“MATH+” Multi-Modal Hospital Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 Infection: Clinical and Scientific Rationale
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, doi:10.14740/jocmr4658, Feb 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the data supporting the MATH+ hospital treatment protocol for COVID-19.
Kory et al., 24 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
“MATH+” Multi-Modal Hospital Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 Infection: Clinical and Scientific Rationale
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, doi:10.14740/jocmr4658
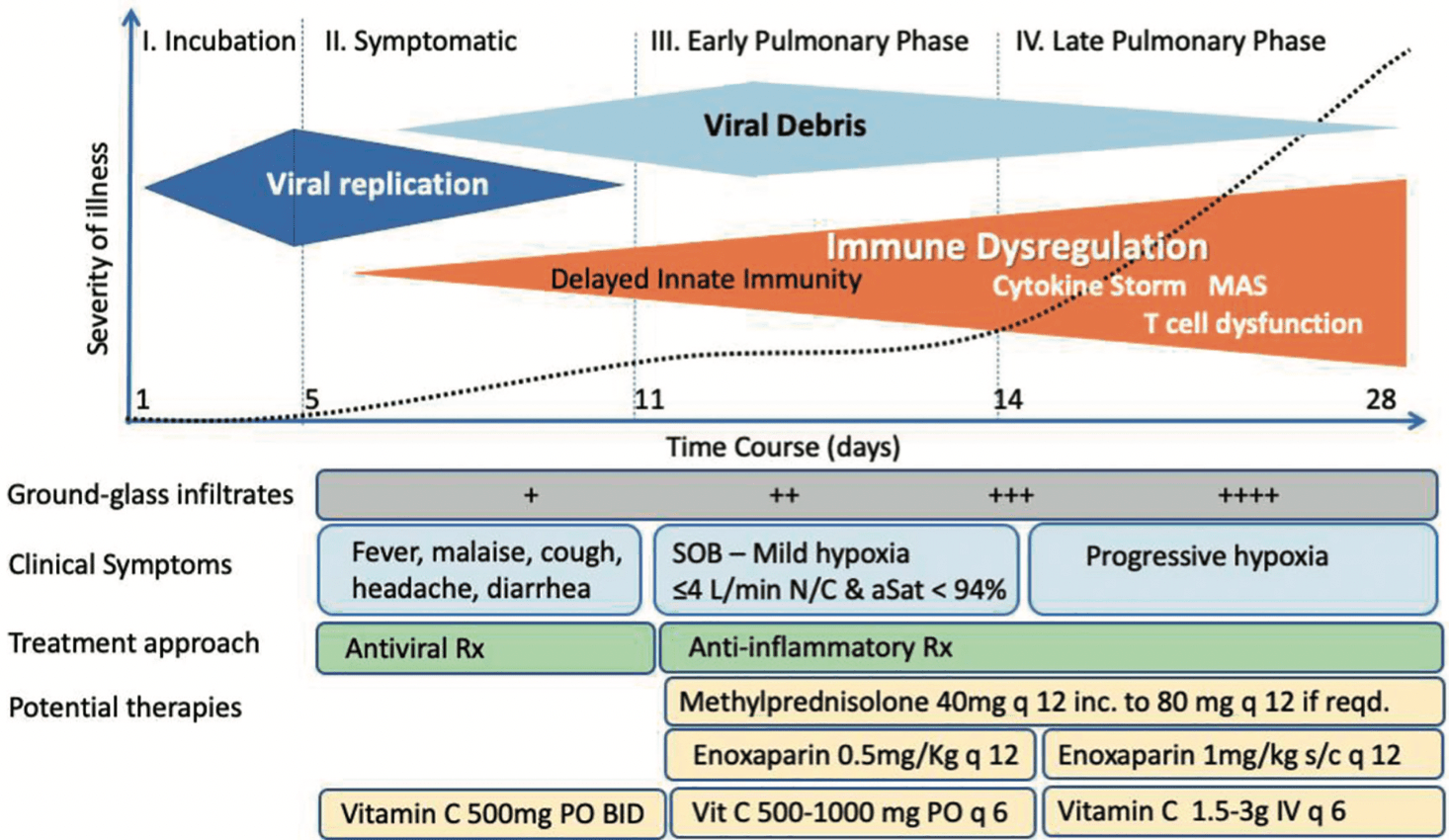
In December 2019, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a severe respiratory illness caused by the new coronavirus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged in Wuhan, China. The greatest impact that COVID-19 had was on intensive care units (ICUs), given that approximately 20% of hospitalized cases developed acute respiratory failure (ARF) requiring ICU admission. Based on the assumption that COVID-19 represented a viral pneumonia and no anti-coronaviral therapy existed, nearly all national and international health care societies recommended "supportive care only" avoiding other therapies outside of randomized controlled trials, with a specific prohibition against the use of corticosteroids in treatment. However, early studies of COVID-19-associated ARF reported inexplicably high mortality rates, with frequent prolonged durations of mechanical ventilation (MV), even from centers expert in such supportive care strategies. These reports led the authors to form a clinical expert panel called the Front-Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (www.flccc.net). The panel collaboratively reviewed the emerging clinical, radiographic, and pathological reports of COVID-19 while initiating multiple discussions among a wide clinical network of front-line clinical ICU experts from initial outbreak areas in China, Italy, and New York. Based on the shared early impressions of "what was working and what wasn't working", the increasing medical journal publications and the rapidly accumulating personal clinical experiences with COVID-19 patients, a treatment protocol was created for the hospitalized patients based on the core therapies of methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, heparin and non-antiviral co-interventions (MATH+). This manuscript reviews the scientific and clinical rationale behind MATH+ based on published in-vitro, pre-clinical, and clinical data in support of each medicine, with a special emphasis of studies supporting their use in the treatment of patients with viral syndromes and COVID-19 specifically.
Financial Disclosure None to declare.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions Dr. Meduri's contribution is the result of work supported with the resources and use of facilities at the Memphis VA Medical Center. The contents of this commentary do not represent the views of the US Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author Note A version of this manuscript was published by The Journal of Intensive Care Medicine and was retracted by the editors after being published and highly cited. The article has been changed, the contested findings have been removed, and we have added the addition of antiandrogen therapy. It is noteworthy that this manuscript emphasizing the benefit of corticosteroid anticoagulant and antioxidant therapy in patients with COVID-19 was conceived of before the results of the recovery trial were known.
References
Acharya, Liu, Gack, Dysregulation of type I interferon responses in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COV-ID-19, N Engl J Med
Adeli, Asghari, Tabarraii, Shajari, Afshari et al., Therapeutic plasma exchange as a rescue therapy in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a case series, Pol Arch Intern Med
