Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Pediatric COVID‐19: A Retrospective Study
et al., Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.70181, Nov 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
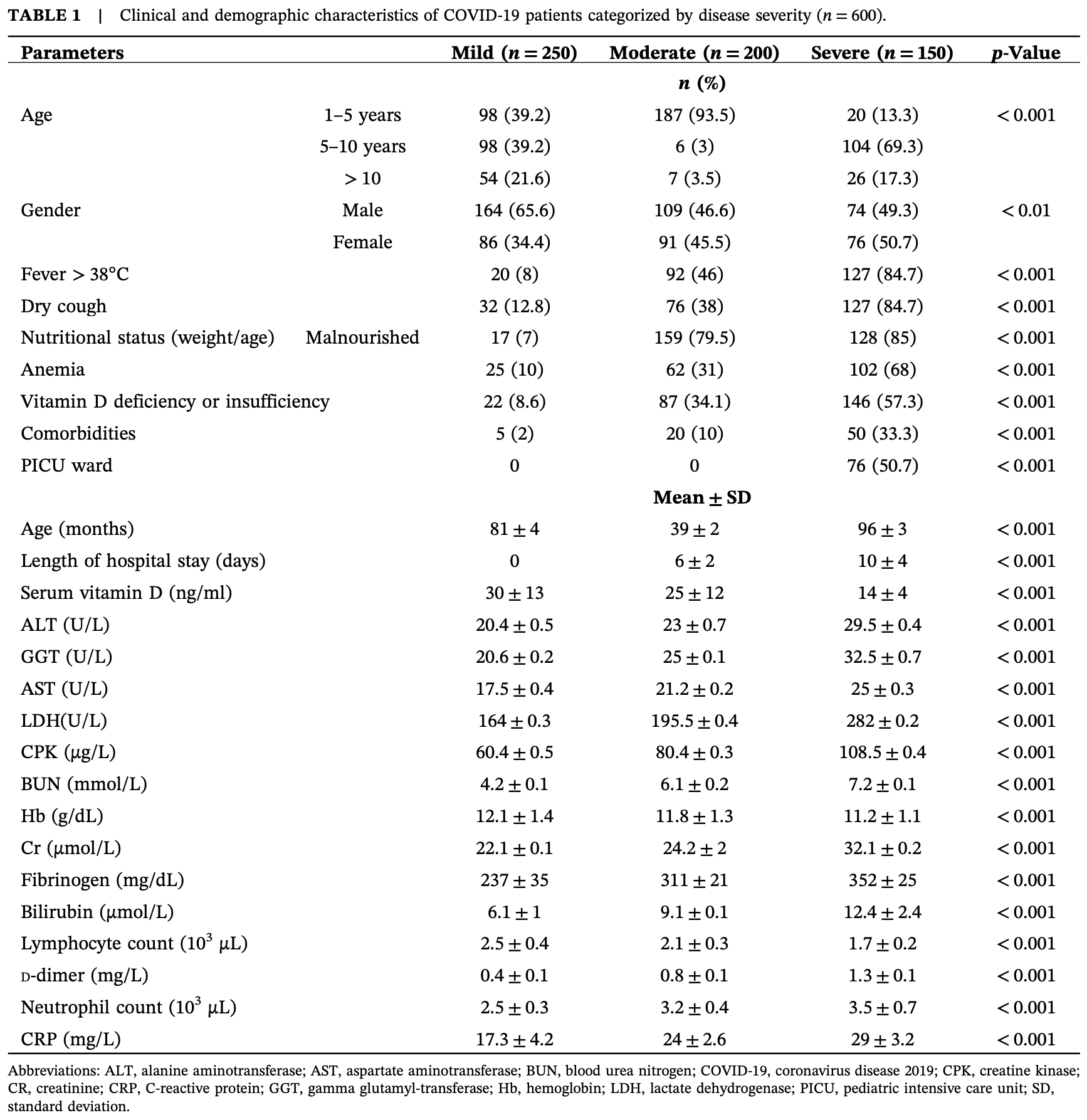
Retrospective 600 hospitalized pediatric COVID-19 patients, showing vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency associated with COVID-19 severity.
