Cellular Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Plays Important Roles in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14040333, Mar 2025
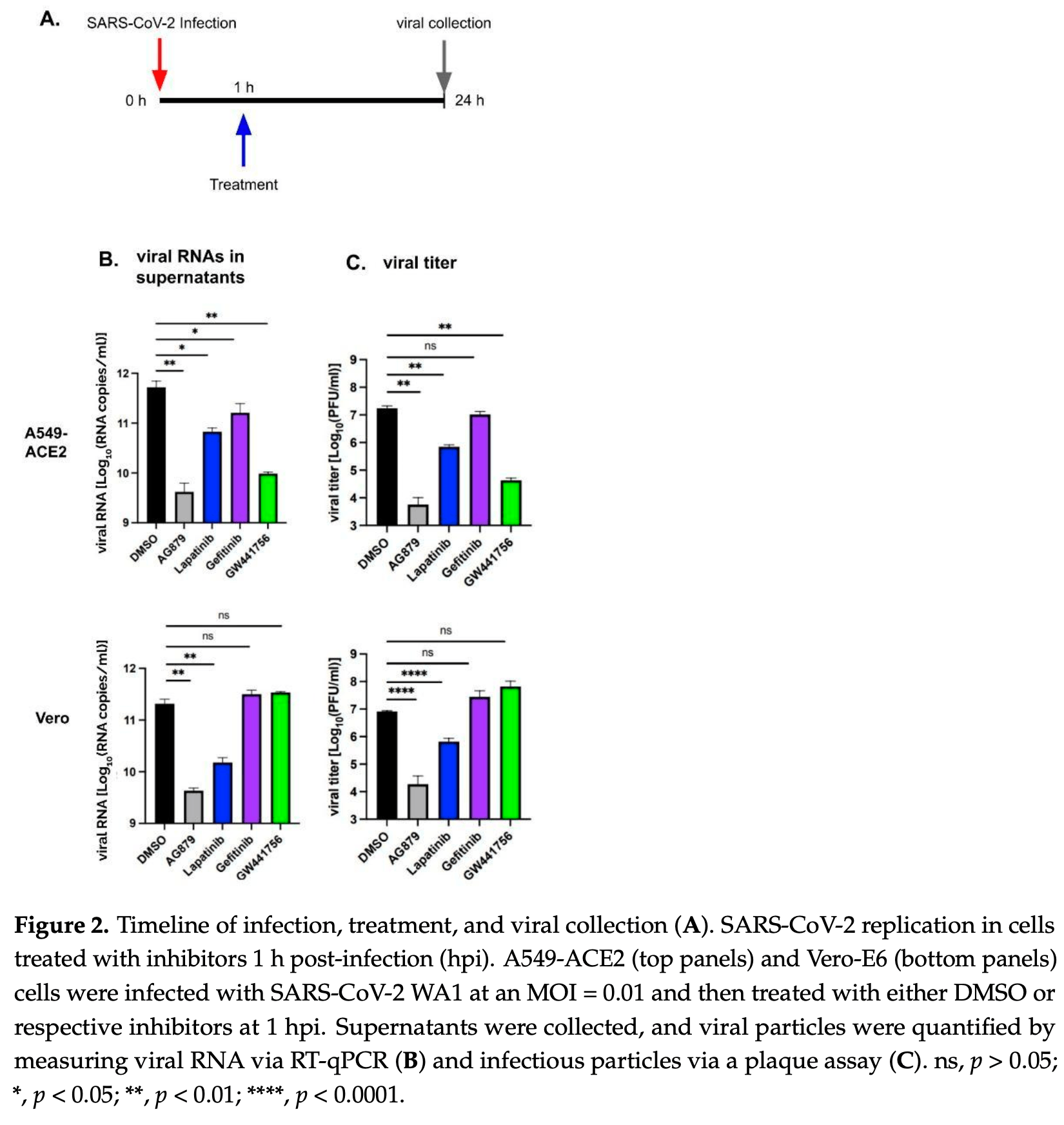
In vitro study showing that tyrosine kinase receptor (RTK) inhibitors lapatinib and GW441756 significantly reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication in human lung epithelial cells. Authors found that the HER2 inhibitor lapatinib reduced viral replication in both A549-ACE2 and Vero-E6 cells, while the TrkA inhibitor GW441756 was effective only in A549-ACE2 cells. Time-of-addition experiments indicated lapatinib acts during early viral entry, while GW441756 affects post-entry steps in the viral life cycle. Both inhibitors demonstrated high therapeutic index values (>11) with minimal cytotoxicity. Western blot analysis confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection activates EGFR and TrkA signaling pathways. The study provides evidence that targeting host RTK signaling pathways, particularly HER2 and TrkA, could be a promising antiviral strategy for COVID-19 treatment with reduced risk of viral resistance.
