The anti-COVID-19 drug Paxlovid crosses biological barriers of the placenta and brain in rats
et al., npj Viruses, doi:10.1038/s44298-023-00013-1, Jan 2024
Animal study showing that paxlovid crosses biological barriers of the blood-placenta and blood-brain in rats. Authors developed a multisite microdialysis coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS to monitor nirmatrelvir levels in maternal blood, conceptus (fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid), and brains of male and nonpregnant female rats after intravenous administration. Results demonstrated that nirmatrelvir rapidly penetrates the blood-placenta barrier to reach the conceptus and crosses the blood-brain barrier in male and nonpregnant female rats. Protein-unbound nirmatrelvir increased significantly during pregnancy but did not differ between nonpregnant female and male rats. Concentrations in blood, conceptus, and brain were higher than the effective concentration of 90% (EC90) after administration of nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir. Ritonavir provided a synergistic pharmacokinetic effect by inhibiting CYP3A enzymes, significantly enhancing nirmatrelvir levels in biological samples. The study highlights that pregnancy is an important factor affecting pharmacokinetics with increased protein-unbound nirmatrelvir in blood and tissues.
Lee et al., 24 Jan 2024, USA, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: thtsai@nycu.edu.tw.
The anti-COVID-19 drug Paxlovid crosses biological barriers of the placenta and brain in rats
npj Viruses, doi:10.1038/s44298-023-00013-1
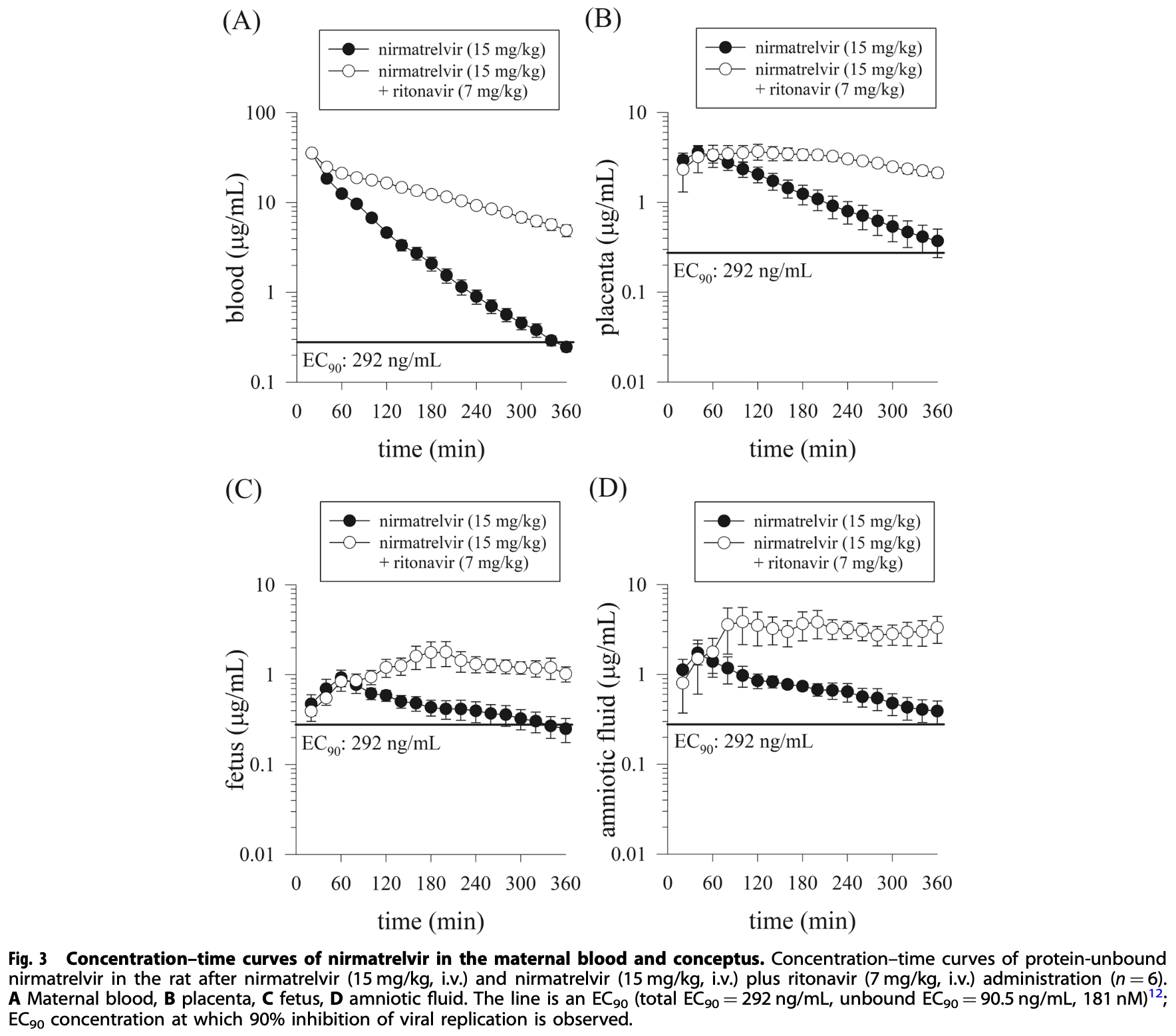
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir) is an orally available drug for the treatment of COVID-19 disease. However, limited information remains on the biological barrier transfer of nirmatrelvir. In the present study, we investigated whether nirmatrelvir crosses the blood-placenta barrier to reach the conceptus (the collective term for the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid) during pregnancy and the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in male rats. Additionally, in this study, gender and pregnancy issues were investigated. Multisite microdialysis coupled with validated UHPLC-MS/MS was developed to monitor nirmatrelvir levels in maternal blood and the conceptus in pregnant rats and of the blood and brain in male and nonpregnant female rats after administration of nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) alone and nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) combined with ritonavir (7 mg/kg, i.v.). Pharmacokinetic results showed that nirmatrelvir rapidly penetrates the blood-placenta barrier to reach the conceptus after administration of nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) alone and nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) combined with ritonavir (7 mg/kg, i.v.) in pregnant rats. Nirmatrelvir also crosses the BBB in male and nonpregnant female rats in the same dose regimen. Compared to sex and pregnancy factors, the results show that protein-unbound nirmatrelvir increased significantly during pregnancy and did not differ between nonpregnant female and male rats. The results indicated that the concentrations of nirmatrelvir in the blood, conceptus, and brain were higher than the effective concentration of 90% (total EC 90 = 292 ng/mL, unbound EC 90 = 90.5 ng/mL, 181 nM) after the administration of nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir. Ritonavir provides a synergistic pharmacokinetic effect. Pregnancy is an important issue with increased protein-unbound nirmatrelvir in the blood and tissues.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s44298-023-00013-1 . Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Tung-Hu Tsai. Reprints and permission information is available at http://www.nature.com/ reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Alexopoulos, Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the CSF, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and neurological outcome: studies in 8 stuporous and comatose patients, Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm
Anderson, Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults, N. Engl. J. Med
Arifin, Zahiruddin, Sample size calculation in animal studies using resource equation approach, Malays. J. Med. Sci
Baig, Khaleeq, Ali, Syeda, Evidence of the COVID-19 virus targeting the CNS: tissue distribution, host-virus interaction, and proposed neurotropic mechanisms, ACS Chem. Neurosci
Banks, Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier, BMC Neurol
Chang, Biotransformation and brain distribution of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir and herb-drug pharmacokinetic interactions between the herbal extract Scutellaria formula-NRICM101, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal
Chang, Transfer and biotransformation of the COVID-19 prodrug molnupiravir and its metabolite β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine across the bloodplacenta barrier, EBioMedicine
