Adequate serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels are correlated with low anti-PF4 levels in mild COVID-19 Patients: An observational study
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000039252, Sep 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 160 COVID-19 patients in Indonesia showing a significant negative correlation between vitamin D levels and anti-PF4 antibodies in mild COVID-19 patients. Severe COVID-19 patients were more likely to have vitamin D deficiency (not statistically significant). Authors hypothesize that vitamin D deficiency may affect endothelial function and elevate inflammatory response, promoting coagulation.
This is the 204th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of severe case, 51.5% lower, RR 0.48, p = 0.37, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 2 of 28 (7.1%), low D levels (<20ng/mL) 19 of 129 (14.7%), NNT 13.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rachman et al., 13 Sep 2024, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, mean age 42.8, 5 authors, study period October 2021 - January 2022.
Contact: andhikarachman@gmail.com.
Adequate serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels are correlated with low anti-PF4 levels in mild COVID-19 Patients: An observational study
Medicine, doi:10.1097/md.0000000000039252
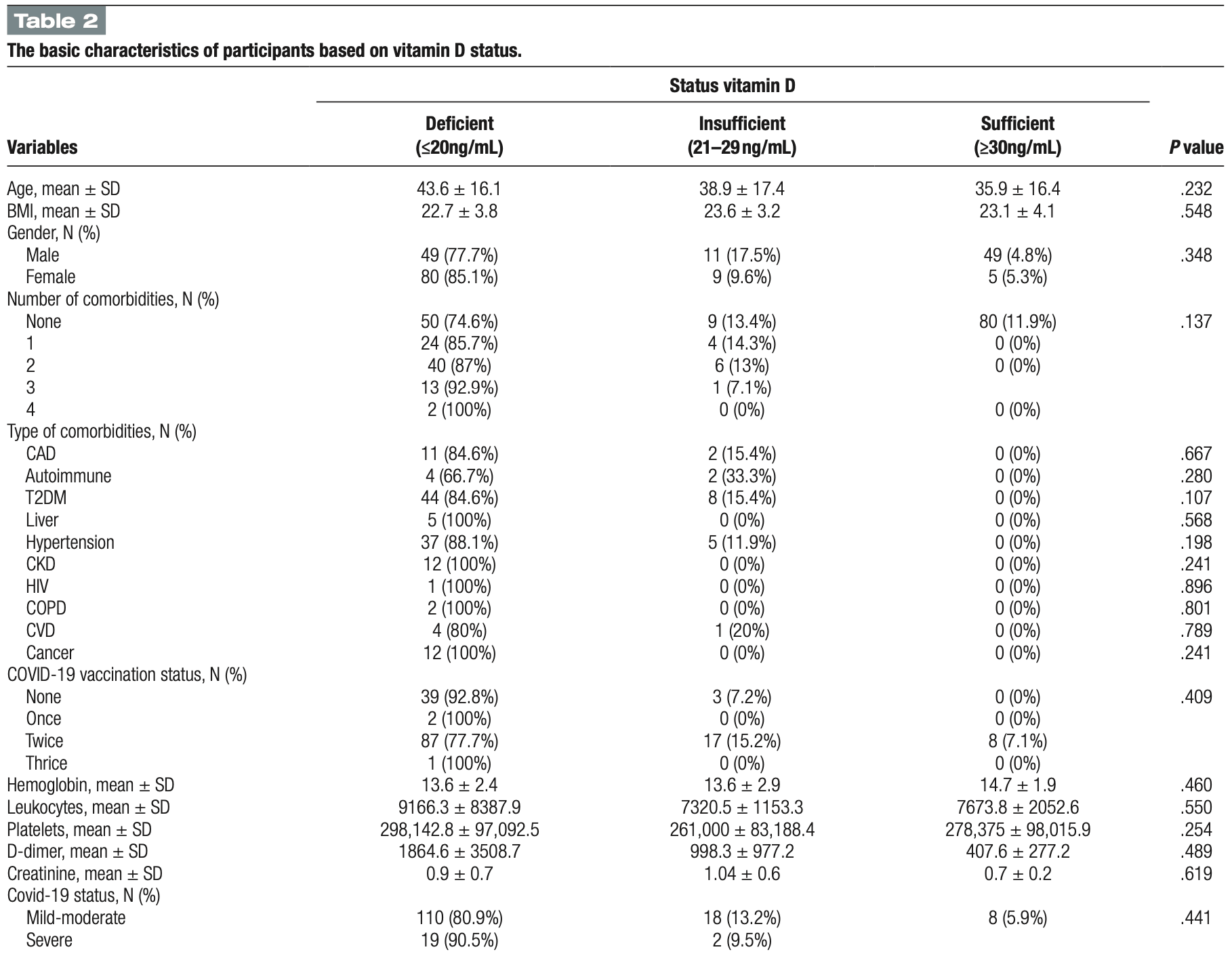
The worldwide spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has resulted in an unparalleled health emergency of global proportions. Around 31% of individuals with COVID-19 experience thrombosis associated with hypercoagulation. COVID-19 patients have shown an increase in platelet activation, but the mechanism has not been fully understood yet. One theory suggests that this could be related to the heparin-induced thrombocytopenia phenomenon, where platelet activation involves anti-PF4 antibodies that are associated with thrombosis. Vitamin D has been established to exert an influence on immunological