The evaluation of vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor in the case of patients with moderate COVID-19
et al., Farmacia, doi:10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.17, Jun 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
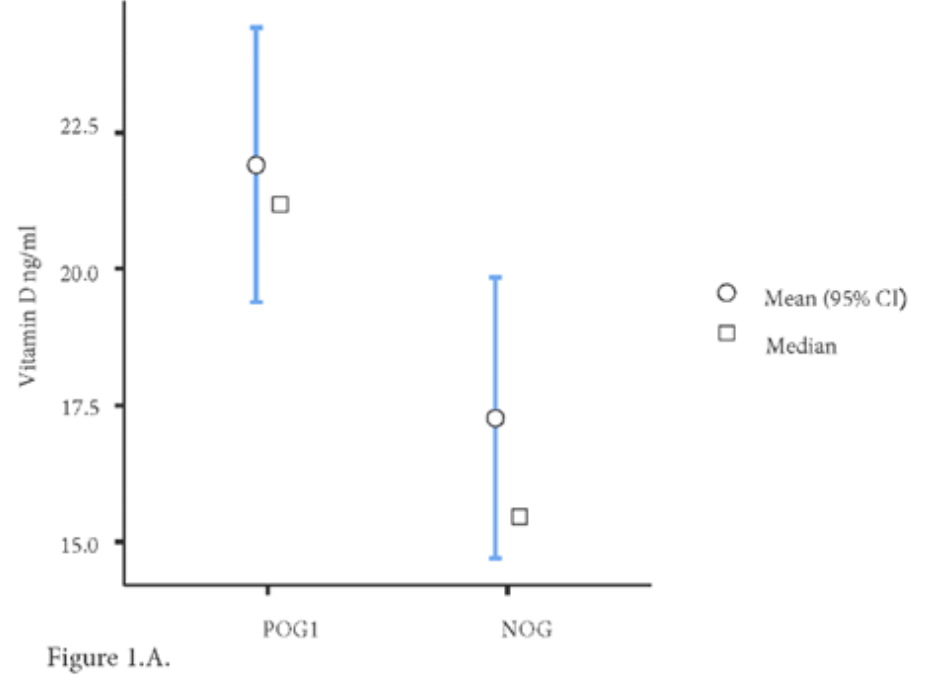
Retrospective 128 hospitalized patients in Romania, showing a negative outcome associated with lower vitamin D levels.
Nicolescu et al., 26 Jun 2022, Romania, peer-reviewed, mean age 66.0, 8 authors, study period January 2021 - April 2021.
Contact: antonius.stanciu@upt.ro.
THE EVALUATION OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY AS A RISK FACTOR IN THE CASE OF PATIENTS WITH MODERATE COVID-19
FARMACIA, doi:10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.17
The paper aimed to evaluate the role of vitamin D in patients with moderate COVID-19. A total number of 128 patients, divided into two groups based on their clinical outcome, were evaluated. The group of patients with a positive outcome consisted of 82 patients (POG), while the group with a negative outcome consisted of 46 patients (NOG). We determined at two different moments (on the patients' admission and their discharge) the plasma level of vitamin D (25-hydroxy vitamin D) along with the levels of inflammatory markers in COVID-19 as C reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), ferritin, fibrinogen, the total leukocyte count and total cholesterol. The level of 25-hydroxy vitamin D was significantly lower in the NOG group when compared to the POG group, while levels of LDH and CRP in the NOG group were significantly higher than those found in the POG group. The levels of CRP and fibrinogen decreased in the POG group during hospitalization. The levels of CRP, as well as the total leukocyte count were inversely correlated with the levels of 25hydroxy vitamin D. This study brings new information on the interaction between vitamin D and pro-inflammatory markers and highlights the role of this vitamin in the modulation of the immune response in patients with moderate COVID-19.