This is the 207th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of moderate/severe case, 62.9% lower, RR 0.37, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥20 ng/mL) 117 of 345 (33.9%), low D levels (<20 ng/mL) 233 of 255 (91.4%), NNT 1.7, moderate/severe vs. mild.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mirkarimi et al., 6 Nov 2024, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period May 2022 - May 2023.
Contact: drmalisamir@yahoo.com.
Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Pediatric COVID‐19: A Retrospective Study
Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.70181
Background and Aims: There is a demand for additional data regarding the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on the pediatric population. This study sought to determine the clinical and epidemiological features of pediatric COVID-19 in Iran. Methods: A retrospective study was performed to assess medical records of children with COVID-19 admitted to Abuzar Hospital in Ahvaz (Iran). Their clinical and demographic data were recorded. Results: In this study, 600 medical records of pediatric COVID-19 patients were evaluated. Over 50% of them were boys. Mild, moderate, and severe manifestations of COVID-19 were identified in 250, 200, and 150 children, respectively. Patients with severe or moderate COVID-19 had substantially higher levels of various inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen, and D-dimer), alanine transaminase (ALT), creatine kinase (CPK), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), neutrophils, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), creatinine (Cr), bilirubin, and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) compared to children with mild COVID-19 (p < 0.001); they also had lower levels of lymphocytes, hemoglobin (Hb), and vitamin D than patients with mild COVID-19 (p < 0.001). In addition, children with severe or moderate COVID-19 had a notably higher incidence of fever or dry cough and longer hospital stays than those with mild COVID-19 (p < 0.001). The prevalence of malnutrition and anemia in patients was 50.6% and 31.5%, respectively. A significant proportion of children who were underweight and stunted experienced moderate to severe COVID-19. Furthermore, there was a considerably higher prevalence of malnutrition, anemia, and vitamin D insufficiency, or deficiency in children with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 compared to patients with mild COVID-19 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The outcomes of this study revealed a significantly higher prevalence of malnutrition, anemia, vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency, elevated liver and kidney function test results, and increased inflammatory markers in children with moderate to severe COVID-19 compared to those with mild COVID-19.
| Introduction Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly pathogenic, contagious, and easily transmissible infection [1] . The outbreak of COVID-19 has created a global public health challenge and an emerging threat [2] . The majority of children with COVID-19 experienced less severe COVID-19 disease progression and had better outcomes than adults [3, 4] . The global prevalence of pediatric deaths and severe cases was approximately 0.3% and 0.6%-5%, respectively [5] . At the population level, children comprise a small percentage of COVID-19 infections, and they are typically acquired through adult contact [6, 7] .
Author Contributions Mohammadreza Mirkarimi: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, writing-review and editing. Solmaz Heidari: data curation, methodology, project administration, supervision, writing-review and editing, resources. Ahmad Shamsizadeh: project administration, writing-review and editing, supervision. Kia Tahouri: data curation, investigation, writing-review and editing. Mohsen Alisamir: conceptualization, data curation, writingreview and editing, project administration, supervision, investigation, methodology, resources. Mohammadreza Fathi: writing-review and editing, supervision, project administration. Shooka Mohammadi: writing-review and editing, writing-original draft, formal analysis, data curation.
Ethics Statement The medical ethics committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (AJUMS) approved the protocol of the study (IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.821).
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Standard of Reporting The STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) checklist has been followed in this study.
