Jinhua Qinggan Granules for Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Controlled Trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074, NCT04723524, May 2022
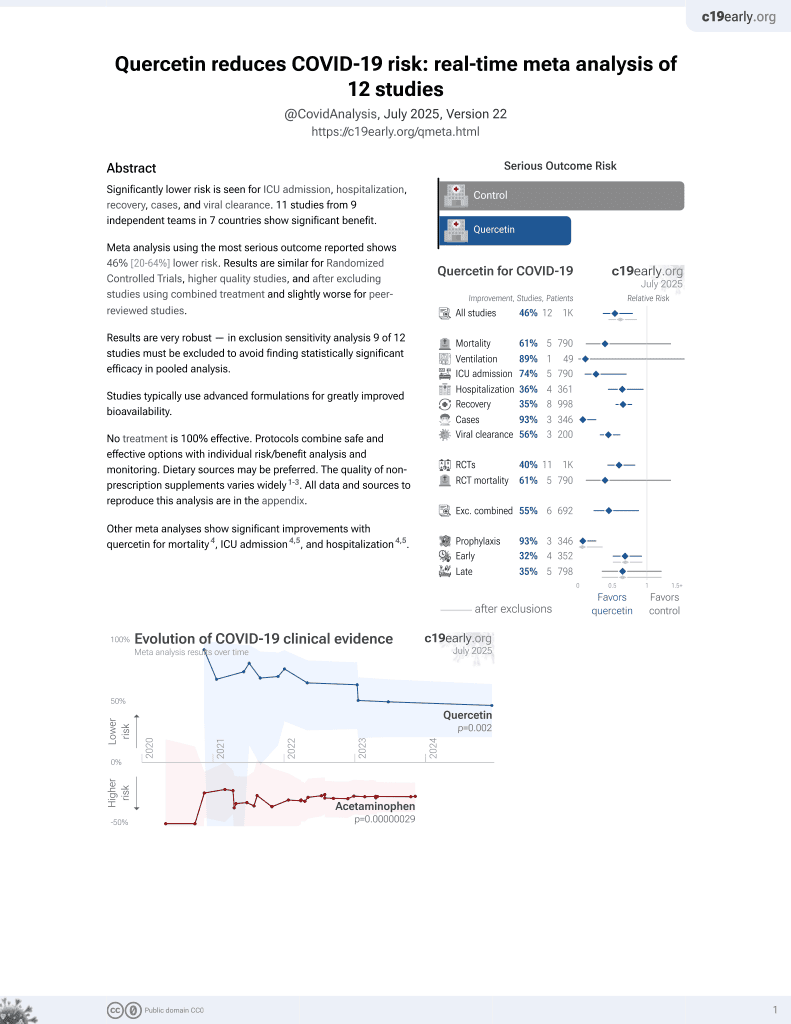
Quercetin for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2022, now with p = 0.0018 from 9 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 300 outpatients in China, showing improved recovery with Jinhua Qinggan treatment, but no significant difference in viral clearance or radiographic findings. Jinhua Qinggan includes quercetin, rutin, luteolin, wogonin, myricetin, ursolic acid, chrysoeriol, glabridin, stigmasterol, and kaempferol.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
combination of several ingredients with unclear dosage.
|
risk of no symptoms decrease ≥30%, 80.6% lower, RR 0.19, p < 0.001, treatment 26 of 150 (17.3%), control 134 of 150 (89.3%), NNT 1.4.
|
|
risk of no symptoms decrease ≥70%, 58.1% lower, RR 0.42, p < 0.001, treatment 62 of 150 (41.3%), control 148 of 150 (98.7%), NNT 1.7.
|
|
risk of no symptoms decrease ≥90%, 35.8% lower, RR 0.64, p < 0.001, treatment 95 of 150 (63.3%), control 148 of 150 (98.7%), NNT 2.8.
|
|
risk of no radiographic improvement, 0.7% lower, RR 0.99, p = 1.00, treatment 112 of 128 (87.5%), control 111 of 126 (88.1%), NNT 168.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 8.1% higher, RR 1.08, p = 0.48, treatment 93 of 150 (62.0%), control 86 of 150 (57.3%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Shah et al., 20 May 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Pakistan, preprint, 10 authors, study period 22 September, 2020 - 23 August, 2021, trial NCT04723524 (history).
Contact: raza.shah@iccs.edu, liuqingquan@bjzhongyi.com, dennislam@hkcmer.com.
Jinhua Qinggan Granules for Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Controlled Trial
doi:10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074
Background: Key findings from the World Health Organization Expert Meeting on Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treating COVID-19 reported that TCMs are beneficial, particularly for mild-to-moderate cases. The efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules (JHQG) in COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms has yet to be clearly defined.
