Evaluation of Glutathione Redox Status and Inflammatory Markers in ICU Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to COVID-19
et al., Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology, doi:10.5812/jjcmb-159606, Mar 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
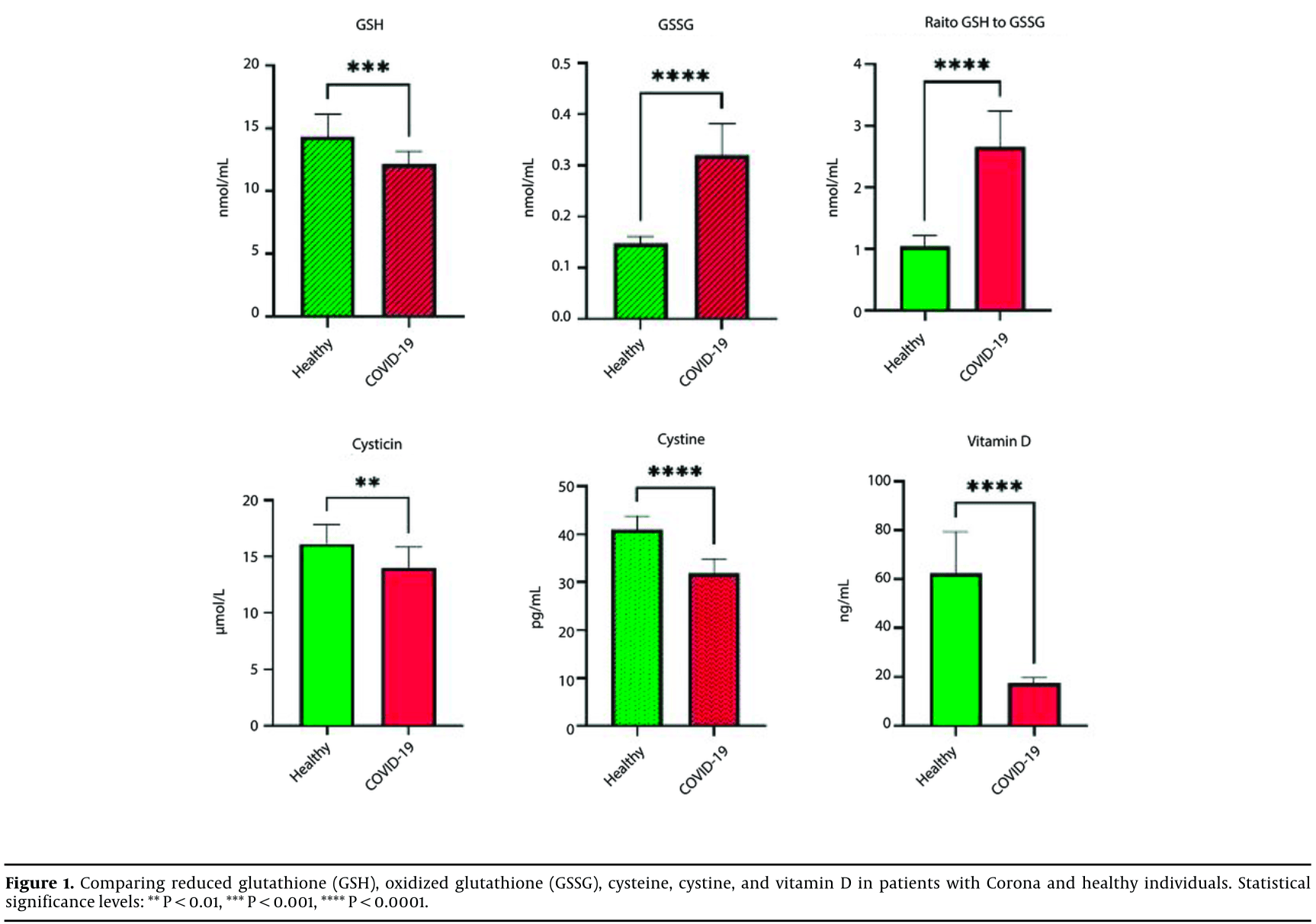
Rerospective 16 COVID-19 ICU patients and 16 healthy controls, showing significantly lower vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients.
