Zinc and vitamin C intake increases spike and neutralising antibody production following SARS‐CoV‐2 infection
et al., Clinical and Translational Medicine, doi:10.1002/ctm2.731, NCT04446104, Feb 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
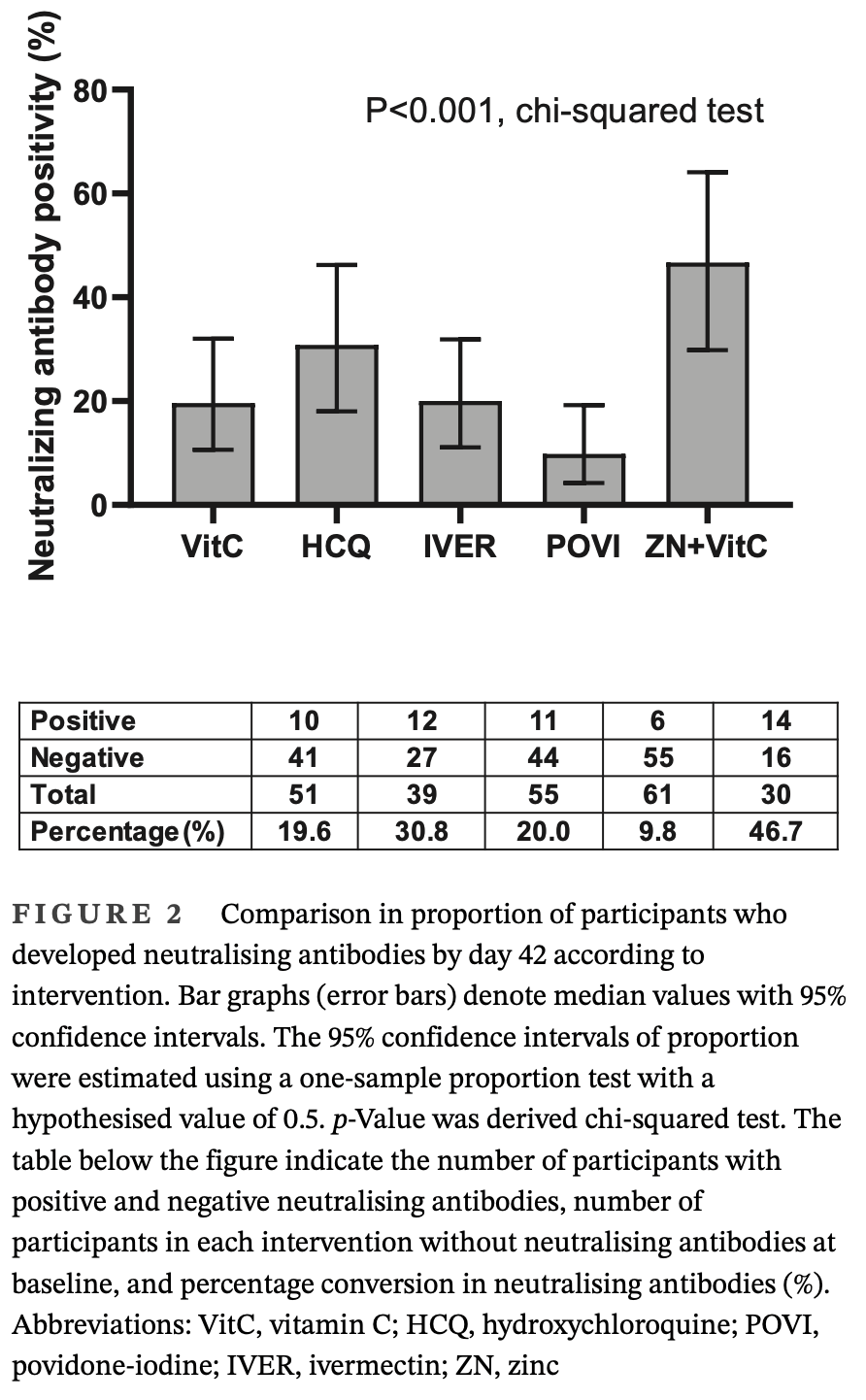
Antibody response analysis of 422 SARS-CoV-2 infected men in an RCT showing zinc + vitamin C treatment increased anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG and neutralizing antibody levels compared to other treatments (vitamin C, hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, povidone-iodine). Seropositive men who were initially negative for neutralising antibodies were approximately four times more likely to develop neutralising antibody positivity by day 42 in the zinc + vitamin C group compared with other treatments, OR 3.75, [1.69-8.32]. The extent of increase in serum zinc levels correlated with the increase in anti-spike IgG. This is a substudy for Seet et al.
Study covers zinc and vitamin C.
Quek et al., 20 Feb 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Singapore, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, trial NCT04446104 (history).
Contact: raymond_seet@nus.edu.sg.
