Effects of a 16-week home-based exercise training programme on health-related quality of life, functional capacity, and persistent symptoms in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19: a randomised controlled trial
et al., British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681, NCT04615052, May 2023
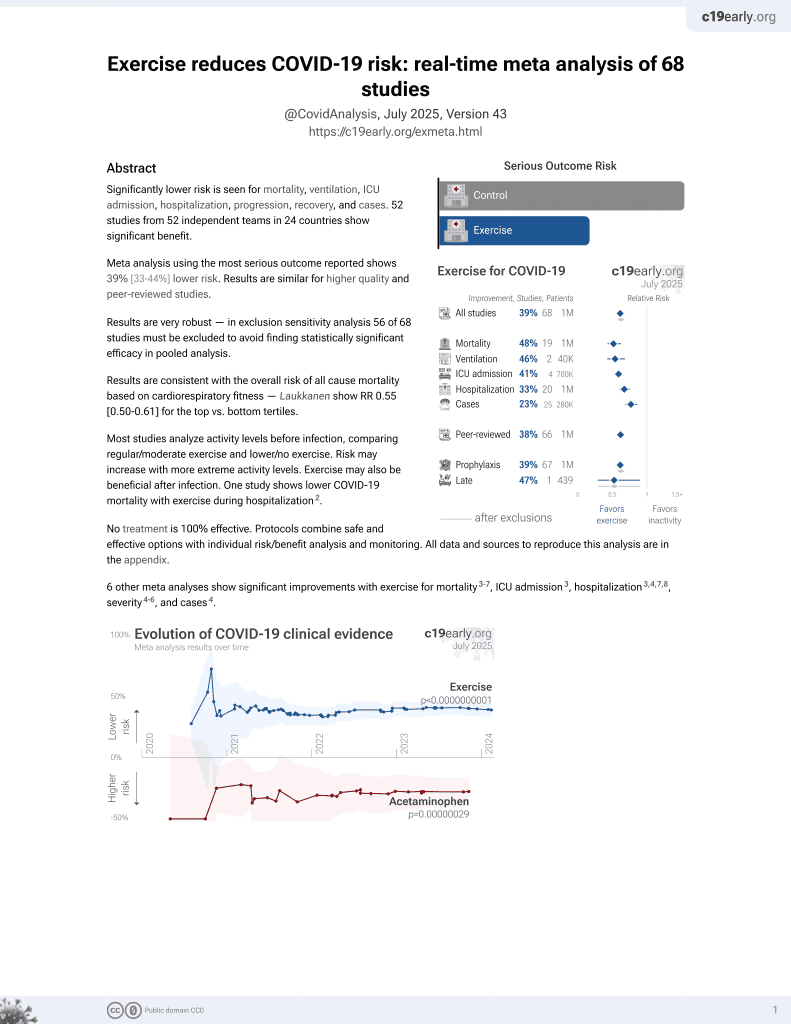
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
