Body temperature variation controls pre-mRNA processing and transcription of antiviral genes and SARS-CoV-2 replication
et al., Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac513, Jun 2022
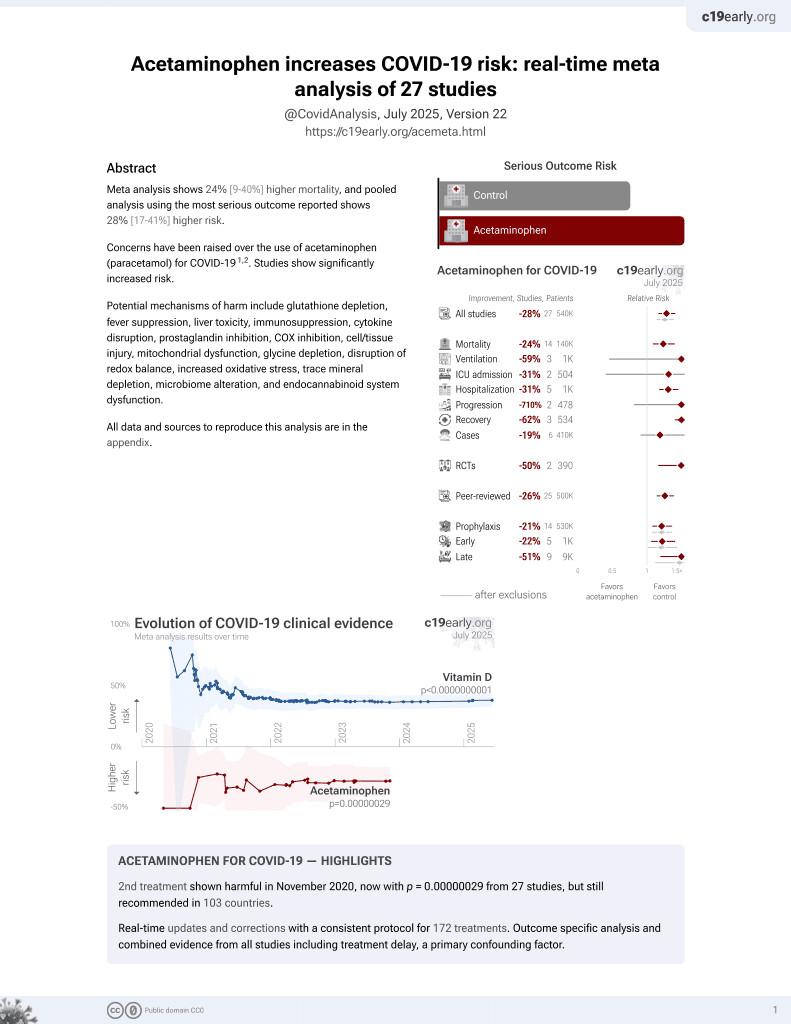
2nd treatment shown to increase risk in
November 2020, now with p = 0.00000029 from 27 studies, but still recommended in 103 countries.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
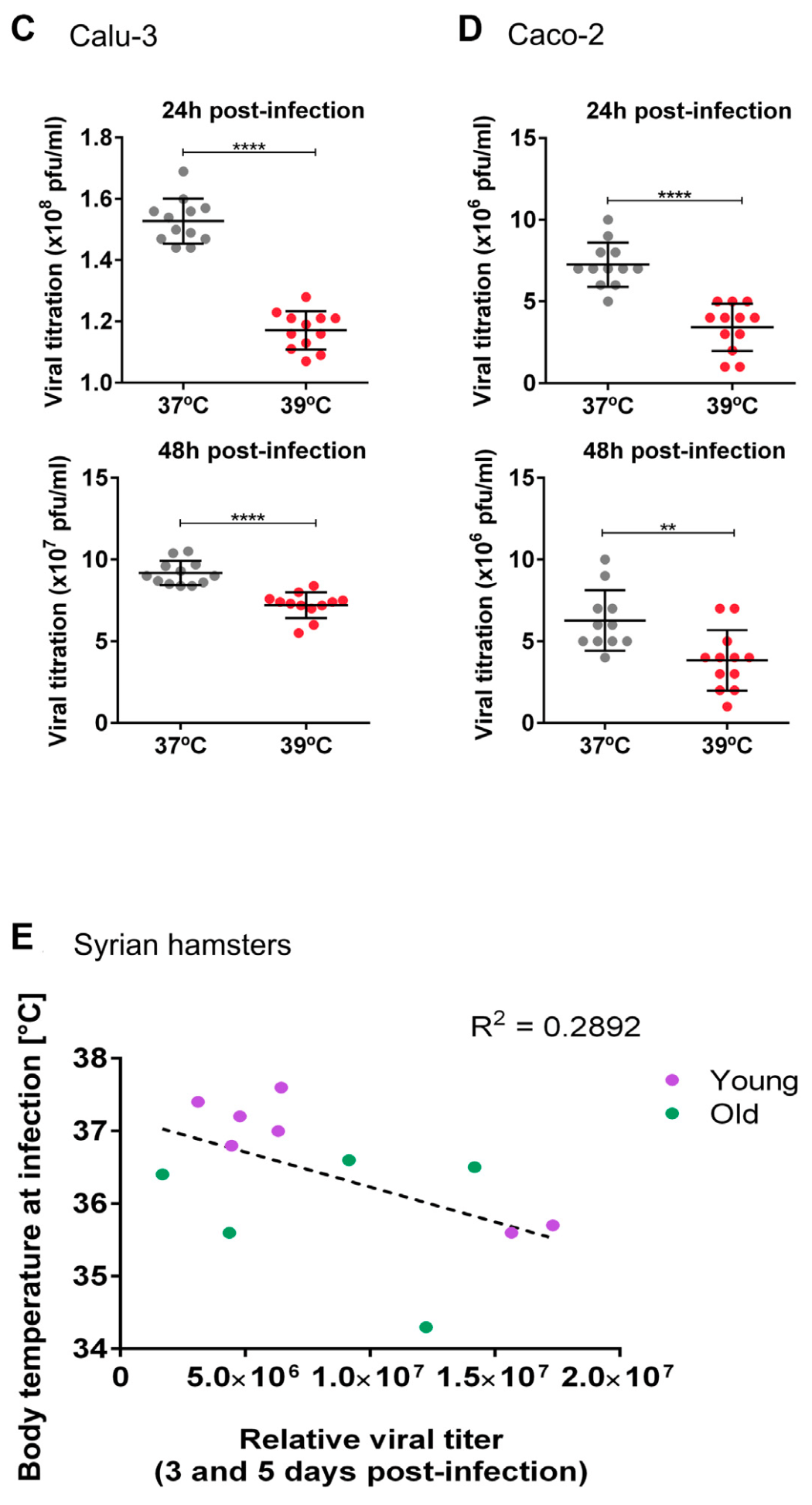
In vitro and hamster study showing that higher temperature reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication. Authors show a 1.5°C increase in temperature (from 36.5 to 38°C) enhanced the expression of antiviral genes. Elevated temperatures were found to reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication in cell cultures of Calu-3 and Caco-2 cells. An in vivo hamster model indicated that higher body temperature at the time of infection correlated with lower viral loads.
Acetaminophen is also known as paracetamol, Tylenol, Panadol, Calpol, Tempra, Calprofen, Doliprane, Efferalgan, Grippostad C, Dolo, Acamol, Fevadol, Crocin, and Perfalgan.
Los et al., 17 Jun 2022, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Contact: florian.heyd@fu-berlin.de.
Body temperature variation controls pre-mRNA processing and transcription of antiviral genes and SARS-CoV-2 replication
Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac513
Antiviral innate immunity represents the first defense against invading viruses and is key to control viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Body temperature is an omnipresent variable but was neglected when addressing host defense mechanisms and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, we show that increasing temperature in a 1.5 • C window, between 36.5 and 38 • C, strongly increases the expression of genes in two branches of antiviral immunity, nitric oxide production and type I interferon response. We show that alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated decay decreases STAT2 expression in colder conditions and suggest that increased STAT2 expression at elevated temperature induces the expression of diverse antiviral genes and SARS-CoV-2 restriction factors. This cascade is activated in a remarkably narrow temperature range below febrile temperature, which reflects individual, circadian and age-dependent variation. We suggest that decreased body temperature with aging contributes to reduced expression of antiviral genes in older individuals. Using cell culture and in vivo models, we show that higher body temperature correlates with reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication, which may affect the different vulnerability of children versus seniors toward severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Altogether, our data connect body temperature and pre-mRNA processing to provide new mechanistic insight into the regulation of antiviral innate immunity.