responses and inflammation. The aim of this study is to analyze the correlation between serum 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol [25(OH)D] levels and anti-PF4 antibodies among COVID-19 patients. A cross-sectional study was conducted among 160 COVID-19 patients at Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital and Wisma Atlit Hospital Jakarta from October 2021 to January 2022. The mean serum 25(OH)D level was 15.1 ng/mL. A significant negative correlation was found between serum 25(OH)D and anti-PF4 levels in mild COVID-19 patients (P = .035; R = -0.236). Remarkably, P-selectin levels were significantly higher in the moderate COVID-19 group compared to the severe group (P = .031). Serum 25(OH)D level had a significant negative correlation with anti-PF4 level in mild COVID-19 patients. Thus, it is highly recommended to ensure that serum 25(OH)D levels are maintained above 30 ng/mL. Remarkably, the P-selectin level was significantly higher in the moderate COVID-19 group compared to the severe group. Abbreviations: 25 (OH)D = 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol, anti-PF4 = antibodies targeting platelet-factor 4, BMI = body mass index, CAD = coronary artery disease, CHF = congestive heart failure, CKD = chronic kidney disease, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COVID-19 = Coronavirus disease 2019, CVD = cerebrovascular disease, DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation, DVT = deep vein thrombosis, ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, HIT = heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, HIV = human immunodeficiency virus, IFN-y = gamma interferon, PE = pulmonary embolism, RNA = ribonucleic acid, SIC = sepsis-induced coagulopathy, T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus, TF = tissue factor, TM = thrombomodulin, TNFα = tumor necrosis factor-alpha, VITT = vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia, WHO = World Health Organization.
