Serum levels of vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care unit
et al., Gene Reports, doi:10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509, Jan 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
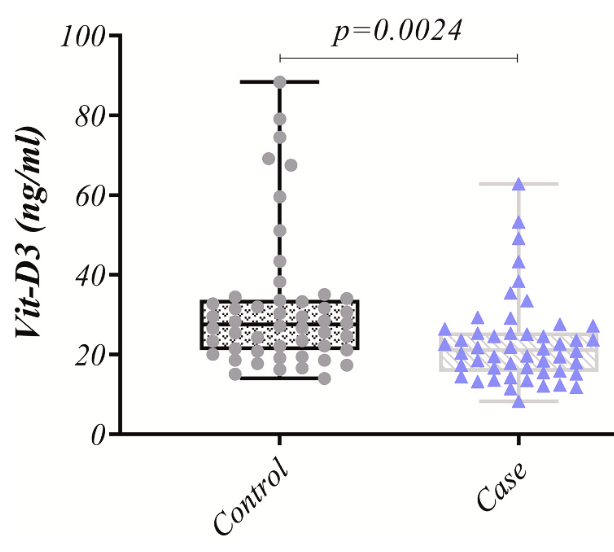
Analysis of 50 COVID-19 ICU patients and 50 healthy controls in Iran, showing significantly lower vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients.
Soltani-Zangbar et al., 15 Jan 2022, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Serum levels of vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care unit
Gene Reports, doi:10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509
Vitamin D is believed to affect the functionality of the immune system for the prevention of coronavirus disease. To investigate the role of this vitamin against the Coronavirus, this study analyzed the serum levels of vitamin D, the transcription pattern of inflammatory cytokines, and the frequency of total lymphocytes, TCD4 + , TCD8 + , and NK cells in 50 COVID-19-affected subjects in comparison to 50 healthy participants. Materials and methods: This study diagnosed and evaluated 100 patients. Frequency of lymphocytes was determined using flow cytometry. Cytokine expression levels were measured using Real-Time PCR. Serum levels of vitamin D and cytokines levels in cultured cell supernatant were measured by ELISA. Results: Patients with COVID-19 exhibited decreased serum levels of vitamin D versus the healthy participants (p = 0.0024). The total number of lymphocytes, TCD4 + , TCD8 + , and NK cells was significantly reduced in patients with COVID-19 (p < 0.0001). Considerable upregulation of IL-12, IFN-γ, and TNF-α was seen in COVID-19 patients compared to the control group, whereas IFN-α was downregulated in COVID-19 patients. ELISA results also had increased levels of IL-12, TNF-α, and IFN-γ (p = 0.0014, 0.0012, and p < 0.0001, respectively), and decreased level of IFN-α (p = 0.0021) in patients with COVID-19 compared to the control group. Conclusion: These findings suggest a probable association among vitamin D concentrations, immune system function, and risk of COVID-19 infection. As a result, it is recommended that vitamin D be considered as a candidate for handling and controlling COVID-19 because of its ability to target the cytokine storm and its antiviral effects.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The current study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tabriz University of Medical Science (No: IR.TBZMED.REC.1398.1313).
Financial disclosure statements The current study was supported by Aging Research Institute, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran (Grant No. 65213 ).
References
Ahmadi, Nouri, Babaloo, Farzadi, Ghasemzadeh et al., Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment modulates peripheral blood Th17 and regulatory T cells in recurrent miscarriage patients: Non randomized, open-label clinical trial, Immunol Lett
Ahn, Shin, Kim, Lee, Kim et al., Current status of epidemiology, diagnosis, therapeutics, and vaccines for novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J. Microbiol. Biotechnol
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's, Arch. Pharmacol
Bae, Kim, Mini-review on the roles of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in the immune system against COVID-19, Molecules
Bikle, Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications, Chem Biol
Bogoch, Watts, Thomas-Bachli, Huber, Kraemer et al., Pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: potential for international spread via commercial air travel, J. Travel Med
Carpagnano, Di Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J. Endocrinol. Investig
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin. Immunopathol
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J. Med. Virol
Etemadi, Bordbar, Soltani-Zangbar, Hajivalili, Aghebati-Maleki et al., Mar. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients, Immunol. Investig
Fan, Lu, Li, Ding, Wang et al., Vitamin D measurement, the debates continue, new analytes have emerged, developments have variable outcomes, Calcif. Tissue Int
Ghasemian, Shamshirian, Heydari, Malekan, Alizadeh-Navaei et al., The role of vitamin D in the age of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int. J. Clin. Pract
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Holick, Disorders, The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord
Jiang, Deng, Zhang, Cai, Cheung et al., Review of the clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J. Gen. Intern. Med
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Mfjpo et al., SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS One
Laird, Rhodes, Rajimj, Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19, Ir. Med. J
Laviano, Koverech, Zanetti, Nutrition support in the time of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), Nutrition
Li, Li, Zhang, Liu, infection and mortality in the United States
Mahmoodpoor, Hosseini, Soltani-Zangbar, Sanaie, Aghebati-Maleki et al., Reduction and exhausted features of T lymphocytes under serological changes, and prognostic factors in COVID-19 progression, Mol. Immunol
Molloy, Murphy, Vitamin, 3. Covid-19 and children, Ir. Med. J
Panfili, Roversi, D'argenio, Rossi, Cappa et al., Possible role of vitamin D in Covid-19 infection in pediatric population, J. Endocrinol. Investig
Pinzon, Pradana, Vitamin d deficiency among patients with COVID-19: case series and recent literature review, Trop. Med. Health
Qayyum, Mohammad, Slominski, Hassan, Tuckey et al., Aug 1. Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab
Slominski, Chaiprasongsuk, Janjetovic, Kim, Stefan et al., Jun. Photoprotective properties of vitamin D and lumisterol hydroxyderivatives, Cell Biochem. Biophys
Slominski, Kim, Janjetovic, Brożyna, Żmijewski et al., Differential and overlapping effects of 20, 23 (OH) 2D3 and 1, 25 (OH) 2D3 on gene expression in human epidermal keratinocytes: identification of AhR as an alternative receptor for 20, 23 (OH) 2D3, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Slominski, Kim, Li, Postlethwaite, Tieu et al., Detection of novel CYP11A1-derived secosteroids in the human epidermis and serum and pig adrenal gland, Sci. Rep
Slominski, Kim, Qayyum, Song, Janjetovic et al., Vitamin D and lumisterol derivatives can act on liver X receptors (LXRs), Sci. Rep
Slominski, Kim, Shehabi, Semak, Tang et al., In vivo evidence for a novel pathway of vitamin D3 metabolism initiated by P450scc and modified by CYP27B1, FASEB J
Slominski, Kim, Shehabi, Tang, Benson et al., Mar 5. In vivo production of novel vitamin D2 hydroxy-derivatives by human placentas, epidermal keratinocytes, Caco-2 colon cells and the adrenal gland, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol
Slominski, Kim, Takeda, Janjetovic, Brożyna et al., RORα and ROR γ are expressed in human skin and serve as receptors for endogenously produced noncalcemic 20-hydroxy-and 20, 23-dihydroxyvitamin D, Jul FASEB J
Slominski, Li, Kim, Semak, Wang et al., Novel activities of CYP11A1 and their potential physiological significance, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Slominski, Raman, Elmets, Jetten, Slominski et al., The significance of CYP11A1 expression in skin physiology and pathology, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol
Slominski, Slominski, Goepfert, Kim, Holick et al., to Jakovac and to Rocha et al.: can vitamin D prevent or manage COVID-19 illness?, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab
Slominski, Stefan, Athar, Holick, Jetten et al., COVID-19 and vitamin D: a lesson from the skin, Exp. Dermatol
