Screening Commercial Tea for Rapid Inactivation of Infectious SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva
et al., Food and Environmental Virology, doi:10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0, Jan 2024
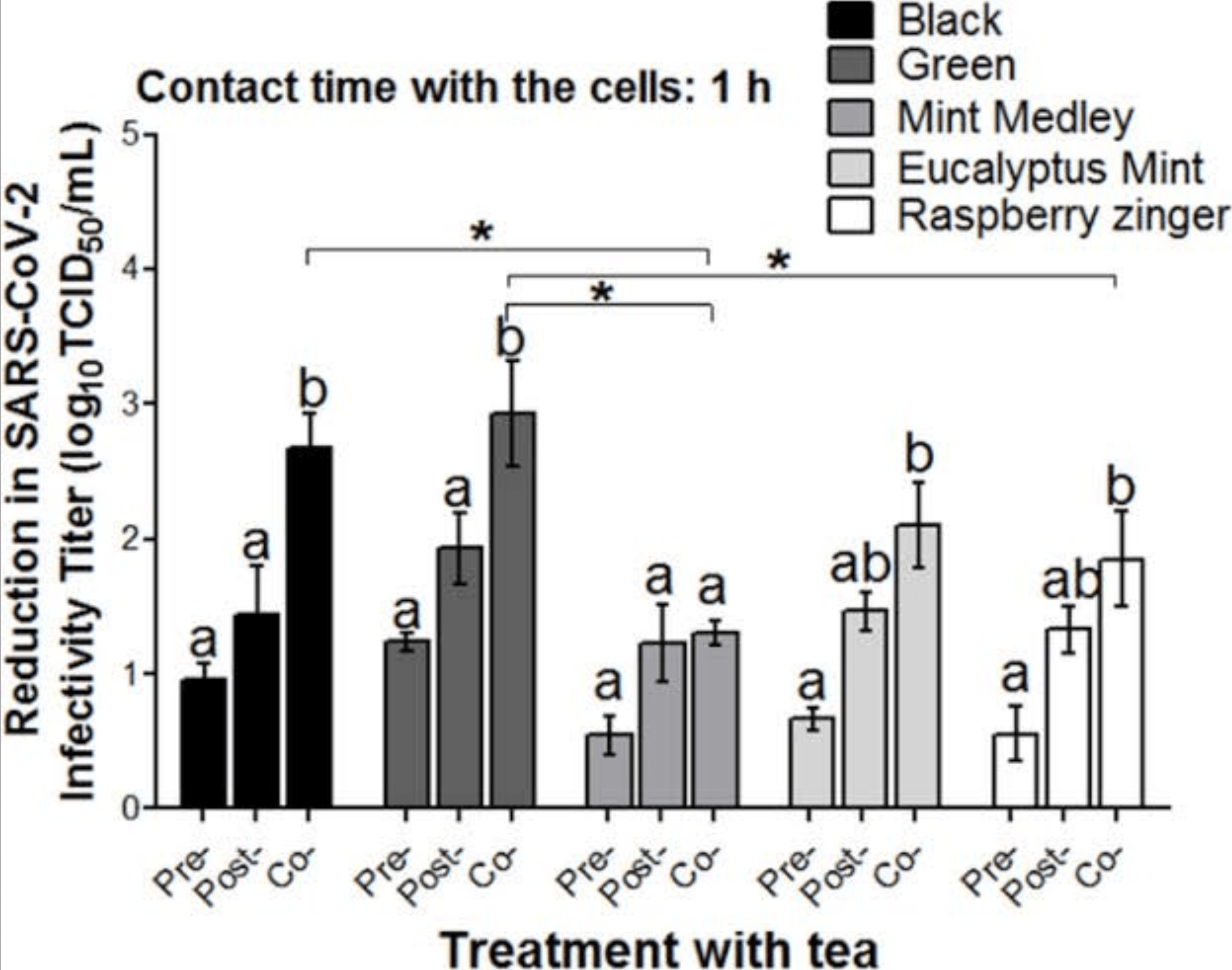
In vitro study showing that certain teas can rapidly inactivate SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. At 10 mg/mL infusion, black tea showed the highest reduction (99.9%) of infectious SARS-CoV-2 within 10 seconds. Green, mint medley, eucalyptus mint, and raspberry zinger teas showed 96-99% inactivation at the same concentration. At 40 mg/mL infusions, all five teas inactivated 99.9% of the virus within 10 seconds. Tea polyphenol content, but not pH, significantly correlated with virus reduction. The teas also exhibited preventive effects against SARS-CoV-2 infection of Vero-E6 cells when added before (68-90% reduction), during (99-99.9% reduction), or after (94-98% reduction) virus infection, with the strongest inhibition observed when teas were added at the time of infection. Authors suggest that drinking or gargling tea could be a rapid at-home intervention to reduce infectious SARS-CoV-2 load in the oral cavity and potentially mitigate infection of the oral mucosa.