References
Abbas, Khalid, Shahbaz, Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Pediatric Population Hospitalized With COVID-19: A Multicenter Longitudinal Study (March 2020-December 2021) From Pakistan, The Lancet Regional Health-Southeast Asia
Alisamir, Mirkarimi, Mirzaee, Heidari, Barouti et al., Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted to a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in Southwest Iran, Acta Medica Iranica
Aminasnafi, Heidari, Alisamir, Mirkarimi, Namehgoshayfard et al., Hematologic Evaluation of Children With COVID-19 Infection: Mortality Biomarkers, Clinical Laboratory
Armin, Mirkarimi, Pourmoghaddas, Evidence-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity in Hospitalized Children, International Journal of Clinical Practice
Armin, Mirkarimi, Pourmoghaddas, Iranian Pediatric COVID-19 Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics, Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology
Aydın, Dalgıç, Kansu, The Significance of Muac Z-Scores in Diagnosing Pediatric Malnutrition: A Scoping Review With Special Emphasis on Neurologically Disabled Children, Frontiers in Pediatrics
Bayramoğlu, Akkoç, Ağbaş, The Association Between Vitamin D Levels and the Clinical Severity and Inflammation Markers in Pediatric COVID-19 Patients: Single-Center Experience From a Pandemic Hospital, European Journal of Pediatrics
Becker, Carney, Corkins, Consensus Statement of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics/American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Indicators Recommended for the Identification and Documentation of Pediatric Malnutrition (Undernutrition), Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics
Benoit, Benoit, De Oliveira, Lippi, Henry, Anemia and COVID-19: A Prospective Perspective, Journal of Medical Virology
Bhuiyan, Stiboy, Hassan, Epidemiology of COVID-19 Infection in Young Children Under Five Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Vaccine
Böger, Fachi, Vilhena, Cobre, Tonin et al., Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of the Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests for Covid-19, American Journal of Infection Control
Castagnoli, Votto, Licari, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review, JAMA Pediatrics
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study, The Lancet
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for Possible Association of Vitamin D Status With Cytokine Storm and Unregulated Inflammation in COVID-19 Patients, Aging Clinical and Experimental Research
Demir, Demir, Aygun, Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated With COVID-19 Positivity and Severity of the Disease, Journal of Medical Virology
Dong, Mo, Hu, Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China, Pediatrics
Fahimzad, Sedighi, Pak, A Comparative Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Laboratory Findings of COVID-19 Between Intensive Care Unit and Non-Intensive Care Unit Pediatric Patients: A Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study From Iranian Network for Research in Viral, Frontiers in Emergency Medicine
Fan, Chen, Li, Clinical Features of COVID-19-related Liver Functional Abnormality, Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Guo, He, Yin, Epidemiological and Clinical Features of Pediatric COVID-19, BMC Medicine
Hariyanto, Kurniawan, Anemia Is Associated With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection, Transfusion and Apheresis Science
Harwood, Yan, Talawila Da, Camara, Which Children and Young People Are at Higher Risk of Severe Disease and Death after Hospitalisation With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Young People: A Systematic Review and Individual Patient Meta-Analysis, EClinicalMedicine
Heidari, Mohammadi, Fathi, Association of Vitamin D Status With COVID-19 Disease Severity in Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study, Health Science Reports
Heidari, Torabizadeh, Shokouhifar, Mirkarimi, Alisamir et al., Association of Asthma With COVID-19 Disease Severity in Pediatric Patients, Current Respiratory Medicine Reviews
Henry, Lippi, Plebani, Laboratory Abnormalities in Children With Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019, Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM)
Hon, Leung, Cheng, Clinical Presentations and Outcome of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in Children, The Lancet
Howard-Jones, Bowen, Danchin, COVID-19 in Children: I. Epidemiology, Prevention and Indirect Impacts, Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical Features of Patients Infected With 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The Lancet
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The Role of Vitamin D in the Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Mortality, Aging Clinical and Experimental Research
James, Ali, Armitage, The Role of Nutrition in COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity of Disease: A Systematic Review, The Journal of Nutrition
Jima, Atomsa, Allard, Nigatu, The Effect of Malnutrition on Adult COVID-19 Patient's ICU Admission and Mortality in COVID-19 Isolation and Treatment Centers in Ethiopia: A Prospective Cohort Study, Plos One
Kurtz, Grant, Marano, Long-Term Effects of Malnutrition on Severity of Covid-19, Scientific Reports
Ludvigsson, Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis Than Adults, Acta Paediatrica
Mansourian, Ghandi, Habibi, Mehrabi, COVID-19 Infection in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Features and Laboratory Findings, Archives de Pédiatrie
Mehraeen, Oliaei, Seyedalinaghi, COVID-19 in Pediatrics: A Systematic Review of Current Knowledge and Practice, Infectious Disorders -Drug Targets
Mirkarimi, Alisamir, Nasiri, Barouti, Mohammadi, Determinants of Complicated Pneumonia in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients, Acta Medica Iranica
Mirkarimi, Alisamir, Saraf, Heidari, Barouti et al., Clinical and Epidemiological Determinants of Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients, International Journal of Pediatrics