Afar, Vivanco, Hubert, Kuo, Chen et al., Catalytic cleavage of the androgen-regulated TMPRSS2 protease results in its secretion by prostate and prostate cancer epithelia, Cancer Res
Akkoyunlu, Cetin, Bolukcu, Okay, Ogun et al., The successful management of an elderly Covid-19 infected patient by plasmapheresis, Transfus Apher Sci
Aldhous, Franey, Wright, Arendt, Plasma concentrations of melatonin in man following oral absorption of different preparations, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Alizadeh, Keyhanian, Ghaderkhani, Dashti-Khavidaki, Shoormasti et al., A pilot study on controlling coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) inflammation using melatonin supplement, Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol
Altmayer, Saheb, Rohaut, Marois, Cao et al., Therapeutic plasma exchange in a critically ill Covid-19 patient, J Clin Apher
Amrein, Martucci, Mcnally, When not to use meta-analysis: Analysing the meta-analyses on vitamin D in critical care, Clin Nutr
Amrein, Schnedl, Berghold, Pieber, Dobnig, Correction of vitamin D deficiency in critically ill patients -VITdAL@ICU study protocol of a double-blind, placebocontrolled randomized clinical trial, BMC Endocr Disord
Amrein, Zajic, Schnedl, Waltensdorfer, Fruhwald et al., Vitamin D status and its association with season, hospital and sepsis mortality in critical illness, Crit Care
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Annane, Arabi et al., Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Arabi, Mandourah, Al-Hameed, Sindi, Almekhlafi et al., Corticosteroid therapy for critically ill patients with middle east respiratory syndrome, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Arshad, Kilgore, Chaudhry, Jacobsen, Wang et al., Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and combination in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis
Barabutis, Khangoora, Marik, Catravas, Hydrocortisone and ascorbic acid synergistically prevent and repair lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction, Chest
Bergman, The link between vitamin D and COVID-19: distinguishing facts from fiction, J Intern Med
Bhowmick, Oft, Dorff, Pal, Agarwal et al., COVID-19 and androgen-targeted therapy for prostate cancer patients, Endocr Relat Cancer
Bhutta, Ahmed, Black, Cousens, Dewey et al., What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival, Lancet
Biancatelli, Berrill, Mohammed, Marik, Melatonin for the treatment of sepsis: the scientific rationale, J Thorac Dis
Biasi, Meschiari, Gibellini, Bellinazzi, Borella et al., Marked T cell activation, senescence, exhaustion and skewing towards TH17 in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Nat Commun
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Uhl, Hoagland et al., Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19, Cell
Boudreault, Pinilla-Vera, Englert, Kho, Isabelle et al., Zinc deficiency primes the lung for ventilator-induced injury, JCI Insight
Bourinbaiar, Fruhstorfer, The effect of histamine type 2 receptor antagonists on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication: identification of a new class of antiviral agents, Life Sci
Bryce, Grimes, Pujadas, Ahuja, Beasley et al., Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: the Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience, Mod Pathol
Cadegiani, Fonseca, Mccoy, Zimerman, Mirza et al., Efficacy of proxalutamide in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-design clinical trial
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, Zimerman, Proxalutamide improves inflammatory, immunologic, and thrombogenic markers in mild-to-moderate COVID-19 males and females: an exploratory analysis of a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial early antiandrogen therapy (EAT) with proxalutamide (The EAT-Proxa Biochemical AndroCoV-Trial
