Effect of Montelukast on Treatment of Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19): A Systematic Review
et al., Biomedical Research Bulletin, doi:10.34172/biomedrb.2023.06, Mar 2023
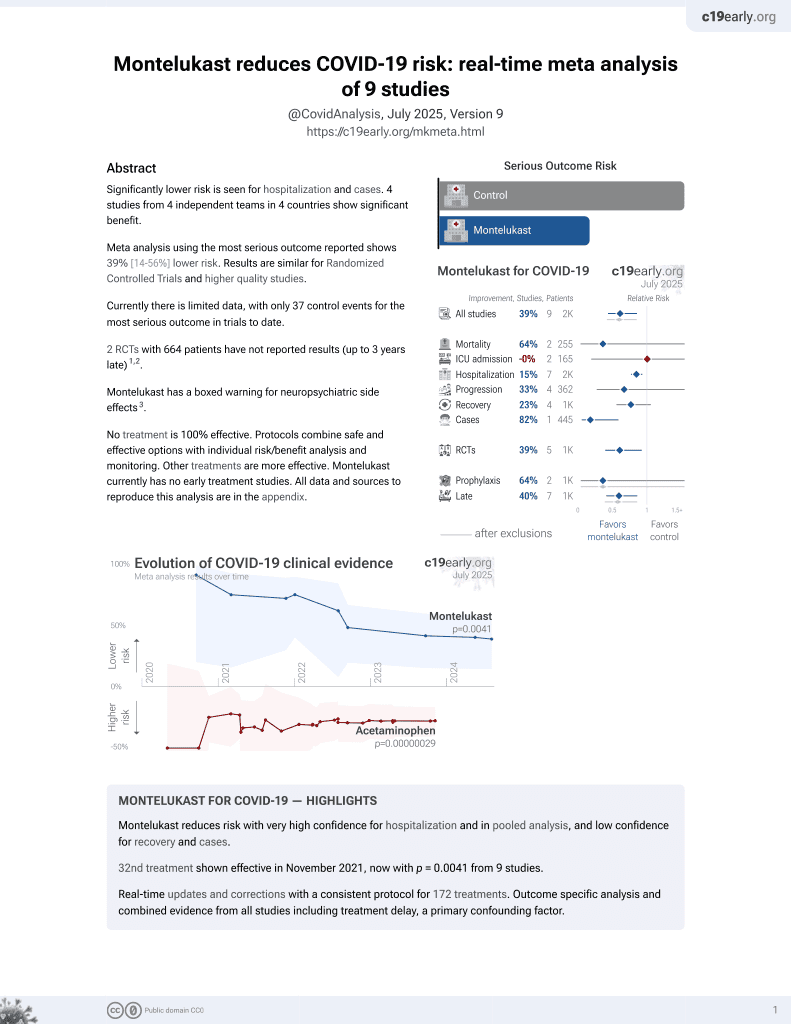
33rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.0041 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for hospitalization and cases.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
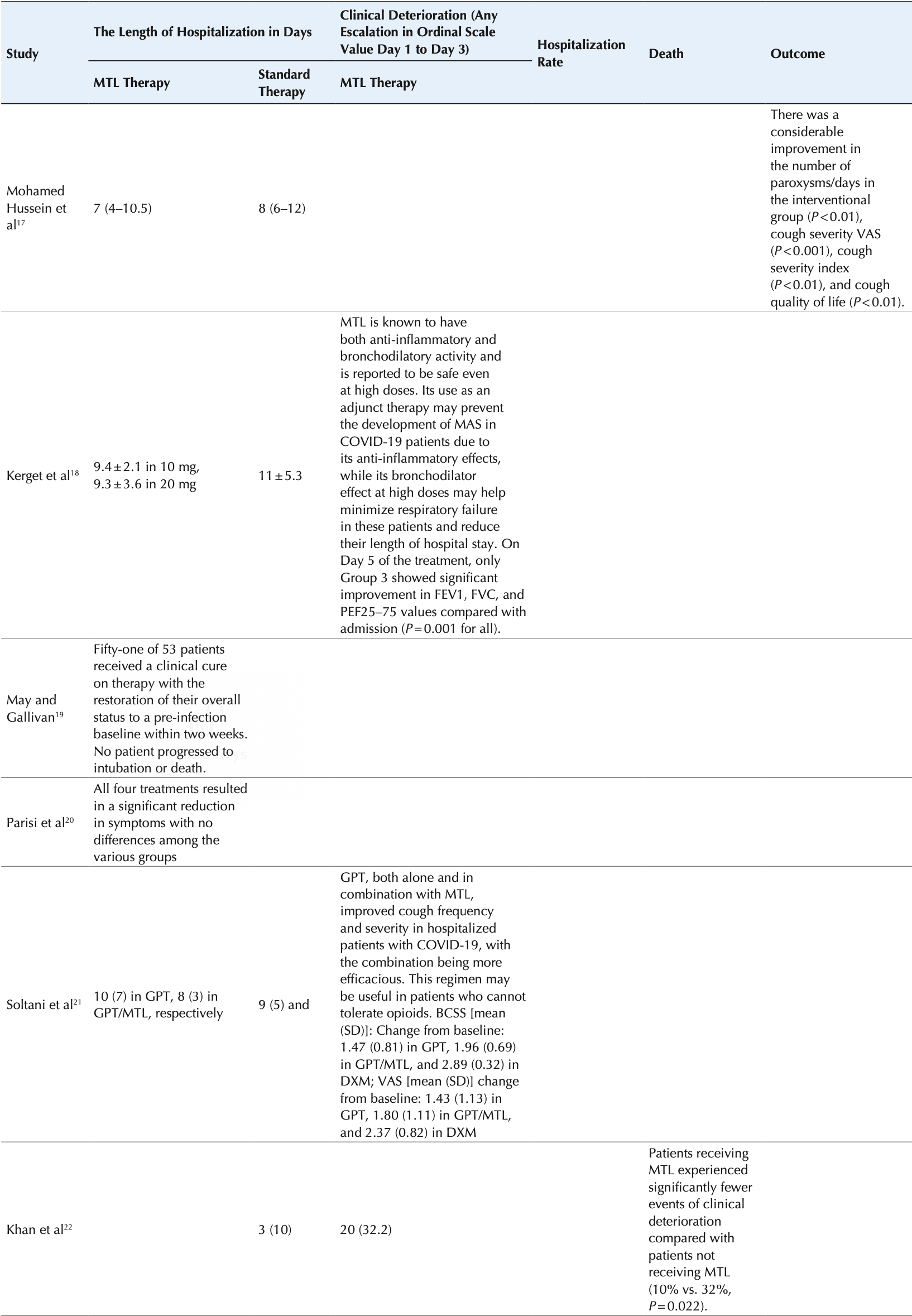
Systematic review of 8 studies showing improved symptoms, clinical deterioration, hospitalization length, and mortality with montelukast treatment for COVID-19 patients.
Currently there are 9 montelukast studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 64% lower [-249‑96%] |
| ICU admission | 0% higher [-81‑421%] |
| Hospitalization | 15% lower [7‑23%] |
| Cases | 82% fewer [41‑94%] |
Salehi-Pourmehr et al., 30 Mar 2023, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Effect of Montelukast on Treatment of Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19): A Systematic Review
Biomedical Research Bulletin, doi:10.34172/biomedrb.2023.06
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) exhibits the most important global public health emergency. Montelukast (MTL), a prototype cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, is commonly considered in the therapy of exercise-and aspirin-induced asthma. The purpose of this study was to present a systematic review of the literature on the effectiveness of MTL against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and exuberant immune activation in COVID-19 disease. Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from the database on August 15, 2021and updated on November 19, 2022. Two reviewers independently screened articles, appraised methodological quality, and extracted the data. Results: A total of 118 related reports were recognized after eliminating duplicates. Of these, 30 references were screened based on titles and abstracts. After removing unrelated studies, 20 studies were included in the full-text review and evaluated for appropriateness. Finally, eight studies fitting the inclusion criteria for data extraction were selected. One of them was a prospective, randomized, controlled, and single-blinded study, three were open-label randomized or non-randomized controlled clinical trials, two were retrospective studies, and two were case series or comparative studies. A total of 1083 patients infected with COVID-19 infection (999 adults and 84 children) were examined on the effectiveness of MTL on symptom severity as well as hospitalization length. The results of the mentioned studies showed a low risk of clinical deterioration in the MTL group. In addition, the length of hospital stay was low in the treatment group compared to the standard management. Conclusion: MTL as a potential adjuvant therapy in COVID-19 may improve lung injury, inflammation, and symptoms. Moreover, the use of MTL could decrease the severity and mortality of COVID-19. Additional well-designed randomized controlled trials are necessary to approve the role of MTL in SARS-CoV-2 prevention or COVID-19 symptoms improvement.
