Hospitalised children with COVID-19 display an aberrant intestinal microbiota and a shift in faecal compounds related with the metabolism of vitamins and lipids
et al., PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0323910, May 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
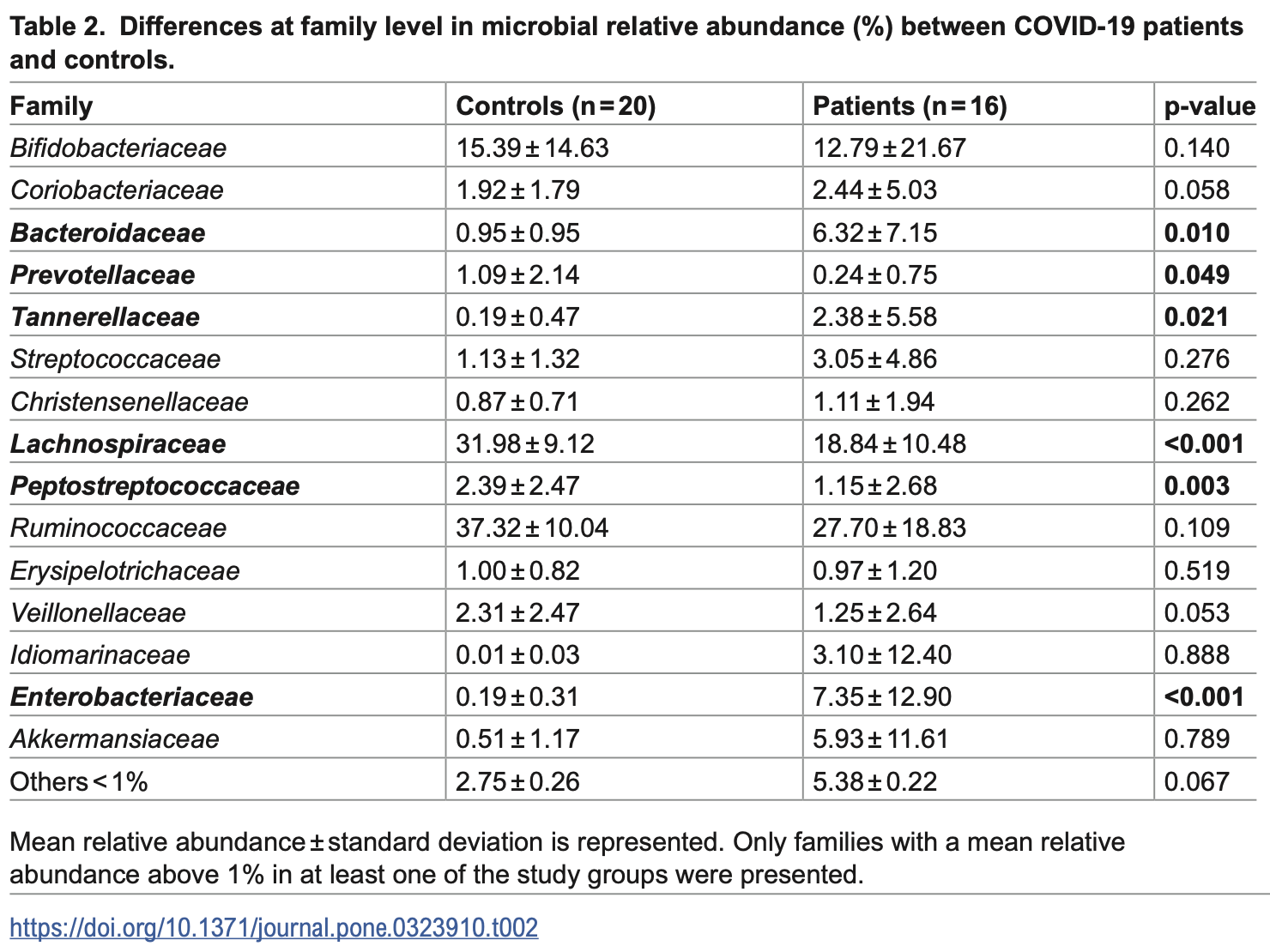
Analysis of 16 children hospitalized with COVID-19 and 20 age-matched healthy controls showing altered gut microbiota and faecal metabolomic profiles in infected children. COVID-19 patients had higher abundance of opportunistic bacteria and lower levels of beneficial commensals. COVID-19 patients had significantly lower faecal levels of vitamins (B1, B3, and vitamin D3 derivatives) compared to controls, with these compounds negatively correlated with pathogenic bacteria. Authors suggest proper nutrition and healthy gut microbiota are crucial for immune response against SARS-CoV-2.