Cadegiani, Lim, Goren, Mccoy, Situm et al., Clinical symptoms of hyperandrogenic women diagnosed with COVID-19, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Cadegiani, Lin, Goren, Wambier, Potential risk for developing severe COVID-19 disease among anabolic steroid users, BMJ Case Rep
Cadegiani, Mccoy, Wambier, Goren, Early antiandrogen therapy with dutasteride reduces viral shedding, inflammatory responses, and time-to-remission in males with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional trial (EAT-DUTA Andro-CoV Trial -Biochemical), Cureus
Cadegiani, Zimerman, Fonseca, Correia, Mccoy et al., placebo-controlled two-arm parallel trial
Cadegiani, Zimerman, Fonseca, Correia, Muller et al., Final results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, two-arm, parallel clinical trial of proxalutamide for hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a multiregional, joint analysis of the Proxa-rescue Andro-CoV trial, Cureus
Cadegiani, Zimerman, Proxalutamide treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients in southern brazil: the south arm of a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled, parallel clinical trial -the South Proxa-Rescue AndroCoV Trial
Cai, Li, Tang, Tsoi, Chen et al., A new mechanism of vitamin C effects on A/ FM/1/47(H1N1) virus-induced pneumonia in restraintstressed mice, Biomed Res Int
Calfee, Delucchi, Sinha, Matthay, Hackett et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome subphenotypes and differential response to simvastatin: secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol Infect
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Kochs, Gripp et al., Pharmacological Inhibition of Acid Sphingomyelinase Prevents Uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by Epithelial Cells, Cell Rep Med
Carr, Shaw, Fowler, Natarajan, Ascorbatedependent vasopressor synthesis: a rationale for vitamin C administration in severe sepsis and septic shock?, Crit Care
Carrillo-Vico, Reiter, Lardone, Herrera, Fernandez-Montesinos et al., The modulatory role of melatonin on immune responsiveness, Curr Opin Investig Drugs
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Diaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Cattaneo, Bertinato, Birocchi, Brizio, Malavolta et al., Pulmonary embolism or pulmonary thrombosis in COVID-19? Is the recommendation to use high-dose heparin for thromboprophylaxis justified?, Thromb Haemost
Chatterjee, Majumder, Nandi, Subramanian, Synthesis and some major functions of vitamin C in animals, Ann N Y Acad Sci
Chen, Tang, Tan, Liang, Wan et al., Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with glucosteroids: the Guangzhou experience, Chest
Christopher, Vitamin D supplementation in the ICU patient, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care
Clagett, Thrombosis research, Journal of Vascular Surgery
Cobes, Guernou, Lussato, Queneau, Songy et al., Ventilation/perfusion SPECT/ CT findings in different lung lesions associated with COVID-19: a case series, Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging
Collie, Greaves, Jones, Lam, Eastwood et al., Vitamin B1 in critically ill patients: needs and challenges, Clin Chem Lab Med
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation, Blood
Corcoran, Neill, Webb, Ho, Prevalence of vitamin deficiencies on admission: relationship to hospital mortality in critically ill patients, Anaesth Intensive Care
Corral-Gudino, Bahamonde, Arnaiz-Revillas, Gómez-Barquero, Abadía-Otero et al., Methylprednisolone in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia, Wien Klin Wochenschr
Costa, Gut, De Souza Dorna, Pimentel, Cozzolino et al., Serum thiamine concentration and oxidative stress as predictors of mortality in patients with septic shock, J Crit Care
Couzin-Frankel, The Mystery of the Pandemic's "Happy Hypoxia, Science
Cui, Chen, Li, Liu, Wang, Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia, J Thromb Haemost
