Vitamin D and zinc supplementation to improve treatment outcomes among COVID-19 patients in India: results from a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial
et al., Current Developments in Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971, NCT04641195, Jul 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
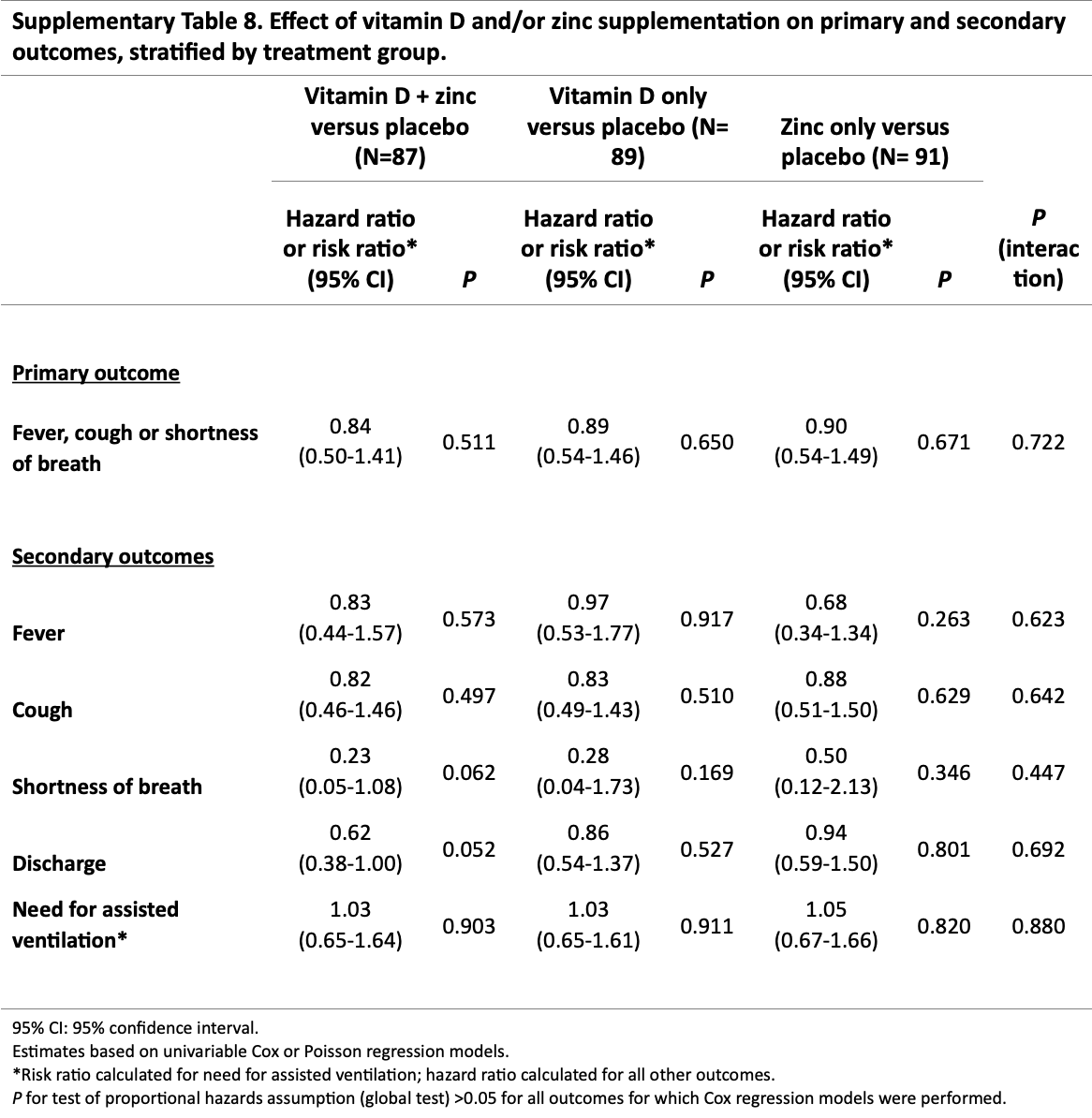
Early terminated factorial RCT with 46 vitamin D, 48 zinc, 44 vitamin D + zinc, and 43 placebo patients in India.
