Clinical outcomes of mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 patients treated with Regdanvimab in delta-variant outbreak: Retrospective cohort study
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000035987, Nov 2023
39th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2022, now with p = 0.00049 from 12 studies, recognized in 27 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
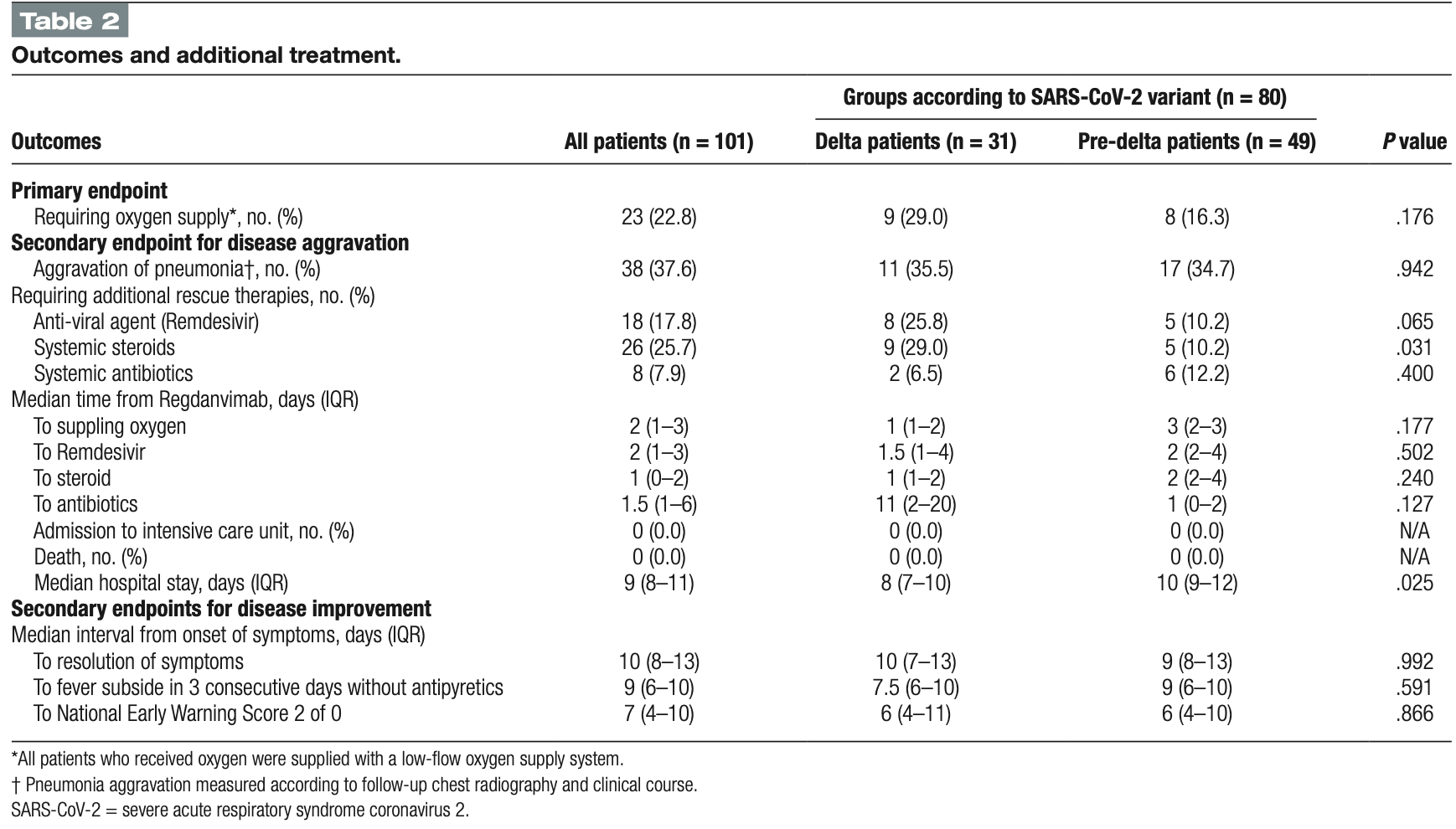
Retrospective 101 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in South Korea examining outcomes with the monoclonal antibody treatment regdanvimab, comparing 31 patients during the delta variant outbreak period to 49 patients with pre-delta variants. About 23% of patients needed oxygen therapy, with no significant difference between delta and pre-delta groups, though delta patients showed higher early risk of requiring oxygen. Around 46% of patients had adverse events, with no significant difference between groups.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2, BA.4, BA.51, ХВВ.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.12.