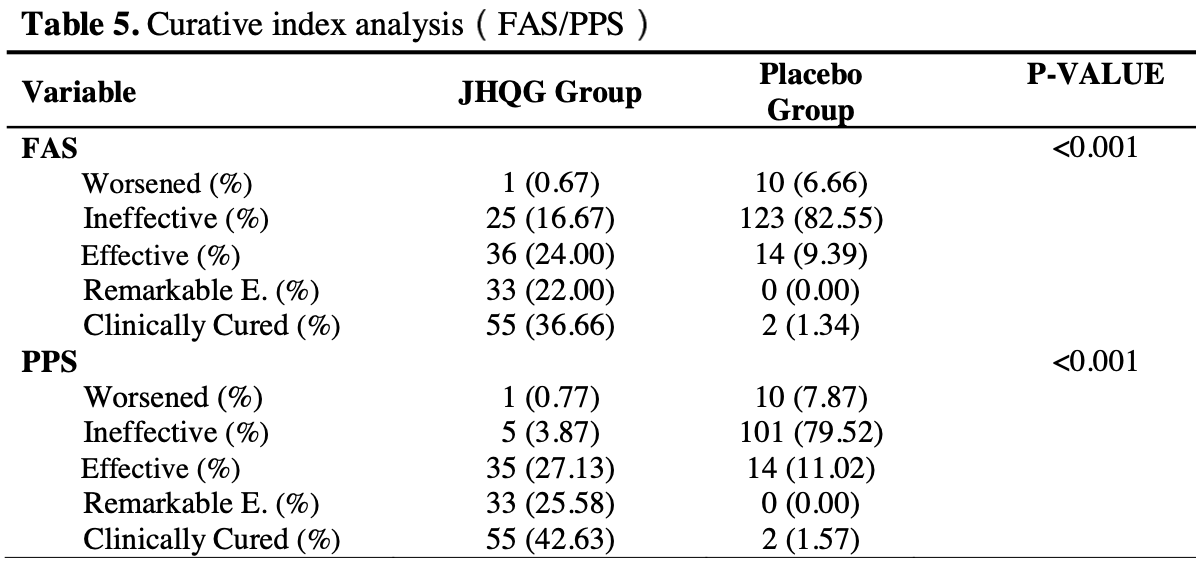
Methods: We conducted a phase 2/3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatment with JHQG in mild, nonhospitalized, laboratoryconfirmed COVID-19 patients. Participants were randomly assigned to receive 5g/sacket of JHQG or placebo granules orally thrice daily for 10 days. The primary outcomes were the improvement in clinical symptoms and proportion tested negative on viral PCR after treatment. Secondary outcomes were the time to recovery from clinical symptoms and changes in white blood cells (WBC) and acute phase reactants (C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin) 10-15 days after treatment. Results: A total of 300 patients were randomly assigned to receive JHQG (150 patients) and placebo (150 patients). Baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups. In the modified intention-to-treat analysis, JHQG showed greater clinical efficacy (82.67%) after 10 days of treatment compared with the placebo group (10.74%) (rate difference: 71.93%; 95% CI 64.09 -79.76). The proportion of patients with a negative PCR after treatment were comparable (rate difference: -4.67%; 95% . While all changes in WBC, ferritin, and CRP levels showed a statistically significant decline in JHQG (P≤0.044) after treatment, but not the latter in placebo (P=0.077). The median time to recovery of COVID-19 related symptoms including cough, sputum, sore throat, dyspnea, headache, nasal obstruction, fatigue, and myalgia were shorter in the JHQG group compared to the placebo group (P<0.001 for all). 3 patients experienced mild to moderate adverse events during the treatment period in the JHQG group. Findings were similar between the modified intention-to-treat and the per-protocol analysis that included only patients who reported 100% adherence to the assigned regimen. Conclusions: JHQG is a safe and effective TCM for the treatment of mild COVID-19 patients.
To our knowledge, this is the first RCT to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of JHQG in the treatment of laboratory-confirmed nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients. Various limitations of this trial should be noted. The basic reason for dropout was that the subjects were unable or unwilling to continue the clinical trial and voluntarily requested to withdraw The study included only COVID-19 patients of Pakistani race, and may limit the geographic generalizability of the findings. This study also excluded patients with severe underlying medical conditions, who are at particularly heightened risk of COVID-19 disease progression. Future studies of JHQG in COVID-19 shall focus on evaluating the clinical efficacy and safety of this TCM in such group of patients. In conclusion, our data show that JHQG is a safe and effective treatment for COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms.