The most serious outcome (ventilation) numbers do not seem realistic. Authors do not specify outcomes per group, but with one event for non-zinc, we know that either the vitamin D only or the placebo group had zero events, which does not match the reported RRs. All 7 RRs are close to 1.0: for D vs. non-D, Z vs. non-Z, D+Z vs. placebo, D vs. placebo, Z vs. placebo, D<20ng/mL vs. non-D, and D>20ng/mL vs. non-D. This suggests unreliable data or analysis (e.g., inappropriate use of Poisson regression). We will update when authors respond.
The trial is also unusual in that the primary analyses are unadjusted and compare one treatment with a combination of another treatment and placebo.
There are very large baseline differences, e.g., 35 vs. 15% 60+ for zinc vs. non-zinc. There was only 181 patients recruited from 700 planned.
There is limited room for improvement with the population studied that recovered very quickly within a median of 3 days. Oral cholecalciferol takes 3-7 days for complete conversion into the biologically active 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Authors could have provided treatment with much faster onset of action, e.g., using calcitriol.
There was very little improvement in D/zinc levels with the administration used and the baseline deficiency levels. Only 4% of people went from zinc deficient to sufficient, and only 8% went from vitamin D <30ng/mL to >30ng/mL, and most or all of these improvements may have been after patients already recovered.
Notwithstanding the limitations above, we note that, while small, the effect for most outcomes is positive for vitamin D and zinc, and in most cases, the effect in the combined vitamin D + zinc group is larger.
Data for this study is not available.
Study covers zinc and vitamin D.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 5.0% higher, RR 1.05, p = 0.82, treatment 43, control 42, zinc vs. placebo.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 6.0% lower, HR 0.94, p = 0.80, treatment 43, control 42, zinc vs. placebo.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 10.0% lower, HR 0.90, p = 0.67, treatment 41, control 42, zinc vs. placebo, dyspnea, cough, or fever, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% lower, HR 0.50, p = 0.35, treatment 43, control 42, zinc vs. placebo, dyspnea, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 32.0% lower, HR 0.68, p = 0.26, treatment 43, control 42, zinc vs. placebo, fever, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 12.0% lower, HR 0.88, p = 0.63, treatment 43, control 42, zinc vs. placebo, cough, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 16.0% lower, HR 0.84, p = 0.51, treatment 39, control 42, zinc + vitamin D vs. placebo, dyspnea, cough, or fever, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 77.0% lower, HR 0.23, p = 0.06, treatment 39, control 42, zinc + vitamin D vs. placebo, dyspnea, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 17.0% lower, HR 0.83, p = 0.57, treatment 39, control 42, zinc + vitamin D vs. placebo, fever, Table S8.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 18.0% lower, HR 0.82, p = 0.50, treatment 39, control 42, zinc + vitamin D vs. placebo, cough, Table S8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Partap et al., 11 Jul 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, India, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 22 April, 2021 - 1 August, 2022, average treatment delay 3.0 days, trial NCT04641195 (history).
