What is the role of proton pump inhibitors consumption on the clinical presentation and severity of COVID-19 infection?
et al., Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises, doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013, Mar 2023
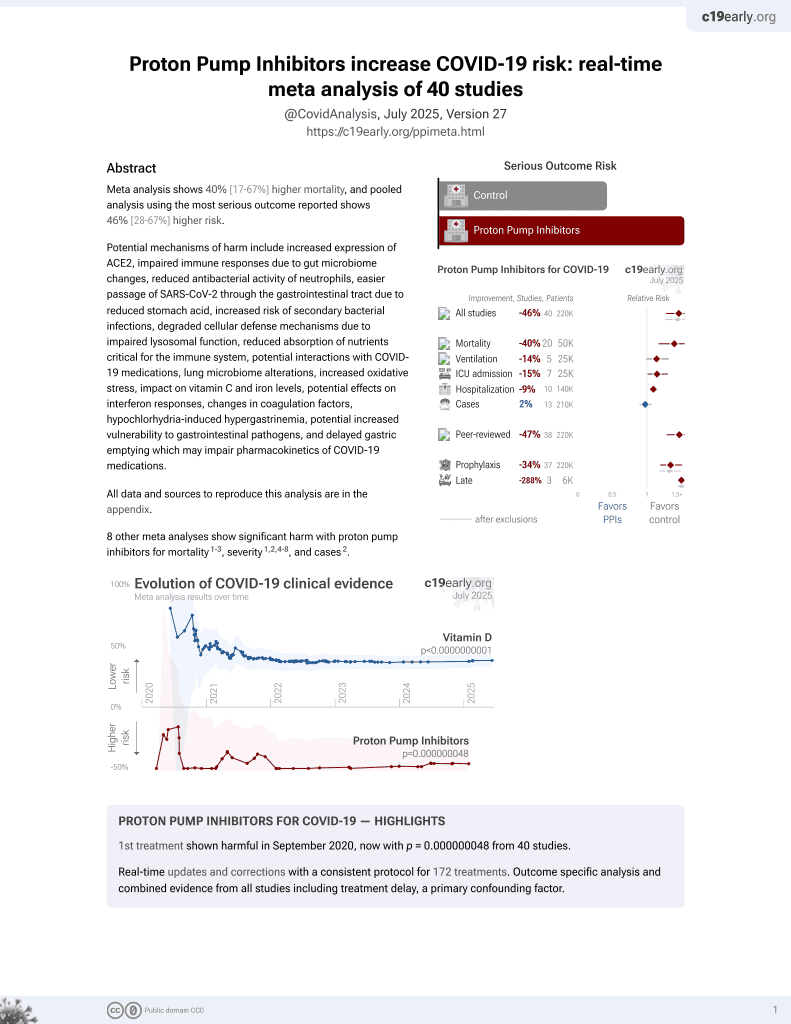
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
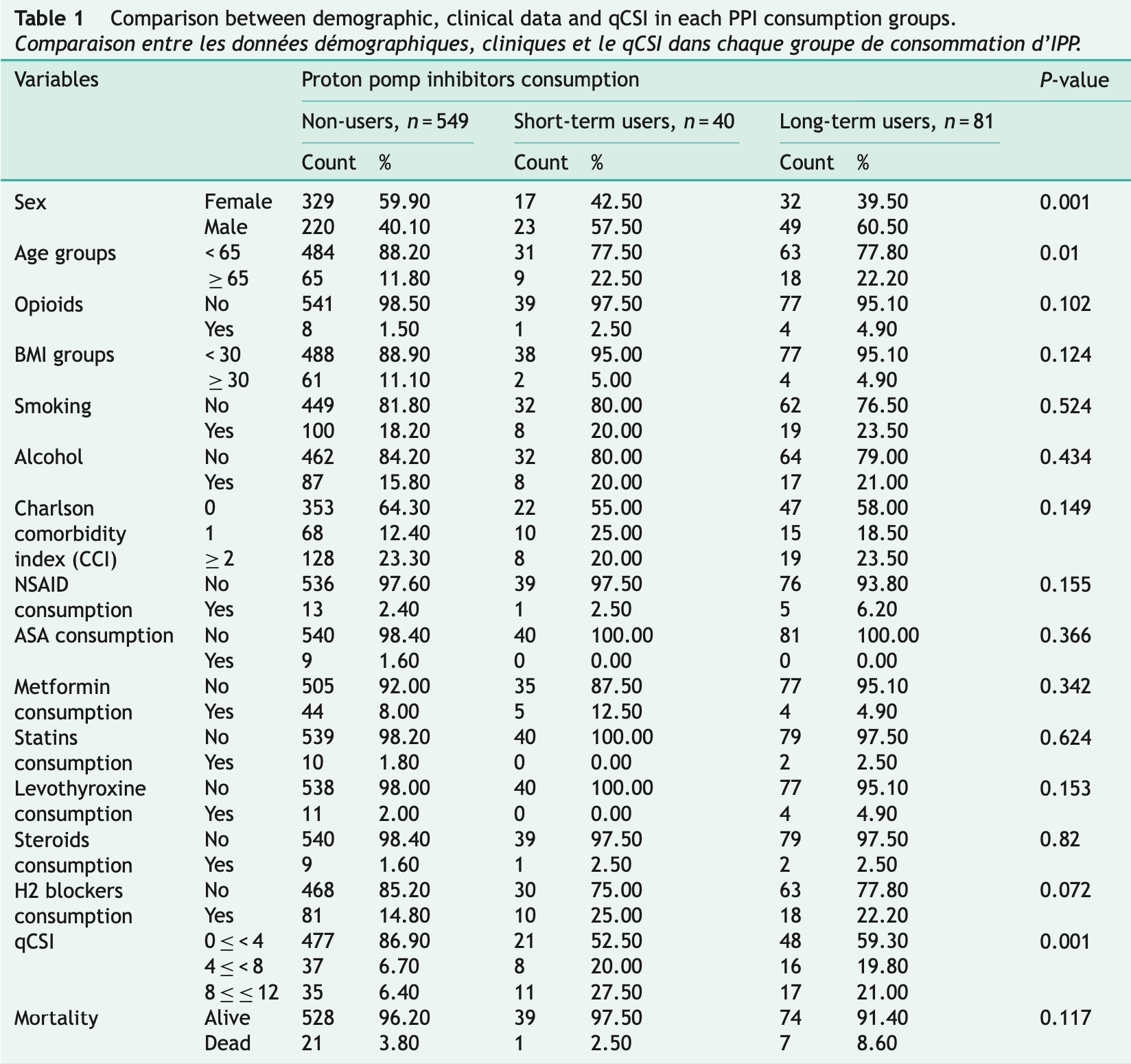
Retrospective 670 COVID-19 patients in Iran showing significantly higher COVID-19 severity scores and more symptomatic presentation in patients with a history of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use. Adjusted results are only provided for severity. Several values in Table 4 are likely misreported raising concern for the reliability of the main result.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
potential data issue.
|
risk of severe case, 81.0% higher, RR 1.81, p = 0.046, treatment 121, control 549, all patients.
|
|
risk of severe case, 137.6% higher, OR 2.38, p < 0.001, treatment 40, control 549, short-term, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 30.5% higher, OR 1.30, p = 0.36, treatment 81, control 549, long-term, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death, 78.0% higher, RR 1.78, p = 0.21, treatment 8 of 113 (7.1%), control 21 of 528 (4.0%), unadjusted.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Shokri et al., 31 Mar 2023, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 44.2, 6 authors, study period 10 September, 2021 - 18 January, 2022.
Contact: mohammadalishokri@yahoo.com, shokri.ma@iums.ac.ir, mfd@yahoo.com, moghadamfard.t@iums.ac.ir, ramim.t@iums.ac.ir, alireza.hejrati@gmail.com, lina1381@gmail.com, marjanmokhtare@yahoo.com, m.mokhtare@iums.ac.ir.
What is the role of proton pump inhibitors consumption on the clinical presentation and severity of COVID-19 infection?
Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises, doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013
The COVID-19 severity scores (qCSI) were significantly higher in PPI users compared to non-users, in population with no comorbidity (Charlson Comorbidity Index = 0). • Mortality rate wasn't significantly different between PPI-users and non-users. • All three types of COVID-19 symptoms investigated in this study (flu-like, respiratory and gastrointestinal) manifested more in PPI users than non-users.
Author contribution All authors had access to the data and a role in data gathering and writing the manuscript.