Morris et al., 31 Jan 2024, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0",
"ISSN": [
"1867-0334",
"1867-0342"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0",
"alternative-id": [
"9581"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 September 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "30 December 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "31 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Julianna N.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1024-0468",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Esseili",
"given": "Malak A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Food and Environmental Virology",
"container-title-short": "Food Environ Virol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-31T10:02:52Z",
"timestamp": 1706695372000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-31T10:33:35Z",
"timestamp": 1706697215000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007699",
"award": [
"Startup Fund"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "University of Georgia"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-01T00:38:30Z",
"timestamp": 1706747910004
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1706659200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1706659200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15030771",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR1",
"unstructured": "Arora, I., White, S., & Mathews, R. (2023). Global dietary and herbal supplement use during COVID-19: A scoping review. Nutrients, 15, 771."
},
{
"key": "9581_CR2",
"unstructured": "CDC. (2022). Symptoms of COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00104",
"author": "O Chou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1428",
"journal-title": "Journal of Natural Products",
"key": "9581_CR3",
"unstructured": "Chou, O., Juang, Y. P., Chao, T. L., Tsai, S. F., Chiu, P. F., Chiou, C. T., Tsai, K. C., Chang, S. Y., Liang, P. H., & Wong, C. H. (2023). Isolation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 natural products extracted from Mentha canadensis and the semi-synthesis of antiviral derivatives. Journal of Natural Products, 86, 1428–1436.",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpls.2022.934651",
"author": "JC D'Auria",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Plant Science",
"key": "9581_CR4",
"unstructured": "D’Auria, J. C., Cohen, S. P., Leung, J., Glockzin, K., Glockzin, K. M., Gervay-Hague, J., Zhang, D., & Meinhardt, L. W. (2022). United States tea: A synopsis of ongoing tea research and solutions to United States tea production issues. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 934651.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.108888",
"author": "S Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Building and Environment",
"key": "9581_CR5",
"unstructured": "Ding, S., Lee, J. S., Mohamed, M. A., & Ng, B. F. (2022). Infection risk of SARS-CoV-2 in a dining setting: Deposited droplets and aerosols. Building and Environment, 213, 108888.",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7431",
"author": "M Eggers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2109",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "9581_CR6",
"unstructured": "Eggers, M., Jungke, P., Wolkinger, V., Bauer, R., Kessler, U., & Frank, B. (2022). Antiviral activity of plant juices and green tea against SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus. Phytotherapy Research, 36, 2109–2115.",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bk-2004-0871.ch016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR7",
"unstructured": "Ekanayake, A., & Li, J. (2004). Processing green tea extracts to make a beverage ingredient. In F. Shahidi & D. K. Weerasinghe (Ed.), Nutraceutical beveages. American Chemical Society."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12275-021-1467-z",
"author": "E Espano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "959",
"journal-title": "Journal of Microbiology",
"key": "9581_CR8",
"unstructured": "Espano, E., Kim, J., Lee, K., & Kim, J. K. (2021). Phytochemicals for the treatment of COVID-19. Journal of Microbiology, 59, 959–977.",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-518",
"author": "MA Esseili",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1472",
"journal-title": "Journal of Food Protection",
"key": "9581_CR9",
"unstructured": "Esseili, M. A., Chin, A., Saif, L., Miller, S. A., Qu, F., Lewis Ivey, M. L., & Wang, Q. (2015). Postharvest survival of porcine sapovirus, a human norovirus surrogate, on phytopathogen-infected leafy greens. Journal of Food Protection, 78, 1472–1480.",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fm.2022.104084",
"author": "MA Esseili",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Food Microbiology",
"key": "9581_CR10",
"unstructured": "Esseili, M. A., Mann, A., Narwankar, R., Kassem, I. I., Diez-Gonzalez, F., & Hogan, R. J. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 remains infectious for at least a month on artificially-contaminated frozen berries. Food Microbiology, 107, 104084.",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12968",
"author": "J Ge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "9581_CR11",
"unstructured": "Ge, J., Song, T., Li, M., Chen, W., Li, J., Gong, S., Zhao, Y., Ma, L., Yu, H., Li, X., & Fu, K. (2023). The medicinal value of tea drinking in the management of COVID-19. Heliyon, 9, e12968.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0253489",
"author": "A Goc",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "9581_CR12",
"unstructured": "Goc, A., Sumera, W., Rath, M., & Niedzwiecki, A. (2021). Phenolic compounds disrupt spike-mediated receptor-binding and entry of SARS-CoV-2 pseudo-virions. PLoS ONE, 16, e0253489.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03640-2",
