UVB Radiation Alone May Not Explain Sunlight Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab070, Feb 2021
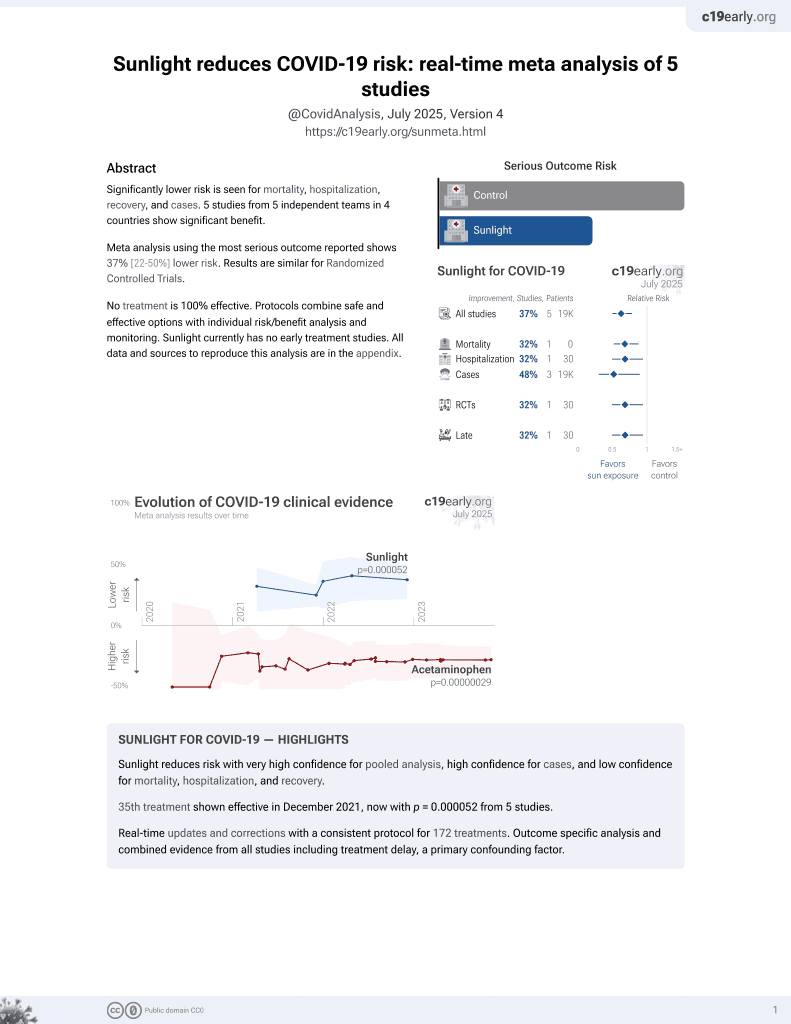
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Experiments have shown that SARS-CoV-2 is inactivated by sunlight much faster than predicted by theory, suggesting that additional mechanisms of inactivation may be involved. Authors note that sensitivity to wavelengths other than UVB mean that sunlight could mitigate outdoor transmission over a broader range of latitudes and daytimes than previously expected, and that inexpensive and energy-efficient wavelength-specific light sources might be used to augment air filtration systems with relatively low risk.
Luzzatto-Fegiz et al., 5 Feb 2021, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Abstract: a consensus on sampling, methodologies for clinical measurement, and cutoff
values to guide the treatment of severe
COVID-19 patients with endothelialstabilizing agents, such as statins, glucocorticoids, and anticoagulants. Moreover,
endothelial function measurement is a
possible alternative method for the early
detection of cardiovascular sequelae.
Notes
Ming Tong,1,2 Fang Chen,2 Qing Zheng,3 and Yimin Zhu2
1
Department of Infectious Diseases, The First-affiliated
Hospital of Hunan Normal University (Hunan Provincial
People’s Hospital), Changsha, Hunan, China, 2Institute of
Emergency Medicine, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory
of Emergency and Critical Care Metabonomics, The Firstaffiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University (Hunan
Provincial People’s Hospital), Changsha, Hunan, China,
3
Department of Geriatrics, The First-affiliated Hospital
of Hunan Normal University (Hunan Provincial People’s
Hospital), Changsha, Hunan, China
References
1. Bauer W, Ulke J, Galtung N, et al.
Role of cell adhesion molecules for
disease development of patients with
and without COVID-19 in the emergency department. J Infect Dis 2021;
223:1497–9.