Study covers vitamin D and probiotics.
Sanz et al., 20 May 2025, Spain, peer-reviewed, mean age 10.1, 17 authors, study period October 2020 - July 2021.
Contact: sdelgado@ipla.csic.es.
Hospitalised children with COVID-19 display an aberrant intestinal microbiota and a shift in faecal compounds related with the metabolism of vitamins and lipids
PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0323910
The SARS-CoV-2 virus and its rapid spread have made it a global health concern. The aim of this was to investigate the microbial and metabolic faecal profiles of paediatric patients hospitalised for COVID-19 to try to identify biomarkers of predisposition to severity. The study included 16 patients (aged 4-14 years old) from six different Spanish hospitals and 20 age-matched healthy controls. The gut microbiota was characterised by sequencing of 16S rDNA amplicons and internal transcribed space amplicons, while the metabolic profile was analysed by liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. A different microbial profile was observed between patients and controls, with a significantly higher abundance of sequences belonging to the phyla Bacteroidota and Pseudomonadota in patients. A different metabolic profile was observed between the two groups. Non-infected children had higher faecal levels of vitamins such as niacin, thiamine, and vitamin D3 derivatives, which were negatively correlated with the abundance of pathogenic bacteria, such as members of Enterobacteriaceae. Hospitalisation due to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children was associated with changes in the gut microbiota and an altered metabolomic profile. For the first time, several relevant biological compounds were found to be reduced in the faeces of children hospitalised with COVID-19 compared to healthy controls. (SAMN40261256-SAMN40261291). Metabolic
Supporting information S1 File. S1 Writing -original draft: Isabel Gutiérrez-Diaz. Writing -review & editing: Susana Delgado, Hector González, Juan J. Díaz.
References
Bacorn, Romero-Soto, Levy, Chen, Hourigan, The Gut Microbiome of Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms10122460
Bohn, Yousef, Steele, Sepiashvili, Adeli, MultiInflammatory Syndrome in Children: A View into Immune Pathogenesis from a Laboratory Perspective, J Appl Lab Med, doi:10.1093/jalm/jfab114
Cariolou, Cupp, Evangelou, Tzoulaki, Berlanga-Taylor, Importance of vitamin D in acute and critically ill children with subgroup analyses of sepsis and respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027666
Chatterjee, Lu, Zhang, Zhang, Dai et al., Vitamin D receptor promotes healthy microbial metabolites and microbiome, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-64226-7
Costea, Zeller, Sunagawa, Pelletier, Alberti et al., Towards standards for human fecal sample processing in metagenomic studies, Nat Biotechnol, doi:10.1038/nbt.3960
De Matos, Adams, Hastings, Moreno, Steinbeck, A database for chemical proteomics: ChEBI, Methods Mol Biol, doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-364-6_19
Doenhardt, Hufnagel, Diffloth, Hübner, Mauer et al., Epidemiology of 7375 children and adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19 in Germany, reported via a prospective, nationwide surveillance study in 2020-2022, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-49210-1
Farsi, Tahvildari, Arbabi, Vazife, Sechi et al., Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Roles of Gut Microbiota in COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.804644
Frenkel, Gomez, Bellanti, COVID-19 in children: Pathogenesis and current status, Allergy Asthma Proc, doi:10.2500/aap.2021.42.200104
Fu, Du, Chen, Shama, Chen et al., Exploring the impact of gut microbial metabolites on inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine efficacy during pregnancy and mother-to-infant antibody transfer, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330497
Geva-Zatorsky, Sefik, Kua, Pasman, Tan et al., Mining the Human Gut Microbiota for Immunomodulatory Organisms, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.022
Ghazanfar, Kandhi, Shin, Muthumanickam, Gurjar et al., Impact of COVID-19 on the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Clinical Review, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.23333
Giacomet, Barcellini, Stracuzzi, Longoni, Folgori et al., Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Severe COVID-19 Children, Pediatr Infect Dis J, doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000002843
Guloyan, Oganesian, Baghdasaryan, Yeh, Singh et al., Glutathione Supplementation as an Adjunctive Therapy in COVID-19, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9100914
Guo, Tao, Flavell, Zhu, Potential intestinal infection and faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00416-6
Gupta, Beg, Jain, Bhatnagar, Paediatric COVID-19 and the GUT, Indian J Med Microbiol, doi:10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_20_331
Gutiérrez-Díaz, Sanz-Martinez, Castro, Rodríguez-Belvís, Carreira et al., Microbial and immune faecal determinants in infants hospitalized with COVID-19 reflect bifidobacterial dysbiosis and immature intestinal immunity, Eur J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-023-05140-8
Harris, Taylor, Thielke, Payne, Gonzalez et al., Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J Biomed Inform, doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Hoque, Akter, Mishu, Islam, Rahman et al., Microbial co-infections in COVID-19: Associated microbiota and underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis, Microb Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104941
Hoque, Sarkar, Rahman, Akter, Banu et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces human nasopharyngeal commensal microbiome with inclusion of pathobionts, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-03245-4
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Islam, Foysal, Hoque, Mehedi, Rob et al., Dysbiosis of Oral and Gut Microbiomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients in Bangladesh: Elucidating the Role of Opportunistic Gut Microbes, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.821777
Jimenez, Velasco Rodríguez-Belvís, Gonzalez, Ortega, Segarra et al., COVID-19 Gastrointestinal Manifestations Are Independent Predictors of PICU Admission in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients, Pediatr Infect Dis J, doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000002935
Larkin, Lassetter, Vitamin D deficiency and acute lower respiratory infections in children younger than 5 years: identification and treatment, J Pediatr Health Care, doi:10.1016/j.pedhc.2014.08.013