Contact: upartap@hsph.harvard.edu, mina@hsph.harvard.edu.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971",
"ISSN": [
"2475-2991"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971",
"alternative-id": [
"S2475299123247940"
],
"article-number": "101971",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Vitamin D and zinc supplementation to improve treatment outcomes among COVID-19 patients in India: results from a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Current Developments in Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of American Society for Nutrition."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2531-1804",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Partap",
"given": "Uttara",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Kamal Kant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marathe",
"given": "Yogesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Molin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "Sanaa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D’Costa",
"given": "Pradeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Gaurav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bromage",
"given": "Sabri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemler",
"given": "Elena C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mistry",
"given": "Nerges",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kain",
"given": "Kevin C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dholakia",
"given": "Yatin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fawzi",
"given": "Wafaie W.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Current Developments in Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Current Developments in Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-11T16:03:32Z",
"timestamp": 1689091412000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-11T16:04:04Z",
"timestamp": 1689091444000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-12T04:32:28Z",
"timestamp": 1689136348223
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688169600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 9,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688947200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2475299123247940?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2475299123247940?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101971",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00327-0",
"article-title": "Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study",
"author": "Menni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1618",
"issue": "10335",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib1",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Descriptive epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Karnataka state, South India: Transmission dynamics of symptomatic vs. asymptomatic infections",
"author": "Kumar",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib3",
"unstructured": "WHO. Therapeutics and COVID-19: Living Guideline (16 September 2022). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib4",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020 [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1",
"article-title": "An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib5",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib6",
"unstructured": "WHO. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update: Edition 129 Published 8 February 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00816-7",
"article-title": "Humoral immune evasion of the omicron subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB",
"author": "Uraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib7",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2214302",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against Omicron Subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib8",
"volume": "388",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Low neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 by parental mRNA vaccine or a BA.5 bivalent booster",
"author": "Kurhade",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01909-w",
"article-title": "Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults",
"author": "Subramanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1706",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib10",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abg6296",
"article-title": "Face masks effectively limit the probability of SARS-CoV-2 transmission",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1439",
"issue": "6549",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib11",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib12",
"unstructured": "WHO. Advice for the public on COVID-19 – World Health Organization [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib13",
"unstructured": "WHO. COVID-19 Vaccines Advice [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19-vaccines/advice."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1377/hlthaff.2020.01409",
"article-title": "Increased Intensity Of PCR Testing Reduced COVID-19 Transmission Within Countries During The First Pandemic Wave",
"author": "Rannan-Eliya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "70",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Health Affairs",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib14",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.21-0200",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Therapeutics for Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Review of Candidate Agents with Potential for Near-Term Use and Impact",
"author": "Maxwell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "584",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib15",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The silent and dangerous inequity around access to COVID-19 testing: A call to action",
"author": "Batista",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Barriers to COVID-19 Health Products in Low-and Middle-Income Countries During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Rapid Systematic Review and Evidence Synthesis",
"author": "Boro",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib18",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003176",
"article-title": "Effect of micronutrient supplements on influenza and other respiratory tract infections among adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Abioye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Glob Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib19",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofx059",
"article-title": "Zinc Acetate Lozenges May Improve the Recovery Rate of Common Cold Patients: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofx059",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib20",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib21",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro",
"author": "Telcian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib22",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.11.013",
"article-title": "Vitamin D attenuates rhinovirus-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFR) in respiratory epithelial cells",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib23",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19",
"author": "Skalny",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib24",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"author": "te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib25",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Twice-Daily Oral Zinc in the Treatment of Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial",
"author": "Ben Abdallah",
"first-page": "ciac807",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1053",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib28",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijph.IJPH_176_16",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status of adult females residing in Ballabgarh health and demographic surveillance system: A community-based study",
"author": "Misra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Indian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib29",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib30",
"unstructured": "Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2021 Dec 17]. GBD Compare. Available from: https://www.healthdata.org/data-visualization/gbd-compare"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2022-061301",
"article-title": "Randomised trial to determine the effect of vitamin D and zinc supplementation for improving treatment outcomes among patients with COVID-19 in India: trial protocol",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib31",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2010-0606",