Abstract: Received: 2 November 2021
Revised: 23 January 2022
Accepted: 25 January 2022
DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.731
LETTER TO EDITOR
Zinc and vitamin C intake increases spike and neutralising
antibody production following SARS-CoV-2 infection
Dear Editor,
Previous studies have not examined whether pharmacologic interventions could increase SARS-CoV-2 antibody
responses. Certain medications (e.g. zinc and vitamin C)
are known to stimulate immunologic responses following infections.1,2 Zinc exerts pluripotent effects on the
immune system and supports the integrity of the epithelial cell barriers,1,3 while vitamin C is an antioxidant that
potentially protects against viral respiratory infections.2
Hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin are anti-parasitic
medications that are known to modulate innate and
adaptive immunity.4,5 By contrast, povidone-iodine is
a topical broad spectrum antiseptic capable of direct
virucidal effects.6 We hypothesise that interventions that
support immune regulatory functions could enhance
production of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike and neutralising
TA B L E 1
antibodies among individuals with prior infection.
Using materials and resources of the DORM trial
(NCT04446104),7 we compared the antibody responses at
baseline and on day 42 among seropositive participants
who received the different medications as part of this trial.
Participants from the study were selected from the
DORM trial, an open label, randomised clinical trial that
examined the efficacy of either oral hydroxychloroquine
(400 mg followed by 200 mg/day), povidone-iodine throat
spray (three times a day, approximately 270 μg/day), oral
ivermectin (12 mg, single dose), oral zinc + vitamin C
(80 mg zinc sulfate, 500 mg vitamin C/day) or oral vitamin
C (500 mg/day), for 42 days to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection (Supporting Information).7 From 4257 recruited participants, those found with new SARS-CoV-2 infection on
recruitment were enrolled into the present substudy.
Clinical characteristics of study participants
Zinc + vitamin
C (n = 68)
Hydroxychloroquine
(n = 67)
Ivermectin
(n = 99)
Povidone-iodine
(n = 107)
Vitamin C
(n = 81)
33.2 (7.8)
30.6 (6.4)
33.6 (6.9)
32.0 (6.6)
32.9 (7.1)
Participant characteristics
Age (years), mean (SD)
Country of origin
Bangladesh
36 (52.9%)
28 (41.8%)
46 (46.5%)
52 (48.6%)
40 (49.4%)
India
32 (47.1%)
38 (56.7%)
51 (51.5%)
55 (51.4%)
41 (50.6%)
Others
0
1 (1.5%)
2 (2.0%)
0
0
Hypertension
1 (1.5%)
1 (1.5%)
3 (3.1%)
1 (0.9%)
0
Diabetes mellitus
1 (1.5%)
0
1 (1.0%)
0
1 (1.3%)
Hyperlipidemia
0
0
1 (1.0%)
0
0
Systolic BP (mmHg)
136.6 (15.9)
127.4 (11.6)
135.7 (15.1)
134.4 (17.7)
133.8 (17.5)
Diastolic BP (mmHg)
86.6 (11.6)
81.2 (6.4)
89.8 (9.3)
86.6 (11.6)
88.5 (10.9)
Medical history
Baseline parameters
a
a
Pulse rate (per min)
97.4 (15.5)
86.9 (7.9)
96.9 (13.4)
93.3 (11.8)
97.1 (13.9)
Body mass index (kg/m2 )
24.34 (3.43)
24.36 (3.44)
25.73 (2.72)
24.62 (3.55)
24.19 (3.02)
Resting heart rate.
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the
original work is properly cited.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics
Clin. Transl. Med. 2022;12:e731.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.731
wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/ctm2
1 of 5
LETTER TO EDITOR
F..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.731",
"ISSN": [
"2001-1326",
"2001-1326"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.731",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ctm2.731"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Division of Neurology Department of Medicine National University Hospital Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Quek",
"given": "Amy May Lin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Khoo Teck Puat‐National University Children's Medical Institute National University Hospital National University Health System Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "Delicia Shu Qin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Teng",
"given": "Ooiean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Khoo Teck Puat‐National University Children's Medical Institute National University Hospital National University Health System Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Chang Yien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Geelyn Jeng Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Mei Yen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Diagnostic Development Hub, Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR) Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Yee",
"given": "Sidney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Diagnostic Development Hub, Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR) Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Cheong",
"given": "Ee Wan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Diagnostic Development Hub, Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR) Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Weng",
"given": "Ruifen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health National University of Singapore and National University Health System Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Alex R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health National University of Singapore and National University Health System Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Department of Surgery Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Hartman",
"given": "Mikael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Immunology Translational Research Programme Department of Microbiology and Immunology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Immunology Programme Life Sciences Institute National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Angeli",
"given": "Veronique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases National University Hospital Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Translational Research Program, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Tambyah",
"given": "Paul Anantharajah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Division of Neurology Department of Medicine National University Hospital Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Healthy Longevity Translational Research Program Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National University of Singapore Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Seet",
"given": "Raymond Chee Seong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical and Translational Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Clinical & Translational Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-20T19:26:36Z",
"timestamp": 1645385196000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-27T05:56:05Z",
"timestamp": 1693115765000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-19T05:48:37Z",
"timestamp": 1713505717351
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 11,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 19,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1645315200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ctm2.731",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/ctm2.731",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ctm2.731",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/68.2.447S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2003.09.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.07.097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1381612826666200707132920",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0165-2427(92)90173-N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jopr.13209",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc7520",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-03041-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90983-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_1_5_11_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ctm2.731"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Zinc and vitamin C intake increases spike and neutralising antibody production following SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
quek2