Mcdowall, Hunter, InterPro protein classification, Methods Mol Biol, doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-977-2_3
Milani, Hevia, Foroni, Duranti, Turroni et al., Assessing the fecal microbiota: an optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068739
Milani, Lugli, Turroni, Mancabelli, Duranti et al., Evaluation of bifidobacterial community composition in the human gut by means of a targeted amplicon sequencing (ITS) protocol, FEMS Microbiol Ecol, doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12410
Mizutani, Ishizaka, Koga, Ikeuchi, Saito et al., Correlation Analysis between Gut Microbiota Alterations and the Cytokine Response in Patients with Coronavirus Disease during Hospitalization, Microbiol Spectr, doi:10.1128/spectrum.01689-21
Nambiar, Metabolomics, None, Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-102723-3.00020-2
Nasser, Younis, Abidreda, Alyasiri, Importance of Vitamin D3 in COVID-19 Patients, Arch Razi Inst, doi:10.22092/ari.2021.356070.1769
Nikolopoulou, Maltezou, COVID-19 in Children: Where do we Stand?, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.07.002
Pandit, Frishman, Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Clinical Manifestations, Cardiac Complications and Medical Management, Cardiol Rev, doi:10.1097/CRD.0000000000000565
Park, Hosomi, Kawashima, Chen, Mohsen et al., Dietary Vitamin B1 Intake Influences Gut Microbial Community and the Consequent Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14102078
Paysan-Lafosse, Blum, Chuguransky, Grego, Pinto et al., InterPro in 2022, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac993
Petkova, Mineva, Botsova, Clinical Study of Vitamin D Levels in Hospitalized Children with Acute Respiratory Infections, Pediatr Rep, doi:10.3390/pediatric16040088
Petrelli, Oldani, Borgonovo, Cabiddu, Dognini et al., Vitamin D3 and COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox12020247
Ren, Ning, Yang, Yang, Li et al., MetaboliteCOVID: A manually curated database of metabolite markers for COVID-19, Comput Biol Med, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107661
Romani, Chierico, Macari, Pane, Ristori et al., The Relationship Between Pediatric Gut Microbiota and SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.908492
Shakoor, Feehan, Mikkelsen, Dhaheri, Ali et al., Be well: A potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Smith, Johnson, Koshy, Hess, Qureshi et al., Thiamine deficiency disorders: a clinical perspective, Ann N Y Acad Sci, doi:10.1111/nyas.14536
Soto-Martin, Warnke, Farquharson, Christodoulou, Horgan et al., Vitamin Biosynthesis by Human Gut Butyrate-Producing Bacteria and Cross-Feeding in Synthetic Microbial Communities, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00886-20
Stutz, Dylla, Pearson, Lecompte-Osorio, Nayak et al., Immunomodulatory fecal metabolites are associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients with respiratory failure, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34260-2
Su, Zhang, Qi, Gao, Yang et al., Gut microbiota-derived metabolite 3-idoleacetic acid together with LPS induces IL-35+ B cell generation, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-021-01205-8
Sud, Fahy, Cotter, Brown, Dennis et al., LMSD: LIPID MAPS structure database, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkl838
Suskun, Kilic, Ciftdogan, Guven, Karbuz et al., Intestinal microbiota composition of children with infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C), Eur J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-022-04494-9
Valentino, Esposito, Colosimo, Caprio, Puzone et al., Gut microbiota and COVID-19: An intriguing pediatric perspective, World J Clin Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8076
Wang, Bryant, Cheng, Wang, Gindulyte et al., PubChem BioAssay: 2017 update, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1118
Wang, Li, Wei, Lian, Sun et al., Respiratory influenza virus infection induces intestinal immune injury via microbiota-mediated Th17 cell-dependent inflammation, J Exp Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20140625
Wang, Xiao, Suzek, Zhang, Wang et al., PubChem's BioAssay Database, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkr1132
Wang, Zhou, Lu, Hu, Xiao et al., Altered gut microbiota composition in children and their caregivers infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, World J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s12519-022-00659-6
Wishart, Guo, Oler, Wang, Anjum et al., HMDB 5.0: the Human Metabolome Database for 2022, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkab1062
Wishart, Oler, Peters, Guo, Girod et al., MiMeDB: the Human Microbial Metabolome Database, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac868
Wu, Cheng, Jiang, Tang, Ming et al., Altered oral and gut microbiota and its association with SARS-CoV-2 viral load in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization, NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes, doi:10.1038/s41522-021-00232-5
Xiao, Tang, Zheng, Liu, Li et al., Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055
Yamamoto, Saito, Tamura, Prawisuda, Mizutani et al., The human microbiome and COVID-19: A systematic review, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0253293
Yao, Devotta, Li, Lunjani, Sadlier et al., Dysrupted microbial tryptophan metabolism associates with SARS-CoV-2 acute inflammatory responses and long COVID, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2429754
Yin, Minacapelli, Parmar, Catalano, Bhurwal et al., Alterations of the fecal microbiota in relation to acute COVID-19 infection and recovery, Mol Biomed, doi:10.1186/s43556-022-00103-1
Zhang, Lau, Liu, Su, Chan et al., Gut microbiota in COVID-19: key microbial changes, potential mechanisms and clinical applications, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00698-4
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0323910",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0323910",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The SARS-CoV-2 virus and its rapid spread have made it a global health concern. The aim of this was to investigate the microbial and metabolic faecal profiles of paediatric patients hospitalised for COVID-19 to try to identify biomarkers of predisposition to severity. The study included 16 patients (aged 4–14 years old) from six different Spanish hospitals and 20 age-matched healthy controls. The gut microbiota was characterised by sequencing of 16S rDNA amplicons and internal transcribed space amplicons, while the metabolic profile was analysed by liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. A different microbial profile was observed between patients and controls, with a significantly higher abundance of sequences belonging to the phyla Bacteroidota and Pseudomonadota in patients. A different metabolic profile was observed between the two groups. Non-infected children had higher faecal levels of vitamins such as niacin, thiamine, and vitamin D3 derivatives, which were negatively correlated with the abundance of pathogenic bacteria, such as members of <jats:italic>Enterobacteriaceae</jats:italic>. Hospitalisation due to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children was associated with changes in the gut microbiota and an altered metabolomic profile. For the first time, several relevant biological compounds were found to be reduced in the faeces of children hospitalised with COVID-19 compared to healthy controls.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gutiérrez-Díaz",