Conflict of interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Statement This study was conducted according to the ethical principles that have their origin in Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional ethics committee
References
An, Efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules Combined With Western Medicine in the Treatment of Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Front Med
An, Efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules Combined With Western Medicine in the Treatment of Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Frontiers in Medicine
Can, Clinical Observation of Jinhua Qinggan Granule in Treating Pneumonia Infected by Novel Coronavirus, Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Chaudhuri, COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the UK: a longitudinal household crosssectional study, BMC public health
Commission, Medicine, Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (Trial Version 7), Chinese Medical Journal
Ding, Bian, Interpretation of pathological changes for" Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 by the National Health Commission (Trial Version 7), Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi= Chinese journal of pathology
Huang, Review on the potential action mechanisms of Chinese medicines in treating Coronavirus Disease, Pharmacological research
Li, Treating influenza patients of wind-heat affecting Fei syndrome by jinhua qinggan granule: a double-blinded randomized control trial
Li, Treating influenza patients of wind-heat affecting Fei syndrome by jinhua qinggan granule: a double-blinded randomized control trial, Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi= Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine
Lin, Study on the network pharmacology of Jinhua Qinggan granules in the treatment of COVID-19, J Chin Med Mater
Liu, Effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules on novel coronavirus pneumonia in patients, J Tradit Chin Med
Liu, Effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules on novel coronavirus pneumonia in patients, Journal of traditional Chinese medicine
Machingaidze, Wiysonge, Understanding COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy, Nature Medicine
Mao, Discussion on the mechanism of Jinhua Qinggan Granule in the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia, J. Chin. Med. Mater
Organization, COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update
Ren, Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine exploring active components and mechanism of Jinhua Qinggan Granules in treatment of COVID-19 based on virus-host interaction, Natural Product Communications
Sanyaolu, Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN comprehensive clinical medicine
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral COVID antiviral drugs, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Servellita, Predominance of antibody-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccine breakthrough cases from the San Francisco Bay Area, California, Nature microbiology
Wang, Oseltamivir compared with the Chinese traditional therapy Maxingshigan-Yinqiaosan in the treatment of H1N1 influenza: a randomized trial, Annals of internal medicine
Wang, Sun, Ding, The therapeutic effects of traditional chinese medicine on COVID-19: a narrative review, International journal of clinical pharmacy
Waris, COVID-19 outbreak: current scenario of Pakistan, New Microbes and New Infections
Who, WHO Expert Meeting on Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of COVID-19
Yang, Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients infected with 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): a review and perspective, International journal of biological sciences
Yates, Obesity, chronic disease, age, and in-hospital mortality in patients with covid-19: analysis of ISARIC clinical characterisation protocol UK cohort, BMC infectious diseases
Yin, Advances in the development of therapeutic strategies against COVID-19 and perspectives in the drug design for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
Zhang, Investigation of anti-SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules based on a network pharmacology and molecular docking approach
Zhong, Yi, He, Zhi, None
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Key findings from the World Health Organization Expert Meeting on Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treating COVID-19 reported that TCMs are beneficial, particularly for mild-to-moderate cases. The efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules (JHQG) in COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms has yet to be clearly defined.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a phase 2/3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatment with JHQG in mild, nonhospitalized, laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patients. Participants were randomly assigned to receive 5g/sacket of JHQG or placebo granules orally thrice daily for 10 days. The primary outcomes were the improvement in clinical symptoms and proportion tested negative on viral PCR after treatment. Secondary outcomes were the time to recovery from clinical symptoms and changes in white blood cells (WBC) and acute phase reactants (C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin) 10-15 days after treatment.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 300 patients were randomly assigned to receive JHQG (150 patients) and placebo (150 patients). Baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups. In the modified intention-to-treat analysis, JHQG showed greater clinical efficacy (82.67%) after 10 days of treatment compared with the placebo group (10.74%) (rate difference: 71.93%; 95% CI 64.09 - 79.76). The proportion of patients with a negative PCR after treatment were comparable (rate difference: -4.67%; 95% CI -15.76 - 6.42). While all changes in WBC, ferritin, and CRP levels showed a statistically significant decline in JHQG (P≤0.044) after treatment, but not the latter in placebo (P=0.077). The median time to recovery of COVID-19 related symptoms including cough, sputum, sore throat, dyspnea, headache, nasal obstruction, fatigue, and myalgia were shorter in the JHQG group compared to the placebo group (P<0.001 for all). 3 patients experienced mild to moderate adverse events during the treatment period in the JHQG group. Findings were similar between the modified intention-to-treat and the per-protocol analysis that included only patients who reported 100% adherence to the assigned regimen.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>JHQG is a safe and effective TCM for the treatment of mild COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Clinical Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>The Trial was prospectively registered on <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"http://www.clinicaltrials.gov\">www.clinicaltrials.gov</jats:ext-link> with registration number: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04723524\">NCT04723524</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
20
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Muhammad Raza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatima",
"given": "Samreen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Sehrosh Naz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafiullah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Himani",
"given": "Gulshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Kelvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Johnson Y.N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Qingquan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lam",
"given": "Dennis S.C.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T06:40:22Z",
"timestamp": 1653288022000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T19:07:20Z",
"timestamp": 1653332840000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-23T19:41:59Z",
"timestamp": 1653334919574
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
17
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
17
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2022.01.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.1",
"unstructured": "Yin, J. , et al., Advances in the development of therapeutic strategies against COVID-19 and perspectives in the drug design for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45538",
"article-title": "Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients infected with 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): a review and perspective",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "International journal of biological sciences",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.2",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100681",
"article-title": "COVID-19 outbreak: current scenario of Pakistan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100681",
"journal-title": "New Microbes and New Infections",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.3",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-01041-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.4",
"unstructured": "Servellita, V. , et al., Predominance of antibody-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants in vaccine breakthrough cases from the San Francisco Bay Area, California. Nature microbiology, 2022: p. 1–12."
