Adherence to Healthy Eating Index-2015 and severity of disease in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19: a cross sectional study
et al., BMJ Military Health, doi:10.1136/military-2022-002173, Oct 2022
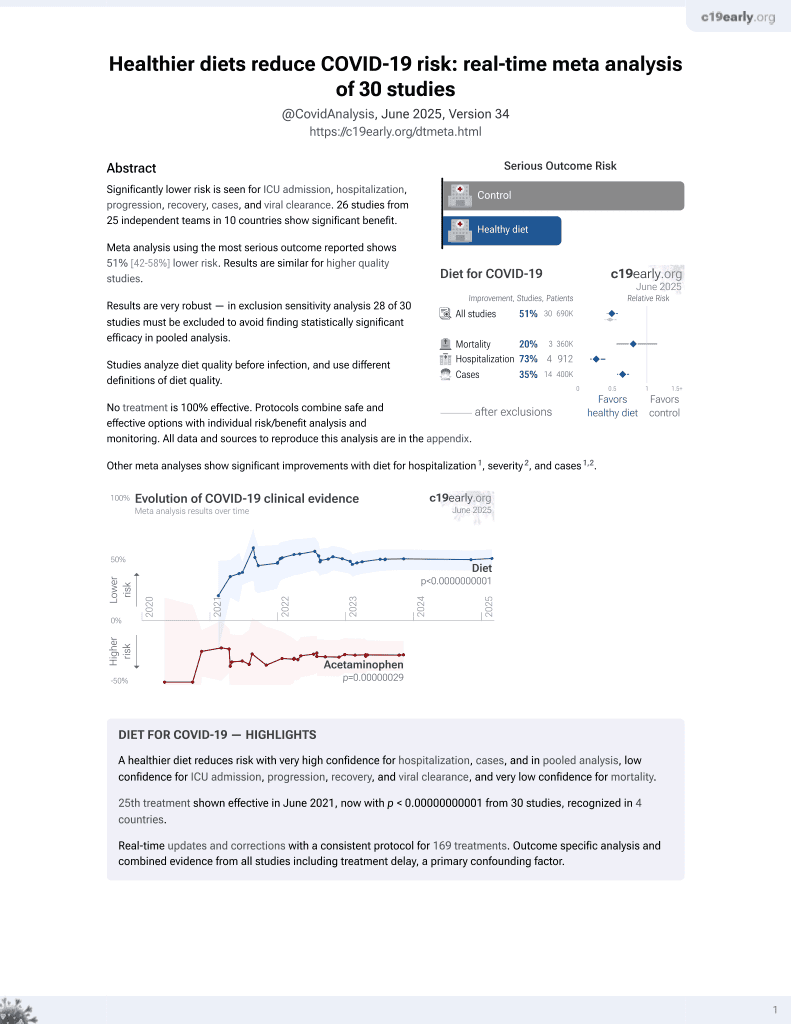
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
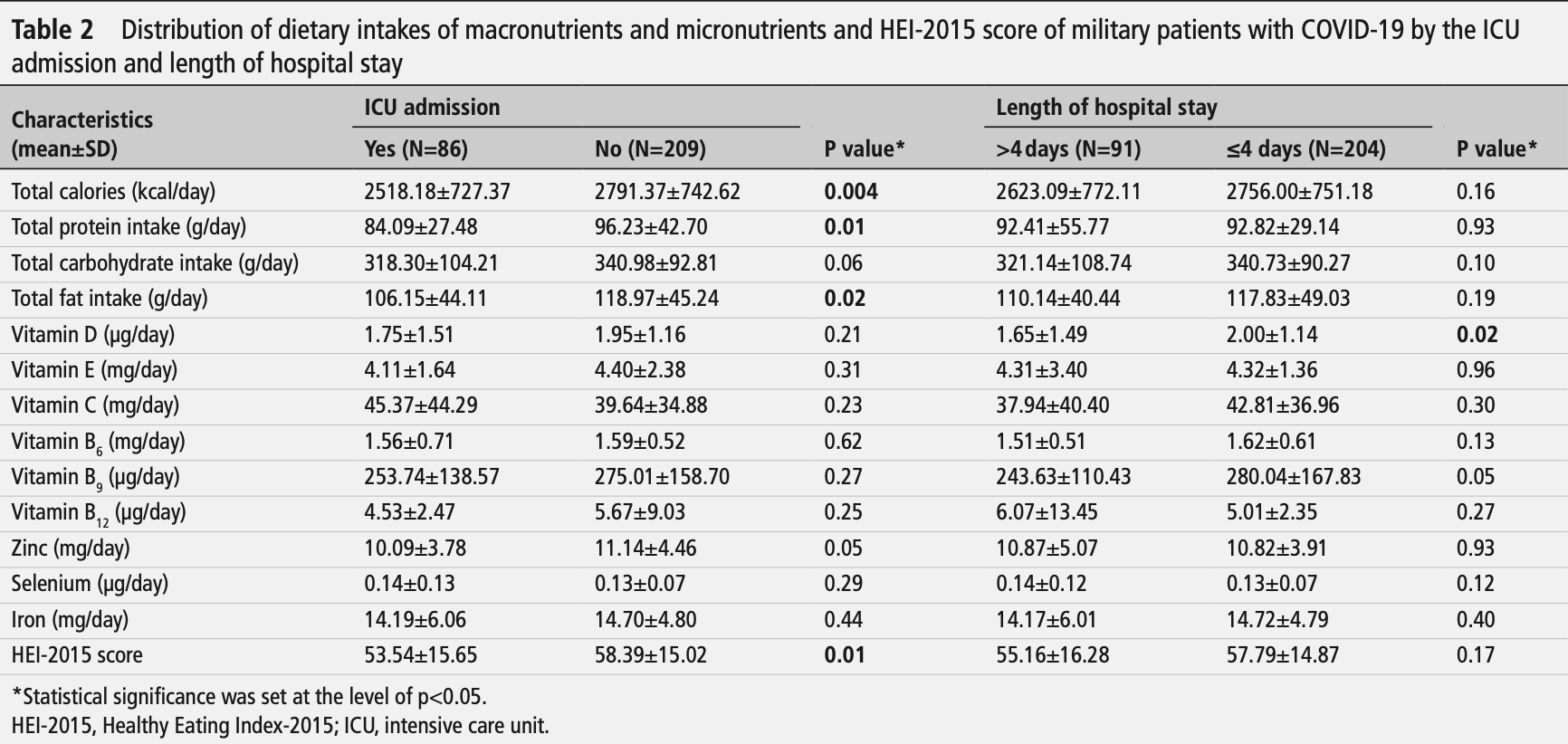
Retrospective 295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing significantly lower HEI-2015 diet scores for patients admitted to the ICU. Adjusted results are only provided for HEI-2015 score as a continuous variable.
Parastouei et al., 6 Oct 2022, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 55.4, 7 authors, study period May 2020 - November 2020.
Contact: mtaghdir@gmail.com.
Adherence to Healthy Eating Index-2015 and severity of disease in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19: a cross sectional study
BMJ Military Health, doi:10.1136/military-2022-002173
Introduction Proper nutrition can play an important role in preventing and improving disease progression in patients with COVID-19. The Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015) is one of the most common measures used to assess overall nutritional quality. This research aimed to identify the relationship between the HEI-2015 score and disease severity in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19. Methods This cross-sectional study was conducted in 295 hospitalised military patients (retired military and military reserve) with COVID-19. A validated food frequency questionnaire was used to assess food intake. To evaluate the quality of the diet, the HEI-2015 score was calculated. A multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to measure the association between HEI-2015 scores and disease severity (intensive care unit (ICU) admission and length of hospital stay greater than 4 days) in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19.