"given": "Isabel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "González",
"given": "Hector",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodríguez-Belvís",
"given": "Marta Velasco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Picáns-Leis",
"given": "Rosaura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiménez",
"given": "Santiago",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8696-9194",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "González",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodríguez",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Queralt",
"given": "Macarena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herrador",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martín-Masot",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrer",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navas-López",
"given": "Víctor M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Espín",
"given": "Beatriz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0540-4210",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Leis",
"given": "Rosaura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Díaz",
"given": "Juan J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1081-2614",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Delgado",
"given": "Susana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS One",
"container-title-short": "PLoS One",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-20T17:29:59Z",
"timestamp": 1747762199000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-20T17:30:11Z",
"timestamp": 1747762211000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chong,",
"given": "Chun Wie",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-21T04:31:42Z",
"timestamp": 1747801902381,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1747699200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0323910",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0323910",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "B Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref001",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000002843",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Severe COVID-19 Children",
"author": "V Giacomet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Infect Dis J",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref002",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000002935",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Gastrointestinal Manifestations Are Independent Predictors of PICU Admission in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients",
"author": "D Gonzalez Jimenez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Infect Dis J",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref003",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_20_331",
"article-title": "Paediatric COVID-19 and the GUT",
"author": "R Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Indian J Med Microbiol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref004",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2500/aap.2021.42.200104",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in children: Pathogenesis and current status",
"author": "LD Frenkel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Allergy Asthma Proc",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref005",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.07.002",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Children: Where do we Stand?",
"author": "GB Nikolopoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref006",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jalm/jfab114",
"article-title": "MultiInflammatory Syndrome in Children: A View into Immune Pathogenesis from a Laboratory Perspective",
"author": "MK Bohn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "311",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Appl Lab Med",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref007",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Clinical Manifestations, Cardiac Complications and Medical Management",
"author": "M Pandit",
"journal-title": "Cardiol Rev",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref008",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-022-00698-4",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota in COVID-19: key microbial changes, potential mechanisms and clinical applications",
"author": "F Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "323",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref009",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104941",
"article-title": "Microbial co-infections in COVID-19: Associated microbiota and underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis",
"author": "MN Hoque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104941",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref010",
"volume": "156",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0253293",
"article-title": "The human microbiome and COVID-19: A systematic review",
"author": "S Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref011",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.821777",
"article-title": "Dysbiosis of Oral and Gut Microbiomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients in Bangladesh: Elucidating the Role of Opportunistic Gut Microbes",
"author": "SM Rafiqul Islam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "821777",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref012",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-03245-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces human nasopharyngeal commensal microbiome with inclusion of pathobionts",
"author": "MN Hoque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24042",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref013",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-023-05140-8",