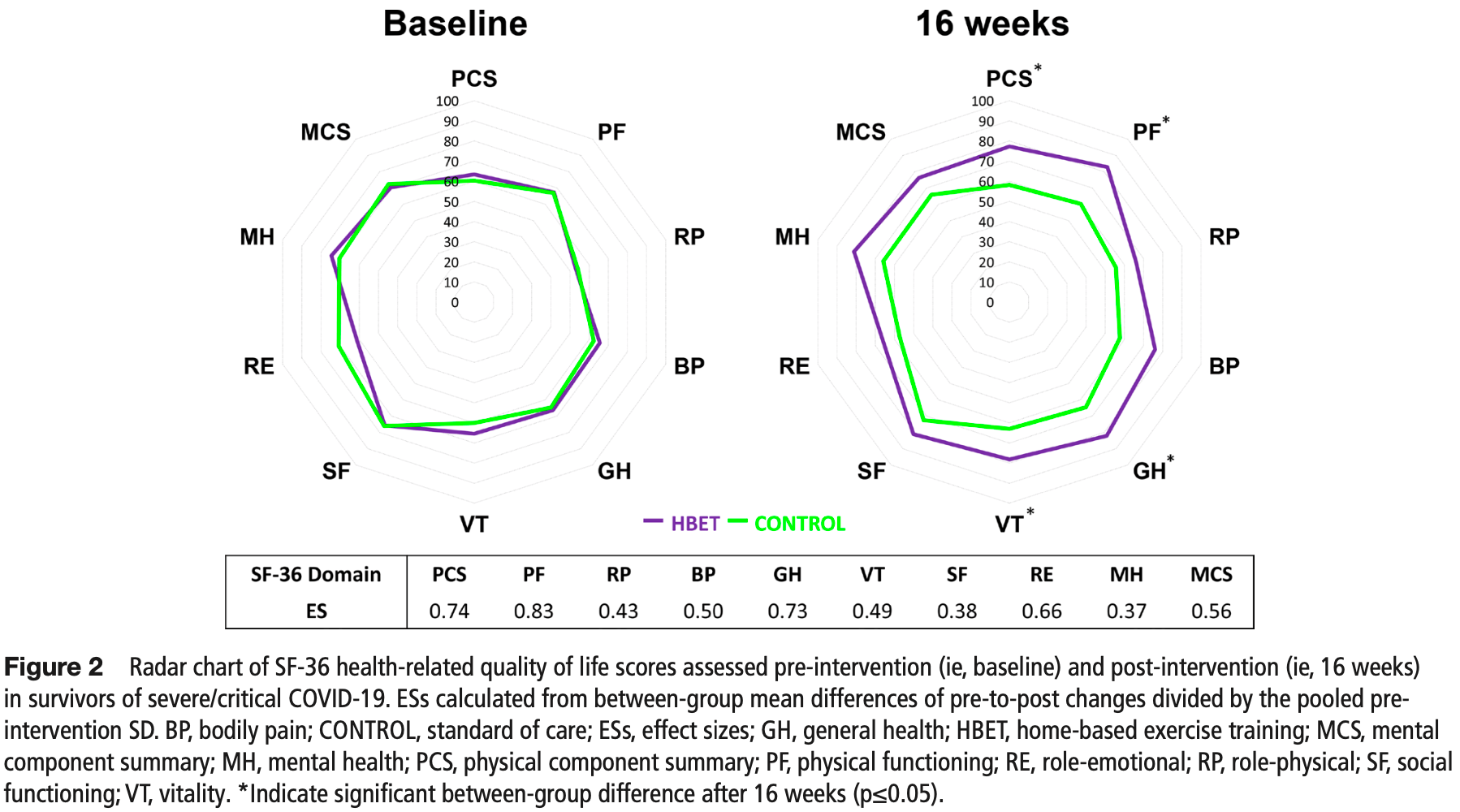
RCT 50 post-severe/critical COVID-19 patients in Brazil, showing improved health-related quality of life with an exercise program (3 times a week, ~60-80 minutes/session, for 16 weeks).
Longobardi et al., 10 May 2023, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period November 2020 - April 2022, trial NCT04615052 (history).
Contact: hars@usp.b.
