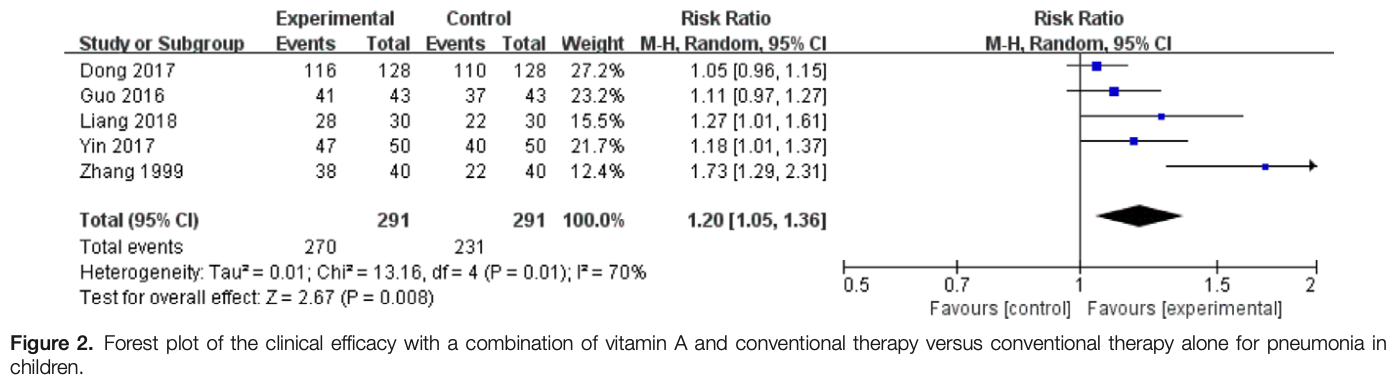
Vitamin A in children’s pneumonia for a COVID-19 perspective: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 trials
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000031289, Oct 2022
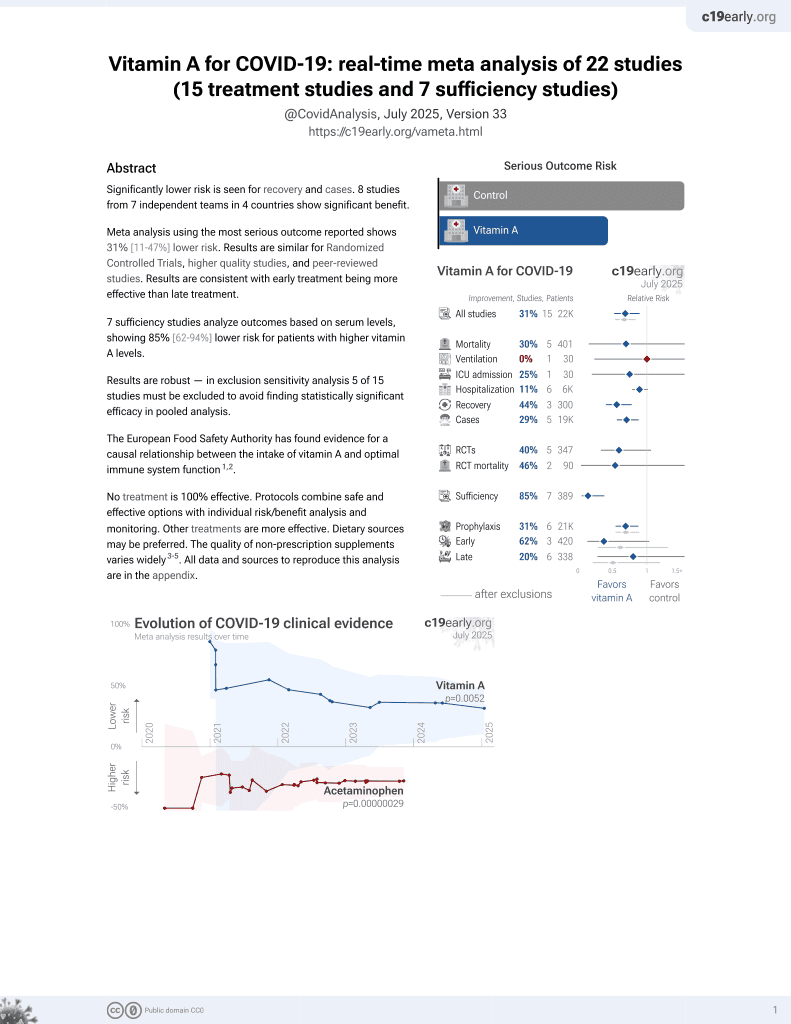
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review and meta analysis of 15 pediatric vitamin A trials for pneumonia, showing improved clinical efficacy and faster resolution of fever, cough, dyspnea, lung rale, and chest x-ray findings. There was no significant difference for mortality (3 studies, dominated by a late treatment study with high control mortality).