"article-title": "Microbial and immune faecal determinants in infants hospitalized with COVID-19 reflect bifidobacterial dysbiosis and immature intestinal immunity",
"author": "I Gutiérrez-Díaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4633",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pediatr",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref014",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.908492",
"article-title": "The Relationship Between Pediatric Gut Microbiota and SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "L Romani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "908492",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref015",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12519-022-00659-6",
"article-title": "Altered gut microbiota composition in children and their caregivers infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant",
"author": "Y-Z Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "478",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "World J Pediatr",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref016",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8076",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota and COVID-19: An intriguing pediatric perspective",
"author": "MS Valentino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8076",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref017",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-08-102723-3.00020-2",
"article-title": "Metabolomics",
"author": "S Nambiar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "758",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref018",
"volume-title": "Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107661",
"article-title": "MetaboliteCOVID: A manually curated database of metabolite markers for COVID-19",
"author": "L Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107661",
"journal-title": "Comput Biol Med",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref019",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"article-title": "Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support",
"author": "PA Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref020",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt.3960",
"article-title": "Towards standards for human fecal sample processing in metagenomic studies",
"author": "PI Costea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1069",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref021",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0068739",
"article-title": "Assessing the fecal microbiota: an optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol",
"author": "C Milani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref022",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of bifidobacterial community composition in the human gut by means of a targeted amplicon sequencing (ITS) protocol",
"author": "C Milani",
"first-page": "493",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "FEMS Microbiol Ecol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref023",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkab1062",
"article-title": "HMDB 5.0: the Human Metabolome Database for 2022",
"author": "DS Wishart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref024",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac868",
"article-title": "MiMeDB: the Human Microbial Metabolome Database",
"author": "DS Wishart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref025",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "PubChem BioAssay: 2017 update",
"author": "Y Wang",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref026",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "PubChem’s BioAssay Database",
"author": "Y Wang",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref027",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-60761-977-2_3",
"article-title": "InterPro protein classification",
"author": "J McDowall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref028",
"volume": "694",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac993",
"article-title": "InterPro in 2022",
"author": "T Paysan-Lafosse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref029",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-61779-364-6_19",
"article-title": "A database for chemical proteomics: ChEBI",
"author": "P de Matos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref030",
"volume": "803",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "LMSD: LIPID MAPS structure database",
"author": "M Sud",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref031",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of COVID-19 on the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Clinical Review",
"author": "H Ghazanfar",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref032",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-49210-1",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of 7375 children and adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19 in Germany, reported via a prospective, nationwide surveillance study in 2020-2022",
"author": "M Doenhardt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref033",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-021-00416-6",
"article-title": "Potential intestinal infection and faecal-oral transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "M Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref034",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41522-021-00232-5",
"article-title": "Altered oral and gut microbiota and its association with SARS-CoV-2 viral load in COVID-19 patients during hospitalization",
"author": "Y Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref035",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055",
"article-title": "Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "F Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref036",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-022-04494-9",
"article-title": "Intestinal microbiota composition of children with infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C)",
"author": "C Suskun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3175",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pediatr",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref037",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.022",
"article-title": "Mining the Human Gut Microbiota for Immunomodulatory Organisms",
"author": "N Geva-Zatorsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref038",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "J Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"issue": "7807",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref039",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.804644",