},
{
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.5",
"unstructured": "Organization, W.H., COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, edition 76, 25 January 2022. 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01459-7",
"article-title": "Understanding COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1338",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.6",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the UK: a longitudinal household cross-sectional study",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC public health",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.7",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1069",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "SN comprehensive clinical medicine",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.8",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-05950-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.10",
"unstructured": "Saravolatz, L.D. , S. Depcinski , and M. Sharma , Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral COVID antiviral drugs. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2022."
},
{
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.11",
"unstructured": "WHO, WHO Expert Meeting on Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of COVID-19, in Integrated Health Services, Traditional, Complementary and Integrative Medicine. 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-020-01153-7",
"article-title": "The therapeutic effects of traditional chinese medicine on COVID-19: a narrative review",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "International journal of clinical pharmacy",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.12",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Interpretation of pathological changes for” Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 by the National Health Commission (Trial Version 7)”",
"first-page": "397",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi= Chinese journal of pathology",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.13",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "[Treating influenza patients of wind-heat affecting Fei syndrome by jinhua qinggan granule: a double-blinded randomized control trial]",
"first-page": "1631",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.14",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules on novel coronavirus pneumonia in patients",
"first-page": "467",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Tradit Chin Med",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.15",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules Combined With Western Medicine in the Treatment of Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial",
"first-page": "728055",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.16",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine exploring active components and mechanism of Jinhua Qinggan Granules in treatment of COVID-19 based on virus-host interaction",
"first-page": "1934578X20947213",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Natural Product Communications",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.17",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/cm9.0000000000000819",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.18"
},
{
"article-title": "Treating influenza patients of wind-heat affecting Fei syndrome by jinhua qinggan granule: a double-blinded randomized control trial",
"first-page": "1631",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi= Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.19",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-155-4-201108160-00005",
"article-title": "Oseltamivir compared with the Chinese traditional therapy Maxingshigan– Yinqiaosan in the treatment of H1N1 influenza: a randomized trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "217",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Annals of internal medicine",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.20",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.21",
"unstructured": "Can, D. , et al., Clinical Observation of Jinhua Qinggan Granule in Treating Pneumonia Infected by Novel Coronavirus. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020."
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules on novel coronavirus pneumonia in patients",
"first-page": "467",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Journal of traditional Chinese medicine",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.22",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.728055",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.23",
"unstructured": "An, X. , et al., Efficacy of Jinhua Qinggan Granules Combined With Western Medicine in the Treatment of Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Frontiers in Medicine, 2021: p. 1804."
},
{
"article-title": "Discussion on the mechanism of Jinhua Qinggan Granule in the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"first-page": "2843",
"journal-title": "J. Chin. Med. Mater",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.24",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Study on the network pharmacology of Jinhua Qinggan granules in the treatment of COVID-19",
"first-page": "2074",
"journal-title": "J Chin Med Mater",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.25",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104939",
"article-title": "Review on the potential action mechanisms of Chinese medicines in treating Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104939",
"journal-title": "Pharmacological research",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.26",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Investigation of anti-SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 effect of Jinhua Qinggan granules based on a network pharmacology and molecular docking approach",
"first-page": "1934578X211020619",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Natural Product Communications",
"key": "2022052309232939000_2022.05.16.22275074v2.27",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2022.05.16.22275074"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Jinhua Qinggan Granules for Nonhospitalized COVID-19 Patients: a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Controlled Trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}