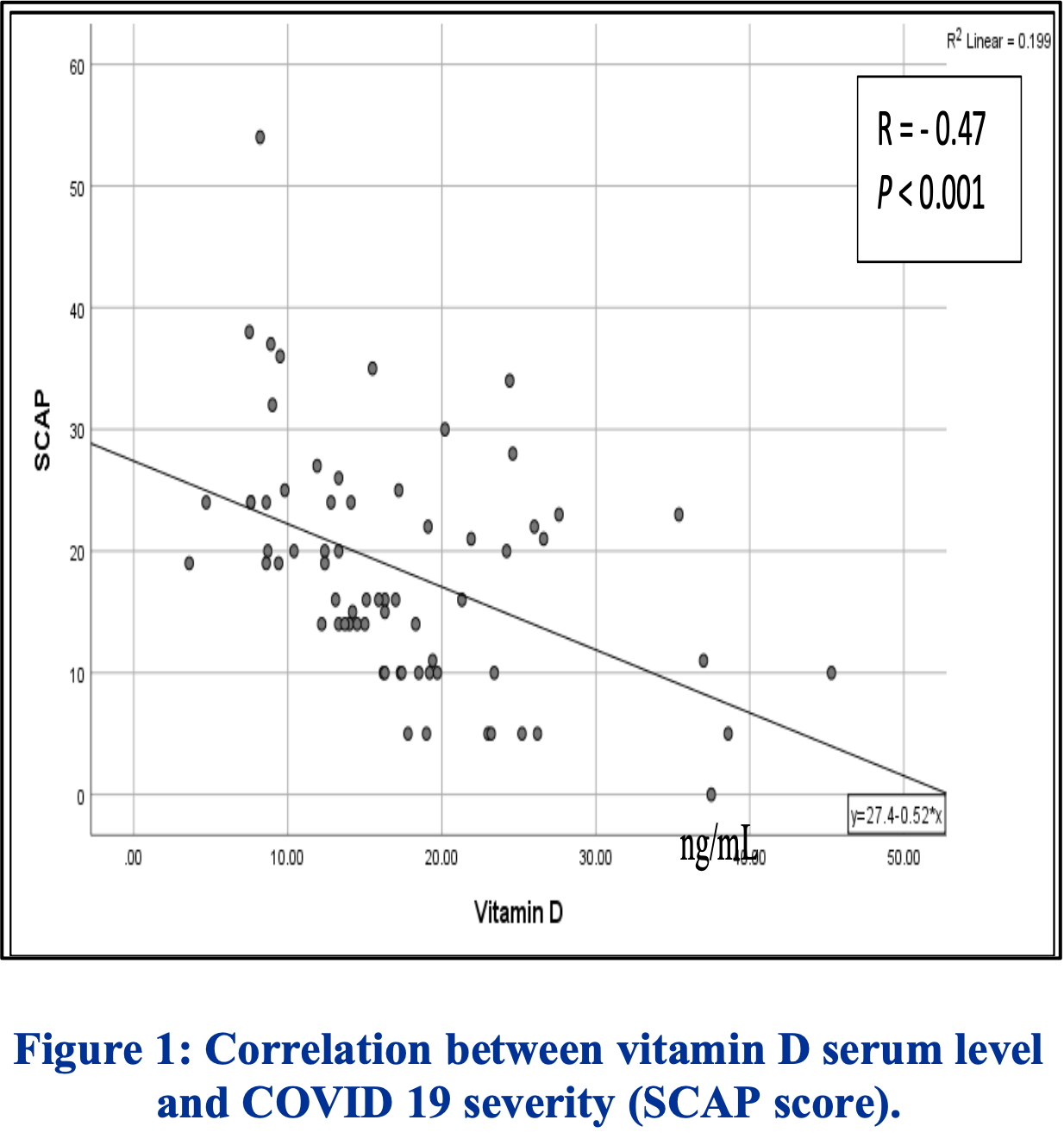
Correlations between level of vitamin D serum and disease severity COVID-19
et al., International Journal of Advances in Medicine, doi:10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20242306, Aug 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 68 COVID-19 patients in Indonesia showing higher vitamin D levels associated with lower COVID-19 severity.
Sajinadiyasa et al., 27 Aug 2024, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, median age 64.0, 3 authors, study period February 2022 - June 2022.
Contact: sajinadiyasa@unud.ac.id.
