Diet and selected elements of lifestyle in the Polish population before and during the COVID-19 pandemic – a population study
et al., Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/156939, Dec 2022
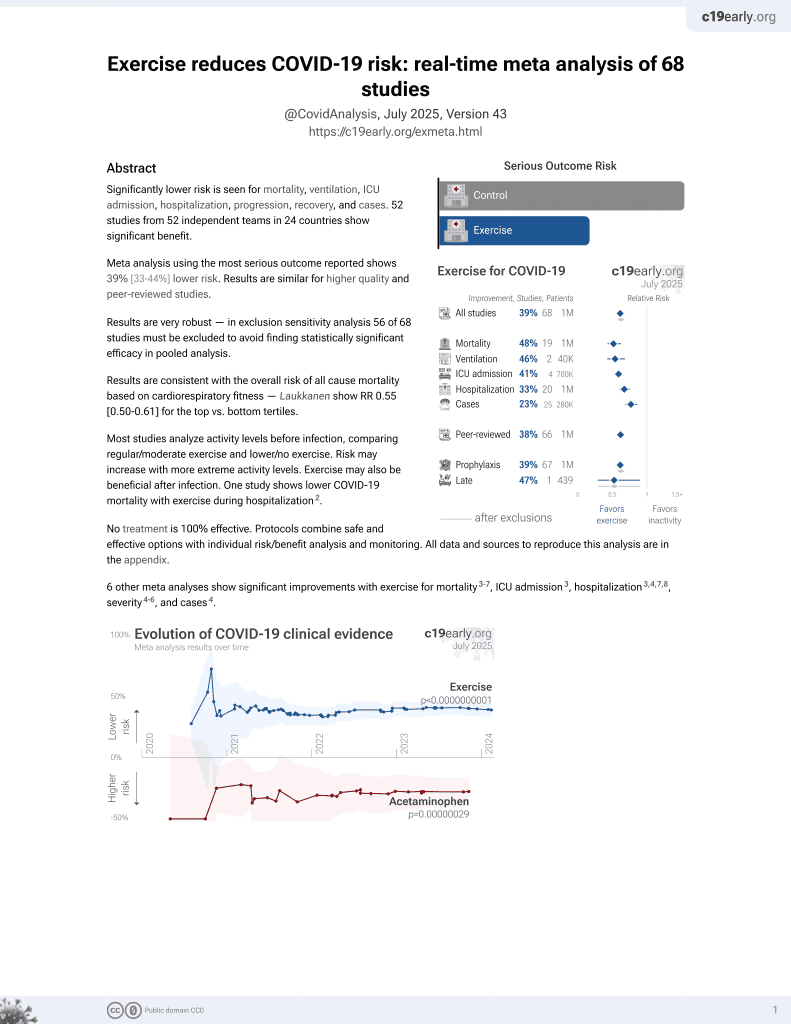
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 964 people in Poland showing decreased physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Study covers exercise and diet.
Kucharska et al., 28 Dec 2022, Poland, peer-reviewed, survey, 9 authors.
Contact: beata.sinska@wum.edu.pl.
