Covid-19 and vit-d: Disease mortality negatively correlates with sunlight exposure
et al., Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology, doi:10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362, Jul 2020
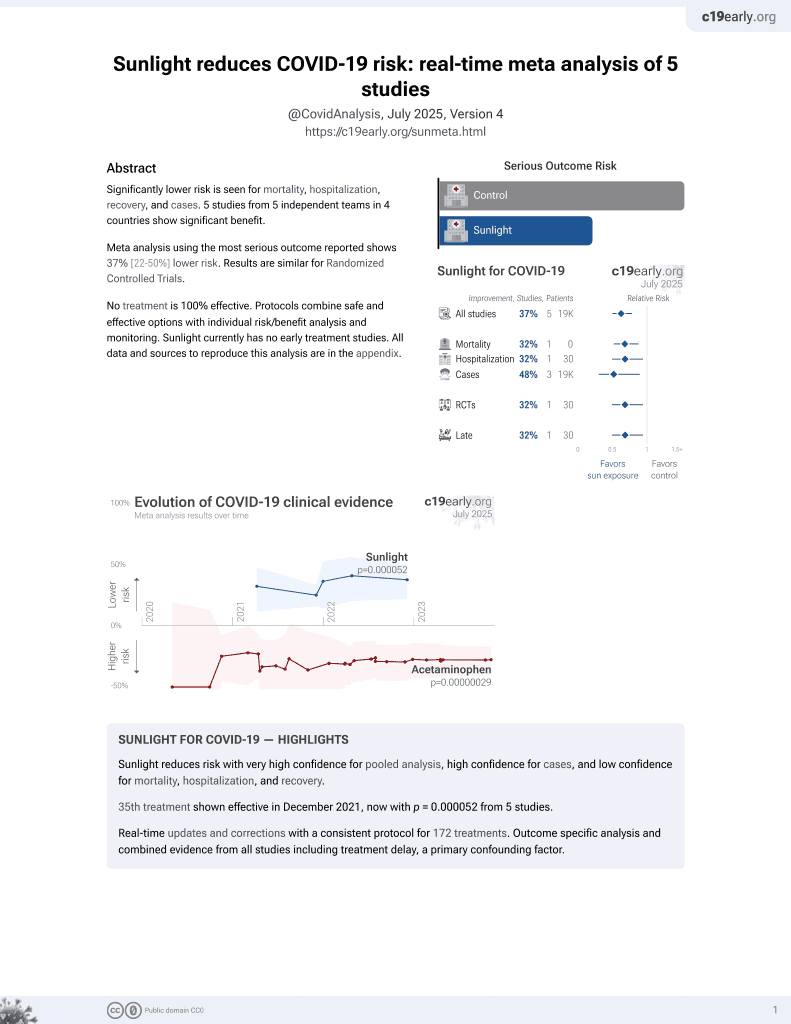
Sunlight for COVID-19
35th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
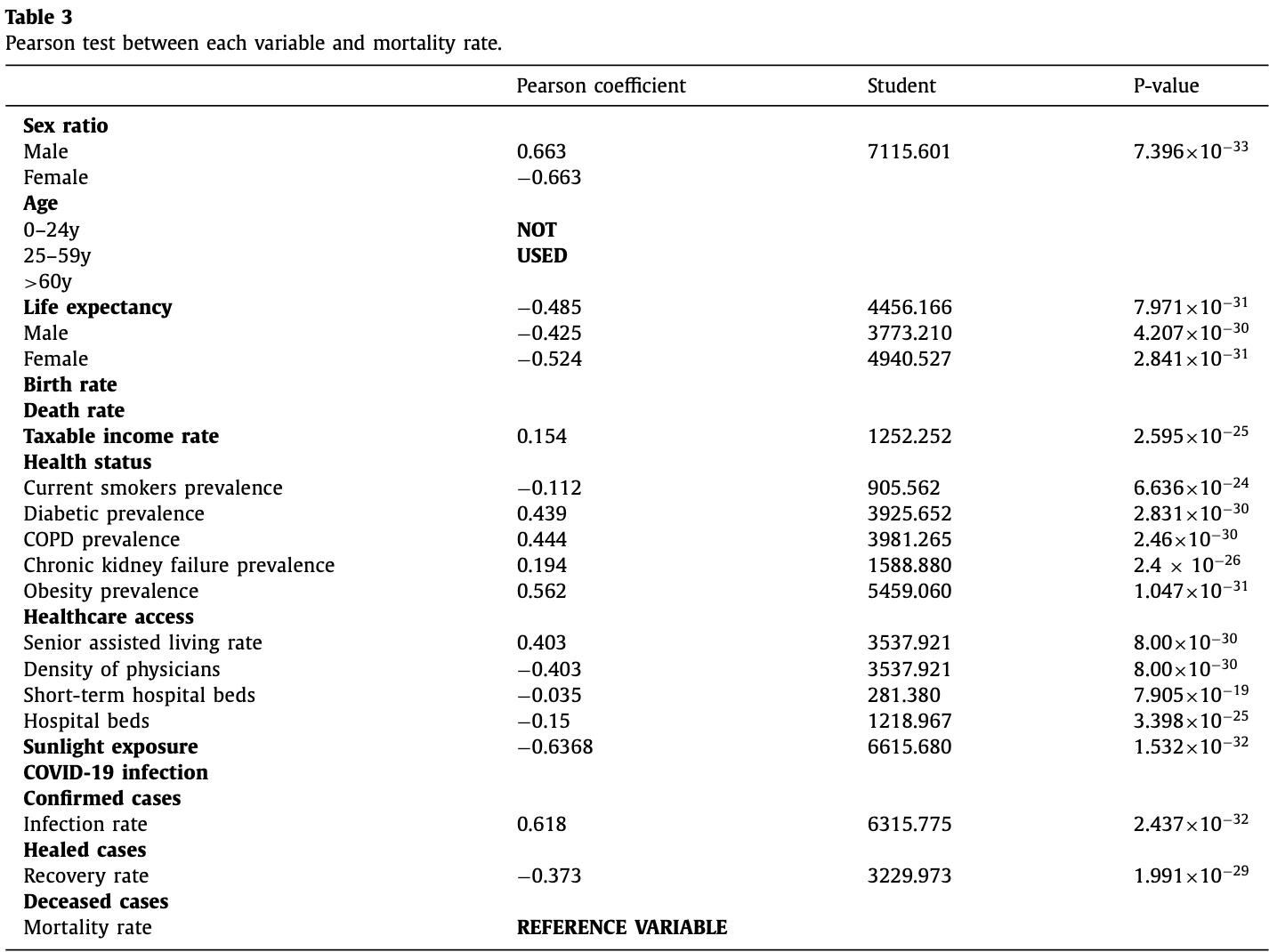
Analysis of COVID-19 mortality and sunlight exposure in continental metropolitan France, showing that average annual sunlight hours were significantly correlated with COVID-19 mortality, with a Pearson coefficient of -0.636. Also see the following comment and response1,2.