Noh et al., 10 Nov 2023, retrospective, Australia, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 10 February, 2021 - 31 December, 2021.
Contact: mango8817@gmail.com.
Clinical outcomes of mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 patients treated with Regdanvimab in delta-variant outbreak: Retrospective cohort study
Medicine, doi:10.1097/md.0000000000035987
Regdanvimab is a novel neutralizing antibody agent used for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the effectiveness of regdanvimab in delta-variant patients has rarely been investigated. We examined the clinical outcomes and adverse events in COVID 19 patients treated with regdanvimab in the delta-variant era. Data were collected from laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 hospitalized patients who received regdanvimab in 2021 and categorized into pre-delta and delta variant groups. The primary outcome was the need for oxygen therapy. Rescue therapy, clinical improvement, and adverse events were analyzed. Among 101 patients treated with regdanvimab, 31 (30.7%) were delta patients and 49 (48.5) were pre-delta patients. 64.4% were male, the mean age was 60.3 years, and 70 patients (69%) had at least one underlying disease. The median interval from symptom onset to injection was 4 days. Twenty-three patients (23%) needed oxygen therapy, including 9 (29%) in the delta and 8 (16.3%) in the pre-delta group. (P = .176) The risk of early oxygen supplement was higher in the delta group (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR), 6.75; 95% confidence interval(CI), 1.53-29.8). The in-hospital survival rate was 100%, and no patients were admitted to the intensive care unit. Adverse events occurred in 43% of patients:13 (42%) delta patients and 23 (47%) pre-delta patients had any adverse events (P = .661). Patients treated with regdanvimab 4 days after symptom onset showed a favorable prognosis (aHR, 0.26; 95% CI, 0.26-0.91). We found that the high-risk mild to moderate COVID-19 patients treated with regdanvimab showed similar disease progression in delta-variant patients and pre-delta variants; however, we need to be more closely observed delta-variant patients than those in the pre-delta group despite regdanvimab treatment due to rapid disease aggravation. Abbreviations: aHR = adjusted hazard ratio, CI = confidence interval, COVID-19 = coronavirus disease 2019, NEWS2 = National Early Warning Score 2, SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
References
Abdulrahman, Mallah, Alqahtani, COVID-19 viral load not associated with disease severity: findings from a retrospective cohort study, BMC Infect Dis
Agarwal, Rochwerg, Lamontagne, A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19, BMJ
Chavez, Long, Koyfman, Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): a primer for emergency physicians, Am J Emerg Med
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gandhi, Lynch, Del Rio, Mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hong, Ryu, Hong, Real world experience with regdanvimab treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease-19 in a COVID-19 designated hospital of Korea, Infect Chemother
Isabwe, Neuer, De, Sanchez, Hypersensitivity reactions to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: Phenotypes and endotypes, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Kdcap, Analysis rate and detection rate of COVID-19 mutant virus in Korea
Kim, Joo, Lee, Real-world efficacy of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, J Clin Med
Kim, Ryoo, Huh, Revised Korean Society of infectious diseases/national evidence-based healthcare collaborating agency guidelines on the treatment of patients with COVID-19, Infect Chemother
Kreuzberger, Hirsch, Chai, SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Lee, Lee, Ko, Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment in high-risk COVID-19 patients to prevent progression to severe disease Original Research, Front Immunol
Long, Carius, Chavez, Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency clinician: presentation and evaluation, Am J Emerg Med
Noh, None, Medicine
Ryu, Hong, Lim, Clinical features of adult COVID-19 patients without risk factors before and after the Nationwide SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta)-variant outbreak in Korea: experience from Gyeongsangnam-do, J Korean Med Sci
Ryu, Kang, Noh, The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against Gamma, Delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Streinu-Cercel, Săndulescu, Preotescu, Efficacy and safety of Regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019, Open Forum Infect Dis
Syed, Regdanvimab: first approval, Drugs
Who, WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard
Zheng, Shao, Chen, Real-world effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines: a literature review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000035987",
"ISSN": [
"0025-7974",
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000035987",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Regdanvimab is a novel neutralizing antibody agent used for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the effectiveness of regdanvimab in delta-variant patients has rarely been investigated. We examined the clinical outcomes and adverse events in COVID 19 patients treated with regdanvimab in the delta-variant era. Data were collected from laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 hospitalized patients who received regdanvimab in 2021 and categorized into pre-delta and delta variant groups. The primary outcome was the need for oxygen therapy. Rescue therapy, clinical improvement, and adverse events were analyzed. Among 101 patients treated with regdanvimab, 31 (30.7%) were delta patients and 49 (48.5) were pre-delta patients. 64.4% were male, the mean age was 60.3 years, and 70 patients (69%) had at least one underlying disease. The median interval from symptom onset to injection was 4 days. Twenty-three patients (23%) needed oxygen therapy, including 9 (29%) in the delta and 8 (16.3%) in the pre-delta group. (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .176) The risk of early oxygen supplement was higher in the delta group (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR), 6.75; 95% confidence interval(CI), 1.53–29.8). The in-hospital survival rate was 100%, and no patients were admitted to the intensive care unit. Adverse events occurred in 43% of patients:13 (42%) delta patients and 23 (47%) pre-delta patients had any adverse events (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .661). Patients treated with regdanvimab 4 days after symptom onset showed a favorable prognosis (aHR, 0.26; 95% CI, 0.26–0.91). We found that the high-risk mild to moderate COVID-19 patients treated with regdanvimab showed similar disease progression in delta-variant patients and pre-delta variants; however, we need to be more closely observed delta-variant patients than those in the pre-delta group despite regdanvimab treatment due to rapid disease aggravation.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Noh",