Diet and selected elements of lifestyle in the Polish population before and during the COVID-19 pandemic – a population study
Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/156939
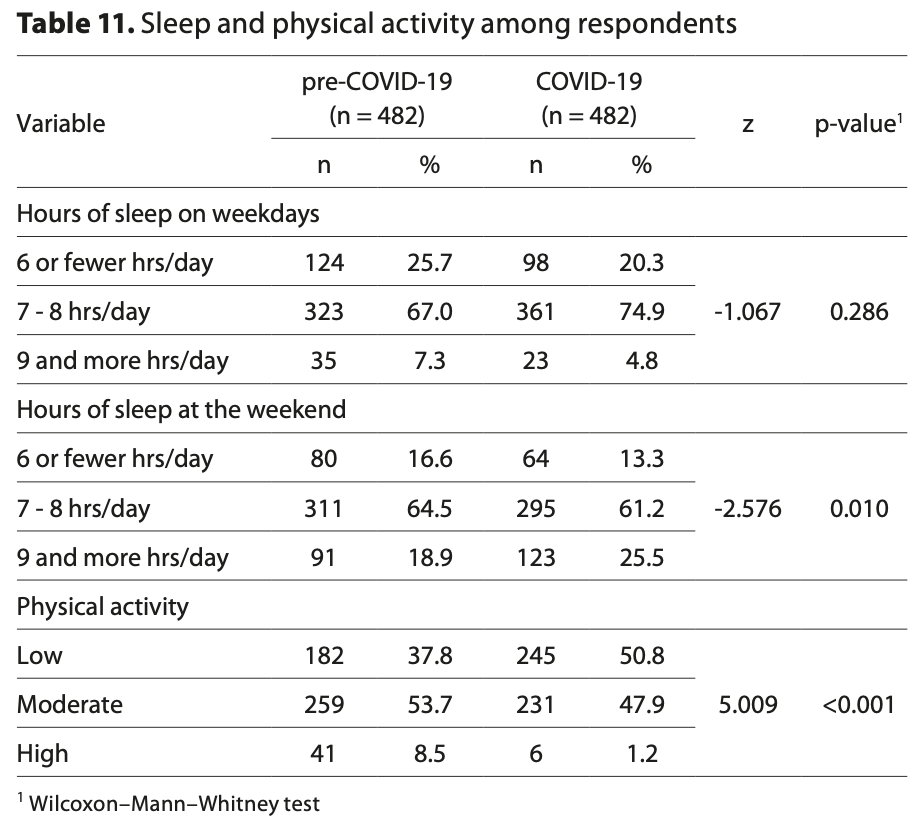
Introduction and Objective. The COVID-19 pandemic led to the introduction of sanitary restrictions in many countries which necessitated numerous lifestyle changes, especially in the diet. The study aimed to compare the diet and selected lifestyle elements in the Polish population during the COVID-19 pandemic. Materials and method. The study group consisted of 964 individuals: 482 before the COVID-19 pandemic (composed using the Propensity Score Matching method) and 482 during the pandemic. The National Health Programme 2017-2020 results were used. Results. During the pandemic increased, e.g. the intake of: total lipids (78.4 g vs. 83 g; p<0.035), saturated fatty acids (SFA) (30.4 g vs. 32.3 g; p=0.01), sucrose (56.5 g vs. 64.6 g; p=0.0001), calcium (602.5 mg vs. 666.6 mg; p=0.004), and folate (261.6 mcg vs. 284.7 mcg; p=0.003). When nutrient densities of pre-Covid-19 and COVID-19 diets were compared, some differences were noted; per 1,000 kcal the amounts decreased of plant protein (13.7 g vs. 13.1 g; p=0.001), carbohydrates (130.8 g vs. 128.0 g; p=0.021), fibre (9.1 g vs. 8.4 g; p=0.000), sodium (1,968.6 mg vs. 1,824.2 mg; p=0.000); while the amounts increased of total lipids (35.9 g vs. 37.0 g; p=0.001), SFA (14.1 g vs. 14.7 g; p=0.003), and sucrose (26.4 g vs. 28.4 g; p=0.001). The COVID-19 pandemic had no effect on alcohol consumption, the number of smokers increased (from 131 to 169), sleep duration during weekdays, and the number of persons with low physical activity (182 vs. 245; p<0.001). Conclusions. Numerous unfavourable changes occurred in the diet and lifestyle during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may contribute to the exacerbation of health problems in the future. Nutrient density in the diet combined with well-designed consumer education may underlie the development of diet recommendations.