Mohammedsaeed, Alsehli, Alfarsi, COVID-19 in Pediatric Patients: A Study Based on Biomarker Levels, Cureus
Munns, Shaw, Kiely, Global Consensus Recommendations on Prevention and Management of Nutritional Rickets, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
Peng, Outbreak of COVID-19: An Emerging Global Pandemic Threat, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie
Polatoğlu, Oncu-Oner, Dalman, Ozdogan, COVID-19 in Early 2023: Structure, Replication Mechanism, Variants of SARS-CoV-2, Diagnostic Tests, and Vaccine & Drug Development Studies, MedComm
Qu, Zhu, Huang, Abnormal Indexes of Liver and Kidney Injury Markers Predict Severity in COVID-19 Patients, Infection and Drug Resistance
Riphagen, Gomez, Gonzalez-Martinez, Wilkinson, Theocharis, Hyperinflammatory Shock in Children During COVID-19 Pandemic, The Lancet
Satdhabudha, Chaiyakulsil, Sritipsukho, Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 in the Tertiary Care System in Thailand: Comparative Delta and Pre-Delta Era, Mediterranean Journal of Hematology and Infectious Diseases
Sedighi, Fahimzad, Pak, A Multicenter Retrospective Study of Clinical Features, Laboratory Characteristics, and Outcomes of 166 Hospitalized Children With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Preliminary Report From Iranian Network for Research in Viral Diseases (INRVD), Pediatric Pulmonology
Shah, Varna, Pandya, Saxena, Low Vitamin D Levels and Prognosis in a COVID-19 Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review, QJM: An International Journal of Medicine
Shen, Yang, Wang, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Infection in Children: Experts' Consensus Statement, World Journal of Pediatrics
Sinaei, Pezeshki, Parvaresh, Sinaei, Why COVID-19 Is Less Frequent and Severe in Children: A Narrative Review, World Journal of Pediatrics
Tang, Zhang, Wang, Clinical Characteristics of 20,662 Patients With COVID-19 in Mainland China: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis, doi:10.1101/2020.04.18.20070565
Tao, Xu, Chen, Anemia Is Associated With Severe Illness in COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Journal of Medical Virology
Tosato, Calvani, Ciciarello, Malnutrition in COVID-19 Survivors: Prevalence and Risk Factors, Aging Clinical and Experimental Research
Tsankov, Allaire, Irvine, Severe COVID-19 Infection and Pediatric Comorbidities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Veronese, Segala, Carruba, Anemia As a Risk Factor for Disease Progression in Patients Admitted for COVID-19: Data From a Large, Multicenter Cohort Study, Scientific Reports
Williams, Howard-Jones, Hsu, SARS-CoV-2 in Children: Spectrum of Disease, Transmission and Immunopathological Underpinnings, Pathology
Yılmaz, Şen, Is Vitamin D Deficiency a Risk Factor for COVID-19 in Children, Pediatric Pulmonology
Zheng, Gao, Wang, Functional Exhaustion of Antiviral Lymphocytes in COVID-19 Patients, Cellular & Molecular Immunology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.70181",
"ISSN": [
"2398-8835",
"2398-8835"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.70181",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background and Aims</jats:title><jats:p>There is a demand for additional data regarding the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) on the pediatric population. This study sought to determine the clinical and epidemiological features of pediatric COVID‐19 in Iran.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A retrospective study was performed to assess medical records of children with COVID‐19 admitted to Abuzar Hospital in Ahvaz (Iran). Their clinical and demographic data were recorded.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In this study, 600 medical records of pediatric COVID‐19 patients were evaluated. Over 50% of them were boys. Mild, moderate, and severe manifestations of COVID‐19 were identified in 250, 200, and 150 children, respectively. Patients with severe or moderate COVID‐19 had substantially higher levels of various inflammatory markers (C‐reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen, and <jats:sc>d</jats:sc>‐dimer), alanine transaminase (ALT), creatine kinase (CPK), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), neutrophils, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), creatinine (Cr), bilirubin, and gamma‐glutamyl transferase (GGT) compared to children with mild COVID‐19 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001); they also had lower levels of lymphocytes, hemoglobin (Hb), and vitamin D than patients with mild COVID‐19 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001). In addition, children with severe or moderate COVID‐19 had a notably higher incidence of fever or dry cough and longer hospital stays than those with mild COVID‐19 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001). The prevalence of malnutrition and anemia in patients was 50.6% and 31.5%, respectively. A significant proportion of children who were underweight and stunted experienced moderate to severe COVID‐19. Furthermore, there was a considerably higher prevalence of malnutrition, anemia, and vitamin D insufficiency, or deficiency in children with moderate‐to‐severe COVID‐19 compared to patients with mild COVID‐19 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The outcomes of this study revealed a significantly higher prevalence of malnutrition, anemia, vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency, elevated liver and kidney function test results, and increased inflammatory markers in children with moderate to severe COVID‐19 compared to those with mild COVID‐19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/hsr2.70181"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-10-05"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-10-21"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2024-11-06"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mirkarimi",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Heidari",
"given": "Solmaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Shamsizadeh",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Tahouri",