Slominski, Tuckey, Manna, Jetten, Postlethwaite et al., Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid biosynthesis: implications for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, Genes Immun
Soltani-Zangbar, Aghebati-Maleki, Hajivalili, Haji-Fatahaliha, Motavalli et al., Application of newly developed SARS-CoV2 serology test along with real-time PCR for early detection in health care workers and on-time plasma donation, Gene Rep
Song, Gui, Wang, Xiang, Cryo-EM structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2, PLoS Pathog
Song, Qayyum, Greer, Slominski, Raman et al., Vitamin D3 and its hydroxyderivatives as promising drugs against covid-19: a computational study, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn
Teymoori-Rad, Samadizadeh, Tabarraei, Moradi, Shahbaz, /check>, 2020. Ten challenging questions about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Expert Rev. Respir. Med
Vaninov, In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm, Nat. Rev. Immunol
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin Med (Lond)
Wu, Hao, Lau, Wong, Leung et al., Real-time tentative assessment of the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus infections in Wuhan, China, as at 22, Euro Surveill
Xu, Baylink, Chen, Reeves, Xiao et al., The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19, J. Transl. Med
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir. Med
Yadav, Birdi, Tomo, Charan, Bhardwaj et al., Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: a cross-sectional study, Indian J Clin Biochem
Zheng, Yang, Hu, Li, Wang et al., Jul. Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition, Biochem. Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509",
"ISSN": [
"2452-0144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509",
"alternative-id": [
"S2452014422000176"
],
"article-number": "101509",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Serum levels of vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care unit"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Gene Reports"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soltani-Zangbar",
"given": "Mohammad Sadegh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmoodpoor",
"given": "Ata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dolati",
"given": "Sanam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shamekh",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valizadeh",
"given": "Sepehr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yousefi",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanaie",
"given": "Sarvin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Gene Reports"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-15T23:52:17Z",
"timestamp": 1642290737000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-11T00:47:32Z",
"timestamp": 1644540452000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004366",
"award": [
"65213"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-11T01:11:56Z",
"timestamp": 1644541916261
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2452-0144"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1646092800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2452014422000176?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2452014422000176?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101509",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2017.10.003",
"article-title": "Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment modulates peripheral blood Th17 and regulatory T cells in recurrent miscarriage patients: Non randomized, open-label clinical trial",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Immunol Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0005",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4014/jmb.2003.03011",
"article-title": "Current status of epidemiology, diagnosis, therapeutics, and vaccines for novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Ahn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "313",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0010",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0015",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage",
"author": "Aygun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1157",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0020",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25225346",
"article-title": "Mini-review on the roles of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in the immune system against COVID-19",
"author": "Bae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5346",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0025",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.12.016",
"article-title": "Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chem Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0030",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taaa008",
"article-title": "Pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: potential for international spread via commercial air travel",
"author": "Bogoch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Travel Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0035",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01370-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0040",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"article-title": "Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "529",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Semin. Immunopathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0045",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25681",
"article-title": "Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0050",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08820139.2021.1899202",
"article-title": "Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients",
"author": "Etemadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0055",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "ACE2 expression in kidney and testis may cause kidney and testis infection in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Fan",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Front Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0060",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00223-019-00620-2",
"article-title": "Vitamin D measurement, the debates continue, new analytes have emerged, developments have variable outcomes",
"author": "Fraser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Calcif. Tissue Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0065",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14675",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the age of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Ghasemian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0070",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0075",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1",
"article-title": "The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0080",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-020-05762-w",
"article-title": "Review of the clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1545",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0085",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0090",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19",
"author": "Laird",
"first-page": "81",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0095",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.110834",
"article-title": "Nutrition support in the time of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Laviano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0100",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Li",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0105",