Lansiaux et al., 23 Jul 2020, France, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: edouard.lansiaux.etu@univ-lille.fr, edouard.lansiaux@orange.fr, philippe.pebay@ng-analytics.com, jl@pi.cards, joachim.son-forget@assemblee-nationale.fr.
Covid-19 and vit-d: Disease mortality negatively correlates with sunlight exposure
Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology, doi:10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
References
Chang, Lin, Wei, Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus infections involving 13 patients outside Wuhan. China, JAMA
Diao, Han, Pang, Li, Yang, HRCT imaging features in representative imported cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia, Precis. Clin. Med
Elf, Asmark, Nygren, Punga, Vitamin D defiency in patients with primary-immune mediated peripheral neuropathies, J. Neurol. Sci
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, New Engl. J. Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China, Lancet
Isaia, Medico, Possibile ruolo preventivo e terapeutico della vitamina D nella gestione della pandemia da COVID-19
Mao, Jin, Wang, Hu, Chen et al., Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan. China, JAMA Neurol
Poyiadji, Shahin, Noujaim, Stone, Patel et al., COVID-19-associated acute Hemorragic necrotizing encephalopathy: CT and MRI features, Radiol Mar
Talbot, Jouvenne, Le potentiel neurotrope des coronavirus, Méd./Sci
Tsujino, Ushikoshi-Nakayama, Yamazaki, Matsumoto, Saito, Pulmonary activation of vitamin D3 and preventive effect against interstitial pneumonia, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan. China, JAMA
Zhao, Shen, Zhou, Liu, Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: causality or coincidence?, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362",
"ISSN": [
"1877-5845"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362",
"alternative-id": [
"S187758452030040X"
],
"article-number": "100362",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Covid-19 and vit-d: Disease mortality negatively correlates with sunlight exposure"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lansiaux",
"given": "Édouard",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pébaÿ",
"given": "Philippe P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Picard",
"given": "Jean-Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forget",
"given": "Joachim",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology",
"container-title-short": "Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-23T06:53:13Z",
"timestamp": 1595487193000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-26T05:51:37Z",
"timestamp": 1619416297000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-03T02:19:06Z",
"timestamp": 1670033946554
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 17,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604188800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 268,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627344000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S187758452030040X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S187758452030040X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100362",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "China. JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0001",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "China. Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0002",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "New Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0003",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1623",
"article-title": "Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus infections involving 13 patients outside Wuhan",
"author": "Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "China. JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0004",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa004",
"article-title": "HRCT imaging features in representative imported cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"author": "Diao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Precis. Clin. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0005",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Le potentiel neurotrope des coronavirus",
"author": "Talbot",
"first-page": "119",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Méd./Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0006",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020201187",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated acute Hemorragic necrotizing encephalopathy: CT and MRI features",
"author": "Poyiadji",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Radiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0007",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30109-5",
"article-title": "Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: causality or coincidence?",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0008",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127",
"article-title": "Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan",
"author": "Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "China. JAMA Neurol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0009",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3164/jcbn.19-48",
"article-title": "Pulmonary activation of vitamin D3 and preventive effect against interstitial pneumonia",
"author": "Tsujino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0010",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2014.07.040",
"article-title": "Vitamin D defiency in patients with primary-immune mediated peripheral neuropathies",
"author": "Elf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0011",
"volume": "345",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Isaia G., Medico E.Possibile ruolo preventivo e terapeutico della vitamina D nella gestione della pandemia da COVID-19. 2020."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0013",
"unstructured": "Santé Publique France. Santé Publique France [Internet]. Santé Publique France. Available from:https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr2020."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0014",
"unstructured": "Météo France. Météo France [Internet]. Météo France. Available from:https://www.meteofrance.com2020."
},
{
"article-title": "Institut National de la statistique et des études économiques [Internet]",
"journal-title": "Insee",
"key": "10.1016/j.sste.2020.100362_bib0015",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S187758452030040X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health, Toxicology and Mutagenesis",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Geography, Planning and Development",
"Epidemiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Covid-19 and vit-d: Disease mortality negatively correlates with sunlight exposure",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "35"
}
lansiaux