"author": "D Harmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "FEBS Letters",
"key": "9581_CR13",
"unstructured": "Harmer, D., Gilbert, M., Borman, R., & Clark, K. L. (2002). Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme. FEBS Letters, 532, 107–110.",
"volume": "532",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jix224",
"author": "R Hirose",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "9581_CR14",
"unstructured": "Hirose, R., Nakaya, T., Naito, Y., Daidoji, T., Watanabe, Y., Yasuda, H., Konishi, H., & Itoh, Y. (2017). Mechanism of human influenza virus RNA persistence and virion survival in feces: Mucus protects virions from acid and digestive juices. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 216, 105–109.",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "9581_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hudson, J. B. (1990). The choice and use of plant materials. In Antiviral compounds from plants. CRC Press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/lam.13591",
"author": "K Ishimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Letters in Applied Microbiology",
"key": "9581_CR16",
"unstructured": "Ishimoto, K., Hatanaka, N., Otani, S., Maeda, S., Xu, B., Yasugi, M., Moore, J. E., Suzuki, M., Nakagawa, S., & Yamasaki, S. (2022). Tea crude extracts effectively inactivate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 74, 2–7.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/froh.2022.1001790",
"author": "P Iyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1001790",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Oral Health",
"key": "9581_CR17",
"unstructured": "Iyer, P., Chino, T., & Ojcius, D. M. (2022). Infection of the oral cavity with SARS-CoV-2 variants: Scope of salivary diagnostics. Frontiers in Oral Health, 3, 1001790.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2021579118",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR18",
"unstructured": "Jan, J. T., Cheng, T. R., Juang, Y. P., Ma, H. H., Wu, Y. T., Yang, W. B., Cheng, C. W., Chen, X., Chou, T. H., Shie, J. J., Cheng, W. C., Chein, R. J., Mao, S. S., Liang, P. H., Ma, C., Hung, S. C., & Wong, C. H. (2021). Identification of existing pharmaceuticals and herbal medicines as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153970",
"author": "E Kicker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "9581_CR19",
"unstructured": "Kicker, E., Tittel, G., Schaller, T., Pferschy-Wenzig, E. M., Zatloukal, K., & Bauer, R. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing activity of polyphenols in a special green tea extract preparation. Phytomedicine, 98, 153970.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12915-022-01468-z",
"author": "VTK Le-Trilling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "BMC Biology",
"key": "9581_CR20",
"unstructured": "Le-Trilling, V. T. K., Mennerich, D., Schuler, C., Sakson, R., Lill, J. K., Kasarla, S. S., Kopczynski, D., Loroch, S., Flores-Martinez, Y., Katschinski, B., Wohlgemuth, K., Gunzer, M., Meyer, F., Phapale, P., Dittmer, U., Sickmann, A., & Trilling, M. (2022). Identification of herbal teas and their compounds eliciting antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. BMC Biology, 20, 264.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13578-021-00680-8",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Cell & Bioscience",
"key": "9581_CR21",
"unstructured": "Liu, J., Bodnar, B. H., Meng, F., Khan, A. I., Wang, Xu., Saribas, S., Wang, T., Lohani, S. C., Wang, P., Wei, Z., Luo, J., Zhou, L., Jianguo, Wu., Luo, G., Li, Q., Wenhui, Hu., & Ho, W. (2021). Epigallocatechin gallate from green tea effectively blocks infection of SARS-CoV-2 and new variants by inhibiting spike binding to ACE2 receptor. Cell & Bioscience, 11, 168.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JPER.21-0277",
"author": "JT Marchesan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1357",
"journal-title": "Journal of Periodontology",
"key": "9581_CR22",
"unstructured": "Marchesan, J. T., Warner, B. M., & Byrd, K. M. (2021). The “oral” history of COVID-19: Primary infection, salivary transmission, and post-acute implications. Journal of Periodontology, 92, 1357–1367.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph14121210",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR23",
"unstructured": "Mieres-Castro, D., Ahmar, S., Shabbir, R., & Mora-Poblete, F. (2021). Antiviral activities of eucalyptus essential oils: Their effectiveness as therapeutic targets against human viruses. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 14, 1210."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2023.116291",
"author": "MS Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Journal of Ethnopharmacology",
"key": "9581_CR24",
"unstructured": "Nair, M. S., Huang, Y., Wang, M., & Weathers, P. J. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants are susceptible in vitro to Artemisia annua hot water extracts. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 308, 116291.",
"volume": "308",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-022-05483-x",
"author": "MM Ngwe Tun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1547",
"journal-title": "Archives of Virology",
"key": "9581_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ngwe Tun, M. M., Luvai, E., Nwe, K. M., Toume, K., Mizukami, S., Hirayama, K., Komatsu, K., & Morita, K. (2022). Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of various PET-bottled Japanese green teas and tea compounds in vitro. Archives of Virology, 167, 1547–1557.",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7883/yoken.JJID.2020.902",
"author": "H Nishimura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "421",