Effects of a 16-week home-based exercise training programme on health-related quality of life, functional capacity, and persistent symptoms in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19: a randomised controlled trial
British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681
Background Long-lasting effects of COVID-19 may include cardiovascular, respiratory, skeletal muscle, metabolic, psychological disorders and persistent symptoms that can impair health-related quality of life (HRQoL). We investigated the effects of a home-based exercise training (HBET) programme on HRQoL and health-related outcomes in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19. Methods This was a single-centre, single-blinded, parallelgroup, randomised controlled trial. Fifty survivors of severe/ critical COVID-19 (5±1 months after intensive care unit discharge) were randomly allocated (1:1) to either a 3 times a week (~60-80 min/session), semi-supervised, individualised, HBET programme or standard of care (CONTROL). Changes in HRQoL were evaluated through the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey, and physical component summary was predetermined as the primary outcome. Secondary outcomes included cardiorespiratory fitness, pulmonary function, functional capacity, body composition and persistent symptoms. Assessments were performed at baseline and after 16 weeks of intervention. Statistical analysis followed intention-to-treat principles. Results After the intervention, HBET showed greater HRQoL score than CONTROL in the physical component summary (estimated mean difference, EMD: 16.8 points; 95% CI 5.8 to 27.9; effect size, ES: 0.74), physical functioning (EMD: 22.5 points, 95% CI 6.1 to 42.9, ES: 0.83), general health (EMD: 17.4 points, 95% CI 1.8 to 33.1, ES: 0.73) and vitality (EMD: 15.1 points, 95% CI 0.2 to 30.1, ES: 0.49) domains. 30-second sit-to-stand (EMD: 2.38 reps, 95% CI 0.01 to 4.76, ES: 0.86), and muscle weakness and myalgia were also improved in HBET compared with CONTROL (p<0.05). No significant differences were seen in the remaining variables. There were no adverse events. Conclusion HBET is an effective and safe intervention to improve physical domains of HRQoL, functional capacity and persistent symptoms in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19. Trial registration number NCT04615052.
ORCID iDs
Contributors Designed research: IL, KG, DCOdA, SG, FRL, BG and HR. Conducted the research: IL and KG. Contributed to data collection: IL, KG, GNdOJ, DMLdP, JVPS, MMM and JASdOB. Analysed data/statistical analysis: IL and HR. Drafted the manuscript: IL, BG and HR. Guarantor: HR. All authors reviewed the manuscript critically and approved the final version. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria.
Competing interests None declared. Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Patient consent for publication Consent obtained directly from patient(s). Ethics approval This study involves human participants. This study was performed in line with the principles of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics approval was obtained from the local Ethical Review Board (CAPPesq; No. 31303720.7.0000.0068). Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and..
References
Attaway, Welch, Dasarathy, Acute skeletal muscle loss in SARS-cov-2 infection contributes to poor clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients, J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.13052
Baba, Nagashima, Goto, Oxygen uptake efficiency slope: a new index of cardiorespiratory functional reserve derived from the relation between oxygen uptake and minute ventilation during incremental exercise, J Am Coll Cardiol, doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(96)00412-3
Balogun, Akomolafe, Amusa, Grip strength: effects of testing posture and elbow position, Arch Phys Med Rehabil, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681on10
Baranauskas, Carter, Evidence for impaired chronotropic responses to and recovery from 6-minute walk test in women with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Exp Physiol, doi:10.1113/EP089965
Bardakci, Ozturk, Ozkarafakili, Evaluation of long-term radiological findings, pulmonary functions, and health-related quality of life in survivors of severe COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27101
Chen, Haupert, Zimmermann, Global prevalence of post-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) condition or long COVID: a meta-analysis and systematic review, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac136
Craig, Marshall, Sjöström, International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity, Med Sci Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB
Do Amaral, Viana, Heubel, Cardiovascular, respiratory, and functional effects of home-based exercise training after COVID-19 hospitalization, Med Sci Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000002977
Durstenfeld, Sun, Tahir, Use of cardiopulmonary exercise testing to evaluate long COVID-19 symptoms in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36057
Ferrans, Zerwic, Wilbur, Conceptual model of health-related quality of life, J Nurs Scholarsh, doi:10.1111/j.1547-5069.2005.00058.x
Figueiredo, De Salles, Trajano, Volume for muscle hypertrophy and health outcomes: the most effective variable in resistance training, Sports Med, doi:10.1007/s40279-017-0793-0
Gil, De Oliveira Júnior, Sarti, Acute muscle mass loss predicts long-term fatigue, myalgia, and health care costs in COVID-19 survivors, J Am Med Dir Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2022.11.013
Gil, Filho, Shinjo, Muscle strength and muscle mass as predictors of hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a prospective observational study, J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12789
Graham, Steenbruggen, Miller, Standardization of spirometry 2019 update. An official American thoracic society and European respiratory society technical statement, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.201908-1590ST
Halpin, Mcivor, Whyatt, Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: a cross-sectional evaluation, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26368