Dabbagh-Bazarbachi, Clergeaud, Quesada, Ortiz, Sullivan et al., Zinc ionophore activity of quercetin and epigallocatechin-gallate: from Hepa 1-6 cells to a liposome model, J Agric Food Chem
Danzi, Loffi, Galeazzi, Gherbesi, Acute pulmonary embolism and COVID-19 pneumonia: a random association?, Eur Heart J
De Grooth, Elbers, Vincent, Vitamin C for sepsis and acute respiratory failure, JAMA
Depace, Soloway, Roshal, Soloway, Colombo, Unexpected SARS-CoV-2 cardiorespiratory arrest in a myopathy patient undergoing immunosuppressive treatment: A case report, Medicine
Dequin, Heming, Meziani, Plantefeve, Voiriot et al., Effect of hydrocortisone on 21-day mortality or respiratory support among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Hardwick, Pius et al., Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ
Dominguez-Rodriguez, Abreu-Gonzalez, Melatonin, cardiovascular disease and COVID-19: a potential therapeutic strategy?, Melatonin Res
Donnino, Andersen, Chase, Berg, Tidswell et al., Randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial of thiamine as a metabolic resuscitator in septic shock: a pilot study, Crit Care Med
Donnino, Carney, Cocchi, Barbash, Chase et al., Thiamine deficiency in critically ill patients with sepsis, J Crit Care
Draghici, Nguyen, Sonna, Ziraldo, Vanciu et al., COVID-19: disease pathways and gene expression changes predict methylprednisolone can improve outcome in severe cases, Bioinformatics
Edalatifard, Akhtari, Salehi, Naderi, Jamshidi et al., Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial, Eur Respir J
Espino, Pariente, Rodriguez, Oxidative stress and immunosenescence: therapeutic effects of melatonin, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Experton, Tetteh, Lurie, Walker, Hein et al., A predictive model for severe COVID-19 in the medicare population: a tool for prioritizing primary and booster COVID-19 vaccination, Biology
Fadel, Morrison, Vahia, Smith, Chaudhry et al., Early short-course corticosteroids in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis
Faqihi, Alharthy, Alodat, Kutsogiannis, Brindley et al., Therapeutic plasma exchange in adult critically ill patients with life-threatening SARS-CoV-2 disease: A pilot study, J Crit Care
Farnoosh, Akbariqomi, Badri, Bagheri, Izadi et al., Efficacy of a low dose of melatonin as an adjunctive therapy in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, Arch Med Res
Fernandez, Gratacos-Gines, Olivas, Costa, Nieto et al., Plasma exchange: an effective rescue therapy in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 infection, Crit Care Med
Fernandez-Cruz, Ruiz-Antoran, Munoz-Gomez, Lopez, Mills-Sanchez et al., A retrospective controlled cohort study of the impact of glucocorticoid treatment in SARS-CoV-2 infection mortality, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Fowler, Syed, Knowlson, Sculthorpe, Farthing et al., Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis, J Transl Med
Fowler, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan et al., Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Fridman, Bullrich, Jimenez-Ruiz, Costantini, Shah et al., Stroke risk, phenotypes, and death in COVID-19: Systematic review and newly reported cases, Neurology
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in Infection and Inflammation, Nutrients
Gao, Li, Jiang, Impact of statins on ALI/ARDS: A meta-analysis, Pulm Pharmacol Ther
Gao, Xu, Wang, Lv, Ma et al., The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Aging
Gebhard, Regitz-Zagrosek, Neuhauser, Morgan, Klein, Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe, Biol Sex Differ
Glickman, Geigle, Paleg, A systematic review of supported standing programs, J Pediatr Rehabil Med
Goldstein, Cimetidine, ranitidine, and Epstein-Barr virus infection, Ann Intern Med
Gooptu, Higgins, James, Treatment of viral warts with cimetidine: an open-label study, Clin Exp Dermatol