Currently there are 14 vitamin A studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 46% lower [-277‑92%] |
| Hospitalization | 19% lower [5‑30%] |
| Cases | 29% fewer [12‑44%] |
Li et al., 21 Oct 2022, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: zhao.ye@staff.krirk.ac.th.
Vitamin A in children’s pneumonia for a COVID-19 perspective: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 trials
Medicine, doi:10.1097/md.0000000000031289
Background: To systematically review and meta-analyze the efficacy of vitamin A as an adjuvant therapy for pneumonia in children. Methods: We searched in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, WanFang Database and Chongqing VIP information network from libraries building to March 2022, screening randomized controlled trials (RCT) about vitamin A combined with conventional therapy for pneumonia in children. Two researchers used the Cochrane risk of bias tool to assess the quality of included studies dependently. Data analysis was conducted in the RevMan 5.3. Results: 15 trials involving 3496 patients (treated group: 1898; control group: 1598) were analyzed in this study. The Meta-analysis showed that vitamin A combined with conventional therapy improved clinical efficacy (P < .05), shortened the duration of fever and cough, negative time of chest X-ray, and the hospitalization, lung rale disappearance, choking milk disappearance, shortness of breath disappearance and perilabial cyanosis disappearance (P < .05). However, vitamin A combined with conventional therapy did not reduce the mortality of pneumonia in children (P > .05).
Conclusion: Vitamin A contributes to relieve the clinical symptoms and signs, and also shorten the hospitalization.
Table 2 The assessment of quality of included studies.
Random sequence generation Allocation concealment Binding of participants and personnel
Binding of outcome assessment Incomplete outcome
Selective reporting Other bias "+" = low risk, "?" = unclear, "-" = high risk.
Li et al. • Medicine (2022) Medicine vitamin as an adjuvant therapy for pneumonia in children is worth promoted.
Perspective High morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 makes it as an urgent global health issue. Vitamin A is believed to form the first line of defense against pathogens by playing a role in stratification, keratinization, differentiation and functional maturation. It participates in the formation of healthy mucinous layer and enhances antigen-specific immune function. RA, the active form of vitamin A, regulates the innate immune system. [42] Research has shown that VAD can reduce the body's resistance to COVID-19 virus infection. [43] It plays an important role in the recovery of lung tissue after injury. Bioinformatics identifies possible targets, therapeutic pathways and pharmacological functions for vitamin A against COVID-19 infection. [44] Vitamin A might treat the COVID-19 in terms of immunomodulatory, antiviral, associated cellular protection, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Conclusion Vitamin A contributes to relieve the clinical symptoms and signs, and shorten the hospitalization.
Author contributions All authors contributed to the design..