Chuang, Transplacental passage of nirmatrelvir in pregnant women with COVID-19, Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet, doi:10.1002/ijgo.15147
Eng, Disposition of nirmatrelvir, an orally bioavailable inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease, across animals and humans, Drug Metab. Dispos
Facchetti, SARS-CoV2 vertical transmission with adverse effects on the newborn revealed through integrated immunohistochemical, electron microscopy and molecular analyses of placenta, EBioMedicine
Fettweis, Borlak, Topics in xenobiochemistryapplication of microdialysis techniques in pharmacokinetic studies, Xenobiotica
Gervasini, Carrillo, Benitez, Potential role of cerebral cytochrome P450 in clinical pharmacokinetics: modulation by endogenous compounds, Clin. Pharmacokinet
Gottlieb, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients, N. Engl. J. Med
Hammond, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Harris, Benet, Schwartz, Gender effects in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, Drugs
Hebert, Effects of pregnancy on CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activities as measured by disposition of midazolam and digoxin: a University of Washington specialized center of research study, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Hoffmann, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hsu, Granneman, Bertz, Ritonavir: clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents, Clin. Pharmacokinet
Lamb, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval, Drugs
Li, Neurological manifestations of patients with COVID-19: potential routes of SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion from the periphery to the brain, Front. Med
Lin, Clinical outcomes of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir use in pregnant women during the Omicron wave of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, J. Infect. Public Health
Mahendroo, Nallasamy, Encyclopedia of Reproduction
Moriguchi, A first case of meningitis/encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2, Int. J. Infect. Dis
Nair, Jacob, A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human, J. Basic Clin. Pharm
Owen, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Paniz-Mondolfi, Central nervous system involvement by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), J. Med. Virol
Percie Du Sert, The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research, PLoS Biol
Perloff, Von Moltke, Greenblatt, Ritonavir and dexamethasone induce expression of CYP3A and P-glycoprotein in rats, Xenobiotica
Pfizer, None
Pfizer, None
Pfizer, None
Polack, Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine, N. Engl. J. Med
Poon, Global interim guidance on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during pregnancy and puerperium from FIGO and allied partners: information for healthcare professionals, Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet
Reagan-Shaw, Nihal, Ahmad, Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited, FASEB J
Rhea, The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier in mice, Nat. Neurosci
Saleh, The PBPK LeiCNS-PK3. 0 framework predicts nirmatrelvir (but not remdesivir or molnupiravir) to achieve effective concentrations against SARS-CoV-2 in human brain cells, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs, Clin. Infect. Dis
Schreurs, Houston, May, Cipolla, The adaptation of the blood-brain barrier to vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor during pregnancy, FASEB J
Singh, Innovative randomized phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther
Tracy, Venkataramanan, Glover, Caritis, Temporal changes in drug metabolism (CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A Activity) during pregnancy, Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol
Tsai, Pharmacokinetics of pefloxacin and its interaction with cyclosporin A, a P-glycoprotein modulator, in rat blood, brain and bile, using simultaneous microdialysis, Br. J. Pharmacol
Vivanti, Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat. Commun
Wastnedge, Pregnancy and COVID-19, Physiol. Rev
Wilkinson, Cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A) metabolism: prediction of in vivo activity in humans, J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm
Woodland, Huang, Gryz, Bendayan, Fawcett, Expression, activity and regulation of CYP3A in human and rodent brain, Drug Metab. Rev
Yang, Lin, Lin, Dalley, Tsai, Biotransformation and transplacental transfer of the anti-viral remdesivir and predominant metabolite, GS-441524 in pregnant rats, EBioMedicine
Zhu, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med
Zizioli, Developmental safety of nirmatrelvir in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos, Birth Defects Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s44298-023-00013-1",
"ISSN": [