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Greos, Vichyanond, Bloedow, Irvin, Larsen et al., Methylprednisolone achieves greater concentrations in the lung than prednisolone. A pharmacokinetic analysis, Am Rev Respir Dis
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Gucyetmez, Atalan, Sertdemir, Cakir, Telci et al., Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in intensive care unit: a retrospective study, Crit Care
Han, Jones, Tangpricha, Brown, Brown et al., High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: a pilot double blind randomized controlled trial, J Clin Transl Endocrinol
Hemila, Chalker, Vitamin C may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: a metaregression analysis, J Intensive Care
Hemila, Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage, JRSM Open
Heyland, Jones, Cvijanovich, Wong, Zinc supplementation in critically ill patients: a key pharmaconutrient?, JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr
Hoeger, Simon, Beeker, Marx, Haase et al., Persistent low serum zinc is associated with recurrent sepsis in critically ill patients -A pilot study, PLoS One
Hoertel, Sanchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Iglesias, Vassallo, Patel, Sullivan, Cavanaugh et al., Outcomes of metabolic resuscitation using ascorbic acid, thiamine, and glucocorticoids in the early treatment of sepsis: the ORANGES trial, Chest
Investigators, Investigators, Investigators, Goligher, Bradbury et al., Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Investigators, Investigators, Investigators, Lawler, Goligher et al., Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Jafarzadeh, Nemati, Khorramdelazad, Hassan, Immunomodulatory properties of cimetidine: Its therapeutic potentials for treatment of immune-related diseases, Int Immunopharmacol
Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Zarezade, Koolaji, Seyedalinaghi, Zendehdel et al., Safety and effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a randomized openlabel clinical trial, Eur J Med Res
Jehi, Ji, Milinovich, Erzurum, Rubin et al., Individualizing risk prediction for positive coronavirus disease 2019 testing: results from 11,672 patients, Chest
Jonmarker, Hollenberg, Dahlberg, Stackelberg, Litorell et al., Dosing of thromboprophylaxis and mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Crit Care
Journal, Kuhbandner, Hammer, Haase, Terbrack et al., None, Oral Presentations
Kanne, Little, Chung, Elicker, Ketai, Essentials for Radiologists on COVID-19: An Update-Radiology Scientific Expert Panel, Radiology
Keith, Day, Choe, Perkins, Moyer et al., The successful use of therapeutic plasma exchange for severe COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome with multiple organ failure, SAGE Open Med Case Rep
Keith, Day, Perkins, Moyer, Hewitt et al., A novel treatment approach to the novel coronavirus: an argument for the use of therapeutic plasma exchange for fulminant COVID-19, Crit Care
Khamis, Al-Zakwani, Hashmi, Dowaiki, Bahrani et al., Therapeutic plasma exchange in adults with severe COVID-19 infection, Int J Infect Dis
Kim, Kim, Bae, Choi, Lim et al., Vitamin C is an essential factor on the anti-viral immune responses through the production of interferon-alpha/beta at the initial stage of influenza A virus (H3N2) infection, Immune Netw
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Arbous, Gommers et al., Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis, Thromb Res
Kory, Kanne, SARS-CoV-2 organising pneumonia: 'Has there been a widespread failure to identify and treat this prevalent condition in COVID-19?, BMJ Open Respir Res
Kruger, Bailey, Bellomo, Cooper, Harward et al., A multicenter randomized trial of atorvastatin therapy in intensive care patients with severe sepsis, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Kruger, Terblanche, Statins in patients with sepsis and ARDS: is it over? No, Intensive Care Med