Hatch, Young, Barber, Anxiety, depression and post traumatic stress disorder after critical illness: a UK-wide prospective cohort study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-018-2223-6
Hematocrit, None
Huang, Huang, Wang, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8
Huang, Li, Gu, Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6
Jimeno-Almazán, Martínez-Cava, Buendía-Romero, Relationship between the severity of persistent symptoms, physical fitness, and cardiopulmonary function in post-COVID-19 condition. A population-based analysis, Intern Emerg Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-022-03039-0
Jones, Rikli, Beam, A 30-S chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults, Res Q Exerc Sport, doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
Klok, Boon, Barco, The post-COVID-19 functional status scale: a tool to measure functional status over time after COVID-19, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01494-2020
Leidy, Functional status and the forward progress of merry-go-rounds: toward a coherent analytical framework, Nurs Res
Longobardi, Original research Podsiadlo D, Richardson S. The timed "Up & go": a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons, J Am Geriatr Soc, doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1991.tb01616.x
Longobardi, Prado, Do, Goessler, Oxygen uptake kinetics and chronotropic responses to exercise are impaired in survivors of severe COVID-19, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00291.2022
Maust, Cristancho, Gray, Psychiatric rating scales, Handb Clin Neurol, doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52002-9.00013-9
Morris, Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs, Organ Res Methods, doi:10.1177/1094428106291059
Munblit, Hara, Akrami, Long COVID: aiming for a consensus, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00135-7
Méndez, Balanzá-Martínez, Luperdi, Short-term neuropsychiatric outcomes and quality of life in COVID-19 survivors, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13262
Norman, Sloan, Wyrwich, De Andrade-Junior, De Salles et al., Interpretation of changes in health-related quality of life: the remarkable universality of half a standard deviation, Front Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.640973
Núñez-Cortés, Rivera-Lillo, Arias-Campoverde, Use of sit-to-stand test to assess the physical capacity and exertional desaturation in patients post COVID-19, Chron Respir Dis, doi:10.1177/1479973121999205
Pedersen, Saltin, Exercise as medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases, Scand J Med Sci Sports, doi:10.1111/sms.12581
Smart, Marwick, Exercise training for patients with heart failure: a systematic review of factors that improve mortality and morbidity, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.11.033
Szekely, Lichter, Sadon, Cardiorespiratory abnormalities in patients recovering from coronavirus disease, J Am Soc Echocardiogr, doi:10.1016/j.echo.2021.08.022
Thoracic, ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.167.2.211
Troosters, Casaburi, Gosselink, Pulmonary rehabilitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.200408-1109SO
Truffaut, Demey, Bruyneel, Post-discharge critical COVID-19 lung function related to severity of radiologic lung involvement at admission, Rev Bras Epidemiol, doi:10.1590/S1415-790X2013000400009
Van Laethem, De Veire, Backer, Response of the oxygen uptake efficiency slope to exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure, Eur J Heart Fail, doi:10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.01.007
Vella, Aidman, Teychenne, Optimising the effects of physical activity on mental health and wellbeing: a joint consensus statement from sports medicine Australia and the Australian psychological Society, J Sci Med Sport, doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2023.01.001
Ware, SF-36 health survey: manual and interpretation guide
Wilson, Cleary, Linking clinical variables with health-related quality of life. A conceptual model of patient outcomes, JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681",
"ISSN": [
"0306-3674",
"1473-0480"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Long-lasting effects of COVID-19 may include cardiovascular, respiratory, skeletal muscle, metabolic, psychological disorders and persistent symptoms that can impair health-related quality of life (HRQoL). We investigated the effects of a home-based exercise training (HBET) programme on HRQoL and health-related outcomes in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This was a single-centre, single-blinded, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial. Fifty survivors of severe/critical COVID-19 (5±1 months after intensive care unit discharge) were randomly allocated (1:1) to either a 3 times a week (~60–80 min/session), semi-supervised, individualised, HBET programme or standard of care (CONTROL). Changes in HRQoL were evaluated through the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey, and physical component summary was predetermined as the primary outcome. Secondary outcomes included cardiorespiratory fitness, pulmonary function, functional capacity, body composition and persistent symptoms. Assessments were performed at baseline and after 16 weeks of intervention. Statistical analysis followed intention-to-treat principles.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>After the intervention, HBET showed greater HRQoL score than CONTROL in the physical component summary (estimated mean difference, EMD: 16.8 points; 95% CI 5.8 to 27.9; effect size, ES: 0.74), physical functioning (EMD: 22.5 points, 95% CI 6.1 to 42.9, ES: 0.83), general health (EMD: 17.4 points, 95% CI 1.8 to 33.1, ES: 0.73) and vitality (EMD: 15.1 points, 95% CI 0.2 to 30.1, ES: 0.49) domains. 30-second sit-to-stand (EMD: 2.38 reps, 95% CI 0.01 to 4.76, ES: 0.86), and muscle weakness and myalgia were also improved in HBET compared with CONTROL (p<0.05). No significant differences were seen in the remaining variables. There were no adverse events.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>HBET is an effective and safe intervention to improve physical domains of HRQoL, functional capacity and persistent symptoms in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial registration number</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04615052\">NCT04615052</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6669-9553",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Longobardi",