Correlations between level of vitamin D serum and disease severity COVID-19
International Journal of Advances in Medicine, doi:10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20242306
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19 ) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The virus spread from Wuhan, Hubei province, China to all over the world in December 2019. On march 2020 WHO reported spread to 114 countries with 4291 death cases. 1 The pathological process that occurs in COVID-19 includes a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic, mild symptoms (flu like symptoms), moderate symptoms and severe symptoms. Patients with COVID-19 often require treatment in an intensive room. The severity of COVID-19 symptom affected by the inflammation process and cytokine storm. 2 Vitamin D well known function to help regulate serum calcium concentrations, also play importance role in inflammation process. Vitamin D enhances cellular innate immunity partly through the induction of antimicrobial peptides, including human cathelicidin, LL-37. Vitamin D also enhances cellular immunity by reducing the cytokine storm induced by the innate immune system. There for, we need to conduct study to know about the correlation between level of vitamin D serum and COVID-19 severity. 3 METHODS This study aims to find out correlation between level of vitamin D serum and COVID-19 severity. Cross sectional study was observed 68 COVID-19 patients in Prof. Dr. I. G. N. G Ngoerah Denpasar hospital in 2022. Sample chose with consecutive sampling from February 2022 until June 2022. The inclusion criteria were COVID-19 patients who confirm using RT-PCR, with age range 18 years old until 80 years old. COVID-19 patient who have been treated or ABSTRACT Background: Corona virus disease (COVID-19) Was a respiratory disease. Severity of the disease was related to inflammation process. SCAP scoring system can be used to asses COVID-19 severity. Asses the severity of the disease is an important thing to determine the management. Vitamin D is shown to have anti-inflammatory effect. Vitamin D can downregulate cytokines storm and also induce innate immune activity. Here we want to know about the correlation between level of vitamin D and disease severity of COVID-19. Methods: Cross sectional study was observed 68 patient COVID-19 in Prof. Dr. I. G. N. G Ngoerah Denpasar hospital. They were asses with SCAP scoring system dan measured their vitamin D level at the same time. The correlation between two variable was analyze by Spearman correlation. Results: Among those 68 Sample, the median age of the sample is 64 years old, and 52.9 % of them are male. There is correlation between level of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19, the coefficient correlation was -0.47 with p<0.001. Conclusions: There is correlation between level of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee
References
Abate, Kassie, Kassaw, Aragie, Masresha, Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Open
Diaz, Appiah, Askie, Baller, Banerjee et al., COVID-19 clinical management: living guidance, World Health Organization
Dror, Morozov, Daoud, Namir, Yakir et al., Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness, PLoS One
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Jude, Ling, Allcock, Yeap, Pappachan, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher hospitalization risk from COVID-19: a retrospective case-control study, J Clin Endocrinol Metabol
Mubina, Wahyuni, Pengaruh Vitamin D terhadap Keparahan dan Mortalitas COVID-19, Med Profession J Lampung
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and Covid-19: an update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin Molecul Aller
Statsenko, Zahmi, Habuza, Almansoori, Smetanina et al., Impact of age and sex on COVID-19 severity assessed from radiologic and clinical findings, Front Cellular Infect Microbiol
Taboada, Rodríguez, Riveiro, Abelleira, Ricoy et al., Short-term outcomes of 50 patients with acute respiratory distress by COVID-19
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20242306",
"ISSN": [
"2349-3933",
"2349-3925"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20242306",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Corona virus disease (COVID-19) Was a respiratory disease. Severity of the disease was related to inflammation process. SCAP scoring system can be used to asses COVID-19 severity. Asses the severity of the disease is an important thing to determine the management. Vitamin D is shown to have anti-inflammatory effect. Vitamin D can downregulate cytokines storm and also induce innate immune activity. Here we want to know about the correlation between level of vitamin D and disease severity of COVID-19.\nMethods: Cross sectional study was observed 68 patient COVID-19 in Prof. Dr. I. G. N. G Ngoerah Denpasar hospital. They were asses with SCAP scoring system dan measured their vitamin D level at the same time. The correlation between two variable was analyze by Spearman correlation.\nResults: Among those 68 Sample, the median age of the sample is 64 years old, and 52.9 % of them are male. There is correlation between level of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19, the coefficient correlation was -0.47 with p<0.001.\nConclusions: There is correlation between level of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sajinadiyasa",
"given": "I. Gede Ketut",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suega",
"given": "Ketut",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andari K.",
"given": "Nova",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Advances in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Int J Adv Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-27T16:06:32Z",
"timestamp": 1724774792000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-27T16:07:11Z",
"timestamp": 1724774831000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-28T00:25:25Z",
"timestamp": 1724804725066
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.ijmedicine.com/index.php/ijam/article/download/4078/2731",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.ijmedicine.com/index.php/ijam/article/download/4078/2731",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "7570",
"original-title": [],
"page": "445-448",
"prefix": "10.18203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Medip Academy",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ijmedicine.com/index.php/ijam/article/view/4078"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Correlations between level of vitamin D serum and disease severity COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}
