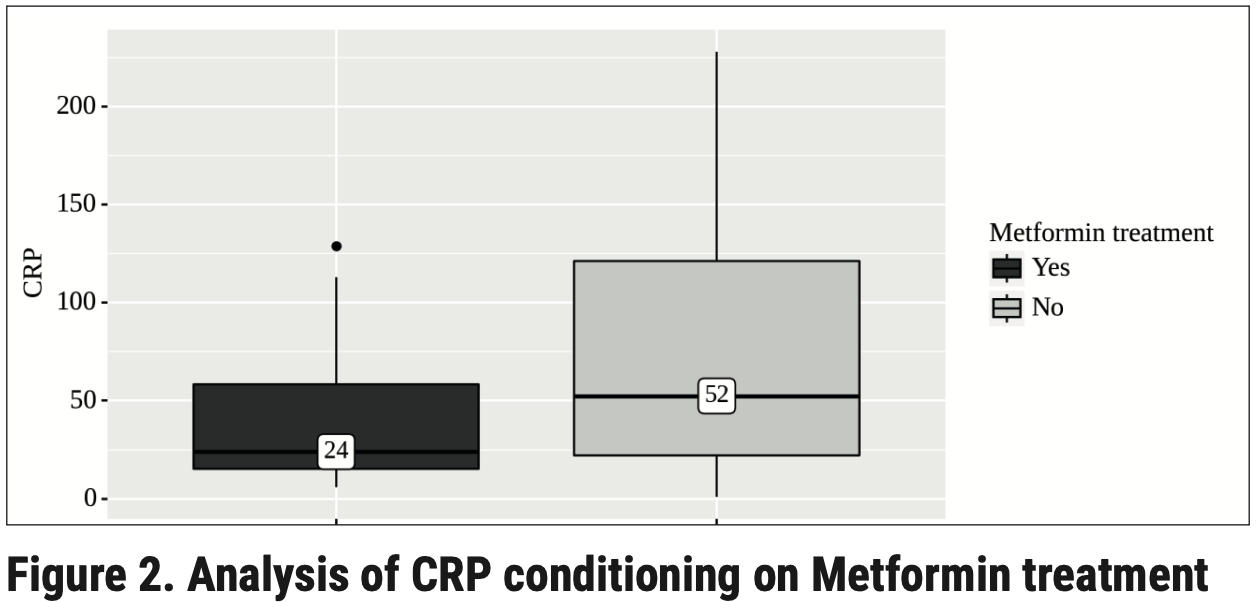
Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Hematological Parameters of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
et al., Medical Archives, doi:10.5455/medarh.2022.76.329-332, Oct 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of hematologic parameters in COVID-19 patients with diabetes in Ukraine, showing significantly lower CRP for patients taking metformin.
Petakh et al., 1 Oct 2022, retrospective, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, median age 62.7, 6 authors, study period January 2022 - March 2022.
Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Hematological Parameters of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Medical Archives, doi:10.5455/medarh.2022.76.329-332
Background: COVID-19 infection caused by SARS-COV-2 can result in multi-organ injuries and significant mortality in severe and critical patients, particularly those with type 2 diabetes as a comorbidity. Metformin and insulin are the main diabetes medications that affect the outcome of patients with COVID-19. Objective: The purpose of our study was to find out the features of the hematological indicators of patients with COVID-19 patients and type 2 diabetes. Methods: This is a retrospective study of the hospital confirmed COVID-19 patients between January to March 2022, who were admitted to Transcarpathian Regional Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital (Uzhhorod, Ukraine). Results: The effect of type 2 diabetes, metformin, and insulin on COVID-19 were analyzed, respectively. Demographics and blood laboratory indices were collected. In patients who took metformin, the level of CRP was significantly lower than in patients who did not take metformin (24 mg/L [IQR 15 -58] vs 52 mg/L, [IQR 22-121], P = 0.046). Conclusion: Our findings suggest that pre-admission metformin use may benefit COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes.