References
Almanzar, Antony, Baghel, Bakerman, Bansal et al., A single-cell transcriptomic atlas characterizes ageing tissues in the mouse, Nature
Christian, Collier, Zu, Licursi, Hough et al., Activated Ras/MEK inhibits the antiviral response of alpha interferon by reducing STAT2 levels, J. Virol
Eccles, An explanation for the seasonality of acute upper respiratory tract viral infections, Acta Otolaryngol
Edgar, Stangherlin, Nagy, Nicoll, Efstathiou et al., Cell autonomous regulation of herpes and influenza virus infection by the circadian clock, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A
Evans, Repasky, Fisher, Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat, Nat. Rev. Immunol
Farlik, Reutterer, Schindler, Greten, Vogl et al., Nonconventional initiation complex assembly by STAT and NF-B transcription factors regulates nitric oxide synthase expression, Immunity
Foxman, Storer, Fitzgerald, Wasik, Hou et al., Temperature-dependent innate defense against the common cold virus limits viral replication at warm temperature in mouse airway cells, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A
Garg, Kim, Whitaker, O'halloran, Cummings et al., Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019, Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep
Geneva, Cuzzo, Fazili, Javaid, Normal body temperature: a systematic review, Open Forum Infect. Dis
Hadjadj, Yatim, Barnabei, Corneau, Boussier, Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients, Science
Hall, Limjunyawong, Vermillion, Robinson, Wohlgemuth et al., Progesterone-based therapy protects against influenza by promoting lung repair and recovery in females, PLoS Pathog
Haltenhof, Kotte, De Bortoli, Schiefer, Meinke et al., A conserved kinase-based body-temperature sensor globally controls alternative splicing and gene expression, Mol. Cell
Hasday, Singh, Fever and the heat shock response: distinct, partially overlapping processes, Cell Stress Chaperones
Heyd, Lynch, Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of PSF by GSK3 controls CD45 alternative splicing, Mol. Cell
Hoffmann, Sánchez-Rivera, Schneider, Luna, Soto-Feliciano et al., Functional interrogation of a SARS-CoV-2 host protein interactome identifies unique and shared coronavirus host factors, Cell Host Microbe
Kamm, Siemens, The TRPM2 channel in temperature detection and thermoregulation, Temperature
Lane, Dunn, Gardner, Lam, Watson et al., The efficacy of the interferon alpha/beta response versus arboviruses is temperature dependent, mBio
Laporte, Raeymaekers, Van Berwaer, Vandeput, Marchand-Casas et al., The SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronavirus spike proteins are fine-tuned towards temperature and proteases of the human airways, PLoS Pathog
Lee, Lee, Choi, Son, Park et al., The SARS-CoV-2 RNA interactome, Mol. Cell
Lee, Zhong, Mace, Repasky, Elevation in body temperature to fever range enhances and prolongs subsequent responsiveness of macrophages to endotoxin challenge, PLoS One
Lieberman, Peddu, Xie, Shrestha, Huang et al., In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age, PLoS Biol
Lisi, Zelikin, Chandrawati, Nitric oxide to fight viral infections, Adv. Sci
Liu, Hu, Murakawa, Yin, Wang et al., Cold-induced RNA-binding proteins regulate circadian gene expression by controlling alternative polyadenylation, Sci. Rep
Loske, Lukassen, Stricker, Magalhães, Liebig et al., Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, Nat. Biotechnol
Martin-Sancho, Lewinski, Pache, Stoneham, Yin et al., Functional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 cellular restriction, Mol. Cell
Mehta, Ashkar, Mossman, The nitric oxide pathway provides innate antiviral protection in conjunction with the type I interferon pathway in fibroblasts, PLoS One
Neumann, Meinke, Goldammer, Strauch, Schubert et al., Alternative splicing coupled mRNA decay shapes the temperature-dependent transcriptome, EMBO Rep
O'driscoll, Ribeiro Dos Santos, Wang, Cummings, Azman et al., Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Osterrieder, Bertzbach, Dietert, Abdelgawad, Age-dependent progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Viruses
Park, Iwasaki, Type I and type III interferons--induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe
Preußner, Goldammer, Neumann, Haltenhof, Rautenstrauch et al., Body temperature cycles control rhythmic alternative splicing in mammals, Mol. Cell
Refinetti, Circadian rhythmicity of body temperature and metabolism, Temperature
Schultze, Aschenbrenner, COVID-19 and the human innate immune system, Cell
Singh, Hasday, Fever, hyperthermia and the heat shock response, Int. J. Hyperthermia
Song, Wang, Kamm, Pohle, De Castro Reis et al., The TRPM2 channel is a hypothalamic heat sensor that limits fever and can drive hypothermia, Science
Strauch, Heyd, Temperature does matter--an additional dimension in kinase inhibitor development, FEBS J
Sun, Wang, Gao, Wang, Luo et al., Transmission heterogeneities, kinetics, and controllability of SARS-CoV-2, Science
V'kovski, Gultom, Kelly, Steiner, Russeil et al., Disparate temperature-dependent virus-host dynamics for SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV in the human respiratory epithelium, PLoS Biol
Waalen, Buxbaum, Is older colder or colder older? The association of age with body temperature in 18,630 individuals, J. Gerontol. A: Biol. Sci. Med. Sci
Wetsel, Sensing hot and cold with TRP channels, Int. J. Hyperthermia
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac513",
"ISSN": [
"0305-1048",
"1362-4962"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac513",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Antiviral innate immunity represents the first defense against invading viruses and is key to control viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Body temperature is an omnipresent variable but was neglected when addressing host defense mechanisms and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, we show that increasing temperature in a 1.5°C window, between 36.5 and 38°C, strongly increases the expression of genes in two branches of antiviral immunity, nitric oxide production and type I interferon response. We show that alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated decay decreases STAT2 expression in colder conditions and suggest that increased STAT2 expression at elevated temperature induces the expression of diverse antiviral genes and SARS-CoV-2 restriction factors. This cascade is activated in a remarkably narrow temperature range below febrile temperature, which reflects individual, circadian and age-dependent variation. We suggest that decreased body temperature with aging contributes to reduced expression of antiviral genes in older individuals. Using cell culture and in vivo models, we show that higher body temperature correlates with reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication, which may affect the different vulnerability of children versus seniors toward severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Altogether, our data connect body temperature and pre-mRNA processing to provide new mechanistic insight into the regulation of antiviral innate immunity.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3061-5113",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Los",