Disclosure of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
References
Almario, Chey, Spiegel, Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors, Am J Gastroenterol
Alzubaidi, Gabbard, GERD: Diagnosing and treating the burn, Cleve Clin J Med
Antunes, Curtis, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Bagherzadeh, Safari, Amanlou, Motevalian, Proton pump inhibitors in Iranian population: from clinical regimens to pharmacogenomics, Physiol Pharmacol
Blanc, Waechter, Vogel, Schorr, Demuynck et al., Therapeutic prevention of COVID-19 in elderly: a case-control study, Geroscience
Blanco, Ambrosioni, Garcia, Martínez, Soriano et al., COVID-19 in patients with HIV: clinical case series, Lancet HIV
Dadras, Afsahi, Pashaei, Mojdeganlou, Karimi et al., The relationship between COVID-19 viral load and disease severity: a systematic review, Immun Inflamm Dis
Domingo, Proton pump inhibitors in the COVID-19 pandemic. Gastroenterología y Hepatología
Fang, Li, Yu, Wang, Zhang et al., Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Aging
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: a review, Allergy
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Albano, Antonelli et al., Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med
Haimovich, Ravindra, Stoytchev, Young, Wilson et al., Development and validation of the quick COVID-19 Severity Index: a prognostic tool for early clinical decompensation, Ann Emerg Med
Hariyanto, Prasetya, Kurniawan, Proton pump inhibitor use is associated with increased risk of severity and mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Dig Liver Dis
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hoteit, Mattar, Allaw, Rached, Epidemiological study assessing the overuse of proton pump inhibitors in Lebanese population, Middle East J Dig Dis
Israelsen, Ernst, Lundh, Lundbo, Sandholdt et al., Proton Pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Izcovich, Ragusa, Tortosa, Marzio, Agnoletti et al., Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: a systematic review, PLOS ONE
Kellerman, Kintanar, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Prim Care
Khatami, Saatchi, Zadeh, Aghamir, Shabestari et al., A meta-analysis of accuracy and sensitivity of chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 diagnosis, Sci Rep
Kow, Hasan, Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of adverse clinical outcomes from COVID-19: a meta-analysis, J Intern Med
Lai, Wang, Wang, Hsueh, Ko et al., Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Lee, Ha, Yeniova, Moon, Kim et al., Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching, Gut
Lighter, Phillips, Hochman, Sterling, Johnson et al., Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for COVID-19 hospital admission, Clin Infect Dis
Liu, Sloan, Owings, Figgins, Gauthier et al., Increased ACE2 levels and mortality risk of patients with COVID-19 on proton pump inhibitor therapy, Am J Gastroenterol
Mokhtare, Alimoradzadeh, Agah, Mirmiranpour, Khodabandehloo, The Association between modulating inflammatory cytokines and constipation of geriatrics in Iran, Middle East J Dig Dis
Novelli, Biancolella, Mehrian-Shai, Erickson, Pollitt et al., COVID-19 update: the first 6 months of the pandemic, Hum Genomics
Pranata, Huang, Lawrensia, Henrina, Lim et al., Proton pump inhibitor on susceptibility to COVID-19 and its severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmacol Rep
Quan, Li, Couris, Fushimi, Graham et al., Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries, Am J Epidemiol
Ramachandran, Perisetti, Gajendran, Louis, Bansal et al., Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Raudenská, Steinerová, Javůrková, Urits, Kaye et al., Occupational burnout syndrome and posttraumatic stress among healthcare professionals during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol
Sung, Kuipers, El-Serag, Systematic review: the global incidence and prevalence of peptic ulcer disease, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Tas ¸temur S ¸, Ataseven, Is it possible to use proton pump inhibitors in COVID-19 treatment and prophylaxis?, Med Hypotheses
Torres, Valencia, Sellares, PNEUMONIA | Nosocomial
Who, Archived: WHO Timeline -COVID-19
Yan, Chen, Sun, Ahmed, Bhan et al., Does proton pump inhibitor use lead to a higher risk of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and progression to severe disease? A meta-analysis, Jpn J Infect Dis
Yibirin, Oliveira, Valera, Plitt, Lutgen, Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitor use, Cureus
Younes, Al-Sadeq, Al-Jighefee, Younes, Daas, Challenges in laboratory diagnosis of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Viruses
Zhang, Kang, Gong, Xu, Wang et al., Digestive system is a potential route of COVID-19: an analysis of singlecell coexpression pattern of key proteins in viral entry process, Gut
Zhang, Li, Wu, Ling, Qian et al., Analysis of the effect of proton-pump inhibitors on the course of COVID-19, J Inflamm Res
Zippi, Fiorino, Budriesi, Micucci, Corazza et al., Paradoxical relationship between proton pump inhibitors and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, World J Clin Cases
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013",
"ISSN": [
"0003-4509"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013",
"alternative-id": [
"S0003450922001122"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "What is the role of proton pump inhibitors consumption on the clinical presentation and severity of COVID-19 infection?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Académie Nationale de Pharmacie. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6979-6375",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Shokri",
"given": "M.A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0024-879X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moghadam Fard",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8929-9357",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramim",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0087-8385",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hejrati",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3736-7928",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hejrati",
"given": "L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4869-9442",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mokhtare",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises",
"container-title-short": "Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-29T15:52:59Z",
"timestamp": 1661788379000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-17T03:00:16Z",
"timestamp": 1679022016000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100012021",
"award": [
"IR.IUMS.FMD.REC.1400.403"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Iran University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-17T03:41:04Z",
"timestamp": 1679024464574
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0003450922001122?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0003450922001122?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "210-219",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40246-020-00298-w",
"article-title": "COVID-19 update: the first 6 months of the pandemic",
"author": "Novelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Hum Genomics",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0205",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105946",
"article-title": "Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105946",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0210",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0215",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa415",
"article-title": "Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for COVID-19 hospital admission",
"author": "Lighter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "896",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0220",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30111-9",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in patients with HIV: clinical case series",
"author": "Blanco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e314",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet HIV",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0225",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0230",
"series-title": "Archived: WHO Timeline – COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpa.2020.07.008",
"article-title": "Occupational burnout syndrome and post-traumatic stress among healthcare professionals during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic",
"author": "Raudenská",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0235",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Antunes",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0240",
"series-title": "Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. StatPearls [Internet]",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03960.x",