Sanchez et al., 31 Mar 2025, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: liangy@umn.edu (corresponding author), sanch737@umn.edu, flann103@umn.edu, murp1625@umn.edu, huangq@umn.edu, hly@umn.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Cellular Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Plays Important Roles in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens14040333
Current antiviral treatments often target specific viral components, which can lead to the rapid emergence of drug-resistant mutants. Targeting host signaling pathways, including their associated cellular factors, that are important for virus replication is a novel approach toward the development of next-generation antivirals to overcome drug resistance. Various cellular receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) have previously been shown to play important roles in mediating viral replication including coronaviruses. In this study, we examined the roles of RTKs in SARS-CoV-2 replication in two cell lines, A549-ACE2 (human lung epithelial cells) and Vero-E6 (African Green Monkey kidney cell), via chemical inhibitors. We showed that the HER2 inhibitor Lapatinib significantly reduced viral replication in both cell lines, the TrkA inhibitor GW441756 was effective only in A549-ACE2 cells, while the EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib had little effect in either cell line. Lapatinib and GW441756 exhibited a high therapeutic index (CC 50 /EC 50 > 10) in A549-ACE2 cells. Time-of-addition experiments indicated that Lapatinib may inhibit the early entry step, whereas GW441756 can affect post-entry steps of the viral life cycle. These findings suggest the important roles of HER2 and TrkA signaling in SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung epithelial cells and support further investigation of RTK inhibitors as potential COVID-19 treatments.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Figure S1 : Dose-response inhibition curves for Lapatinib and GW441756.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations The
References
Cdc, Types of COVID-19 Treatment
Dave, Shah, Chorawala, Shah, Patel et al., An antiviral drug against COVID-19, Arch. Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-023-05881-9
Harford, Grove, Rezaee, Scheraga, Olman et al., RSV infection potentiates TRPV1-mediated calcium transport in bronchial epithelium of asthmatic children, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00531.2020
Hu, Zhang, Shen, Yang, Epidermal growth factor receptor is a co-factor for transmissible gastroenteritis virus entry, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2018.05.009
Karaman, Herrgard, Treiber, Gallant, Atteridge et al., A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity, Nat. Biotechnol, doi:10.1038/nbt1358
Kindrachuk, Ork, Hart, Mazur, Holbrook et al., Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.03659-14
Kris, Natale, Herbst, Lynch, Prager et al., Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.290.16.2149
Kumar, Liang, Parslow, Liang, Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors block multiple steps of influenza a virus replication, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01969-10
Kumar, Sharma, Kumar, Tripathi, Barua et al., None, Clin. Microbiol. Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00168-19
Kuroda, Halfmann, Kawaoka, HER2-mediated enhancement of Ebola virus entry, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008900
Lamers, Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0
Liang, Pathogenicity and virulence of influenza, Virulence, doi:10.1080/21505594.2023.2223057
Malone, Urakova, Snijder, Campbell, Structures and functions of coronavirus replication-transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00432-z
Narayanan, Jamison, Guarnieri, Zaksas, Topper et al., A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: Host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Hum. Genet, doi:10.1038/s41431-023-01462-1
Purcaru, Artene, Barcan, Silosi, Stanciu et al., The Interference between SARS-CoV-2 and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Signaling in Cancer, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22094830
Raymonda, Ciesla, Monaghan, Leach, Asantewaa et al., Pharmacologic profiling reveals lapatinib as a novel antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2021.11.008
Rusnak, Lackey, Affleck, Wood, Alligood et al., The effects of the novel, reversible epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, GW2016, on the growth of human normal and tumor-derived cell lines in vitro and in vivo, Mol. Cancer Ther
Santaniello, Perruolo, Cristiano, Agognon, Cabaro et al., SARS-CoV-2 Affects Both Humans and Animals: What Is the Potential Transmission Risk? A Literature Review, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020514
Saul, Karim, Ghita, Huang, Chiu et al., Anticancer pan-ErbB inhibitors reduce inflammation and tissue injury and exert broad-spectrum antiviral effects, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI169510
Su, Xu, Jiang, Drug discovery and development targeting the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2, Fundam. Res, doi:10.1016/j.fmre.2021.01.013
Tomuleasa, Tigu, Munteanu, Moldovan, Kegyes et al., Therapeutic advances of targeting receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01899-w
Verma, Dileepan, Huang, Phan, Hu et al., Influenza A virus activates cellular Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) signaling to promote viral replication and lung inflammation, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1010874
Zabidi, Liew, Farouk, Puniyamurti, Yip et al., Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Implications on Immune Escape, Vaccination, Therapeutic and Diagnostic Strategies, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15040944
Zhou, Li, Zhang, Li, Sun et al., Identification of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor CP-724714 inhibits SADS-CoV related swine diarrhea coronaviruses infection in vitro, Virol. Sin, doi:10.1016/j.virs.2023.06.010
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens14040333",
"ISSN": [
"2076-0817"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040333",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Current antiviral treatments often target specific viral components, which can lead to the rapid emergence of drug-resistant mutants. Targeting host signaling pathways, including their associated cellular factors, that are important for virus replication is a novel approach toward the development of next-generation antivirals to overcome drug resistance. Various cellular receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) have previously been shown to play important roles in mediating viral replication including coronaviruses. In this study, we examined the roles of RTKs in SARS-CoV-2 replication in two cell lines, A549-ACE2 (human lung epithelial cells) and Vero-E6 (African Green Monkey kidney cell), via chemical inhibitors. We showed that the HER2 inhibitor Lapatinib significantly reduced viral replication in both cell lines, the TrkA inhibitor GW441756 was effective only in A549-ACE2 cells, while the EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib had little effect in either cell line. Lapatinib and GW441756 exhibited a high therapeutic index (CC50/EC50 > 10) in A549-ACE2 cells. Time-of-addition experiments indicated that Lapatinib may inhibit the early entry step, whereas GW441756 can affect post-entry steps of the viral life cycle. These findings suggest the important roles of HER2 and TrkA signaling in SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung epithelial cells and support further investigation of RTK inhibitors as potential COVID-19 treatments.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"pathogens14040333"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"family": "Sanchez",
