Importance of Microminerals for Maintaining Antioxidant Function After COVID-19-induced Oxidative Stress
et al., Reports of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 11:3, Oct 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 100 COVID-19 patients and 100 healthy controls in India, showing significantly lower zinc levels in COVID-19 patients.
Maradi et al., 31 Oct 2022, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Importance of Microminerals for Maintaining Antioxidant Function After COVID-19-induced Oxidative Stress
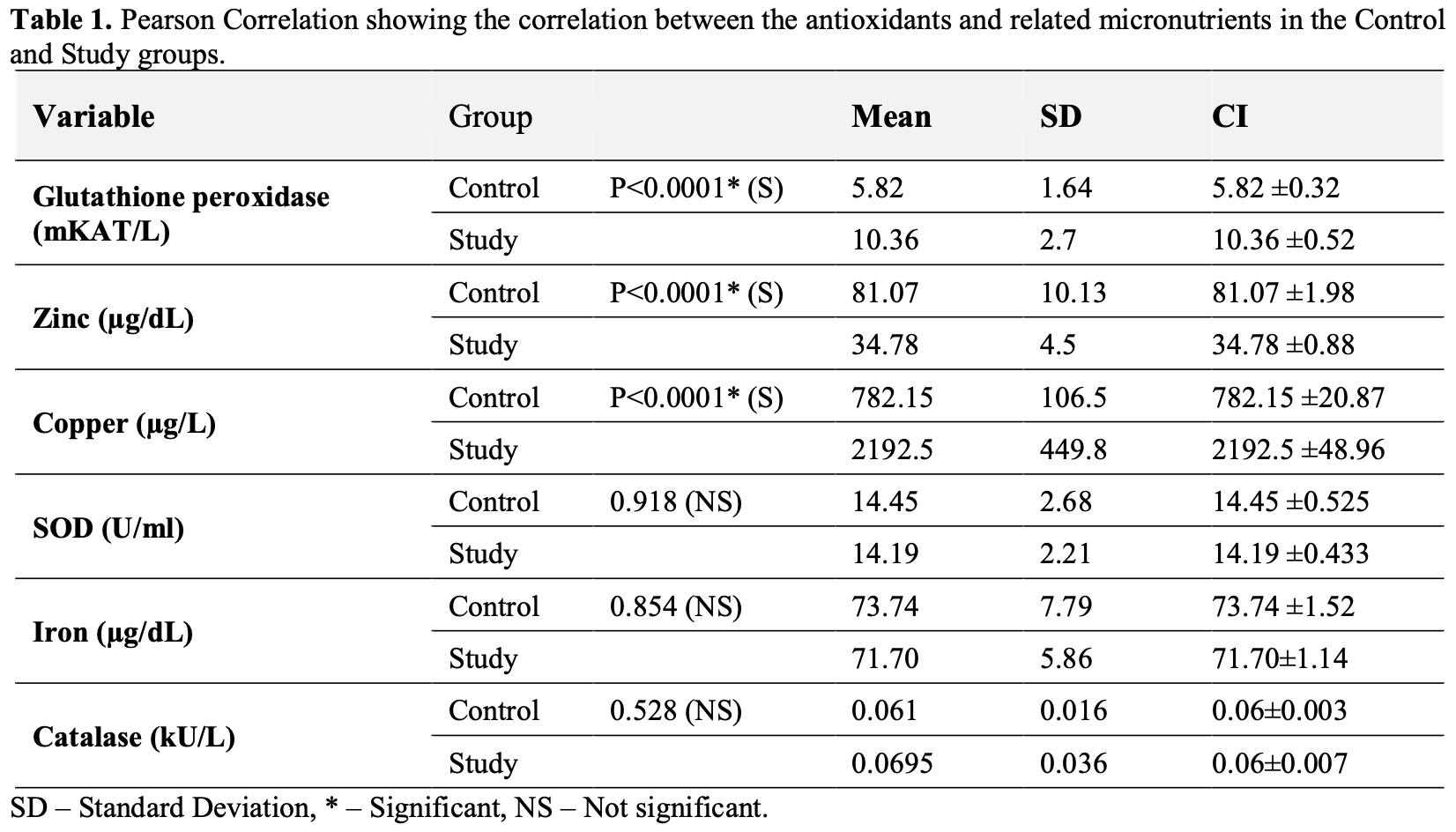
Background: COVID-19 is caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Since the antioxidant mechanisms such as glutathione peroxidase or superoxide dismutase are downregulated during infection by the virus, there is an imbalance in the oxidant-antioxidant system. In this study we aimed to identify the effect of COVID-19 on the antioxidant defense mechanism by comparing the concentrations of antioxidants and microminerals in COVID-19 patients and healthy controls. Methods: This cross-sectional analytical study involved 200 patients at Kasturba Hospital, Manipal University. The serum concentrations of antioxidants and minerals were determined to establish the impact of COVID-19 on antioxidants mechanism and nutrient status in COVID-19 patients.