References
Agarwal, Schechter, Southern, Crandall, Tomer, Preadmission diabetes-specific risk factors for mortality in hospitalized patients with diabetes and coronavirus disease 2019, J Diabetes Care
Alberti, Zimmet, Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation, J Diabetic medicine
Bornstein, Rubino, Khunti, Mingrone, Hopkins et al., Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19, J The lancet Diabetes endocrinology
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, J Diabetes care
Guo, Li, Dong, Zhou, Zhang et al., Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19, J Diabetes/metabolism research reviews
Hu, Chen, Fu, Gao, Long et al., Risk factors associated with clinical outcomes in 323 coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) hospitalized patients in Wuhan, China, J Clinical infectious diseases
Li, Wang, Li, Yang, Zhang, Metformin-induced reduction of CD39 and CD73 blocks myeloid-derived suppressor cell activity in patients with ovarian cancer, J Cancer research
Mendy, Gopal, Alcorn, Forno, Reduced mortality from lower respiratory tract disease in adult diabetic patients treated with metformin, J Respirology
Menendez, Metformin and SARS-CoV-2: mechanistic lessons on air pollution to weather the cytokine/thrombotic storm in COVID-19, J Aging
Penlioglou, Papachristou, Papanas, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: May old anti-diabetic agents become the new philosopher's stone?, J Diabetes Therapy
Petakh, Kamyshna, Nykyforuk, Yao, Imbery et al., Immunoregulatory Intestinal Microbiota and COVID-19 in Patients with Type Two Diabetes: A Double-Edged Sword, J Viruses
Remuzzi, Remuzzi, COVID-19 and Italy: what next?, J The Lancet Neurology
Riahi, Sombra, Lo, Chacko, Neto et al., Insulin use, diabetes control, and outcomes in patients with COVID-19, J Endocrine Research
Salem, Grobe, Elased, Insulin treatment attenuates renal ADAM17 and ACE2 shedding in diabetic Akita mice, American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology
Scheen, Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality, J Diabetes metabolism
Sharma, Ray, Sadasivam, Metformin in COVID-19: a possible role beyond diabetes. Diabetes research and clinical practice
Stawicki, Jeanmonod, Miller, Paladino, Gaieski et al., The 2019-2020 novel coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) pandemic: A joint american college of academic international medicine-world academic council of emergency medicine multidisciplinary COVID-19 working group consensus paper, J Journal of global infectious diseases
Ursini, Ciaffi, Landini, Meliconi, COVID-19 and diabetes: Is metformin a friend or foe? J Diabetes research clinical practice
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, J Jama
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes, J Cell metabolism
Zheng, Ley, Hu, Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications, J Nature reviews endocrinology
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, J The lancet Diabetes endocrinology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5455/medarh.2022.76.329-332",
"ISSN": [
"0350-199X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2022.76.329-332",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: COVID-19 infection caused by SARS-COV-2 can result in multi-organ injuries and significant mortality in severe and critical patients, particularly those with type 2 diabetes as a comorbidity. Metformin and insulin are the main diabetes medications that affect the outcome of patients with COVID-19. Objective: The purpose of our study was to find out the features of the hematological indicators of patients with COVID-19 patients and type 2 diabetes. Methods: This is a retrospective study of the hospital confirmed COVID-19 patients between January to March 2022, who were admitted to Transcarpathian Regional Clinical Infectious Diseases Hospital (Uzhhorod, Ukraine). Results: The effect of type 2 diabetes, metformin, and insulin on COVID-19 were analyzed, respectively. Demographics and blood laboratory indices were collected. In patients who took metformin, the level of CRP was significantly lower than in patients who did not take metformin (24 mg/L [IQR 15 - 58] vs 52 mg/L, [IQR 22–121], P = 0.046). Conclusion: Our findings suggest that pre-admission metformin use may benefit COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petakh",
"given": "Pavlo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griga",
"given": "Vasilij",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammed",
"given": "Issah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loshak",
"given": "Kateryna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poliak",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamyshnyiy",
"given": "Aleksandr",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medical Archives",
"container-title-short": "Med Arch",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-05T21:34:06Z",
"timestamp": 1667684046000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-05T21:34:20Z",
"timestamp": 1667684060000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-06T04:57:04Z",
"timestamp": 1667710624342
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://www.medarch.org//?sec=licenseinfo",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 308,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667606400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.medarch.org/?mno=126969",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "3407",
"original-title": [],
"page": "329",
"prefix": "10.5455",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"publisher": "ScopeMed",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.medarch.org/?mno=126969"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Hematological Parameters of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "76"
}