"given": "Bruna",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5155-0844",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Preußner",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Omiqa Bioinformatics , Altensteinstraße 40, 14195 Berlin, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Eschke",
"given": "Kathrin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Omiqa Bioinformatics , Altensteinstraße 40, 14195 Berlin, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Vidal",
"given": "Ricardo Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Omiqa Bioinformatics , Altensteinstraße 40, 14195 Berlin, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Abdelgawad",
"given": "Azza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Virology, Freie Universität Berlin , Robert-von-Ostertag-Straße 7-13, 14163 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"family": "Olofsson",
"given": "Didrik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"family": "Keiper",
"given": "Sandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"family": "Paulo-Pedro",
"given": "Margarida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"family": "Grindel",
"given": "Alica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"family": "Meinke",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Omiqa Bioinformatics , Altensteinstraße 40, 14195 Berlin, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Trimpert",
"given": "Jakob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9377-9882",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of RNA Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Freie Universität Berlin , Takustrasse 6, 14195 Berlin , Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Heyd",
"given": "Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Nucleic Acids Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T13:56:41Z",
"timestamp": 1655474201000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-08T00:04:09Z",
"timestamp": 1657238649000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001659",
"award": [
"HE5398/4-2",
"278001972—TRR 186"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100007537",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Freie Universität Berlin"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-31T14:34:23Z",
"timestamp": 1722436463056
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0305-1048"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1362-4962"
}
],
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655424000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/nar/article-pdf/50/12/6769/44455533/gkac513.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/nar/article-pdf/50/12/6769/44455533/gkac513.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "6769-6785",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23328940.2016.1258445",
"article-title": "The TRPM2 channel in temperature detection and thermoregulation",
"author": "Kamm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Temperature",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B1",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofz032",
"article-title": "Normal body temperature: a systematic review",
"author": "Geneva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofz032",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect. Dis.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B2",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23328940.2020.1743605",
"article-title": "Circadian rhythmicity of body temperature and metabolism",
"author": "Refinetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Temperature",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B3",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.006",
"article-title": "Body temperature cycles control rhythmic alternative splicing in mammals",
"author": "Preußner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "433",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B4",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1005840",
"article-title": "Progesterone-based therapy protects against influenza by promoting lung repair and recovery in females",
"author": "Hall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1005840",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B5",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glr001",
"article-title": "Is older colder or colder older? The association of age with body temperature in 18,630 individuals",
"author": "Waalen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "487",
"journal-title": "J. Gerontol. A: Biol. Sci. Med. Sci.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B6",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aaf7537",
"article-title": "The TRPM2 channel is a hypothalamic heat sensor that limits fever and can drive hypothermia",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1393",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B7",
"volume": "353",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/02656736.2011.554337",
"article-title": "Sensing hot and cold with TRP channels",
"author": "Wetsel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "388",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Hyperthermia",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B8",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.01.028",
"article-title": "A conserved kinase-based body-temperature sensor globally controls alternative splicing and gene expression",
"author": "Haltenhof",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B9",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3843",
"article-title": "Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat",
"author": "Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "335",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B10",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0471:FATHSR>2.0.CO;2",
"article-title": "Fever and the heat shock response: distinct, partially overlapping processes",
"author": "Hasday",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "471",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperones",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B11",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/02656736.2013.808766",
"article-title": "Fever, hyperthermia and the heat shock response",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Hyperthermia",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B12",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00535-18",
"article-title": "The efficacy of the interferon alpha/beta response versus arboviruses is temperature dependent",
"author": "Lane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00535-18",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.12.009",
"article-title": "Functional interrogation of a SARS-CoV-2 host protein interactome identifies unique and shared coronavirus host factors",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B14",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009500",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronavirus spike proteins are fine-tuned towards temperature and proteases of the human airways",
