Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms role in COVID‐19 severity: Results of a Mexican patients’ cohort
et al., International Journal of Immunogenetics, doi:10.1111/iji.12674, Apr 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
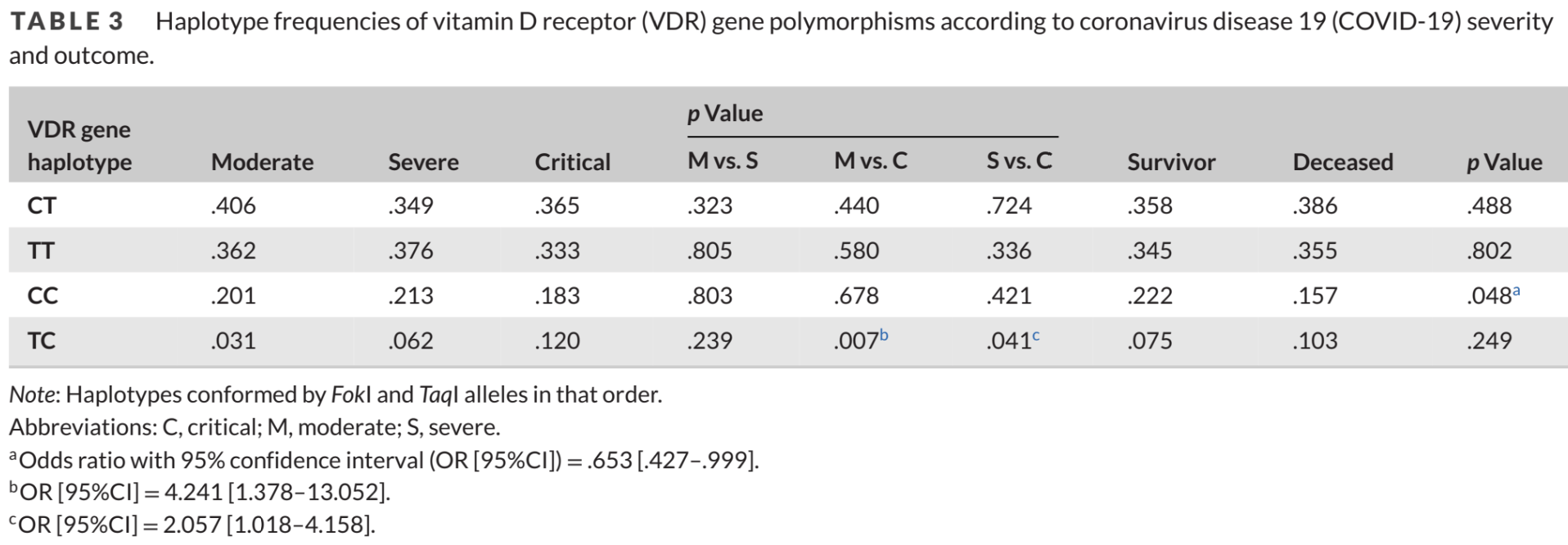
Retrospective 292 COVID-19 patients finding that haplotype TC of the FokI and TaqI vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms was associated with an increased risk of critical COVID-19.
Ochoa-Ramírez et al., 28 Apr 2024, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/iji.12674",
"ISSN": [
"1744-3121",
"1744-313X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/iji.12674",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D status has been involved with coronavirus disease 19 (COVID‐19) severity. This may be mediated by vitamin D metabolism regulatory genes. Of interest is the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene, which has been previously associated with other inflammatory and respiratory diseases. In order to investigate the role of VDR gene polymorphisms in COVID‐19 severity and outcome, a total of 292 COVID‐19 patients were classified according to severity in moderate (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 56), severe (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 89) and critical (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 147) and, according to outcome in survivor (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 163) and deceased (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 129), and analysed for <jats:italic>Fok</jats:italic>I and <jats:italic>Taq</jats:italic>I VDR gene polymorphisms by polymerase chain reaction‐based restriction enzyme digestion. The <jats:italic>Fok</jats:italic>I and <jats:italic>Taq</jats:italic>I single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were not associated with COVID‐19 severity or mortality individually but when analysed by haplotype, TC was associated with an increased risk of presenting critical COVID‐19. Additionally, <jats:italic>Fok</jats:italic>I CT genotype was more frequent in COVID‐19 patients with hypertension, and T allele carriers presented higher aspartate aminotransferase levels. Our results suggest a relationship between VDR <jats:italic>Fok</jats:italic>I and <jats:italic>Taq</jats:italic>I SNPs and COVID‐19 severity in Mexican population. Although there are some previous reports of VDR polymorphisms in COVID‐19, this represents the first report in Latin American population. Further studies on other populations are encouraged.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/iji.12674"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-10-18"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-04-14"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-04-28"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5912-6500",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital General de Culiacán, Servicios de Salud de Sinaloa Culiacan Mexico"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ochoa‐Ramírez",
"given": "Luis Antonio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Maestría en Ciencias Biomédicas, Facultad de Ciencias Químico Biológicas Culiacan Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Corona‐Angulo",
"given": "Alba Lissy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital General de Culiacán, Servicios de Salud de Sinaloa Culiacan Mexico"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación y Docencia en Ciencias de la Salud Culiacan Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Ríos‐Burgueño",
"given": "Efrén Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Facultad de Biología Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa Culiacán Sinaloa Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Sánchez‐Zazueta",
"given": "Jorge Guillermo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1251-3383",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departamento de Aparatos y Sistemas II Universidad Autónoma de Guadalajara Zapopan Jalisco México"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Becerra‐Loaiza",
"given": "Denisse Stephania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital General de Culiacán, Servicios de Salud de Sinaloa Culiacan Mexico"
},
{
"name": "Maestría en Ciencias Biomédicas, Facultad de Ciencias Químico Biológicas Culiacan Mexico"
},
{
"name": "Facultad de Biología Universidad Autónoma de Sinaloa Culiacán Sinaloa Mexico"
}
],
"family": "Velarde‐Félix",
"given": "Jesús Salvador",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Immunogenetics",
"container-title-short": "Int J Immunogenetics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-29T04:04:25Z",
"timestamp": 1714363465000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-29T04:04:32Z",
"timestamp": 1714363472000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-30T00:30:37Z",
"timestamp": 1714437037969
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
28
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714262400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/iji.12674",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes13122346",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14664",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11020400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584‐023‐00944‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgab892",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17179/excli2022‐4976",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen‐2022‐064058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2023.11920",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.689419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365‐2133.2012.11132.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.22877",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1",
"unstructured": "Mexico Government. (2021).Reporte de vigilancia genómica del virus SARS‐CoV‐2 en México.Mexico Government.https://coronavirus.gob.mx/wp‐content/uploads/2021/09/2021.08.30_ReporteVariantesCOVID‐2.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmaa076",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijd.14508",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22034/iji.2022.92641.2162",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21249626",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcmd.2013.02.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2023.03.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization (WHO)",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1",
"volume-title": "Living guidance for clinical management of COVID‐19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12016‐022‐08921‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08820139.2019.1674325",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/iji.12674"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms role in COVID‐19 severity: Results of a Mexican patients’ cohort",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}