Rezumat Studiul și-a propus evaluarea rolului vitaminei D la pacienți diagnosticați cu COVID-19, formă moderată. Au fost incluși 128 de pacienți care au fost împărțiți, în funcție de evoluția clinică, în două grupuri. Grupul cu evoluție favorabilă (POG) a inclus 82 de pacienți, iar grupul cu evoluție nefavorabilă (NOG) a inclus 46 de pacienți. S-a determinat în două momente diferite (la admisia și la externarea pacienților) nivelul plasmatic al vitaminei D (25-hidroxi-vitamina D), împreună cu cel al markerilor inflamatori precum proteina C reactivă (PCR), lactat-dehidrogenaza (LDH), feritina, fibrinogenul, numărul total de leucocite și colesterolul total. Nivelul plasmatic al 25-hidroxi-vitaminei D a fost semnificativ mai scăzut în NOG comparativ cu POG, în timp ce nivelul LDH-ului și al PCR-ului în NOG au fost semnificativ mai mari comparativ cu cel găsit în POG. Nivelurile PRC-ului și al fibrinogenului au scăzut semnificativ în grupul POG pe timpul spitalizării. Nivelul plasmatic al PCR-ului, precum și numărul total de leucocite s-au corelat invers proporțional cu cel al 25-hidroxi-vitaminei D. Acest studiu aduce noi informații cu privire la interacțiunea între vitamina D și markerii pro-inflamatori și evidențiază rolul acestei vitamine în modularea răspunsului imun în infecția COVID-19, formă moderată.
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum Levels of Vitamin C and Vitamin D in a Cohort of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients of a North American Community Hospital Intensive Care Unit in May 2020: A Pilot Study, Med Drug Discov
Bartziokas, Kostikas, Lactate dehydrogenase, COVID-19 and mortality, Med Clin
Bennouar, Cherif, Kessira, Bennouar, Abdi et al., Deficiency and Low Serum Calcium as Predictors of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Severe COVID-19, J Am Coll Nutr
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest
Chen, Zheng, Liu, Yan, Xu et al., Plasma CRP level is positively associated with the severity of COVID-19, Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob
Cheng, Li, Li, Liu, Yan et al., Ferritin in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Lab Anal
Clyne, Olshaker, The C-reactive protein, J Emerg Med
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation, Blood
Dibaba, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Nutr Rev
Garcia, Fumeaux, Guerci, Heuberger, Montomoli et al., RISC-19-ICU Investigators, Prognostic factors associated with mortality risk and disease progression in 639 critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Europe: Initial report of the international RISC-19-ICU prospective observational cohort, EClinical-Medicine
Ghashut, Talwar, Kinsella, Duncan, Mcmillan, The effect of the systemic inflammatory response on plasma vitamin 25 (OH) D concentrations adjusted for albumin, PLoS One
Giemza-Stokłosa, Islam, Kotyla, Hyperferritinaemia: An Iron Sword of Autoimmunity, Curr Pharm Des
Glueck, Jetty, Rothschild, Duhon, Shah et al., Associations between Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Lipids, Lipoprotein Cholesterols, and Homocysteine, N Am J Med Sci
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients
Gómez-Pastora, Weigand, Kim, Wu, Strayer et al., Hyperferritinemia in critically ill COVID-19 patients -Is ferritin the product of inflammation or a pathogenic mediator?, Clin Chim Acta
Henry, Aggarwal, Wong, Benoit, Vikse et al., Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis, Am J Emerg Med
Herold, Jurinovic, Arnreich, Lipworth, Hellmuth et al., Elevated levels of IL-6 and CRP predict the need for mechanical ventilation in COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Iba, Levy, Levi, Connors, Thachil, Coagulopathy of Coronavirus Disease 2019, Crit Care Med
Islam, Salehi, Karampelas, Sharifi-Rad, Docea et al., High skin melanin content, vitamin D deficiency and immunity: potential interference for severity of COVID-19, Farmacia
Ji, Zhu, Zhong, Li, Pang et al., Association of elevated inflammatory markers and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis, Medicine (Baltimore)
Kappert, Jahić, Tauber, Assessment of serum ferritin as a biomarker in COVID-19: bystander or participant? Insights by comparison with other infectious and non-infectious diseases, Biomarkers
Kishaba, Tamaki, Shimaoka, Fukuyama, Yamashiro, Staging of acute exacerbation in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Lung
Laaksi, Ruohola, Tuohimaa, Auvinen, Haataja et al., An association of serum vitamin D concentrations < 40 nmol/L with acute respiratory tract infection in young Finnish men, Am J Clin Nutr