2. Page AV, Liles WC. Biomarkers of endothelial activation/dysfunction in
infectious diseases. Virulence 2013;
4:507–16.
3. Pons S, Fodil S, Azoulay E, Zafrani L.
The vascular endothelium: the cornerstone of organ dysfunction in
severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Crit
Care 2020; 24:353.
4. Tong M, Jiang Y, Xia D, et al. Elevated
expression of serum endothelial cell
adhesion molecules in COVID-19
patients. J Infect Dis 2020; 222:894–8.
5. Kong Y, Han J, Wu X, Zeng H, Liu J,
Zhang H. VEGF-D: a novel biomarker
Received 28 December 2020; editorial decision 20 January
2021; accepted 28 January 2021; published online January
30, 2021.
Correspondence: Yimin Zhu, MD, PhD, Institute of
Emergency Medicine, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory
of Emergency and Critical Care Metabonomics, The FirstAffiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University (Hunan
Provincial People’s Hospital), Changsha, Hunan 410005, P. R.
China (cszhuyimin@163.com).
2021;223:1499–500
The Journal of Infectious Diseases®
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for
the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved.
For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab041
UVB Radiation Alone May Not
Explain Sunlight Inactivation of
SARS-CoV-2
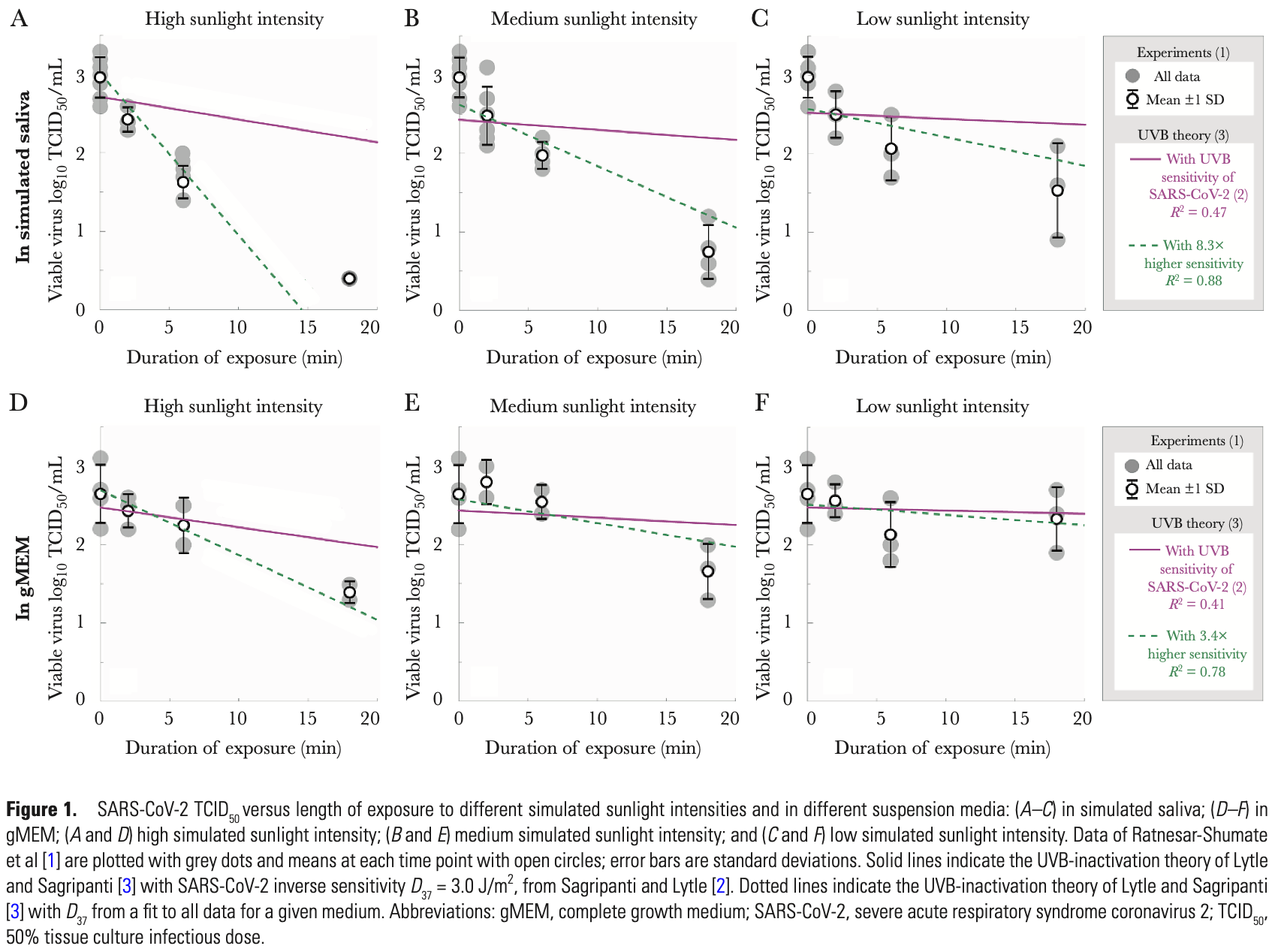
To the Editor—Recently, RatnesarShumate et al [1] reported rapid
1500 • jid 2021:223 (15 April) • CORRESPONDENCE
sunlight inactivation of severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) in simulated saliva and
in complete growth medium (gMEM).
Independently and essentially simultaneously, Sagripanti and Lytle [2] introduced a theory for sunlight inactivation
of SARS-CoV-2, building on their earlier
work with similar viruses [3]. To the
best of our knowledge, these data and
theory had not been compared. When
establishing this comparison, the experimentally reported sunlight inactivation
in Ratnesar-Shumate et al [1] is several
times faster than predicted by theory,
suggesting that additional experiments
and hypotheses may be needed to fully
elucidate the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2
sunlight inactivation.
Briefly, the theory of Sagripanti and
Lytle [2, 3] considers direct photochemical damage to viral RNA, which is maximal for UVC (wavelengths between
200 and 280 nm). The effectiveness of
UVC is expressed as the exposure that
produces one e-fold reduction..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab070",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab070",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3614-552X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Luzzatto-Fegiz",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2179-3148",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Temprano-Coleto",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0295-4556",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Environmental Engineering, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Peaudecerf",
"given": "François J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3159-8749",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Mathematics, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Landel",