"journal-title": "Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "9581_CR26",
"unstructured": "Nishimura, H., Okamoto, M., Dapat, I., Katsumi, M., & Oshitani, H. (2021). Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by catechins from green tea. Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases, 74, 421–423.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060721",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR27",
"unstructured": "Ohgitani, E., Shin-Ya, M., Ichitani, M., Kobayashi, M., Takihara, T., Kawamoto, M., Kinugasa, H., & Mazda, O. (2021a). Rapid inactivation in vitro of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva by black tea and green tea. Pathogens, 10, 721."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26123572",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR28",
"unstructured": "Ohgitani, E., Shin-Ya, M., Ichitani, M., Kobayashi, M., Takihara, T., Kawamoto, M., Kinugasa, H., & Mazda, O. (2021b). Significant inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro by a green tea catechin, a catechin-derivative, and black tea galloylated theaflavins. Molecules, 26, 3572."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0271112",
"author": "T Ohishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "9581_CR29",
"unstructured": "Ohishi, T., Hishiki, T., Baig, M. S., Rajpoot, S., Saqib, U., Takasaki, T., & Hara, Y. (2022). Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) attenuates severe acute respiratory coronavirus disease 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection by blocking the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. PLoS ONE, 17, e0271112.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "9581_CR30",
"unstructured": "Payment, P., & Trudel, M. (1993). Isolation and identification of viruses. In P. Payment & M. Trudel (Eds.), Methods and techniques in virology. Mercel Deckker."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fm.2023.104297",
"author": "A Saulnier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Food Microbiology",
"key": "9581_CR31",
"unstructured": "Saulnier, A., Wendling, J. M., Hermant, B., & Lepelletier, D. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 transmission modes: Why and how contamination occurs around shared meals and drinks? Food Microbiology, 114, 104297.",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10030446",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9581_CR32",
"unstructured": "Thakur, V., Ratho, R. K., Kumar, P., Bhatia, S. K., Bora, I., Mohi, G. K., Saxena, S. K., Devi, M., Yadav, D., & Mehariya, S. (2021). Multi-organ involvement in COVID-19: Beyond pulmonary manifestations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10, 446."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.606782",
"author": "FU Umeoguaju",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Nutrition",
"key": "9581_CR33",
"unstructured": "Umeoguaju, F. U., Ephraim-Emmanuel, B. C., Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K. C., Zelikoff, J. T., & Orisakwe, O. E. (2021). Plant-derived food grade substances (PDFGS) active against respiratory viruses: A systematic review of non-clinical studies. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8, 606782.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241539",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "9581_CR34",
"unstructured": "Wang, Y., Xu, G., & Huang, Y. W. (2020). Modeling the load of SARS-CoV-2 virus in human expelled particles during coughing and speaking. PLoS ONE, 15, e0241539.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "9581_CR35",
"unstructured": "WHO. (2023). COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update. Accessed 8 August 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---3-august-2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0074-x",
"author": "H Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Oral Science",
"key": "9581_CR36",
"unstructured": "Xu, H., Zhong, L., Deng, J., Peng, J., Dan, H., Zeng, X., Li, T., & Chen, Q. (2020). High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. International Journal of Oral Science, 12, 8.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/acm.2006.12.669",
"author": "H Yamada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine",
"key": "9581_CR37",
"unstructured": "Yamada, H., Takuma, N., Daimon, T., & Hara, Y. (2006). Gargling with tea catechin extracts for the prevention of influenza infection in elderly nursing home residents: A prospective clinical study. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 12, 669–672.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.027",
"author": "H Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "9581_CR38",
"unstructured": "Zhang, H., Li, H. B., Lyu, J. R., Lei, X. M., Li, W., Wu, G., Lyu, J., & Dai, Z. M. (2020). Specific ACE2 expression in small intestinal enterocytes may cause gastrointestinal symptoms and injury after 2019-nCoV infection. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 96, 19–24.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"author": "P Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9581_CR39",
"unstructured": "Zhou, P., Yang, X. L., Wang, X. G., Hu, B., Zhang, L., Zhang, W., Si, H. R., Zhu, Y., Li, B., Huang, C. L., Chen, H. D., Chen, J., Luo, Y., Guo, H., Jiang, R. D., Liu, M. Q., Chen, Y., Shen, X. R., Wang, X., … Shi, Z. L. (2020). A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature, 579, 270–273.",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12560-023-09581-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Health, Toxicology and Mutagenesis",
"Food Science",
"Epidemiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Screening Commercial Tea for Rapid Inactivation of Infectious SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}