"article-title": "A 16-week randomized clinical trial of 2000 international units daily vitamin D3 supplementation in black youth: 25-hydroxyvitamin D, adiposity, and arterial stiffness",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4584",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib32",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4158/EP13265.RA",
"article-title": "Large, single-dose, oral vitamin D supplementation in adult populations: a systematic review",
"author": "Kearns",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib33",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0267918",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D versus placebo to prevent complications in COVID-19 patients: Multicentre randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Mariani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib34",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib35",
"unstructured": "Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc [Internet]. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2001 [cited 2022 Mar 2]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222310/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"article-title": "Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib36",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.035",
"article-title": "Positive impact of oral hydroxychloroquine and povidone-iodine throat spray for COVID-19 prophylaxis: An open-label randomized trial",
"author": "Seet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib37",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib38",
"unstructured": "ODK - Collect data anywhere [Internet]. [cited 2021 Dec 17]. Available from: https://getodk.org."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib39",
"unstructured": "AIIMS/ICMR National Task Force/Joint Monitoring Group. Clinical Guidelines for Management of Adult COVID-19 Patients: Revised on 14/01/2022 [Internet]. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India; [cited 2022 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ClinicalGuidanceforManagementofAdultCovid19Patientsupdatedason17thJanuary2022.pdf."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib40",
"unstructured": "MOHFW, GOI. Clinical Management Protocol for COVID-19 (In Adults) - Version 6 (24.05.21) [Internet]. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India; 2021 May [cited 2022 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/UpdatedDetailedClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19adultsdated24052021.pdf"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib41",
"unstructured": "MOHFW, GOI. Revised Discharge Policy for COVID-19: Updated on 9th January 2022 [Internet]. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India; [cited 2022 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/RevisedDischargePolicyforCOVID19updatedon9thJanuary2022.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00393-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality during the first epidemic wave in Madurai, south India: a prospective, active surveillance study",
"author": "Laxminarayan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1665",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib42",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0277000",
"article-title": "D-dimer levels in non-COVID-19 ARDS and COVID-19 ARDS patients: A systematic review with meta-analysis",
"author": "Tóth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLOS ONE",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib43",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"article-title": "Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study)",
"author": "Rastogi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "87",
"issue": "1156",
"journal-title": "Postgraduate Medical Journal",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib44",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965",
"article-title": "Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D",
"author": "Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib45",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072170",
"article-title": "Effects of a 2-Week 5000 IU versus 1000 IU Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Recovery of Symptoms in Patients with Mild to Moderate Covid-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Sabico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib46",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"author": "Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1242",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Endocr Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib47",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14153048",
"article-title": "Positive Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial",
"author": "De Niet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib48",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04928-5",
"article-title": "COvid-19 and high-dose VITamin D supplementation TRIAL in high-risk older patients (COVIT-TRIAL): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1031",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib49",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqab426",
"article-title": "Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on cytokines, chemokines, and growth factor in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib50",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bone.2021.116175",
"article-title": "A randomized pilot study using calcitriol in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Elamir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Bone",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib51",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003",
"article-title": "Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Villasis-Keever",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib52",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of a test-and-treat approach to vitamin D supplementation on risk of all cause acute respiratory tract infection and covid-19: phase 3 randomised controlled trial (CORONAVIT)",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib53",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevention of covid-19 and other acute respiratory infections with cod liver oil supplementation, a low dose vitamin D supplement: quadruple blinded, randomised placebo controlled trial",
"author": "Brunvoll",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib54",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030505",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Intake May Reduce SARS-CoV-2 Infection Morbidity in Health Care Workers",
"author": "Karonova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib55",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib56",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02290-8",
"article-title": "A single-oral bolus of 100,000 IU of cholecalciferol at hospital admission did not improve outcomes in the COVID-19 disease: the COVID-VIT-D-a randomised multicentre international clinical trial",
"author": "Cannata-Andía",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib57",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.016",
"article-title": "COVID-19 prophylaxis with doxycycline and zinc in health care workers: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Stambouli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib58",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.731",
"article-title": "Zinc and vitamin C intake increases spike and neutralising antibody production following SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Quek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib59",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02546-5",
"article-title": "Olfactory Disturbances as Presenting Manifestation Among Egyptian Patients with COVID-19: Possible Role of Zinc",
"author": "Abdelmaksoud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4101",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib60",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02512-1",
"article-title": "Do Zinc Supplements Enhance the Clinical Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine?: a Randomized, Multicenter Trial",
"author": "Abd-Elsalam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3642",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.101971_bib61",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 61,
"references-count": 61,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2475299123247940"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Food Science",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D and zinc supplementation to improve treatment outcomes among COVID-19 patients in India: results from a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