"given": "Hyeong-Jun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Jin Hwa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Ham",
"given": "Sin Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "Yeonkyung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Won",
"given": "Ha-Kyeong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Soo Jung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Keun Bum",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Choon Kwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Ahn",
"given": "Young Mee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Byoung-Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8852-8736",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kang",
"given": "Hye-Rin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-10T19:00:59Z",
"timestamp": 1699642859000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-13T18:00:33Z",
"timestamp": 1699898433000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-14T00:38:48Z",
"timestamp": 1699922328228
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "45",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "45",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1699574400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000035987",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e35987",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.036",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): a primer for emergency physicians.",
"author": "Chavez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "220",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "R2-20231113",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2022.01.028",
"article-title": "Clinical update on COVID-19 for the emergency clinician: presentation and evaluation.",
"author": "Long",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med",
"key": "R3-20231113",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.11.009",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines: a literature review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "R4-20231113",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Kreuzberger",
"first-page": "CD013825",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "R5-20231113",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19.",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R6-20231113",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac053",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Regdanvimab (CT-P59): a phase 2/3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in outpatients with mild-to-moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019.",
"author": "Streinu-Cercel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofac053",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "R8-20231113",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.772320",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of regdanvimab treatment in high-risk COVID-19 patients to prevent progression to severe disease Original Research.",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "772320",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "R10-20231113",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2021.0143",
"article-title": "Real world experience with regdanvimab treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease-19 in a COVID-19 designated hospital of Korea.",
"author": "Hong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Infect Chemother",
"key": "R11-20231113",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11051412",
"article-title": "Real-world efficacy of regdanvimab on clinical outcomes in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1412",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "R12-20231113",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.023",
"article-title": "The in vitro and in vivo efficacy of CT-P59 against Gamma, Delta and its associated variants of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Ryu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "R13-20231113",
"volume": "578",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19.",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "R14-20231113",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-021-01626-7",
"article-title": "Regdanvimab: first approval.",
"author": "Syed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2133",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "R15-20231113",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2021.0303",
"article-title": "Revised Korean Society of infectious diseases/national evidence-based healthcare collaborating agency guidelines on the treatment of patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "Infect Chemother",
"key": "R16-20231113",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009249",
"article-title": "Mild or moderate Covid-19.",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1757",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R17-20231113",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e341",
"article-title": "Clinical features of adult COVID-19 patients without risk factors before and after the Nationwide SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta)-variant outbreak in Korea: experience from Gyeongsangnam-do.",
"author": "Ryu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e341",
"journal-title": "J Korean Med Sci",
"key": "R18-20231113",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.018",
"article-title": "Hypersensitivity reactions to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: Phenotypes and endotypes.",
"author": "Isabwe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "R20-20231113",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06376-1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 viral load not associated with disease severity: findings from a retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Abdulrahman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "688",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "R21-20231113",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 17,
"references-count": 17,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000035987"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical outcomes of mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 patients treated with Regdanvimab in delta-variant outbreak: Retrospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "102"
}