"given": "Julien R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9185-3161",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, California, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Yangying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9353-5498",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Translational and Integrative Sciences Center, Department of Molecular Toxicology, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "McMurry",
"given": "Julie A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-03T21:41:33Z",
"timestamp": 1612388493000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T01:23:20Z",
"timestamp": 1644369800000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "University of California, Santa Barbara"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000183",
"award": [
"W911NF-17-1-0306"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Army Research Office"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T05:15:41Z",
"timestamp": 1680239741888
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
23
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612483200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab070/36548935/jiab070.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/223/8/1500/37313619/jiab070.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/223/8/1500/37313619/jiab070.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1500-1502",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa274",
"article-title": "Simulated sunlight rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces",
"author": "Ratnesar-Shumate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "2022020901032822000_CIT0001",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/php.13293",
"article-title": "Estimated inactivation of coronaviruses by solar radiation with special reference to COVID-19",
"author": "Sagripanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"journal-title": "Photochem Photobiol",
"key": "2022020901032822000_CIT0002",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.22.14244-14252.2005",
"article-title": "Predicted inactivation of viruses of relevance to biodefense by solar radiation",
"author": "Lytle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14244",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "2022020901032822000_CIT0003",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C8EM00047F",
"article-title": "Sunlight-mediated inactivation of health-relevant microorganisms in water: a review of mechanisms and modeling approaches",
"author": "Nelson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1089",
"journal-title": "Environ Sci Process Impacts",
"key": "2022020901032822000_CIT0004",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/es061716i",
"article-title": "Sunlight-mediated inactivation of MS2 coliphage via exogenous singlet oxygen produced by sensitizers in natural waters",
"author": "Kohn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "192",
"journal-title": "Environ Sci Technol",
"key": "2022020901032822000_CIT0005",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2007"
}
],
"reference-count": 5,
"references-count": 5,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/223/8/1500/6129304"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "UVB Radiation Alone May Not Explain Sunlight Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "223"
}