References
Agrati, Sacchi, Tartaglia, The role of P-Selectin in COVID-19 coagulopathy: an updated review, Int J Mol Sci
Arepally, Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, Blood
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Burhan, Isbaniyah, Susanto, Aditama, Pneumonia COVID-19: Diagnosis Dan Penatalaksanaan Di Indonesia
Chao, Rebetz, Bläckberg, Distinct phenotypes of platelet, monocyte, and neutrophil activation occur during the acute and convalescent phase of COVID-19, Platelets
Fenyves, Mehta, Kays, MGH COVID-19 Collection & Processing Team. Plasma P-selectin is an early marker of thromboembolism in COVID-19, medRxiv
Godino, Scotti, Maugeri, Antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19? -rationale and evidence, Int J Cardiol
Greinacher, Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia, N Engl J Med
Greinacher, Thiele, Warkentin, Weisser, Kyrle et al., Thrombotic thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccination, N Engl J Med
Hejazi, Modarresi-Ghazani, Hamishehkar, Mesgari-Abbasi, Dousti et al., The effect of treatment of vitamin D deficiency on the level of P-Selectin and hs-CRP in patients with thromboembolism: a pilot randomized clinical trial, J Clin Pharmacol
Hottz, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Palhinha, Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19, Blood
Manne, Denorme, Middleton, Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19, Blood
Nazy, Jevtic, Moore, Platelet-activating immune complexes identified in critically ill COVID-19 patients Table 3 Levels of P-selectin and anti-PF4 variables based on COVID-19 status
Ohsawa, Koyama, Yamamoto, Hirosawa, Kamei et al., 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 and its potent synthetic analogs downregulate tissue factor and upregulate thrombomodulin expression in monocytic cells, counteracting the effects of tumor necrosis factor and oxidized LDL, Circulation
Rachman, Iriani, Priantono, Rumondor, Betsy et al., The correlation between serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels and anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG and neutralizing antibody levels among cancer patients receiving COVID-19 vaccines, Front Nutr
Rachman, Rahmaniyah, Khomeini, Iriani, Impact of vitamin D deficiency in relation to the clinical outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Res
Słomka, Kowalewski, Zekanowska, Hemostasis in Coronavirus disease 2019-lesson from viscoelastic methods: a systematic review, Thromb Haemost
Tao, Lou, Liu, The role of vitamin D in the relationship between gender and deep vein thrombosis among stroke patients, Front Nutr
Targher, Pichiri, Lippi, Vitamin D, thrombosis, and hemostasis: more than skin deep, Semin Thromb Hemost
Thachil, What do monitoring platelet counts in COVID-19 teach us?, J Thromb Haemost
Yang, Yang, Wang, Thrombocytopenia and its association with mortality in patients with COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Zaid, Puhm, Allaeys, Platelets can associate with SARS-CoV-2 RNA and are hyperactivated in COVID-19, Circ Res
Zhang, Shen, Le, Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Cardiovasc Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000039252",
"ISSN": [
"0025-7974",
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000039252",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The worldwide spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has resulted in an unparalleled health emergency of global proportions. Around 31% of individuals with COVID-19 experience thrombosis associated with hypercoagulation. COVID-19 patients have shown an increase in platelet activation, but the mechanism has not been fully understood yet. One theory suggests that this could be related to the heparin-induced thrombocytopenia phenomenon, where platelet activation involves anti-PF4 antibodies that are associated with thrombosis. Vitamin D has been established to exert an influence on immunological responses and inflammation. The aim of this study is to analyze the correlation between serum 25-hydroxy-cholecalciferol [25(OH)D] levels and anti-PF4 antibodies among COVID-19 patients. A cross-sectional study was conducted among 160 COVID-19 patients at Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital and Wisma Atlit Hospital Jakarta from October 2021 to January 2022. The mean serum 25(OH)D level was 15.1 ng/mL. A significant negative correlation was found between serum 25(OH)D and anti-PF4 levels in mild COVID-19 patients (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .035; <jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">R</jats:italic> = −0.236). Remarkably, P-selectin levels were significantly higher in the moderate COVID-19 group compared to the severe group (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .031). Serum 25(OH)D level had a significant negative correlation with anti-PF4 level in mild COVID-19 patients. Thus, it is highly recommended to ensure that serum 25(OH)D levels are maintained above 30 ng/mL. Remarkably, the P-selectin level was significantly higher in the moderate COVID-19 group compared to the severe group.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3246-3352",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo National Referral Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rachman",
"given": "Andhika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pathology, YARSI University, Jakarta, Indonesia"
}
],
"family": "Iriani",
"given": "Anggraini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital – Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia."
}
],
"family": "Irawan",
"given": "Attaufiq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital – Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia."
