Real-World Effectiveness of Bebtelovimab Versus Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Outpatients with COVID-19
et al., Pulmonary Therapy, doi:10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w, Dec 2024
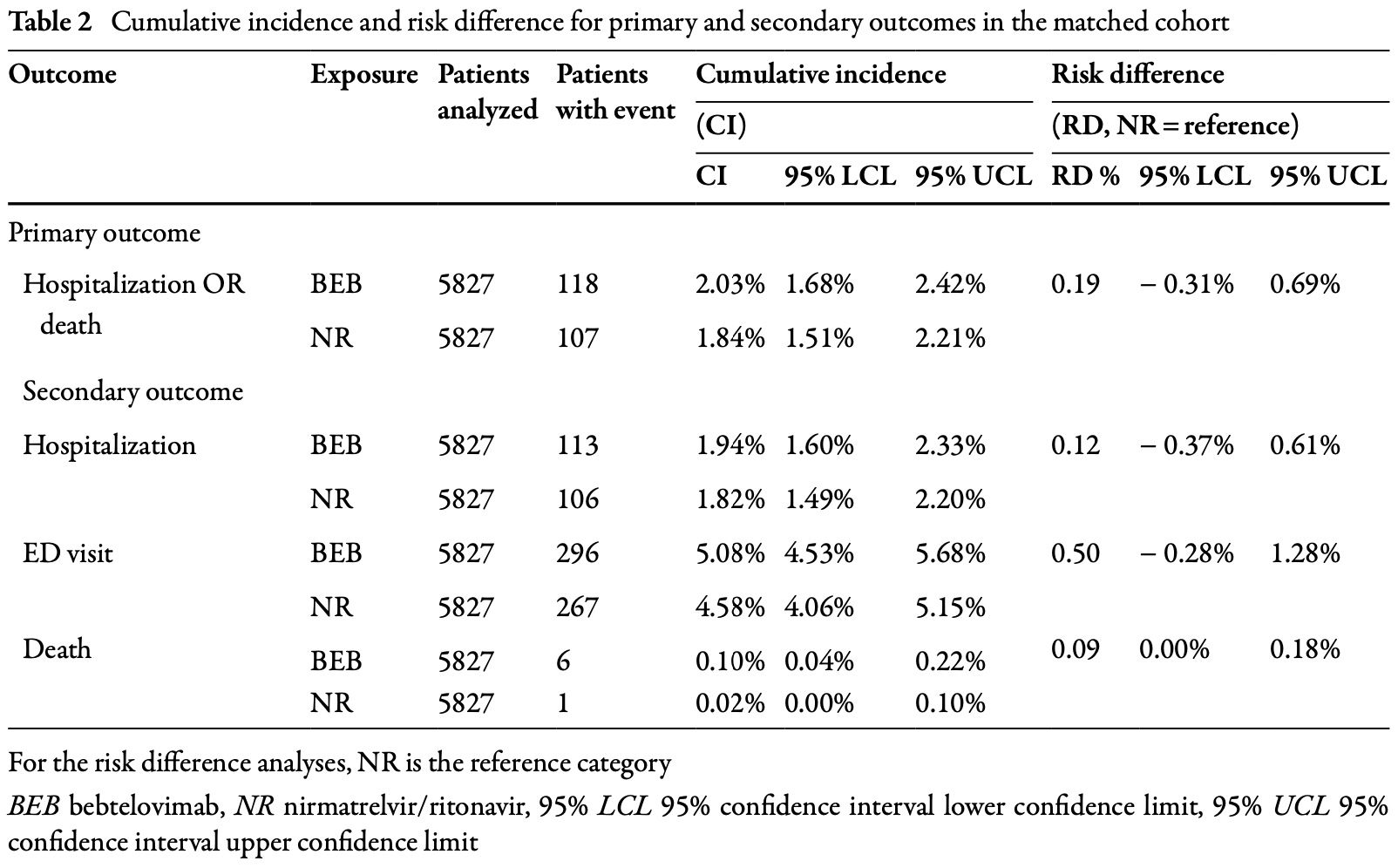
Retrospective 5,827 matched pairs of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences between bebtelovimab and paxlovid treatment. Authors do not exclude patients with contraindications for paxlovid.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.9.13.
Study covers bebtelovimab and paxlovid.
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
Rowan et al., 25 Dec 2024, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 16 February, 2022 - 31 August, 2022.
Contact: rnichols@lilly.com.
Real-World Effectiveness of Bebtelovimab Versus Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Outpatients with COVID-19
Pulmonary Therapy, doi:10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w
for 30 days. Cohorts were constructed using deidentified electronic health record data from Tri-NetX Dataworks USA. The study assessed 30-day all-cause hospitalization or death (composite) using the risk difference (RD) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI). Results: Unmatched cohorts included 12,920 BEB-and 70,741 NR-treated patients. After exact matching on key baseline covariates (age > 65 years, immunocompromised, recent emergency department [ED] visit, and COVID-19 vaccination) and high-dimensional propensity score matching (1:1) on a broader set of covariates, 5827 patients were included in each cohort. BEB-treated patients were older and had more comorbidities compared to NRtreated patients prior to matching. After matching, baseline characteristics were well balanced. The cumulative incidence of the primary outcome (hospitalization or death) was 2.0% and 1.8% for BEB and NR, respectively (RD 0.2%; 95% CI -0.3%, 0.7%). The upper bound of the RD 95% CI (0.7%) excluded the noninferiority margin (1.795%), demonstrating that BEB was not inferior to NR. The RDs of the secondary outcomes were (BEB vs NR): hospitalization (RD 0.1%; 95% CI -0.4%, 0.6%); ED visit (RD 0.5%; 95% CI -0.3%, 1.3%); and death (RD 0.09%; 95% CI -0.003%, 0.2%). Results from subgroup, sensitivity, and linked analyses (EHR + claims + mortality data) were consistent with the main results.