Competing Interests There is no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval Not applicable.
Supplementary Files Supplementary file 1 depicts search strategy methods in PubMed and Cochrane databases.
References
Aigner, Pietrantonio, De Sousa, Michael, Schuster et al., The leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast as a potential COVID-19 therapeutic, Front Mol Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.610132
Almerie, Kerrigan, The association between obesity and poor outcome after COVID-19 indicates a potential therapeutic role for montelukast, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109883
Barré, Sabatier, Annweiler, Montelukast drug may improve COVID-19 prognosis: a review of evidence, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01344
Bourgonje, Abdulle, Timens, Hillebrands, Navis et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.5471
Bozek, Winterstein, Montelukast's ability to fight COVID-19 infection, J Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2020.1786112
Cardani, Boulton, Kim, Braciale, Alveolar macrophages prevent lethal influenza pneumonia by inhibiting infection of type-1 alveolar epithelial cells, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006140
Chen, Li, Wang, Zou, Montelukast, an antiasthmatic drug, inhibits Zika virus infection by disrupting viral integrity, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.03079
Cingi, Muluk, Ipci, Şahin, Antileukotrienes in upper airway inflammatory diseases, Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, doi:10.1007/s11882-015-0564-7
Funk, Ardakani, A novel strategy to mitigate the hyperinflammatory response to COVID-19 by targeting leukotrienes, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01214
Hallstrand, Henderson, An update on the role of leukotrienes in asthma, Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1097/ACI.0b013e32833489c3
Hm, Gareeb, Almulaiky, Cruz-Martins, Batiha, Role of leukotriene pathway and montelukast in pulmonary and extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: the enigmatic entity, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174196
Hussein, Ibrahim, Makhlouf, Makhlouf, Abd-Elaal et al., Value of montelukast as a potential treatment of post-COVID-19 persistent cough: a non-randomized controlled pilot study, Egypt J Bronchol
Jiang, Deng, Zhang, Cai, Cheung et al., Review of the clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J Gen Intern Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-020-05762-w
Kerget, Kerget, Aydın, Karaşahin, Effect of montelukast therapy on clinical course, pulmonary function, and mortality in patients with COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27552
Khan, Misdary, Yegya-Raman, Kim, Narayanan et al., Montelukast in hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19, J Asthma, doi:10.1080/02770903.2021.1881967
Kim, Outbreak of novel coronavirus (COVID-19): what is the role of radiologists?, Eur Radiol, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-06748-2
Lima-Morales, Méndez-Hernández, Flores, Osorno-Romero, Hernández et al., Effectiveness of a multidrug therapy consisting of Ivermectin, Azithromycin, Montelukast, and Acetylsalicylic acid to prevent hospitalization and death among ambulatory COVID-19 cases in Tlaxcala, Mexico, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.014
Lin, Huang, Lee, Hsieh, Kuo et al., Effects of montelukast on M2-related cytokine and chemokine in M2 macrophages, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2016.04.005
May, Gallivan, Levocetirizine and montelukast in the COVID-19 treatment paradigm, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108412
Mostafaei, Ghojazadeh, Hajebrahimi, Abolhasanpour, Salehi-Pourmehr, Clinical presentation of Iranian patients affected with COVID-19: a thousand faces disease, Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol
Mostafaei, Hajebrahimi, Sadeghi-Ghyassi, Mostafaei, Abolhasanpour et al., Can wearing a face mask protect from COVID-19? A systematic review, Iran J Med Microbiol, doi:10.30699/ijmm.14.2.101
Norouzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) cases by the oral administration of montelukast tablets, Rev Bionatura, doi:10.21931/rb/2020.05.04.5
Okunishi, Peters-Golden, Leukotrienes and airway inflammation, Biochim Biophys Acta, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.02.005
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, Int J Surg, doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
Parisi, Manti, Papale, Giallongo, Indolfi et al., Addition of a nutraceutical to montelukast or inhaled steroid in the treatment of wheezing during COVID-19 pandemic: a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial, Acta Biomed, doi:10.23750/abm.v93i2.11958
Shahsavarinia, Faridaalaee, Soleimanpour, Sadeghi-Ghyassi, Atashgahi et al., Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) Following COVID-19 vaccination: an umbrella review of systematic reviews, Iran J Med Microbiol
Soltani, Nasirharandi, Khorvash, Nasirian, Dolatshahi et al., The effectiveness of gabapentin and gabapentin/montelukast combination compared with dextromethorphan in the improvement of COVID-19-related cough: a randomized, controlled clinical trial, Clin Respir J, doi:10.1111/crj.13529
