Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Increased COVID-19 Severity: Prospective Screening of At-Risk Groups is Medically Indicated
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-83262/v1, Sep 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 37 hospitalized patients in the USA, showing higher risk of ICU admission with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 16th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
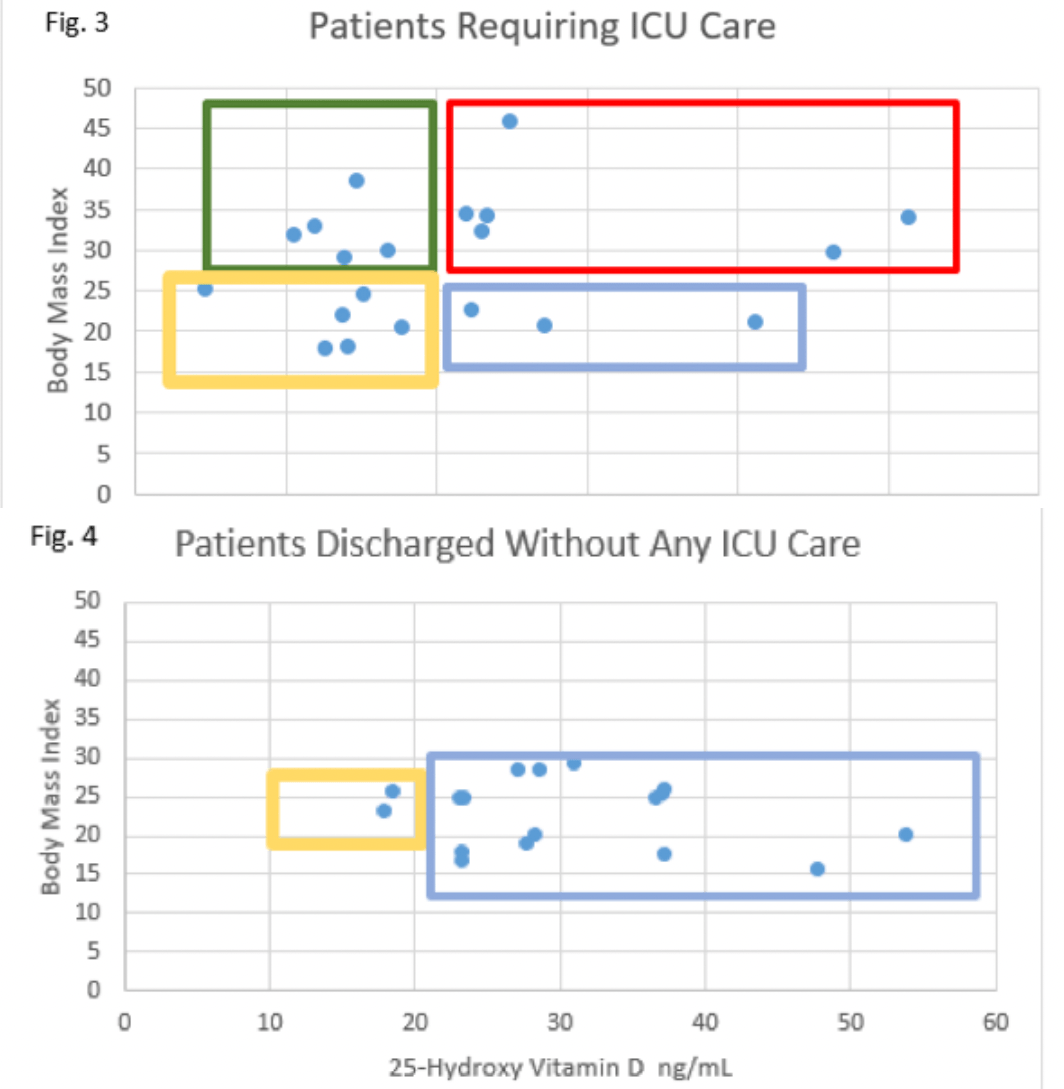
risk of ICU admission, 55.8% lower, RR 0.44, p = 0.01, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 9 of 24 (37.5%), low D levels (<20ng/mL) 11 of 13 (84.6%), NNT 2.1, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels (≥20ng/mL).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pepkowitz et al., 29 Sep 2020, retrospective, USA, preprint, 7 authors.
Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Increased COVID-19 Severity: Prospective Screening of At-Risk Groups is Medically Indicated
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-83262/v1
Non-classical actions of Vitamin D are involved in regulation of the immune system including a role in mitigation of excessive in ammation. We hypothesized that vitamin D de ciency existing prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection could contribute to patients developing severe pulmonary compromise as a result of dysfunctional hyperin ammation. Serum vitamin D concentrations of patients experiencing such severe COVID-19 manifestations that they required ICU care at any point of their hospitalization were compared to serum vitamin D concentrations of patients achieving discharge without the need for any ICU care. Having serum vitamin D < 20 ng/mL was signi cantly associated with increased COVID-19 severity, p=0.001. It is conjectured that population groups know to have low serum vitamin D should be prospectively screened for de ciency and if found emergently treated. Such action could both decrease the maximum severity suffered by infected individuals and lessen the strain on medical resources by decreasing the percentage of COVID-19 hospital admissions requiring ICU care.