References
Booij, De Kerkhof, Acitretin revisited in the era of biologics, J Dermatolog Treat
Caiyun, Effect observation of vitamin A adjuvant treatment on respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia, Clin Med
De Medeiros, Pinto, De Almeida, Modulation of intestinal immune and barrier functions by vitamin A: implications for current understanding of malnutrition and enteric infections in children, Nutrients
Fawzi, Mbise, Fataki, Vitamin A supplementation and severity of pneumonia in children admitted to the hospital in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, Am J Clin Nutr
Ferreira, Sant, Cc, De Fátima, March, Lethality by pneumonia and factors associated to death, J Pediatr
Green, Mellanby, Vitamin A as an anti-infective agent, Br Med J
Huanli, Adjuvant therapeutic effect of low-dose vitamin A or combination of multiple nutrients on neonatal pneumonia, J Clin Pulm Med
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Imdad, Mayo-Wilson, Herzer, Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Jain, Williams, Arnold, Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children, N Engl J Med
Jishan, Observation of curative effect of vitamin A in 40 children with recurrent bronchopneumonia, J Jining Med College
Kuzdan, Soysal, Özdemir, Rahnella aquatilis sepsis in a premature newborn, Case Rep Pediatr
Li, Bingbing, Liping, Study on adjuvant efficacy of vitamin A combined with nutrients in newborns with pulmonary infection, Chin Med Sci
Li, Guo, Zhang, The correlation between vitamin a status and refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (RMPP) incidence in children, BMC Pediatr
Li, Wu, Li, Revealing the targets and mechanisms of vitamin A in the treatment of COVID-19, Aging
Liu, Shefali, Dan, Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the sustainable development goals, Lancet
Mahalanabis, Lahiri, Paul, Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the efficacy of treatment with zinc or vitamin A in infants and young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection, Am J Clin Nutr
Manyi, Discussion on the mechanism of vitamin A in the adjuvant treatment of pediatric pneumonia, Drugs Clin
Mohamed, Mougi, Mansour, Administration of lycopene and beta-carotene decreased risks of pneumonia among children, Pak J Nutr
Nacul, Kirkwood, Arthur, Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial of efficacy of vitamin A treatment in non-measles childhood pneumonia, BMJ
O'brien, Wolfson, Watt, Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates, Lancet
Orfanos, Zouboulis, Oral retinoids in the treatment of seborrhoea and acne, Dermatology
Penkert, Smith, Hrincius, Effect of vitamin A deficiency in dysregulating immune responses to influenza virus and increasing mortality rates after bacterial coinfections, J Infect Dis
Penkert, Surman, Jones, Vitamin A deficient mice exhibit increased viral antigens and enhanced cytokine/chemokine production in nasal tissues following respiratory virus infection despite the presence of FoxP3+ T cells, Int Immunol
Qianqian, Exploration of the effect of vitamin A adjuvant therapy on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children, Contemp Med Theor Clust
Rider, Frazee, Community-acquired pneumonia, Emerg Med Clin North Am
Rodríguez, Hamer, Rivera, Effects of moderate doses of vitamin A as an adjunct to the treatment of pneumonia in underweight and normal-weight children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Am J Clin Nutr
Si, Grytter, Vy, High dose vitamin A supplementation in the course of pneumonia in Vietnamese children, Acta Paediatr
Spinas, Saggini, Kritas, Can vitamin A mediate immunity and inflammation?, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Stephensen, Franchi, Hernandez, Adverse effects of high-dose vitamin A supplements in children hospitalized with pneumonia, Pediatrics
Stephensen, Lietz, Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2, Br J Nutr
Stephensen, Vitamina, infection, and immune function, Annu Rev Nutr
Sufang, Observation of curative effect of vitamin A on 60 children with pneumonia, Chin J Compr Med
Swami, Thakur, Bhatia, Impact of mass supplementation of vitamin A, Indian J Pediatr
Thielitz, Gollnick, Topical retinoids in acne vulgaris: update on efficacy and safety, Am J Clin Dermatol
Thornton, Mora-Plazas, Marín, Vitamin A deficiency is associated with gastrointestinal and respiratory morbidity in schoolage children, J Nutr
Tingyu, Hongmei, Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of vitamin A deficiency, J Pract Pediatr Clin
Velasquez-Melendez, Okani, Kiertsman, Vitamin A status in children with pneumonia, Eur J Clin Nutr
Weiping, Shuming, Efficacy analysis of vitamin A in the adjuvant treatment of 68 cases of persistent pneumonia, J Nanhua Univ (Medical Edition)
Weiss, Ellis, Headington, Topical tretinoin improves photoaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled study, JAMA
Xing, Sheng, Xiao, Vitamin A deficiency is associated with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children, Ann Transl Med
Yaofeng, Low-dose vitamin A or multiple nutrients as adjuvant therapy for neonatal pneumonia, Matern Child Health Care China
Zengfang, Zhaoping, Clinical study of low-dose vitamin A or multiple nutrients in the adjuvant treatment of neonatal pneumonia, J Pract Clin Med
Zhang, Li, Zhang, Effects of vitamin A on expressions of apoptosis genes Bax and Bcl-2 in epithelial cells of corneal tissues induced by benzalkonium chloride in mice with dry eye, Med Sci Monit
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000031289",
"ISSN": [
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000031289",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ruoxi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Wenli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Hongwu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toshiyoshi",
"given": "Maeda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bu",
"given": "Huaien",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-24T19:12:16Z",
"timestamp": 1666638736000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T15:55:56Z",
"timestamp": 1666713356000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-25T16:17:53Z",
"timestamp": 1666714673192
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "42",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "42",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000031289",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e31289",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.emc.2018.07.001",