"given": "Shania",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"family": "Flannery",
"given": "Brigitte H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5958-8345",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Qinfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8271-2033",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ly",
"given": "Hinh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6002-6868",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Yuying",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pathogens",
"container-title-short": "Pathogens",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T09:10:07Z",
"timestamp": 1743412207000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T12:22:45Z",
"timestamp": 1743423765000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T12:40:03Z",
"timestamp": 1743424803358,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743379200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/4/333/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "333",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11020514",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Santaniello, A., Perruolo, G., Cristiano, S., Agognon, A.L., Cabaro, S., Amato, A., Dipineto, L., Borrelli, L., Formisano, P., and Fioretti, A. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 Affects Both Humans and Animals: What Is the Potential Transmission Risk? A Literature Review. Microorganisms, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41431-023-01462-1",
"article-title": "A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 2: Host extracellular to systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Narayanan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Hum. Genet.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis",
"author": "Lamers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15040944",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Zabidi, N.Z., Liew, H.L., Farouk, I.A., Puniyamurti, A., Yip, A.J.W., Wijesinghe, V.N., Low, Z.Y., Tang, J.W., Chow, V.T.K., and Lal, S.K. (2023). Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Implications on Immune Escape, Vaccination, Therapeutic and Diagnostic Strategies. Viruses, 15."
},
{
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (2025, February 21). Coronavirus (COVID-19)|Drugs, Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs."
},
{
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "CDC (2025, February 28). “Types of COVID-19 Treatment”, COVID-19, Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/covid/treatment/index.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-023-05881-9",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir: An antiviral drug against COVID-19",
"author": "Dave",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Arch. Virol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00168-19",
"article-title": "Host-Directed Antiviral Therapy",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00168-19",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-024-01899-w",
"article-title": "Therapeutic advances of targeting receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer",
"author": "Tomuleasa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21505594.2023.2223057",
"article-title": "Pathogenicity and virulence of influenza",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2223057",
"journal-title": "Virulence",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22094830",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Purcaru, O.-S., Artene, S.-A., Barcan, E., Silosi, C.A., Stanciu, I., Danoiu, S., Tudorache, S., Tataranu, L.G., and Dricu, A. (2021). The Interference between SARS-CoV-2 and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Signaling in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2018.05.009",
"article-title": "Epidermal growth factor receptor is a co-factor for transmissible gastroenteritis virus entry",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "521",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03659-14",
"article-title": "Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis",
"author": "Kindrachuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "The effects of the novel, reversible epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, GW2016, on the growth of human normal and tumor-derived cell lines in vitro and in vivo",
"author": "Rusnak",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cancer Ther.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.290.16.2149",
"article-title": "Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized trial",
"author": "Kris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2149",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt1358",
"article-title": "A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity",
"author": "Karaman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127",
"journal-title": "Nat. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01969-10",
"article-title": "Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors block multiple steps of influenza a virus replication",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2818",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2021.11.008",
"article-title": "Pharmacologic profiling reveals lapatinib as a novel antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Raymonda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "60",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "566",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI169510",
"article-title": "Anticancer pan-ErbB inhibitors reduce inflammation and tissue injury and exert broad-spectrum antiviral effects",
"author": "Saul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e169510",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fmre.2021.01.013",
"article-title": "Drug discovery and development targeting the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Fundam. Res.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00432-z",
"article-title": "Structures and functions of coronavirus replication–transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design",
"author": "Malone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010874",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Verma, V., Dileepan, M., Huang, Q., Phan, T., Hu, W.-S., Ly, H., and Liang, Y. (2022). Influenza A virus activates cellular Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) signaling to promote viral replication and lung inflammation. PLoS Pathog., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virs.2023.06.010",
"article-title": "Identification of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor CP-724714 inhibits SADS-CoV related swine diarrhea coronaviruses infection in vitro",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "778",
"journal-title": "Virol. Sin.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008900",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Kuroda, M., Halfmann, P., and Kawaoka, Y. (2020). HER2-mediated enhancement of Ebola virus entry. PLoS Pathog., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00531.2020",
"article-title": "RSV infection potentiates TRPV1-mediated calcium transport in bronchial epithelium of asthmatic children",
"author": "Harford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L1074",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "320",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/4/333"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Cellular Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Plays Important Roles in SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}