References
Ammar, Brach, Trabelsi, Effects of COVID-19 Home Confinement on Eating Behaviour and Physical Activity: Results of the ECLB-COVID19 International Online Survey, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061583
Astrup, Magkos, Bier, Saturated Fats and Health: A Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review, J Am Coll Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.077
Bailey, Jr, Black, The epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies, Ann Nut Metab, doi:10.1159/000371618
Brooks, Webster, Smith, The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8
Brzozowska, Roszkowski, Dietary Research. Metody badań sposobu żywienia osób starszych (Dietary Research Methods for Elderly People), Warszaw: The Committee of Human Nutrition Science, Polish Academy of Sciences
Budreviciute, Damiati, Sabir, Management and Prevention Strategies for Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs) and Their Risk Factors, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.574111
Calder, Nutrition, immunity and COVID-19, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000085
Castañeda-Babarro, Arbillaga-Etxarri, Gutiérrez-Santamaría, Physical Activity Change during COVID-19 Confinement, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17186878
Connell, Zoellner, Yadrick, Energy density, nutrient adequacy, and cost per serving can provide insight into food choices in the lower Mississippi Delta, J Nutr Educ Behav, doi:10.1016/j.jneb.2011.02.003
Drewnowski, Concept of a nutritious food: toward a nutrient density score, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/82.4.721
Drywień, Hamulka, Zielinska-Pokus, The COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns and Changes in Body Weight among Polish Women. A Cross-Sectional Online Survey PLifeCOVID-19 Study, Sustainability, doi:10.3390/su12187768
Efsa, Guidance on the EU Menu methodology, EFSA J, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3944
García-Álvarez, Fuente-Tomás, Sáiz, Will changes in alcohol and tobacco use be seen during the COVID-19 lockdown?, Adicciones, doi:10.20882/adicciones.1546
Grossman, Benjamin-Neelon, Sonnenschein, Alcohol Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Survey of US Adults, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17249189
Górnicka, Drywień, Zielinska, Dietary and Lifestyle Changes During COVID-19 and the Subsequent Lockdowns among Polish Adults: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey PLifeCOVID-19 Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082324
Haileamlak, Physical Inactivity: The Major Risk Factor for Non-Communicable Diseases, Ethiop J Health Sci
Hamulka, Jeruszka-Bielak, Górnicka, Dietary supplements during COVID-19 outbreak. Results of Google trends analysis supported by PLifeCOVID-19 online studies, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010054
Jackson, Garnett, Shahab, Association of the COVID-19 lockdown with smoking, drinking and attempts to quit in England: an analysis of 2019-20 data, Addiction, doi:10.1111/add.15295
Jeżewska-Zychowicz, Gawęcki, Wadolowska, Dietary Habits and Nutrition Beliefs Questionnaire for people 15-65 years old, version 1.1.-interviewer administered questionnaire
Jiménez-Ruiz, López-Padilla, COVID-19 and Smoking: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Evidence, Arch Bronconeumol, doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2020.06.024
Kim, Rebholz, Hegde, Plant-based diets, pescatarian diets and COVID-19 severity: a population-based case-control study in six countries, BMJ Nutr Prev Health, doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2021-000272
Kris-Etherton, Krauss, Public health guidelines should recommend reducing saturated fat consumption as much as possible: YES, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa110
Larsson, Kaluza, Wolk, Combined impact of healthy lifestyle factors on lifespan: two prospective cohorts, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.12637
Lee, Shiroma, Lobelo, Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Effect of physical inactivity on major noncommunicable diseases worldwide: an analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12
Lordan, Dietary supplements and nutraceuticals market growth during the coronavirus pandemic -Implications for consumers and regulatory oversight, PharmaNutrition, doi:10.1016/j.phanu.2021.100282
Lordan, Rando, COVID-19 Review Consortium, Greene CS. Dietary supplements and nutraceuticals under investigation for COVID-19 prevention and treatment, mSystems, doi:10.1128/mSystems.00122-21
Manthey, Kilian, Carr, Use of alcohol, tobacco, cannabis, and other substances during the first wave of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Europe: a survey on 36,000 European substance users, Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy, doi:10.1186/s13011-021-00373-y
Mello, Silva, Guerreiro, Sleep and COVID-19: considerations about immunity, pathophysiology, and treatment, Sleep Sci, doi:10.5935/1984-0063.20200062
Morin, Carrier, Bastien, Canadian Sleep and Circadian Network. Sleep and circadian rhythm in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Can J Public Health, doi:10.17269/s41997-020-00382-7
Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, Dudek, Filipiak, Leczenie nadwagi i otyłości w czasie i po pandemii. Nie czekajmy na rozwój powikłań -nowe wytyczne dla lekarzy, Nadciśnienie Tętnicze w Praktyce
Onishi, Häggblom, Shapses, Can Dietary Fatty Acids Affect the COVID-19 Infection Outcome in Vulnerable Populations?, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.01723-20