Liu, Schenk, Walker, Dempsey, Kanchanapoomi et al., Convergence of IL-1beta and VDR activation pathways in human TLR2/1-induced antimicrobial responses, PLoS One
Lu, Wei, Jiang, Cheng, Chen et al., Lactate dehydrogenase is associated with 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis: a retrospective observational study, J Surg Res
Malik, Patel, Mehta, Patel, Kelkar et al., Biomarkers and outcomes of COVID-19 hospitalisations: systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Evid Based Med
Martha, Wibowo, Pranata, Prognostic value of elevated lactate dehydrogenase in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Postgrad Med J
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mititelu, Stanciu, Udeanu, Popa, Drăgănescu et al., The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the lifestyle and dietary patterns among Romanian population, Farmacia
Muldoon, Bachen, Manuck, Waldstein, Bricker et al., Acute cholesterol responses to mental stress and change in posture, Arch Intern Med
Nair, Maseeh, Vitamin, The "sunshine" vitamin, J Pharmacol Pharmacother
Owen, Tran, Hammarberg, Kirkman, Fisher, Restrictions Impact Research Group. Poor appetite and overeating reported by adults in Australia during the Coronavirus-19 disease pandemic: a population-based study, Public Health Nutr
Patterson, Gottdiener, Hecht, Vargot, Krantz, Effects of acute mental stress on serum lipids: mediating effects of plasma volume, Psychosom Med
Rashedi, Poor, Asgharzadeh, Pourostadi, Samadikafil et al., Risk Factors for COVID-19, Infez Med
Rodebaugh, Frumkin, Reiersen, Lenze, Avidan et al., Acute Symptoms of Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Are Highly Heterogeneous Across Individuals and Over Time, Open Forum Infect Dis
Roth, Abrams, Aloia, Bergeron, Bourassa et al., Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: a roadmap for action in lowand middle-income countries, Ann N Y Acad Sci
Sadeghi-Haddad-Zavareh, Bayani, Shokri, Ebrahimpour, Babazadeh et al., Reactive Protein as a Prognostic Indicator in COVID-19 Patients, Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis
Salari, Hosseinian-Far, Jalali, Vaisi-Raygani, Rasoulpoor et al., Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Global Health
Shu, Wang, Li, Chen, Ji et al., Clinical characteristics of moderate COVID-19 patients aggravation in Wuhan Stadium Cabin Hospital: A 571 cases of retrospective cohort study, J Med Virol
Soraya, Ulhaq, Crucial laboratory parameters in COVID-19 diagnosis and prognosis: An updated meta-analysis, Med Clin
Thachil, The protective rather than prothrombotic fibrinogen in COVID-19 and other inflammatory states, J Thromb Haemost
Tunescu, Christodorescu, Sharma, Barsac, Rogobete et al., The preoperative evaluation of post-COVID-19 patients scheduled for elective surgery What is important not to miss!, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Vargas-Vargas, Cortés-Rojo, Ferritin levels and COVID-19, Rev Panam Salud Publica
Vidal-Cevallos, Higuera-De-La-Tijera, Chávez-Tapia, Sanchez-Giron, Cerda-Reyes et al., Lactate-dehydrogenase associated with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Mexico: a multi-centre retrospective cohort study, Ann Hepatol
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin Med
Who, WHO announces COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic
Xu, Chen, Wang, Feng, Zhou et al., Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission, Sci China Life Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.17",
"ISSN": [
"0014-8237"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.31925/farmacia.2022.3.17",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "NICOLESCU",
"given": "LAURA-CORINA",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "FARMACIA",
"container-title-short": "FARMACIA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-14T07:38:11Z",
"timestamp": 1657784291000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-14T07:39:18Z",
"timestamp": 1657784358000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-19T05:10:33Z",
"timestamp": 1663564233709
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
}
},
"member": "17217",
"original-title": [],
"page": "507-513",
"prefix": "10.31925",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Societatea de Stiinte Farmaceutice din Romania",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://farmaciajournal.com/issue-articles/the-evaluation-of-vitamin-d-deficiency-as-a-risk-factor-in-the-case-of-patients-with-moderate-covid-19/"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "THE EVALUATION OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY AS A RISK FACTOR IN THE CASE OF PATIENTS WITH MODERATE COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "70"
}
