-naive HCV-HIV-coinfected patients: lopinavir-ritonavir versus nelfinavir, Clin Infect Dis
Zhang, Shi, Wang, Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5",
"ISSN": [
"2210-7703",
"2210-7711"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5",
"alternative-id": [
"1311"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "4 May 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "21 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "30 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflicts of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "HT is a consultant for Evidpro, LLC. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5814-6657",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tang",
"given": "Huilin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Liyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xiaotong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kinlaw",
"given": "Alan C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Jeff Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "Andrew M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "Edward L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Tiansheng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy",
"container-title-short": "Int J Clin Pharm",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-30T15:02:53Z",
"timestamp": 1627657373000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-09T19:30:57Z",
"timestamp": 1628537457000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-19T07:27:12Z",
"timestamp": 1668842832298
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627603200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627603200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1116-1122",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR1",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30057-1",
"author": "C Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "428",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "1311_CR2",
"unstructured": "Zhang C, Shi L, Wang FS. Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(5):428–30.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40264-020-00954-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR3",
"unstructured": "Olry A, Meunier L, Delire B, Larrey D, Horsmans Y, Le Louet H. Drug-Induced Liver Injury and COVID-19 Infection: The Rules Remain the Same. Drug Saf. 2020;43(7):615–7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40264-020-00966-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR4",
"unstructured": "Osborne V, Davies M, Lane S, Evans A, Denyer J, Dhanda S, Roy D, Shakir S. Lopinavir-ritonavir in the treatment of COVID-19: a dynamic systematic benefit-risk assessment. Drug Saf. 2020;43(8):809–21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR5",
"unstructured": "Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, Ruan L, Song B, Cai Y, Wei M, Li X, Xia J, Chen N, Xiang J, Yu T, Bai T, Xie X, Zhang L, Li C, Yuan Y, Chen H, Li H, Huang H, Tu S, Gong F, Liu Y, Wei Y, Dong C, Zhou F, Gu X, Xu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li H, Shang L, Wang K, Li K, Zhou X, Dong X, Qu Z, Lu S, Hu X, Ruan S, Luo S, Wu J, Peng L, Cheng F, Pan L, Zou J, Jia C, Wang J, Liu X, Wang S, Wu X, Ge Q, He J, Zhan H, Qiu F, Guo L, Huang C, Jaki T, Hayden FG, Horby PW, Zhang D, Wang C. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(19):1787–99"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.662",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR6",
"unstructured": "Gahr M, Zeiss R, Lang D, Connemann BJ, Hiemke C, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C. Drug-induced liver injury associated with antidepressive psychopharmacotherapy: an explorative assessment based on quantitative signal detection using different MedDRA terms. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;56(6):769–78."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.1001",
"author": "KJ Rothman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "519",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf",
"key": "1311_CR7",
"unstructured": "Rothman KJ, Lanes S, Sacks ST. The reporting odds ratio and its advantages over the proportional reporting ratio. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2004;13(8):519–23.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.clpt.6100258",
"author": "JS Almenoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "157",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "1311_CR8",
"unstructured": "Almenoff JS, Pattishall EN, Gibbs TG, DuMouchel W, Evans SJ, Yuen N. Novel statistical tools for monitoring the safety of marketed drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(2):157–66",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/444501",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR9",
"unstructured": "Sherman KE, Shire NJ, Cernohous P, Rouster SD, Omachi JH, Brun S, Da Silva B. Liver injury and changes in hepatitis C Virus (HCV) RNA load associated with protease inhibitor-based antiretroviral therapy for treatment-naive HCV-HIV-coinfected patients: lopinavir-ritonavir versus nelfinavir. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41(8):1186–95."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR10",
"unstructured": "Cai Q, Huang D, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Su Y, Li Z, Zhou G, Gou J, Qu J, Sun Y, Liu Y, He Q, Chen J, Liu L, Xu L. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J Hepatol. 2020;73(3):566–74."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002",
"author": "Z Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1561",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "1311_CR11",
"unstructured": "Fan Z, Chen L, Li J, Cheng X, Yang J, Tian C, Zhang Y, Huang S, Liu Z, Cheng J. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(7):1561–6.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2005.11.027",
"author": "M Nunez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S132",
"issue": "1 Suppl",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "1311_CR12",
"unstructured": "Nunez M. Hepatotoxicity of antiretrovirals: incidence, mechanisms and management. J Hepatol. 2006;44(1 Suppl):S132–9.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-0372-x",
"author": "E Schrezenmeier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "1311_CR13",
"unstructured": "Schrezenmeier E, Dorner T. Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: implications for rheumatology. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(3):155–66.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1311_CR14",
"unstructured": "Recovery Collaborative Group. Lopinavir-ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;396(10259):1345–52."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1311_CR15",
"unstructured": "Rochwerg B, Agarwal A, Siemieniuk RA, Agoritsas T, Lamontagne F, Askie L, Lytvyn L, Leo YS, Macdonald H, Zeng L, Amin W, Burhan E, Bausch FJ, Calfee CS, Cecconi M, Chanda D, Du B, Geduld H, Gee P, Harley N, Hashimi M, Hunt B, Kabra SK, Kanda S, Kawano-Dourado L, Kim YJ, Kissoon N, Kwizera A, Mahaka I, Manai H, Mino G, Nsutebu E, Preller J, Pshenichnaya N, Qadir N, Sabzwari S, Sarin R, Shankar-Hari M, Sharland M, Shen Y, Ranganathan SS, Souza JP, Stegemann M, De Sutter A, Ugarte S, Venkatapuram S, Dat VQ, Vuyiseka D, Wijewickrama A, Maguire B, Zeraatkar D, Bartoszko JJ, Ge L, Brignardello-Petersen R, Owen A, Guyatt G, Diaz J, Jacobs M, Vandvik PO. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ. 2020;370m3379."
},
{
"key": "1311_CR16",
"unstructured": "Infections disease society of America. IDSA guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. 2021 June 25,2021 [cited 2021 July 8]; Available from: https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/."
},
{
"key": "1311_CR17",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine. 2020 06/15 [cited 2021 July 9]; Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-chloroquine-and."
}
],
"reference-count": 17,
"references-count": 17,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11096-021-01311-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"Pharmacology",
"Toxicology",
"Pharmacy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Drug-induced liver injury associated with lopinavir-ritonavir in patients with COVID-19: a disproportionality analysis of U.S. food and drug administration adverse event reporting system (FAERS) data",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "43"
}