Results The mean HEI-2015 score was significantly higher in non-ICU patients than in ICU patients (58.39±15.02 vs 53.54±15.65, p=0.01). After adjusting for possible confounding factors including age, sex, comorbidities, calorie intake, body mass index and physical activity, adherence to HEI-2015 inversely related to ICU admission (OR 0.98; 95% CI 0.95 to 1.00) and length of hospital stay of more than 4 days (OR 0.99; 95% CI 0.97 to 1.00) in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19, although statistically not significant. Conclusions According to the results of the study, adherence to HEI-2015 inversely related to both ICU admission and length of hospital stay in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19, although it was not statistically significant.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC ⇒ To our knowledge, this is the first study to examine the relationship between the Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015) score and severity of illness in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19. WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS ⇒ The mean HEI-2015 score was significantly higher in non-intensive care unit (ICU) military patients than in ICU patients. ⇒ Adherence to HEI-2015 inversely related to ICU admission and length of hospital stay of more than 4 days in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19, although it was not statistically significant. HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY ⇒ It appears that a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, protein foods, dairy products and healthy fats could be effective in reducing the severity of COVID-19 disease.
Original research otherwise determined by BMJ. You may download and print the article for any lawful, non-commercial purpose (including text and data mining) provided that all copyright notices and trade marks are retained.
ORCID iDs M Sepandi http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6441-5887 M Taghdir http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2853-0196
References
Aadahl, Jørgensen, Validation of a new self-report instrument for measuring physical activity, Med Sci Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000074446.02192.14
Alamdari, Moghaddam, Amini, Application of methylene blue -vitamin C-N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494
Alimohamadi, Tola, Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, Case fatality rate of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Prev Med Hyg, doi:10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.2.1627
Asher, Tintle, Myers, Blood omega-3 fatty acids and death from COVID-19: a pilot study, Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2021.102250
Batiha, Alqarni, Awad, Algammal, Dairy-derived and egg white proteins in enhancing immune system against COVID-19, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.629440
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041181
Dai, Gu, Su, Inhibition of curcumin on influenza A virus infection and influenzal pneumonia via oxidative stress, TLR2/4, p38/JNK MAPK and NF-κB pathways, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.009
De Faria Coelho-Ravagnani, Corgosinho, Sanches, Dietary recommendations during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuaa067
García-Montero, Fraile-Martínez, Gómez-Lahoz, Nutritional components in western diet versus Mediterranean diet at the gut microbiota-immune system interplay. Implications for health and disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020699
Gavriatopoulou, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Korompoki, Emerging treatment strategies for COVID-19 infection, Clin Exp Med, doi:10.1007/s10238-020-00671-y
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061562
Kelishadi, Rabiee, Khosravi, Assessment of physical activity in adolescents of Isfahan, Shahrekord University Of med Sci J
Krebs-Smith, Pannucci, Subar, Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2015, J Acad Nutr Diet, doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
Li, Yin, Li, Amino acids and immune function, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711450769936X
Mirmiran, Esfahani, Mehrabi, Reliability and relative validity of an FFQ for nutrients in the Tehran lipid and glucose study, Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980009991698
Moscatelli, Sessa, Valenzano, COVID-19: role of nutrition and supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030976
Nikpouraghdam, Farahani, Alishiri, Epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in Iran: a single center study, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104378
Perez-Araluce, Martinez-Gonzalez, Ci, Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the 'Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra' cohort, Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001
Reedy, Lerman, Krebs-Smith, Evaluation of the healthy eating Index-2015, J Acad Nutr Diet, doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.019
Saini, Nile, Park, Carotenoids from fruits and vegetables: chemistry, analysis, occurrence, bioavailability and biological activities, Food Res Int, doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2015.07.047
Sepandi, Taghdir, Alimohamadi, Factors associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Iran J Public Health, doi:10.18502/ijph.v49i7.3574
Sheikhi, Yousefian, Tehranipoor, Estimation of the basic reproduction number of alpha and delta variants of COVID-19 pandemic in Iran, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0265489
Zadeh, Boffetta, Hosseinzadeh, Dietary patterns and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.02.009
Zhu, Ji, Pang, Clinical characteristics of 3062 COVID-19 patients: a metaanalysis, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25884
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/military-2022-002173",
"ISSN": [
"2633-3767",