"author": "Laporte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B15",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3001158",
"article-title": "Disparate temperature-dependent virus–host dynamics for SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV in the human respiratory epithelium",
"author": "V’kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3001158",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B16",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.029",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the human innate immune system",
"author": "Schultze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1671",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B17",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008",
"article-title": "Type I and type III interferons—induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B18",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-021-01037-9",
"article-title": "Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children",
"author": "Loske",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Nat. Biotechnol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B19",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6027",
"article-title": "Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Hadjadj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "718",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B20",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.013",
"article-title": "Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of PSF by GSK3 controls CD45 alternative splicing",
"author": "Heyd",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B21",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2021.04.022",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 RNA interactome",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2838",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B22",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0031688",
"article-title": "The nitric oxide pathway provides innate antiviral protection in conjunction with the type I interferon pathway in fibroblasts",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e31688",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202003895",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide to fight viral infections",
"author": "Lisi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2003895",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B24",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0030077",
"article-title": "Elevation in body temperature to fever range enhances and prolongs subsequent responsiveness of macrophages to endotoxin challenge",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e30077",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B25",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.202051369",
"article-title": "Alternative splicing coupled mRNA decay shapes the temperature-dependent transcriptome",
"author": "Neumann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e51369",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B26",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep02054",
"article-title": "Cold-induced RNA-binding proteins regulate circadian gene expression by controlling alternative polyadenylation",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2054",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B27",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15564",
"article-title": "Temperature does matter—an additional dimension in kinase inhibitor development",
"author": "Strauch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3148",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B28",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2021.04.008",
"article-title": "Functional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 cellular restriction",
"author": "Martin-Sancho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2656",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B29",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2496-1",
"article-title": "A single-cell transcriptomic atlas characterizes ageing tissues in the mouse",
"author": "Almanzar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "590",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B30",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12070779",
"article-title": "Age-dependent progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Osterrieder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B31",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1601895113",
"article-title": "Cell autonomous regulation of herpes and influenza virus infection by the circadian clock",
"author": "Edgar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10085",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B32",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02213-08",
"article-title": "Activated Ras/MEK inhibits the antiviral response of alpha interferon by reducing STAT2 levels",
"author": "Christian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6717",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B33",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1411030112",
"article-title": "Temperature-dependent innate defense against the common cold virus limits viral replication at warm temperature in mouse airway cells",
"author": "Foxman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B34",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2010.07.001",
"article-title": "Nonconventional initiation complex assembly by STAT and NF-κB transcription factors regulates nitric oxide synthase expression",
"author": "Farlik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B35",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00016480252814207",
"article-title": "An explanation for the seasonality of acute upper respiratory tract viral infections",
"author": "Eccles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Acta Otolaryngol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B36",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3",
"article-title": "Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "458",
"journal-title": "Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B37",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0",
"article-title": "Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "O’Driscoll",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B38",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe2424",
"article-title": "Transmission heterogeneities, kinetics, and controllability of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabe2424",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B39",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000849",
"article-title": "In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age",
"author": "Lieberman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3000849",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol.",
"key": "2022070800014908500_B40",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/50/12/6769/6609820"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Body temperature variation controls pre-mRNA processing and transcription of antiviral genes and SARS-CoV-2 replication"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "50"
}
los