"article-title": "Community-acquired pneumonia.",
"author": "Rider",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "665",
"journal-title": "Emerg Med Clin North Am",
"key": "R1-20221025",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Rahnella aquatilis sepsis in a premature newborn.",
"author": "Kuzdan",
"first-page": "860671",
"journal-title": "Case Rep Pediatr",
"key": "R2-20221025",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jped.2013.05.008",
"article-title": "Lethality by pneumonia and factors associated to death.",
"author": "Ferreira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr (Rio J)",
"key": "R3-20221025",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31593-8",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000–15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the sustainable development goals.",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3027",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R4-20221025",
"volume": "388",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61204-6",
"article-title": "Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates.",
"author": "O’Brien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "893",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R5-20221025",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1405870",
"article-title": "Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children.",
"author": "Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "835",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R6-20221025",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/MSM.913478",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin A on expressions of apoptosis genes Bax and Bcl-2 in epithelial cells of corneal tissues induced by benzalkonium chloride in mice with dry eye.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4583",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Monit",
"key": "R7-20221025",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091128",
"article-title": "Modulation of intestinal immune and barrier functions by vitamin A: implications for current understanding of malnutrition and enteric infections in children.",
"author": "de Medeiros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1128",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "R8-20221025",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of vitamin A deficiency.",
"author": "Tingyu",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "J Pract Pediatr Clin",
"key": "R9-20221025",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Can vitamin A mediate immunity and inflammation?",
"author": "Spinas",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Biol Regul Homeost Agents",
"key": "R10-20221025",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12887-020-02254-y",
"article-title": "The correlation between vitamin a status and refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (RMPP) incidence in children.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "BMC Pediatr",
"key": "R11-20221025",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin A status in children with pneumonia.",
"author": "Velasquez-Melendez",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "R12-20221025",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm.2020.02.33",
"article-title": "Vitamin A deficiency is associated with severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.",
"author": "Xing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "Ann Transl Med",
"key": "R13-20221025",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/82.5.1090",
"article-title": "Effects of moderate doses of vitamin A as an adjunct to the treatment of pneumonia in underweight and normal-weight children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Rodríguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1090",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "R14-20221025",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Observation of curative effect of vitamin A in 40 children with recurrent bronchopneumonia.",
"author": "Jishan",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "J Jining Med College",
"key": "R15-20221025",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.101.5.e3",
"article-title": "Adverse effects of high-dose vitamin A supplements in children hospitalized with pneumonia.",
"author": "Stephensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E3",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "R16-20221025",
"volume": "101",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1651-2227.1997.tb14805.x",
"article-title": "High dose vitamin A supplementation in the course of pneumonia in Vietnamese children.",
"author": "Si",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1052",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr",
"key": "R17-20221025",
"volume": "86",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.315.7107.505",
"article-title": "Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial of efficacy of vitamin A treatment in non-measles childhood pneumonia.",
"author": "Nacul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "R18-20221025",
"volume": "315",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/68.1.187",
"article-title": "Vitamin A supplementation and severity of pneumonia in children admitted to the hospital in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania.",
"author": "Fawzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "187",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "R19-20221025",
"volume": "68",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect observation of vitamin A adjuvant treatment on respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia.",
"author": "Caiyun",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Clin Med",
"key": "R20-20221025",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"article-title": "Observation of curative effect of vitamin A on 60 children with pneumonia.",
"author": "Sufang",
"first-page": "429",
"journal-title": "Chin J Compr Med",
"key": "R21-20221025",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy analysis of vitamin A in the adjuvant treatment of 68 cases of persistent pneumonia.",