"2633-3775"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/military-2022-002173",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Proper nutrition can play an important role in preventing and improving disease progression in patients with COVID-19. The Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015) is one of the most common measures used to assess overall nutritional quality. This research aimed to identify the relationship between the HEI-2015 score and disease severity in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This cross-sectional study was conducted in 295 hospitalised military patients (retired military and military reserve) with COVID-19. A validated food frequency questionnaire was used to assess food intake. To evaluate the quality of the diet, the HEI-2015 score was calculated. A multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to measure the association between HEI-2015 scores and disease severity (intensive care unit (ICU) admission and length of hospital stay greater than 4 days) in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The mean HEI-2015 score was significantly higher in non-ICU patients than in ICU patients (58.39±15.02 vs 53.54±15.65, p=0.01). After adjusting for possible confounding factors including age, sex, comorbidities, calorie intake, body mass index and physical activity, adherence to HEI-2015 inversely related to ICU admission (OR 0.98; 95% CI 0.95 to 1.00) and length of hospital stay of more than 4 days (OR 0.99; 95% CI 0.97 to 1.00) in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19, although statistically not significant.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>According to the results of the study, adherence to HEI-2015 inversely related to both ICU admission and length of hospital stay in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19, although it was not statistically significant.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/military-2022-002173"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parastouei",
"given": "Karim",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shokooee Jud",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6441-5887",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sepandi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbaszadeh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samadi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meftahi",
"given": "GH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2853-0196",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Taghdir",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMJ Military Health",
"container-title-short": "BMJ Mil Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T09:48:57Z",
"timestamp": 1666604937000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T09:49:15Z",
"timestamp": 1666604955000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T05:03:31Z",
"timestamp": 1666674211630
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://bmj.com/coronavirus/usage",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1665014400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/military-2022-002173",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e002173",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0265489",
"article-title": "Estimation of the basic reproduction number of alpha and delta variants of COVID-19 pandemic in Iran",
"author": "Sheikhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25884",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.4"
},
{
"article-title": "Case fatality rate of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Alimohamadi",
"first-page": "E311",
"journal-title": "J Prev Med Hyg",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.5",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Sepandi",
"journal-title": "Iran J Public Health",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.6",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238-020-00671-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.8",
"unstructured": "Calder P , Carr A , Gombart A , et al . Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections. Nutrients 2020;12:1181.doi:10.3390/nu12041181"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030976",
"article-title": "COVID-19: role of nutrition and supplementation",
"author": "Moscatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.9",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.019",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the healthy eating Index-2015",
"author": "Reedy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1622",
"journal-title": "J Acad Nutr Diet",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.10",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Assessment of physical activity in adolescents of Isfahan",
"author": "Kelishadi",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Shahrekord University Of med Sci J",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.11",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/01.MSS.0000074446.02192.14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980009991698",
"article-title": "Reliability and relative validity of an FFQ for nutrients in the Tehran lipid and glucose study",
"author": "Mirmiran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "654",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001",
"article-title": "Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the 'Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra' cohort",
"author": "Perez-Araluce",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494",
"article-title": "Application of methylene blue -vitamin C–N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial",
"author": "Alamdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.16",
"volume": "885",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.009",
"article-title": "Inhibition of curcumin on influenza A virus infection and influenzal pneumonia via oxidative stress, TLR2/4, p38/JNK MAPK and NF-κB pathways",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.17",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuaa067",
"article-title": "Dietary recommendations during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "de Faria Coelho-Ravagnani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.18",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodres.2015.07.047",
"article-title": "Carotenoids from fruits and vegetables: chemistry, analysis, occurrence, bioavailability and biological activities",
"author": "Saini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Food Res Int",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.19",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.02.009",
"article-title": "Dietary patterns and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies",
"author": "Hassani Zadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.20",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.plefa.2021.102250",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711450769936X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.629440",
"article-title": "Dairy-derived and egg white proteins in enhancing immune system against COVID-19",
"author": "Batiha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "394",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.24",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020699",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022102402485147000_military-2022-002173v1.25"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://militaryhealth.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/military-2022-002173"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Adherence to Healthy Eating Index-2015 and severity of disease in hospitalised military patients with COVID-19: a cross sectional study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy"
}