"given": "Igor",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goessler",
"given": "Karla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Oliveira Júnior",
"given": "Gersiel Nascimento",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prado",
"given": "Danilo Marcelo Leite do",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Jhonnatan Vasconcelos Pereira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meletti",
"given": "Matheus Molina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Andrade",
"given": "Danieli Castro Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9050-0073",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gil",
"given": "Saulo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boza",
"given": "João Antonio Spott de Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Fernanda Rodrigues",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7100-8681",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gualano",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9513-6132",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Roschel",
"given": "Hamilton",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04615052",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
},
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04615052",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Sports Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Br J Sports Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T17:55:30Z",
"timestamp": 1683741330000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T17:55:57Z",
"timestamp": 1683741357000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003593",
"award": [
"#308307/2021-6"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001807",
"award": [
"#2017/13552-2",
"#2019/18039-7",
"#2020/07540-4",
"#2020/15678-6",
"#2021/13580-1"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-11T04:39:29Z",
"timestamp": 1683779969199
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://bmj.com/coronavirus/usage",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683676800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "bjsports-2022-106681",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/INFDIS/JIAC136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.1"
},
{
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.2",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization . Clinical management of COVID-19: living guideline. 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00291.2022",
"article-title": "Oxygen uptake kinetics and chronotropic responses to exercise are impaired in survivors of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Longobardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H569",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.3",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36057",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.4",
"unstructured": "Durstenfeld MS , Sun K , Tahir P , et al . Use of cardiopulmonary exercise testing to evaluate long COVID-19 symptoms in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2022;5:e2236057. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36057"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1479973121999205",
"article-title": "Use of sit-to-stand test to assess the physical capacity and exertional desaturation in patients post COVID-19",
"author": "Núñez-Cortés",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1479973121999205",
"journal-title": "Chron Respir Dis",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.5",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2022.11.013",
"article-title": "Acute muscle mass loss predicts long-term fatigue, myalgia, and health care costs in COVID-19 survivors",
"author": "Gil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Dir Assoc",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.6",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13262",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6",
"article-title": "Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "863",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26368",
"article-title": "Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: a cross-sectional evaluation",
"author": "Halpin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1013",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.10",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27101",
"article-title": "Evaluation of long-term radiological findings, pulmonary functions, and health-related quality of life in survivors of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Bardakci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5574",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.11",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/sms.12581",
"article-title": "Exercise as medicine-evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Scand J Med Sci Sports",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.12",
"volume": "25 Suppl 3",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/MSS.0000000000002977",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular, respiratory, and functional effects of home-based exercise training after COVID-19 hospitalization",
"author": "Teixeira Do Amaral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1795",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Sports Exerc",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.13",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.14",
"unstructured": "Ware J . SF-36 health survey: manual and interpretation guide; 1993."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.167.2.211",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0735-1097(96)00412-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201908-1590ST",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.17"
},
{