Tavares, Farraia, Silva, Ribeiro, Severo et al., Impact of montelukast as add on treatment to the novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19): protocol for an investigator-initiated open labeled randomized controlled pragmatic trial, Porto Biomed J, doi:10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000134
Vaninov, In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0305-6
Wu, Hao, Lau, Wong, Leung et al., Real-time tentative assessment of the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus infections in Wuhan, China, as at 22 January 2020, Euro Surveill, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.es.2020.25.3.2000044
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30076-x
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.34172/biomedrb.2023.06",
"ISSN": [
"2980-9924"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/biomedrb.2023.06",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) exhibits the most important global public health emergency. Montelukast (MTL), a prototype cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, is commonly considered in the therapy of exercise- and aspirin-induced asthma. The purpose of this study was to present a systematic review of the literature on the effectiveness of MTL against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) and exuberant immune activation in COVID‐19 disease. Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from the database on August 15, 2021and updated on November 19, 2022. Two reviewers independently screened articles, appraised methodological quality, and extracted the data. Results: A total of 118 related reports were recognized after eliminating duplicates. Of these, 30 references were screened based on titles and abstracts. After removing unrelated studies, 20 studies were included in the full-text review and evaluated for appropriateness. Finally, eight studies fitting the inclusion criteria for data extraction were selected. One of them was a prospective, randomized, controlled, and single-blinded study, three were open-label randomized or non-randomized controlled clinical trials, two were retrospective studies, and two were case series or comparative studies. A total of 1083 patients infected with COVID-19 infection (999 adults and 84 children) were examined on the effectiveness of MTL on symptom severity as well as hospitalization length. The results of the mentioned studies showed a low risk of clinical deterioration in the MTL group. In addition, the length of hospital stay was low in the treatment group compared to the standard management. Conclusion: MTL as a potential adjuvant therapy in COVID-19 may improve lung injury, inflammation, and symptoms. Moreover, the use of MTL could decrease the severity and mortality of COVID-19. Additional well-designed randomized controlled trials are necessary to approve the role of MTL in SARS-CoV-2 prevention or COVID-19 symptoms improvement. </jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-12-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-01-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-03-30"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9030-2106",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Centre: A Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Center of Excellence, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Salehi-Pourmehr",
"given": "Hanieh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Research Center, Aging Research Institute, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Dolati",
"given": "Sanam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Centre: A Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Center of Excellence, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mehdipour",
"given": "Robab",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Memar",
"given": "Afra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghafourian",
"given": "Farnaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Centre: A Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Center of Excellence, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Shakiba",
"given": "Avin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2606-5772",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Centre: A Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Center of Excellence, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Abolhasanpour",
"given": "Nasrin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedical Research Bulletin",
"container-title-short": "Biomed Res Bull",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"biomedrb.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-08T08:39:22Z",
"timestamp": 1691483962000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-08T08:39:22Z",
"timestamp": 1691483962000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-09T04:28:57Z",
"timestamp": 1691555337423
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://biomedrb.com/PDF/brb-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://biomedrb.com/PDF/brb-9.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "20123",
"original-title": [],
"page": "19-29",
"prefix": "10.34172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Maad Rayan Publishing Company",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://biomedrb.com/Article/brb-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Montelukast on Treatment of Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19): A Systematic Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "1"
}