"2948-1767"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s44298-023-00013-1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir) is an orally available drug for the treatment of COVID-19 disease. However, limited information remains on the biological barrier transfer of nirmatrelvir. In the present study, we investigated whether nirmatrelvir crosses the blood-placenta barrier to reach the conceptus (the collective term for the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid) during pregnancy and the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in male rats. Additionally, in this study, gender and pregnancy issues were investigated. Multisite microdialysis coupled with validated UHPLC-MS/MS was developed to monitor nirmatrelvir levels in maternal blood and the conceptus in pregnant rats and of the blood and brain in male and nonpregnant female rats after administration of nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) alone and nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) combined with ritonavir (7 mg/kg, i.v.). Pharmacokinetic results showed that nirmatrelvir rapidly penetrates the blood–placenta barrier to reach the conceptus after administration of nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) alone and nirmatrelvir (15 mg/kg, i.v.) combined with ritonavir (7 mg/kg, i.v.) in pregnant rats. Nirmatrelvir also crosses the BBB in male and nonpregnant female rats in the same dose regimen. Compared to sex and pregnancy factors, the results show that protein-unbound nirmatrelvir increased significantly during pregnancy and did not differ between nonpregnant female and male rats. The results indicated that the concentrations of nirmatrelvir in the blood, conceptus, and brain were higher than the effective concentration of 90% (total EC<jats:sub>90</jats:sub> = 292 ng/mL, unbound EC<jats:sub>90</jats:sub> = 90.5 ng/mL, 181 nM) after the administration of nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir. Ritonavir provides a synergistic pharmacokinetic effect. Pregnancy is an important issue with increased protein-unbound nirmatrelvir in the blood and tissues.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"13"
],
"article-number": "4",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "25 October 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "10 December 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "24 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Wan-Hsin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Chung-Kai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Chun-Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Muh-Hwa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsai",
"given": "Tung-Hu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "npj Viruses",
"container-title-short": "npj Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-24T06:02:23Z",
"timestamp": 1706076143000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-09T00:06:15Z",
"timestamp": 1731110775000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-26T02:32:30Z",
"timestamp": 1745634750090,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1706054400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1706054400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-023-00013-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-023-00013-1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-023-00013-1.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhu, N. et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028436",
"author": "EJ Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2427",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13_CR2",
"unstructured": "Anderson, E. J. et al. Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine in older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2427–2438 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2034577",
"author": "FP Polack",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2603",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13_CR3",
"unstructured": "Polack, F. P. et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"author": "RL Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13_CR4",
"unstructured": "Gottlieb, R. L. et al. Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 305–315 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"author": "LD Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "13_CR5",
"unstructured": "Saravolatz, L. D., Depcinski, S. & Sharma, M. Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 76, 165–171 (2023).",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "13_CR6",
"unstructured": "Pfizer. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05011513 (2022)."
},
{
"key": "13_CR7",
"unstructured": "Pfizer. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05047601 (2022)."
},
{
"key": "13_CR8",
"unstructured": "Pfizer. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04960202 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "13_CR9",
"unstructured": "Hammond, J. et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1397–1408 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2603",
"author": "RSP Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "13_CR10",
"unstructured": "Singh, R. S. P. et al. Innovative randomized phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 112, 101–111 (2022).",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "13_CR11",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Emergency use authorization. https://www.fda.gov/media/155049/download (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"author": "DR Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "13_CR12",