Seifi Skishahr et al., 3 Mar 2025, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Evaluation of Glutathione Redox Status and Inflammatory Markers in ICU Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to COVID-19
Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology, doi:10.5812/jjcmb-159606
Background: The use of biomarkers may significantly predict the need for special care and mortality risk in patients with COVID-19. Objectives: This study examines the glutathione redox status, inflammatory markers, and vitamin D levels in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods: A cohort of COVID-19 patients (n = 16) was compared to a healthy control group. Levels of reduced glutathione (GSH), oxidized glutathione (GSSG), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6), cysteine, cystine, and vitamin D were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Independent t-tests and Cohen's d were employed to analyze differences. Results: COVID-19 patients exhibited significant differences from healthy controls in all measured indicators, including GSH, GSSG, CRP, IL-10, IL-6, cysteine, cystine, and the GSH/GSSG ratio (P ≤ 0.001). Additionally, all patients demonstrated vitamin D deficiency, with levels ranging from 10 to 20 ng/dL. Ratios of GSH to GSSG, IL-6 to IL-10, and CRP to cysteine also indicated significant differences between COVID-19 patients and healthy controls (P ≤ 0.001). Conclusions: Measurement of glutathione redox indicators, IL-6 and IL-10 levels, and their respective ratios, along with vitamin D and cysteine/cystine levels, could serve as effective predictors for timely interventions in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the ICU.
Jentashapir J Cell Mol Biol. 2025; 16(1): e159606 7 covered part of the costs (contract number: 1401/15944d/9). Informed Consent: Written informed consent was obtained from the participant.
References
Bartolini, Dallaglio, Torquato, Piroddi, Galli, Nrf2-p62 autophagy pathway and its response to oxidative stress in hepatocellular carcinoma, Transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2017.11.007
Chalmers, Khawaja, Wieruszewski, Gajic, Odeyemi, Diagnosis and treatment of acute pulmonary inflammation in critically ill patients: The role of inflammatory biomarkers, World J Crit Care Med, doi:10.5492/wjccm.v8.i5.59
Checconi, Limongi, Baldelli, Ciriolo, Nencioni et al., Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11081952
Christakos, Ajibade, Dhawan, Fechner, Mady, Vitamin D: metabolism, Rheum Dis Clin North Am, doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2012.03.003
Ciriolo, Palamara, Incerpi, Lafavia, Bue et al., Loss of GSH, oxidative stress, and decrease of intracellular pH as sequential steps in viral infection, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.272.5.2700
Eleftheriadis, Antoniadi, Liakopoulos, Stefanidis, Galaktidou, Inverse association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with markers of inflammation and suppression of osteoclastic activity in hemodialysis patients, Iran J Kidney Dis
Flora, Grassi, Carati, Attenuation of influenza-like symptomatology and improvement of cell-mediated immunity with long-term N-acetylcysteine treatment, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/09031936.97.10071535
Fung, Liu, Human Coronavirus: Host-Pathogen Interaction, Annu Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-020518-115759
Giustarini, Santucci, Bartolini, Galli, Rossi, The agedependent decline of the extracellular thiol-disulfide balance and its role in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.101902
Jafari, Jahani, Pour, The effect of aerobic exercise combined with supplementation of l-arginine on the response of creactive protein in obese men, J Appl Health Stud Sport Physiol, doi:10.22049/jassp.2016.13750
Jain, Parsanathan, Can Vitamin D and L-Cysteine Co-Supplementation Reduce 25(OH)-Vitamin D Deficiency and the Mortality Associated with COVID-19 in African Americans?, J Am Coll Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2020.1789518
Lee, Kang, N-acetylcysteine modulates lipopolysaccharideinduced intestinal dysfunction, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-37296-x
Lee, Lin, Lei, Chang, Lee et al., Does Vitamin D Deficiency Affect the Immunogenic Responses to Influenza Vaccination? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10040409
Liu, Yao, Xu, Qiu, Cao et al., The anti-inflammatory effects of acetaminophen and N-acetylcysteine through suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in LPS-challenged piglet mononuclear phagocytes, Innate Immun, doi:10.1177/1753425914566205
Liu, Zhao, Feng, Xu, SARS-CoV-2 infection threatening intestinal health: A review of potential mechanisms and treatment strategies, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2103090
Mandel, Harari, Gurevich, Achiron, Cytokine prediction of mortality in COVID19 patients, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155190
Matsumoto, Kasai, Sato, Ishiwata, Yatsu et al., Association between C-reactive protein levels at hospital admission and long-term mortality in patients with acute decompensated heart failure, Heart Vessels, doi:10.1007/s00380-019-01435-9
Mcelvaney, Hobbs, Qiao, Mcelvaney, Moll et al., A linear prognostic score based on the ratio of interleukin-6 to interleukin-10 predicts outcomes in COVID-19, E Bio Med, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103026
Narayanan, Huang, Makino, SARS coronavirus accessory proteins, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2007.10.009
Park, Skerrett, IL-10 enhances the growth of Legionella pneumophila in human mononuclear phagocytes and reverses the protective effect of IFN-gamma: differential responses of blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.157.6.2528
Ragab, Salah Eldin, Taeimah, Khattab, Salem, The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Sanguinetti, N-acetylcysteine in COPD: why, how, and when?, Multidiscip Respir Med, doi:10.1186/s40248-016-0039-2
Scheffel, Scurti, Wyatt, Garrett-Mayer, Paulos et al., N-acetyl cysteine protects anti-melanoma cytotoxic T cells from exhaustion induced by rapid expansion via the downmodulation of Foxo1 in an Akt-dependent manner, Cancer Immunol Immunother, doi:10.1007/s00262-018-2120-5
Seifi-Skishahr, Nabilpour, Investigation the concentration of interleukin-6, interleukin-10, and vitamin D in diabetic patients with covid-19 hospitalized in the intensive care unit, Feyz Med Sci J, doi:10.48307/fmsj.2023.27.1.61
Skishahr, Nabilpour, Anthropometric and Physiological Changes in Bodybuilders During the COVID Pandemic, Zahedan J Res Med Sci, doi:10.5812/zjrms-127999
Timpson, Lawlor, Harbord, Gaunt, Day et al., C-reactive protein and its role in metabolic syndrome: mendelian randomisation study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67786-0
Violi, Loffredo, Carnevale, Pignatelli, Pastori, Atherothrombosis and Oxidative Stress: Mechanisms and Management in Elderly, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2016.6963