Ortiz-Prado, Simbaña-Rivera, Gómez-Barreno, Clinical, molecular and epidemiological characterization of the SARS-CoV2 virus and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a comprehensive literature review, Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115094
Palmer, Trender, Tyacke, Impact of COVID-19 restrictions on alcohol consumption behaviours, BJPsych Open, doi:10.1192/bjo.2021.986
Przysławski, Borawska, Biernat, Przewodnik metodyczny badań sposobu żywienia (Dietary Research Methodological Guide, Warszaw: The Committee of Human Nutrition Science
Rautiainen, Manson, Lichtenstein, Dietary supplements and disease prevention -a global overview, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.54
Renzo, Gualtieri, Pivari, Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: an Italian survey, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02399-5
Ruthsatz, Candeias, Non-communicable disease prevention, nutrition and aging, Acta Biomed, doi:10.23750/abm.v91i2.9721
Sidor, Rzymski, Dietary Choices and Habits during COVID-19 Lockdown: Experience from Poland, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061657
Sińska, Jaworski, Panczyk, The Role of Resilience and Basic Hope in the Adherence to Dietary Recommendations in the Polish Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13062108
Stanaway, Afshin, Gakidou, Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736
Stanton, To, Khalesi, Williams, Depression, Anxiety and Stress during COVID-19: Associations with Changes in Physical Activity, Sleep, Tobacco and Alcohol Use in Australian Adults, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17114065
Stefan, Birkenfeld, Schulze, Obesity and impaired metabolic health in patients with COVID-19, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020
Tamara, Tahapary, Obesity as a predictor for a poor prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.020
Traczyk, Raciborski, Kucharska, A National Study of Nutrition and Nutritional Status of the Adult Polish Population in the Years 2017-2020 before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic-Design and Methods, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082568
Tsigaris, Da Silva, Smoking Prevalence and COVID-19 in Europe, Nicotine Tob Res, doi:10.1093/ntr/ntaa121
Wajszczyk, Chwojnowska, Nasiadko, Instructions for the Use of the 6.0 Diet Program for Planning and Ongoing Evaluation of Individual and Collective Nutrition in Methodical Guide of Dietary Research
Worm, Weingärtner, Schulze, Gesättigte Fettsäuren und kardiovaskuläres Risiko: Ist eine Revision der Ernährungsempfehlungen angezeigt? (Saturated fatty acids and cardiovascular risk: Is a revision of the recommendations on nutrition indicated?, Herz, doi:10.1007/s00059-021-05067-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.26444/aaem/156939",
"ISSN": [
"1232-1966",
"1898-2263"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.26444/aaem/156939",
"alternative-id": [
"156939"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6738-2088",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kucharska",
"given": "Alicja",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5644-8731",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sińska",
"given": "Beata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1830-2114",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Panczyk",
"given": "Mariusz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5265-8176",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Szostak-Węgierek",
"given": "Dorota",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0562-0260",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Raciborski",
"given": "Filip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4043-7747",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Samoliński",
"given": "Bolesław",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2055-8354",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Borowicz",
"given": "Jacek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1360-2540",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wronka",
"given": "Leszek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7413-1212",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Traczyk",
"given": "Iwona",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Ann Agric Environ Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-28T15:58:20Z",
"timestamp": 1672243100000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T07:13:14Z",
"timestamp": 1680246794000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T07:52:57Z",
"timestamp": 1680249177581
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672185600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672185600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/pl/deed.en",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672185600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/pdf-156939-85063",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/pdf-156939-85063",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10974",
"original-title": [],
"page": "118-126",
"prefix": "10.26444",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
28
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Institute of Rural Health",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.aaem.pl/Diet-and-selected-elements-of-lifestyle-in-the-Polish-population-before-and-during,156939,0,2.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Waste Management and Disposal",
"Ecology, Evolution, Behavior and Systematics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Diet and selected elements of lifestyle in the Polish population before and during the COVID-19 pandemic – a population study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "30"
}
kucharska