"unstructured": "Owen, D. R. et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 374, 1586–1593 (2021).",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5",
"author": "YN Lamb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "13_CR13",
"unstructured": "Lamb, Y. N. Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval. Drugs 82, 585–591 (2022).",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "13_CR14",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for molnupiravir. https://www.fda.gov/media/155054/download (2021)."
},
{
"key": "13_CR15",
"unstructured": "U. S. Food and Drug Administration. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovid. https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104748",
"author": "CH Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104748",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "13_CR16",
"unstructured": "Chang, C. H. et al. Transfer and biotransformation of the COVID-19 prodrug molnupiravir and its metabolite β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine across the blood-placenta barrier. EBioMedicine 95, 104748 (2023).",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115499",
"author": "CH Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "115499",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.",
"key": "13_CR17",
"unstructured": "Chang, C. H. et al. Biotransformation and brain distribution of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir and herb-drug pharmacokinetic interactions between the herbal extract Scutellaria formula-NRICM101. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 234, 115499 (2023).",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2023.10.007",
"author": "CW Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1942",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "13_CR18",
"unstructured": "Lin, C. W. et al. Clinical outcomes of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir use in pregnant women during the Omicron wave of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. J. Infect. Public Health 16, 1942–1946 (2023).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00024.2020",
"author": "EAN Wastnedge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "13_CR19",
"unstructured": "Wastnedge, E. A. N. et al. Pregnancy and COVID-19. Physiol. Rev. 101, 303–318 (2021).",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijgo.13156",
"author": "LC Poon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet.",
"key": "13_CR20",
"unstructured": "Poon, L. C. et al. Global interim guidance on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) during pregnancy and puerperium from FIGO and allied partners: information for healthcare professionals. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 149, 273–286 (2020).",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00122",
"author": "AM Baig",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Neurosci.",
"key": "13_CR21",
"unstructured": "Baig, A. M., Khaleeq, A., Ali, U. & Syeda, H. Evidence of the COVID-19 virus targeting the CNS: tissue distribution, host-virus interaction, and proposed neurotropic mechanisms. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 11, 995–998 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271.e8",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "13_CR22",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181, 271.e8–280.e8 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25915",
"author": "A Paniz‐Mondolfi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "13_CR23",
"unstructured": "Paniz‐Mondolfi, A. et al. Central nervous system involvement by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus‐2 (SARS‐CoV‐2). J. Med. Virol. 92, 699–702 (2020).",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.062",
"author": "T Moriguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "13_CR24",
"unstructured": "Moriguchi, T. et al. A first case of meningitis/encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 94, 55–58 (2020).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-020-0786-5",
"author": "Z Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "13_CR25",
"unstructured": "Li, Z. et al. Neurological manifestations of patients with COVID-19: potential routes of SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion from the periphery to the brain. Front. Med. 14, 533–541 (2020).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104095",
"author": "L Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104095",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "13_CR26",
"unstructured": "Yang, L., Lin, I. H., Lin, L. C., Dalley, J. W. & Tsai, T. H. Biotransformation and transplacental transfer of the anti-viral remdesivir and predominant metabolite, GS-441524 in pregnant rats. EBioMedicine 81, 104095 (2022).",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0703927",