References
Aucoin, Weaver, Thomas, Jones, Vitamin D status of refugees arriving in Canada: ndings from the Calgary Refugee Health Program, Can Fam Physician
Baig, Khaleeq, Ali, Syeda, Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms, ACS Chem Neurosci, doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122
Bodnar, Simhan, Powers, Frank, Cooperstein et al., High prevalence of vitamin D insu ciency in black and white pregnant women residing in the northern United States and their neonates, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/137.2.447
Burton, Fort, Seoane, Hospitalization and Mortality among Black Patients and White Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsa2011686
Chowkwanyun, Reed, Racial Health Disparities and Covid-19 -Caution and Context, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp2012910
Chun, Shieh, Gottlieb, Vitamin D Binding Protein and the Biological Activity of Vitamin D, Front Endocrinol, doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00718
Colotta, Jansson, Bonelli, Modulation of in ammatory and immune responses by vitamin D, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2017.07.007
Currie, Findlay, Mcfarlane, Cathelicidins Have Direct Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus In Vitro and Protective Function In Vivo in Mice and Humans, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1502478
Facchiano, Facchiano, Bartoli, Ricci, Facchiano, Reply to Jakovac: About COVID-19 and vitamin D, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00185.2020
Flood-Nichols, Tinnemore, Huang, Napolitano, Ippolito, Vitamin D de ciency in early pregnancy, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123763
Gentile, Aimo, Forfori, COVID-19 and risk of pulmonary brosis: the importance of planning ahead, Eur J Prev Cardiol, doi:10.1177/2047487320932695
Gombart, Borregaard, Koe, Hp, Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.04-3284com
Hamid, Riggs, Spencer, Redman, Bodenner, Vitamin D de ciency in residents of academic long-term care facilities despite having been prescribed vitamin D, J Am Med Dir Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2006.07.005
Hamid, Riggs, Spencer, Redman, Bodenner, Vitamin D de ciency in residents of academic long-term care facilities despite having been prescribed vitamin D, J Am Med Dir Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2006.07.005
Hatcher, Agnew-Brune, Anderson, COVID-19 Among American Indian and Alaska Native Persons -23 States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6934e1externalicon
Hooper, Nápoles, Pérez-Stable, COVID-19 and Racial/Ethnic Disparities
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19 -Preliminary Report
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020
Kalligeros, Shehadeh, Mylona, Association of Obesity with Disease Severity Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019, Obesity (Silver Spring), doi:10.1002/oby.22859
Lips, De Jongh, Vitamin D de ciency in immigrants, Bone Rep, doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2018.06.001
Nikolich-Zugich, Knox, Rios, Natt, Bhattacharya et al., Correction to: SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: what we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes, Geroscience, doi:10.1007/s11357-020-00193-1
Parva, Tadepalli, Singh, Prevalence of Vitamin D De ciency and Associated Risk Factors in the US Population (2011-2012), Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.2741
Ritterhouse, Lu, Shah, Vitamin d de ciency in a multiethnic healthy control cohort and altered immune response in vitamin D de cient European-American healthy controls, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094500
Smet, Smet, Herroelen, Vitamin D de ciency as a risk factor for severe COVID-19: a convergence of two pandemics, medRXiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.01.20079376
Sousa, Casanova, Findlay, Cathelicidins display conserved direct antiviral activity towards rhinovirus, Peptides, doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2017.07.013
Taksler, Cutler, Giovannucci, Keating, Vitamin D de ciency in minority populations, Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980014000457
Tay, Poh, Rénia, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, in ammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Toren-Wielema, Veenhuizen, Kappelle, Veeger, Van Roon, E cacy of a Standardized Oral Vitamin D Dosing Regimen in Nursing Home Residents, Drugs Aging, doi:10.1007/s40266-018-0601-z
Vabret, Britton, Gruber, -19: current state of the science, Immunology of COVID, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002
Vranić, Mikolašević, Milić, Vitamin D De ciency: Consequence or Cause of Obesity?, Medicina (Kaunas), doi:10.3390/medicina55090541
Zhang, Leung, Richers, Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proin ammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102412
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-83262/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-83262/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Non-classical actions of Vitamin D are involved in regulation of the immune system including a role in mitigation of excessive inflammation. We hypothesized that vitamin D deficiency existing prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection could contribute to patients developing severe pulmonary compromise as a result of dysfunctional hyperinflammation. Serum vitamin D concentrations of patients experiencing such severe COVID-19 manifestations that they required ICU care at any point of their hospitalization were compared to serum vitamin D concentrations of patients achieving discharge without the need for any ICU care. Having serum vitamin D < 20 ng/mL was significantly associated with increased COVID-19 severity, p=0.001. It is conjectured that population groups know to have low serum vitamin D should be prospectively screened for deficiency and if found emergently treated. Such action could both decrease the maximum severity suffered by infected individuals and lessen the strain on medical resources by decreasing the percentage of COVID-19 hospital admissions requiring ICU care.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
24
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8384-3227",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pepkowitz",
"given": "Samuel H",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"family": "Hobel",
"given": "Calvin J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"family": "MS",
"given": "James M Mirocha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"family": "Kimia.Sobhani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"family": "BS",
"given": "Carissa A Huynh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Center"
}
],
"family": "Jawanda",
"given": "Harneet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cedars-Sinai Medical Cente"
}
],
"family": "Hasan",
"given": "Wohaib",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-29T14:42:09Z",
"timestamp": 1601390529000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-29T14:42:10Z",
"timestamp": 1601390530000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-09T08:57:13Z",
"timestamp": 1639040233798
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601337600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-83262/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-83262/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Increased COVID-19 Severity: Prospective Screening of At-Risk Groups is Medically Indicated"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}