"author": "Weiping",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "J Nanhua Univ (Medical Edition)",
"key": "R22-20221025",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "Low-dose vitamin A or multiple nutrients as adjuvant therapy for neonatal pneumonia.",
"author": "Yaofeng",
"first-page": "2558",
"journal-title": "Matern Child Health Care China",
"key": "R23-20221025",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Adjuvant therapeutic effect of low-dose vitamin A or combination of multiple nutrients on neonatal pneumonia.",
"author": "Huanli",
"first-page": "1432",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pulm Med",
"key": "R24-20221025",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical study of low-dose vitamin A or multiple nutrients in the adjuvant treatment of neonatal pneumonia.",
"author": "Zengfang",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "J Pract Clin Med",
"key": "R25-20221025",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Exploration of the effect of vitamin A adjuvant therapy on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.",
"author": "Qianqian",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Contemp Med Theor Clust",
"key": "R26-20221025",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Study on adjuvant efficacy of vitamin A combined with nutrients in newborns with pulmonary infection.",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Chin Med Sci",
"key": "R27-20221025",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Discussion on the mechanism of vitamin A in the adjuvant treatment of pediatric pneumonia.",
"author": "Manyi",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "Drugs Clin",
"key": "R28-20221025",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxv064",
"article-title": "Vitamin A deficient mice exhibit increased viral antigens and enhanced cytokine/chemokine production in nasal tissues following respiratory virus infection despite the presence of FoxP3+ T cells.",
"author": "Penkert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Int Immunol",
"key": "R29-20221025",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa597",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin A deficiency in dysregulating immune responses to influenza virus and increasing mortality rates after bacterial coinfections.",
"author": "Penkert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1806",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "R30-20221025",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.113.185876",
"article-title": "Vitamin A deficiency is associated with gastrointestinal and respiratory morbidity in school-age children.",
"author": "Thornton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "R31-20221025",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age.",
"author": "Imdad",
"first-page": "CD008524",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "R32-20221025",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12098-007-0074-2",
"article-title": "Impact of mass supplementation of vitamin A.",
"author": "Swami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "443",
"journal-title": "Indian J Pediatr",
"key": "R33-20221025",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3923/pjn.2008.273.277",
"article-title": "Administration of lycopene and beta-carotene decreased risks of pneumonia among children.",
"author": "Mohamed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Pak J Nutr",
"key": "R34-20221025",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/79.3.430",
"article-title": "Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the efficacy of treatment with zinc or vitamin A in infants and young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection.",
"author": "Mahalanabis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "R35-20221025",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.2.3537.691",
"article-title": "Vitamin A as an anti-infective agent.",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "691",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "R36-20221025",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1928"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167",
"article-title": "Vitamina, infection, and immune function.",
"author": "Stephensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Nutr",
"key": "R37-20221025",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/09546630903578582",
"article-title": "Acitretin revisited in the era of biologics.",
"author": "Booij",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "86",
"journal-title": "J Dermatolog Treat",
"key": "R38-20221025",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000017848",
"article-title": "Oral retinoids in the treatment of seborrhoea and acne.",
"author": "Orfanos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Dermatology",
"key": "R39-20221025",
"volume": "196",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/0128071-200809060-00003",
"article-title": "Topical retinoids in acne vulgaris: update on efficacy and safety.",
"author": "Thielitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Dermatol",
"key": "R40-20221025",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1988.03720040019020",
"article-title": "Topical tretinoin improves photoaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled study.",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "527",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R41-20221025",
"volume": "259",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis.",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "R42-20221025",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114521000246",
"article-title": "Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2.",
"author": "Stephensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1663",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "R43-20221025",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103888",
"article-title": "Revealing the targets and mechanisms of vitamin A in the treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15784",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "R44-20221025",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000031289"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin A in children’s pneumonia for a COVID-19 perspective: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "101"
}