"article-title": "Grip strength: effects of testing posture and elbow position",
"author": "Balogun",
"first-page": "280",
"journal-title": "Arch Phys Med Rehabil",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.18",
"volume": "72",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1532-5415.1991.tb01616.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00006199-199407000-00002",
"article-title": "Functional status and the forward progress of merry-go-rounds: toward a coherent analytical framework",
"author": "Leidy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"journal-title": "Nurs Res",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.21",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1995.03520250075037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01494-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-444-52002-9.00013-9",
"article-title": "Psychiatric rating scales",
"author": "Maust",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Handb Clin Neurol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.24",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1094428106291059",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00135-7",
"article-title": "Long COVID: aiming for a consensus",
"author": "Munblit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.27",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1547-5069.2005.00058.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-021-01625-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.29",
"unstructured": "Truffaut L , Demey L , Bruyneel AV , et al . Post-discharge critical COVID-19 lung function related to severity of radiologic lung involvement at admission. Respir Res 2021;22:29. doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01625-y"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S1415-790X2013000400009",
"article-title": "Brazilian normative data for the short form 36 questionnaire, version 2",
"author": "Laguardia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "889",
"journal-title": "Rev Bras Epidemiol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.30",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005650-200305000-00004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2021.640973",
"article-title": "Skeletal muscle wasting and function impairment in intensive care patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "de Andrade-Junior",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "640973",
"journal-title": "Front Physiol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.13052",
"article-title": "Acute skeletal muscle loss in SARS-cov-2 infection contributes to poor clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Attaway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2436",
"journal-title": "J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.33",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12789",
"article-title": "Muscle strength and muscle mass as predictors of hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a prospective observational study",
"author": "Gil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1871",
"journal-title": "J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.34",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40279-017-0793-0",
"article-title": "Volume for muscle hypertrophy and health outcomes: the most effective variable in resistance training",
"author": "Figueiredo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "Sports Med",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.35",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1113/EP089965",
"article-title": "Evidence for impaired chronotropic responses to and recovery from 6-minute walk test in women with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Baranauskas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "722",
"journal-title": "Exp Physiol",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.36",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.echo.2021.08.022",
"article-title": "Cardiorespiratory abnormalities in patients recovering from coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Szekely",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1273",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Echocardiogr",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.37",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.01.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.200408-1109SO",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.11.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-022-03039-0",
"article-title": "Relationship between the severity of persistent symptoms, physical fitness, and cardiopulmonary function in post-COVID-19 condition. A population-based analysis",
"author": "Jimeno-Almazán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2199",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.41",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-018-2223-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.42",
"unstructured": "Hatch R , Young D , Barber V , et al . Anxiety, depression and post traumatic stress disorder after critical illness: a UK-wide prospective cohort study. Crit Care 2018;22:310. doi:10.1186/s13054-018-2223-6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsams.2023.01.001",
"article-title": "Optimising the effects of physical activity on mental health and wellbeing: a joint consensus statement from sports medicine Australia and the Australian psychological Society",
"author": "Vella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "J Sci Med Sport",
"key": "2023051010250705000_bjsports-2022-106681v1.43",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bjsm.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bjsports-2022-106681"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Physical Therapy, Sports Therapy and Rehabilitation",
"Orthopedics and Sports Medicine",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of a 16-week home-based exercise training programme on health-related quality of life, functional capacity, and persistent symptoms in survivors of severe/critical COVID-19: a randomised controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy"
}