References
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Liu, Huang, Wu, Clinical effectiveness of nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir in patients with COVID-19 and substance use disorders based on real-world data, J Med Virol
Mccreary, Kip, Collins, Evaluation of bebtelovimab for treatment of COVID-19 during the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant era, Open Forum Infect Dis
Razonable, Horo, Hanson, Comparable outcomes for bebtelovimab and ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir treatment in high-risk patients with coronavirus disease-2019 during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 BA.2 omicron epoch, J Infect Dis
Schneeweiss, Rassen, Glynn, Highdimensional propensity score adjustment in studies of treatment effects using health care claims data, Epidemiology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w",
"ISSN": [
"2364-1754",
"2364-1746"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w",
"alternative-id": [
"284"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "17 October 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "6 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "25 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of Interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Russell M. Nichols, Jennifer M. Alyea, Baojin Zhu, and Elsie L. Grace are employees and stockholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Neil Dhopeshwarkar and Kinwei Arnold Chan are employees and stockholders of TriNetX, LLC, Cambridge, MA, USA. Christopher G. Rowan served as a consultant for TriNetX, LLC. Sengwee Toh serves as a methods consultant for TriNetX, LLC for this work and unrelated work for Pfizer, Inc, manufacturer of NR."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical Approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "No ethics committee was consulted for this study, as it is not considered human subjects research. Exemption from an ethics committee is not required by law or TriNetX policies because the data are fully de-identified per the de-identification standard defined in Sect. 164.514(a) of the HIPAA Privacy Rule and as assessed through formal determination by a qualified expert as defined in Sect. 164.514(b)(1) of the HIPAA Privacy Rule. Additionally, this retrospective study is exempt from informed consent."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "Christopher G.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7771-7366",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nichols",
"given": "Russell M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhopeshwarkar",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alyea",
"given": "Jennifer M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Baojin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toh",
"given": "Sengwee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "K. Arnold",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grace",
"given": "Elsie L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pulmonary Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Pulm Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-25T16:03:38Z",
"timestamp": 1735142618000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-25T17:03:57Z",
"timestamp": 1735146237000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004312",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100004312",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-25T17:40:17Z",
"timestamp": 1735148417332,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735084800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735084800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "284_CR1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) Global research and innovation forum. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-(pheic)-global-research-and-innovation-forum#:~:text=On%2030%20January%202020%20following,of%20International%20Concern%20(PHEIC). Accessed 13 Dec 2023."
},
{
"key": "284_CR2",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program (CTAP). 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs/coronavirus-treatment-acceleration-program-ctap. Accessed 12 Feb 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR3",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization 090. 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/143602/download. Accessed 15 Jan 2023."
},
{
"key": "284_CR4",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization 094. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/145801/download. Accessed 16 Jan 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR5",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization 091. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/145610/download. Accessed 12 Jan 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR6",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization 100. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/149532/download. Accessed 15 Jan 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR7",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA revises letter of authorization for the emergency use authorization for Paxlovid. 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-revises-letter-authorization-emergency-use-authorization-paxlovid. Accessed 12 Jun 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR8",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Bebtelovimab (LY-CoV1404). 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/156396/download. Accessed 16 Jan 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR9",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Emergency Use Authorization 090. 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/147629/download. Accessed 15 Jan 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR10",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug administration (FDA). Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization for Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/145808/download. Accessed 12 Feb 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR11",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug administration (FDA). Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization of REGEN-COV (Casirivimab and Imdevimab). 2022. Available https://www.fda.gov/media/143894/download. Accessed 12 Feb 2024."
},
{
"key": "284_CR12",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA updates Sotrovimab emergency use authorization. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-updates-sotrovimab-emergency-use-authorization#:~:text=%5B2%2F25%2F2022%5D,not%20susceptible%20to%20this%20treatment. Accessed 15 Jan 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac517",
"author": "EK McCreary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofac517",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "284_CR13",
"unstructured": "McCreary EK, Kip KE, Collins K, et al. Evaluation of bebtelovimab for treatment of COVID-19 during the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant era. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022;9(10):ofac517.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac346",
"author": "RR Razonable",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1683",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "284_CR14",
"unstructured": "Razonable RR, O’Horo JC, Hanson SN, et al. Comparable outcomes for bebtelovimab and ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir treatment in high-risk patients with coronavirus disease-2019 during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 BA.2 omicron epoch. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(10):1683–7.",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "284_CR15",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Announces Bebtelovimab is Not Currently Authorized in Any US Region. 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-announces-bebtelovimab-not-currently-authorized-any-us-region. Accessed 6 Jun 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a663cc",
"author": "S Schneeweiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology",
"key": "284_CR16",
"unstructured": "Schneeweiss S, Rassen JA, Glynn RJ, et al. High-dimensional propensity score adjustment in studies of treatment effects using health care claims data. Epidemiology. 2009;20(4):512–22.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"key": "284_CR17",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Non-Inferiority Clinical Trials to Establish Effectiveness. Guidance for Industry. 2016. https://www.fda.gov/media/78504/download. Accessed 16 Jan 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "284_CR18",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28801",
"author": "TH Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "284_CR19",
"unstructured": "Liu TH, Huang PY, Wu JY, et al. Clinical effectiveness of nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir in patients with COVID-19 and substance use disorders based on real-world data. J Med Virol. 2023;95(5):e28801.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s41030-024-00284-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Real-World Effectiveness of Bebtelovimab Versus Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in Outpatients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}