"series-title": "Sunlight and vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infection and mortality in the United States",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molimm.2021.06.001",
"article-title": "Reduction and exhausted features of T lymphocytes under serological changes, and prognostic factors in COVID-19 progression",
"author": "Mahmoodpoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0110",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19 and children",
"author": "Molloy",
"first-page": "64",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0115",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01327-0",
"article-title": "Possible role of vitamin D in Covid-19 infection in pediatric population",
"author": "Panfili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0120",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41182-020-00277-w",
"article-title": "Vitamin d deficiency among patients with COVID-19: case series and recent literature review",
"author": "Pinzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trop. Med. Health.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0125",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00174.2021",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and lumisterol novel metabolites can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication machinery enzymes",
"author": "Qayyum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E246",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0130",
"volume": "321",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.12-208975",
"article-title": "In vivo evidence for a novel pathway of vitamin D3 metabolism initiated by P450scc and modified by CYP27B1",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3901",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0135",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.012",
"article-title": "In vivo production of novel vitamin D2 hydroxy-derivatives by human placentas, epidermal keratinocytes, Caco-2 colon cells and the adrenal gland",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0140",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.13-242040",
"article-title": "RORα and ROR γ are expressed in human skin and serve as receptors for endogenously produced noncalcemic 20-hydroxy-and 20, 23-dihydroxyvitamin D",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2775",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0145",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep14875",
"article-title": "Detection of novel CYP11A1-derived secosteroids in the human epidermis and serum and pig adrenal gland",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0150",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.11.010",
"article-title": "Novel activities of CYP11A1 and their potential physiological significance",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0155",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19103072",
"article-title": "Differential and overlapping effects of 20, 23 (OH) 2D3 and 1, 25 (OH) 2D3 on gene expression in human epidermal keratinocytes: identification of AhR as an alternative receptor for 20, 23 (OH) 2D3",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3072",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0160",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12013-020-00913-6",
"article-title": "Photoprotective properties of vitamin D and lumisterol hydroxyderivatives",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0165",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00348.2020",
"article-title": "Reply to Jakovac and to Rocha et al.: can vitamin D prevent or manage COVID-19 illness?",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E455",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0170",
"volume": "319",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/exd.14170",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and vitamin D: a lesson from the skin",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "885",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Exp. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0175",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41435-020-0096-6",
"article-title": "Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid biosynthesis: implications for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Genes Immun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0180",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-87061-w",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and lumisterol derivatives can act on liver X receptors (LXRs)",
"author": "Slominski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0185",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The significance of CYP11A1 expression in skin physiology and pathology",
"author": "Slominski",
"issue": "530",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0190",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Application of newly developed SARS-CoV2 serology test along with real-time PCR for early detection in health care workers and on-time plasma donation",
"author": "Soltani-Zangbar",
"journal-title": "Gene Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0195",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1007236",
"article-title": "Cryo-EM structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0200",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 and its hydroxyderivatives as promising drugs against covid-19: a computational study",
"author": "Song",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0205",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2020.1782197",
"article-title": "Ten challenging questions about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Teymoori-Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0210",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0305-6",
"article-title": "In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm",
"author": "Vaninov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0215",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0220",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e107",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Med (Lond).",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0225",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000044",
"article-title": "Real-time tentative assessment of the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus infections in Wuhan, China, as at 22 January 2020",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0230",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02488-5",
"article-title": "The importance of vitamin d metabolism as a potential prophylactic, immunoregulatory and neuroprotective treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Transl. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0235",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0240",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Yadav",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Indian J Clin Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0245",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113955",
"article-title": "Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.genrep.2022.101509_bb0250",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": null
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Gene Reports"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Genetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Serum levels of vitamin D and immune system function in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care unit"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "26"
}