"given": "Kia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3050-7801",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alisamir",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0546-7633",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fathi",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9157-1922",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mohammadi",
"given": "Shooka",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Health Science Reports",
"container-title-short": "Health Science Reports",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-07T05:43:57Z",
"timestamp": 1730958237000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-07T05:44:11Z",
"timestamp": 1730958251000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T05:12:14Z",
"timestamp": 1731042734006,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 5,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1730851200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/hsr2.70181",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.228",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110499",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15270",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12519-020-00392-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4084/MJHID.2022.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpc.15791",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pathol.2020.08.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871526521666210929121705",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcped.2020.12.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101287",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxab059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.078",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.569",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573398X18666220819153000",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25756",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/1918177",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/4914371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_22_1"
},
{
"article-title": "A Comparative Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Laboratory Findings of COVID‐19 Between Intensive Care Unit and Non‐Intensive Care Unit Pediatric Patients: A Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study From Iranian Network for Research in Viral",
"author": "Fahimzad A.",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Emergency Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_13_23_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Hematologic Evaluation of Children With COVID‐19 Infection: Mortality Biomarkers",
"author": "Aminasnafi A.",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clinical Laboratory",
"key": "e_1_2_13_24_1",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2020.07.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12519-020-00343-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2015-2175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_28_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_13_29_1",
"unstructured": "\"Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity \" World Health Organization 2011."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jand.2014.08.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2023.1081139",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_31_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_13_32_1",
"unstructured": "\"WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height‐For‐Age Weight‐For‐Age Weight‐For‐Length Weight‐For‐Height and Body Mass Index‐For‐Age: Methods and Development \" World Health Organization 2006."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13364-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_34_1"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID‐19 in Pediatric Patients: A Study Based on Biomarker Levels",
"author": "Mohammedsaeed W.",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_13_35_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S321915",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.18.20070565",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_13_38_1",
"unstructured": "C.Tang K.Zhang W.Wang et al. \"Clinical Characteristics of 20 662 Patients With COVID‐19 in Mainland China: A Systemic Review and Meta‐Analysis \"MedRxiv. Published ahead of print April 23 2020 https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.18.20070565."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-023-02526-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0298215",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcab202",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-0702",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01719-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-94138-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102926",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26444",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26530",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_54_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-36208-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_55_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/8844420",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_56_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Determinants of Complicated Pneumonia in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients",
"author": "Mirkarimi M.",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Acta Medica Iranica",
"key": "e_1_2_13_57_1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted to a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in Southwest Iran",
"author": "Alisamir M.",
"first-page": "646",
"journal-title": "Acta Medica Iranica",
"key": "e_1_2_13_58_1",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hsr2.70181"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Pediatric COVID‐19: A Retrospective Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "7"
}