}
],
"family": "Juanputra",
"given": "Samuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital – Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia."
}
],
"family": "Betsy",
"given": "Rachelle",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"lww.com",
"ovid.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-17T17:21:32Z",
"timestamp": 1726593692000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-17T17:21:38Z",
"timestamp": 1726593698000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-18T04:04:25Z",
"timestamp": 1726632265613
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "37",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "37",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1726185600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000039252",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e39252",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.00151",
"article-title": "Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "R1-20240917",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19.",
"key": "R3-20240917",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2016-11-709873",
"article-title": "Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.",
"author": "Arepally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2864",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "R4-20240917",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1346-3178",
"article-title": "Hemostasis in Coronavirus disease 2019-lesson from viscoelastic methods: a systematic review.",
"author": "Słomka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1181",
"journal-title": "Thromb Haemost",
"key": "R5-20240917",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15283",
"article-title": "Platelet‐activating immune complexes identified in critically ill COVID‐19 patients suspected of heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia.",
"author": "Nazy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1342",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "R6-20240917",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007214",
"article-title": "Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Manne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1317",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "R7-20240917",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007252",
"article-title": "Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19.",
"author": "Hottz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "R8-20240917",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp1411910",
"article-title": "Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia.",
"author": "Greinacher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R9-20240917",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.132214.3",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D deficiency in relation to the clinical outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Rachman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "394",
"journal-title": "F1000 Res",
"key": "R10-20240917",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.1066411",
"article-title": "The correlation between serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels and anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG and neutralizing antibody levels among cancer patients receiving COVID-19 vaccines.",
"author": "Rachman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1066411",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "R11-20240917",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.774",
"article-title": "The effect of treatment of vitamin D deficiency on the level of P‐Selectin and hs‐CRP in patients with thromboembolism: a pilot randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Hejazi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "40",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "R12-20240917",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.755883",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the relationship between gender and deep vein thrombosis among stroke patients.",
"author": "Tao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "R13-20240917",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2104840",
"article-title": "Thrombotic thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccination.",
"author": "Greinacher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2092",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R14-20240917",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.102.23.2867",
"article-title": "1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its potent synthetic analogs downregulate tissue factor and upregulate thrombomodulin expression in monocytic cells, counteracting the effects of tumor necrosis factor and oxidized LDL.",
"author": "Ohsawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2867",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "R15-20240917",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage.",
"author": "Aygun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1157",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol",
"key": "R16-20240917",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0031-1300957",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, thrombosis, and hemostasis: more than skin deep.",
"author": "Targher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Semin Thromb Hemost",
"key": "R17-20240917",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Plasma P-selectin is an early marker of thromboembolism in COVID-19.",
"author": "Fenyves",
"first-page": "E468",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "R18-20240917",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09537104.2021.1921721",
"article-title": "Distinct phenotypes of platelet, monocyte, and neutrophil activation occur during the acute and convalescent phase of COVID-19.",
"author": "Chao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1092",
"journal-title": "Platelets",
"key": "R19-20240917",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22157942",
"article-title": "The role of P-Selectin in COVID-19 coagulopathy: an updated review.",
"author": "Agrati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7942",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "R20-20240917",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317703",
"article-title": "Platelets can associate with SARS-CoV-2 RNA and are hyperactivated in COVID-19.",
"author": "Zaid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1404",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "R21-20240917",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14879",
"article-title": "What do monitoring platelet counts in COVID‐19 teach us?",
"author": "Thachil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2071",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "R22-20240917",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14848",
"article-title": "Thrombocytopenia and its association with mortality in patients with COVID‐19.",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1469",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "R23-20240917",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.064",
"article-title": "Antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19? -rationale and evidence-.",
"author": "Godino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Int J Cardiol",
"key": "R24-20240917",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000039252"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Adequate serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels are correlated with low anti-PF4 levels in mild COVID-19 Patients: An observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/lww.0000000000001000",
"volume": "103"
}