Results: The serum concentrations of GPX (10.36 ± 2.70 ≥ 5.82 ± 1.64 mKAT/L, p < 0.0001) and copper (2192.5 ± 449.8 ≥ 782.15 ± 106.5 µg/dL, p < 0.0001) were significantly greater, and zinc (34.78 ± 4.5 ≤ 81.07 ± 10.13 µg/dL, p < 0.0001) was significantly less, in the study group than in controls. The Pearson correlation between serum SOD and zinc was significant (r = 0.491, p < 0.0001) indicating the importance of zinc in maintaining and improving SOD activity. No significant correlations were observed between copper and SOD (r = -0.089) or iron and CAT (r = -0.027). Conclusions: Our study demonstrated the expected increase in oxidant-radical production during COVID-19 by estimating the altered concentrations of antioxidants and the minerals required to neutralize the elevated ROS. This finding is not novel but adds to the existing literature, which recommends nutritional supplementation of microminerals and antioxidants.
Conflict of Interest There is no conflict of interest with anyone.
Ethical Approval The study was carried out after obtaining approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee, Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. The first participant in the study was enrolled after registration in the Clinical Trial Registration of India.
References
Anuk, Polat, Akdas, Erol, Tanacan et al., The Relation Between Trace Element Status (Zinc, Copper, Magnesium) and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Infection During Pregnancy, Biol Trace Elem Res
Armstrong, Niemann, Smeekens, Rottier, Warren, Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus, Nature
Banerjee, Joshi, Maradi, Mallick, Effect of altered levels of micronutrients on lipid parameters in thyroid dysfunction, Int J Appl Biol Pharm
Bastin, Shiri, Zanganeh, Fooladi, Moghaddam et al., The Correlation between Selenium-Dependent Glutathione Peroxidase Activity and Oxidant/Antioxidant Balance in Sera of Diabetic Patients with Nephropathy, Rep Biochem Mol Biol
Beniac, Andonov, Grudeski, Booth, Architecture of the SARS coronavirus prefusion spike, Nat Struct Mol Biol
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Uhl, Hoagland et al., Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19, Cell
Cecchini, Cecchini, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression, Med Hypotheses
Chabot, Mitchell, Gutteridge, Evans, Reactive oxygen species in acute lung injury, Eur Respir J
Dittrich, Meyer, Krokowski, Quarcoo, Ahrens et al., Glutathione peroxidase-2 protects from allergen-induced airway inflammation in mice, Eur Respir J
Fontanet, Autran, Lina, Kieny, Karim et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants and ending the COVID-19 pandemic, Lancet
Hanschmann, Berndt, Hecker, Garn, Bertrams et al., Glutaredoxin 2 Reduces Asthma-Like Acute Airway Inflammation in Mice, Front Immunol
Ivanov, Valuev-Elliston, Ivanova, Kochetkov, Starodubova et al., Oxidative Stress during HIV Infection: Mechanisms and Consequences, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Joshi, Mallick, Goud, Maradi, Reddy, Effect of serum copper concentration and ceruloplasmin on lipid parameters leading to increased propensity to cardiovascular risk, Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci
Kim, Jeong, Kang, Shin, Sohn, Transduced human PEP-1-catalase fusion protein attenuates ischemic neuronal damage, Free Radic Biol Med
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat Med
Macdougall, Red cell metabolism in iron-deficiency anemia, J Pediatr
Maradi, Joshi, Mallick, Reddy, Shorey et al., A correlation study between serum zinc and plasma total cholesterol, high density, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in thyroid dysfunction, Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res
Mariani, Mangialasche, Feliziani, Cecchetti, Malavolta et al., Effects of zinc supplementation on antioxidant enzyme activities in healthy old subjects, Exp Gerontol
Mostafa-Hedeab, ACE2 as Target of COVID-19 Virus Treatment, Simplified Updated Review, Rep Biochem Mol Biol
Mrityunjaya, Pavithra, Neelam, Janhavi, Halami et al., Immune-Boosting, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Food Supplements Targeting Pathogenesis of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The Role of Micronutrients in Support of the Immune Response against Viral Infections, Nutrients
Raoult, Zumla, Locatelli, Ippolito, Kroemer, Coronavirus infections: Epidemiological, clinical and immunological features and hypotheses, Cell Stress
Ratajczak, Bujko, Ciechanowicz, Sielatycka, Cymer et al., SARS-CoV-2 Entry Receptor ACE2 Is Expressed on Very Small CD45 -Precursors of Hematopoietic and Endothelial Cells and in Response to Virus Spike Protein Activates the Nlrp3 Inflammasome, Stem Cell Rev Rep
Shah, Firmal, Alam, Ganguly, Chattopadhyay, Overview of Immune Response During SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Lessons from the Past, Front Immunol
Swanson, Deng, Ting, The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics, Nat Rev Immunol
Umakanthan, Sahu, Ranade, Bukelo, Rao et al., Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wan, Shang, Graham, Baric, Li, Receptor Recognition by the Novel Coronavirus from Wuhan: an Analysis Based on Decade-Long Structural Studies of SARS Coronavirus, J Virol
Wang, Du, Zhu, Cao, An et al., Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19, Lancet
Weiss, Navas-Martin, Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, COVID-19: The Inflammation Link and the Role of Nutrition in Potential Mitigation, Nutrients