"author": "TH Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1310",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "13_CR27",
"unstructured": "Tsai, T. H. Pharmacokinetics of pefloxacin and its interaction with cyclosporin A, a P‐glycoprotein modulator, in rat blood, brain and bile, using simultaneous microdialysis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 132, 1310–1316 (2001).",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"key": "13_CR28",
"unstructured": "National Research Council, Division on Earth and Life Studies, Institute for Laboratory Animal Research & Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition (National Academies Press, 2010)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.64404-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "13_CR29",
"unstructured": "Mahendroo, M. & Nallasamy, S. in Encyclopedia of Reproduction (Second Edition) (ed Skinner, M. K.) 339–346 (Academic Press, 2018)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000410",
"author": "N Percie du Sert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3000410",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol.",
"key": "13_CR30",
"unstructured": "Percie du Sert, N. et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18, e3000410 (2020).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0976-0105.177703",
"author": "AB Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "J. Basic Clin. Pharm.",
"key": "13_CR31",
"unstructured": "Nair, A. B. & Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 7, 27–31 (2016).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.121.000801",
"author": "H Eng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "576",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "13_CR32",
"unstructured": "Eng, H. et al. Disposition of nirmatrelvir, an orally bioavailable inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease, across animals and humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 50, 576–590 (2022).",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-199835040-00002",
"author": "A Hsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "275",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacokinet.",
"key": "13_CR33",
"unstructured": "Hsu, A., Granneman, G. R. & Bertz, R. J. Ritonavir: clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 35, 275–291 (1998).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00498259609046725",
"author": "G Fettweis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "13_CR34",
"unstructured": "Fettweis, G. & Borlak, J. Topics in xenobiochemistry – application of microdialysis techniques in pharmacokinetic studies. Xenobiotica 26, 473–485 (1996).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.07-9574LSF",
"author": "S Reagan-Shaw",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "659",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "13_CR35",
"unstructured": "Reagan-Shaw, S., Nihal, M. & Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 22, 659–661 (2008).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21315/mjms2017.24.5.12",
"author": "WN Arifin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Malays. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "13_CR36",
"unstructured": "Arifin, W. N. & Zahiruddin, W. M. Sample size calculation in animal studies using resource equation approach. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 24, 101–105 (2017).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijgo.15147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "13_CR37",
"unstructured": "Chuang, M. T. et al. Transplacental passage of nirmatrelvir in pregnant women with COVID-19. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.15147 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102951",
"author": "F Facchetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102951",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "13_CR38",
"unstructured": "Facchetti, F. et al. SARS-CoV2 vertical transmission with adverse effects on the newborn revealed through integrated immunohistochemical, electron microscopy and molecular analyses of placenta. EBioMedicine 59, 102951 (2020).",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17436-6",
"author": "AJ Vivanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "13_CR39",
"unstructured": "Vivanti, A. J. et al. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 11, 3572 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.reprotox.2022.01.006",
"author": "NR Catlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Reprod. Toxicol.",
"key": "13_CR40",
"unstructured": "Catlin, N. R. et al. Reproductive and developmental safety of nirmatrelvir (PF-07321332), an oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor in animal models. Reprod. Toxicol. 108, 56–61 (2022).",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bdr2.2128",
"author": "D Zizioli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Birth Defects Res.",
"key": "13_CR41",
"unstructured": "Zizioli, D. et al. Developmental safety of nirmatrelvir in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Birth Defects Res. 115, 430–440 (2023).",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-020-00771-8",