"article-title": "Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Roles of Gut Microbiota in COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review",
"author": "Y Farsi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "804644",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref040",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43556-022-00103-1",
"article-title": "Alterations of the fecal microbiota in relation to acute COVID-19 infection and recovery",
"author": "YS Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol Biomed",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref041",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330497",
"article-title": "Exploring the impact of gut microbial metabolites on inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine efficacy during pregnancy and mother-to-infant antibody transfer",
"author": "X Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref042",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-34260-2",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory fecal metabolites are associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients with respiratory failure",
"author": "MR Stutz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6615",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref043",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.01689-21",
"article-title": "Correlation Analysis between Gut Microbiota Alterations and the Cytokine Response in Patients with Coronavirus Disease during Hospitalization",
"author": "T Mizutani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Spectr",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref044",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms10122460",
"article-title": "The Gut Microbiome of Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "M Bacorn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2460",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Microorganisms",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref045",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20140625",
"article-title": "Respiratory influenza virus infection induces intestinal immune injury via microbiota-mediated Th17 cell-dependent inflammation",
"author": "J Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2397",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref046",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007",
"article-title": "Be well: A potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19",
"author": "H Shakoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref047",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.14536",
"article-title": "Thiamine deficiency disorders: a clinical perspective",
"author": "TJ Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann N Y Acad Sci",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref048",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin Biosynthesis by Human Gut Butyrate-Producing Bacteria and Cross-Feeding in Synthetic Microbial Communities",
"author": "EC Soto-Martin",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref049",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14102078",
"article-title": "Dietary Vitamin B1 Intake Influences Gut Microbial Community and the Consequent Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids",
"author": "J Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2078",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref050",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Importance of Vitamin D3 in COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "FA Nasser",
"first-page": "1545",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Arch Razi Inst",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref051",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox12020247",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 and COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses",
"author": "F Petrelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref052",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9100914",
"article-title": "Glutathione Supplementation as an Adjunctive Therapy in COVID-19",
"author": "V Guloyan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "914",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref053",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-64226-7",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor promotes healthy microbial metabolites and microbiome",
"author": "I Chatterjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7340",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref054",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-021-01205-8",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota-derived metabolite 3-idoleacetic acid together with LPS induces IL-35+ B cell generation",
"author": "X Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref055",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2024.2429754",
"article-title": "Dysrupted microbial tryptophan metabolism associates with SARS-CoV-2 acute inflammatory responses and long COVID",
"author": "L Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2429754",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref056",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pedhc.2014.08.013",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and acute lower respiratory infections in children younger than 5 years: identification and treatment",
"author": "A Larkin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Health Care",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref057",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pediatric16040088",
"article-title": "Clinical Study of Vitamin D Levels in Hospitalized Children with Acute Respiratory Infections",
"author": "GS Petkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1034",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Rep",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref058",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027666",
"article-title": "Importance of vitamin D in acute and critically ill children with subgroup analyses of sepsis and respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "M Cariolou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "pone.0323910.ref059",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0323910"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Hospitalised children with COVID-19 display an aberrant intestinal microbiota and a shift in faecal compounds related with the metabolism of vitamins and lipids",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "20"
}