Yaghoubian, Niktale, Yazdi, Ghorani, Rashed et al., Evaluate the Therapeutic Effect of Allicin (L-cysteine) on Clinical Presentation and Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19, Eur J Transl Myol, doi:10.4081/ejtm.2021.9518
Zhao, Qin, Zhang, Li, Liang et al., Longitudinal COVID-19 profiling associates IL-1RA and IL-10 with disease severity and RANTES with mild disease, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.139834
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5812/jjcmb-159606",
"ISSN": [
"2717-2724"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5812/jjcmb-159606",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The use of biomarkers may significantly predict the need for special care and mortality risk in patients with COVID-19. Objectives: This study examines the glutathione redox status, inflammatory markers, and vitamin D levels in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods: A cohort of COVID-19 patients (n = 16) was compared to a healthy control group. Levels of reduced glutathione (GSH), oxidized glutathione (GSSG), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6), cysteine, cystine, and vitamin D were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Independent t-tests and Cohen's d were employed to analyze differences. Results: COVID-19 patients exhibited significant differences from healthy controls in all measured indicators, including GSH, GSSG, CRP, IL-10, IL-6, cysteine, cystine, and the GSH/GSSG ratio (P ≤ 0.001). Additionally, all patients demonstrated vitamin D deficiency, with levels ranging from 10 to 20 ng/dL. Ratios of GSH to GSSG, IL-6 to IL-10, and CRP to cysteine also indicated significant differences between COVID-19 patients and healthy controls (P ≤ 0.001). Conclusions: Measurement of glutathione redox indicators, IL-6 and IL-10 levels, and their respective ratios, along with vitamin D and cysteine/cystine levels, could serve as effective predictors for timely interventions in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the ICU.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"728ba95af3ff4d5d6941b19e2a62f6acc4756942"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seifi Skishahr",
"given": "Farnaz",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nabilpour",
"given": "Maghsoud",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology",
"container-title-short": "Jentashapir J Cell Mol Biol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"brieflands.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-08T07:43:16Z",
"timestamp": 1741419796000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-08T07:43:20Z",
"timestamp": 1741419800000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-08T08:10:13Z",
"timestamp": 1741421413264,
"version": "3.38.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
3
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740441600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jjcmb-159606",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jjcmb-159606",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "3819",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.5812",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Brieflands",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2022.2103090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF1-1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2020.1789518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF2-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2016.6963",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF3-3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF4-4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67786-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF5-5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22049/jassp.2016.13750",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF6-6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.48307/fmsj.2023.27.1.61",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF7-7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155190",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF8-8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF9-9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.157.6.2528",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF10-10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.139834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF11-11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF12-12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40248-016-0039-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF13-13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.97.10071535",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF14-14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/zjrms-127999",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF15-15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rdc.2012.03.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF16-16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-micro-020518-115759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF17-17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.10.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF18-18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2017.11.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF19-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.272.5.2700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF20-20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11081952",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF21-21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.101902",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF22-22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5492/wjccm.v8.i5.59",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF23-23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00380-019-01435-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF24-24"
},
{
"author": "Eleftheriadis T",
"first-page": "129",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Iran J Kidney Dis.",
"key": "key-A159606REF25-25",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4081/ejtm.2021.9518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF26-26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753425914566205",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF27-27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-37296-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF28-28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00262-018-2120-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF29-29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10040409",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A159606REF30-30"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jjcmb-159606"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of Glutathione Redox Status and Inflammatory Markers in ICU Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.5812/crossmark_update_policy",
"volume": "16"
}