"author": "EM Rhea",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "368",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "13_CR42",
"unstructured": "Rhea, E. M. et al. The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood–brain barrier in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 368–378 (2021).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/NXI.0000000000000893",
"author": "H Alexopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e893",
"journal-title": "Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm.",
"key": "13_CR43",
"unstructured": "Alexopoulos, H. et al. Anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the CSF, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and neurological outcome: studies in 8 stuporous and comatose patients. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 7, e893 (2020).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106345",
"author": "MA Saleh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106345",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "13_CR44",
"unstructured": "Saleh, M. A. et al. The PBPK LeiCNS-PK3. 0 framework predicts nirmatrelvir (but not remdesivir or molnupiravir) to achieve effective concentrations against SARS-CoV-2 in human brain cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 181, 106345 (2023).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajog.2004.08.030",
"author": "TS Tracy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "633",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.",
"key": "13_CR45",
"unstructured": "Tracy, T. S., Venkataramanan, R., Glover, D. D. & Caritis, S. N. Temporal changes in drug metabolism (CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A Activity) during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 192, 633–639 (2005).",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/clpt.2008.1",
"author": "MF Hebert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "13_CR46",
"unstructured": "Hebert, M. F. et al. Effects of pregnancy on CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activities as measured by disposition of midazolam and digoxin: a University of Washington specialized center of research study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 84, 248–253 (2008).",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003495-199550020-00003",
"author": "RZ Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "13_CR47",
"unstructured": "Harris, R. Z., Benet, L. Z. & Schwartz, J. B. Gender effects in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Drugs 50, 222–239 (1995).",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02353475",
"author": "GR Wilkinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.",
"key": "13_CR48",
"unstructured": "Wilkinson, G. R. Cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A) metabolism: prediction of in vivo activity in humans. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 24, 475–490 (1996).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2377-9-S1-S3",
"author": "WA Banks",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMC Neurol.",
"key": "13_CR49",
"unstructured": "Banks, W. A. Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier. BMC Neurol. 9, S3 (2009).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-200443110-00001",
"author": "G Gervasini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacokinet.",
"key": "13_CR50",
"unstructured": "Gervasini, G., Carrillo, J. A. & Benitez, J. Potential role of cerebral cytochrome P450 in clinical pharmacokinetics: modulation by endogenous compounds. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 43, 693–706 (2004).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03602530701836712",
"author": "C Woodland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Rev.",
"key": "13_CR51",
"unstructured": "Woodland, C., Huang, T. T., Gryz, E., Bendayan, R. & Fawcett, J. P. Expression, activity and regulation of CYP3A in human and rodent brain. Drug Metab. Rev. 40, 149–168 (2008).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00498250310001630215",
"author": "MD Perloff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Xenobiotica",
"key": "13_CR52",
"unstructured": "Perloff, M. D., von Moltke, L. L. & Greenblatt, D. J. Ritonavir and dexamethasone induce expression of CYP3A and P-glycoprotein in rats. Xenobiotica 34, 133–150 (2004).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.11-191916",
"author": "MP Schreurs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "13_CR53",
"unstructured": "Schreurs, M. P., Houston, E. M., May, V. & Cipolla, M. J. The adaptation of the blood-brain barrier to vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor during pregnancy. FASEB J. 26, 355–362 (2012).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2012"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-023-00013-1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The anti-COVID-19 drug Paxlovid crosses biological barriers of the placenta and brain in rats",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "2"
}