"article-title": "Systematic review: the global incidence and prevalence of peptic ulcer disease",
"author": "Sung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "938",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0245",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3949/ccjm.82a.14138",
"article-title": "GERD: Diagnosing and treating the burn",
"author": "Alzubaidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "685",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Cleve Clin J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0250",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pop.2017.07.001",
"article-title": "Gastroesophageal reflux disease",
"author": "Kellerman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Prim Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0255",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Epidemiological study assessing the overuse of proton pump inhibitors in Lebanese population",
"author": "Hoteit",
"first-page": "265",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Middle East J Dig Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0260",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gastre.2021.04.003",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors in the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Sebastián Domingo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "611",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition)",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0265",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15171/mejdd.2017.78",
"article-title": "The Association between modulating inflammatory cytokines and constipation of geriatrics in Iran",
"author": "Mokhtare",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Middle East J Dig Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0270",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-021-00397-z",
"article-title": "Therapeutic prevention of COVID-19 in elderly: a case-control study",
"author": "Blanc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2333",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Geroscience",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0275",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110018",
"article-title": "Is it possible to use proton pump inhibitors in COVID-19 treatment and prophylaxis?",
"author": "Taştemur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110018",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0280",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0285",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013",
"article-title": "Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0290",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241955",
"article-title": "Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Izcovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0241955",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLOS ONE",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0295",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.074",
"article-title": "Does proton pump inhibitor use lead to a higher risk of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and progression to severe disease? A meta-analysis",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Jpn J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0300",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12060582",
"article-title": "Challenges in laboratory diagnosis of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Younes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "582",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0305",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwq433",
"article-title": "Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries",
"author": "Quan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0310",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annemergmed.2020.07.022",
"article-title": "Development and validation of the quick COVID-19 Severity Index: a prognostic tool for early clinical decompensation",
"author": "Haimovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "442",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ann Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0315",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-80061-2",
"article-title": "A meta-analysis of accuracy and sensitivity of chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 diagnosis",
"author": "Khatami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22402",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0320",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitor use",
"author": "Yibirin",
"first-page": "e12759",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0325",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32598/ppj.24.4.40",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors in Iranian population: from clinical regimens to pharmacogenomics",
"author": "Bagherzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "230",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Physiol Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0330",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001311",
"article-title": "Increased ACE2 levels and mortality risk of patients with COVID-19 on proton pump inhibitor therapy",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1638",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0335",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00263-x",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor on susceptibility to COVID-19 and its severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1642",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0340",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.011",
"article-title": "Proton Pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis",
"author": "Israelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0345",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1707",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0350",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dld.2020.10.001",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use is associated with increased risk of severity and mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Hariyanto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1410",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Dig Liver Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0355",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13183",
"article-title": "Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of adverse clinical outcomes from COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0360",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S292303",
"article-title": "Analysis of the effect of proton-pump inhibitors on the course of COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "J Inflamm Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0365",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2763",
"article-title": "Paradoxical relationship between proton pump inhibitors and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zippi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2763",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0370",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "PNEUMONIA | Nosocomial",
"author": "Torres",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0375",
"series-title": "Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320953",
"article-title": "Digestive system is a potential route of COVID-19: an analysis of single-cell coexpression pattern of key proteins in viral entry process",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0380",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0385",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.580",
"article-title": "The relationship between COVID-19 viral load and disease severity: a systematic review",
"author": "Dadras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e580",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Immun Inflamm Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0390",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103579",
"article-title": "Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12493",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0395",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"article-title": "Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: a review",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.pharma.2022.08.013_bib0400",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0003450922001122"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "What is the role of proton pump inhibitors consumption on the clinical presentation and severity of COVID-19 infection?",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "81"
}