Kumar, Zuo, Yalavarthi, Hunker, Knight et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1-mediated endothelial injury and pro-inflammatory state is amplified by dihydrotestosterone and prevented by mineralocorticoid antagonism, Viruses
Kumari, Dembra, Dembra, Bhawna, Gul et al., The role of vitamin C as adjuvant therapy in COVID-19, Cureus
Lakkireddy, Gadiga, Malathi, Karra, Raju et al., Impact of daily high dose oral vitamin D therapy on the inflammatory markers in patients with COVID 19 disease, Sci Rep
Lee, Eisman, Center, Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill patients, N Engl J Med
Lee, Heberer, Gao, Becker, Loeb et al., A Population-Level Analysis of the Protective Effects of Androgen Deprivation
Lee, Yousaf, Fang, Kolodney, Male balding is a major risk factor for severe COVID-19, J Am Acad Dermatol
Lemos, Do, Santo, Salvetti, Gilio et al., Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for severe COVID-19: A randomized phase II clinical trial (HESACOVID), Thromb Res
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Li, Ching, Hipple, Lopez, Sahibzada et al., Use of intravenous vitamin C in critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection, J Pharm Pract
Li, Miller, Yates, Evaluation of AP-1 and NF-KB inhibitory potency for oral glucocorticoids. In proceedings of the American review of respiratory disease, PharmSci
Li, Yang, Gu, Zhang, Yan et al., Effect of low-to-moderate-dose corticosteroids on mortality of hospitalized adolescents and adults with influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viral pneumonia, Influenza Other Respir Viruses
Lim, Jeon, Kim, Kim, Song et al., Antifactor Xa levels in critically ill Korean patients receiving enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis: a prospective observational study, J Korean Med Sci
Lim, Meade, Lauzier, Zarychanski, Mehta et al., Failure of anticoagulant thromboprophylaxis: risk factors in medical-surgical critically ill patients*, Crit Care Med
Lim, Vos, Flaxman, Danaei, Shibuya et al., A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet
Linko, Karlsson, Pettila, Varpula, Okkonen et al., Serum zinc in critically ill adult patients with acute respiratory failure, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand
Liu, Clough, Hutchinson, Adamah-Biassi, Popovska-Gorevski et al., MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors: a therapeutic perspective, Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
Llitjos, Leclerc, Chochois, Monsallier, Ramakers et al., High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients, J Thromb Haemost
Long, Xu, Wang, Zhang, Jia et al., Clinical Recommendations from an observational study on MERS: glucocorticoids was benefit in treating SARS patients, Int J Clin Exp Med
Lv, Xu, Cheng, Ke, Zhang et al., A novel cell-based assay for dynamically detecting neutrophil extracellular traps-induced lung epithelial injuries, Exp Cell Res
Maggini, Wenzlaff, Hornig, Essential role of vitamin C and zinc in child immunity and health, J Int Med Res
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One
Maier, Truong, Auld, Polly, Tanksley et al., COVID-19-associated hyperviscosity: a Kory et al, J Clin Med Res
Mandal, Dam, Franco, Sellami, Mandal et al., A rapid systematic review of the efficacy of face masks and respirators against coronaviruses and other respiratory transmissible viruses for the community, healthcare workers and sick patients, Int J Nurs Stud
Marik, Iglesias, Varon, Kory, A scoping review of the pathophysiology of COVID-19, Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol
Marik, Khangoora, Rivera, Hooper, Catravas, Hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective before-after study, Chest
Marik, Varon, Kory, Treatment of COVID-19 is critically phase, Crit Care Shock
Marik, Vitamin C for the treatment of sepsis: The scientific rationale, Pharmacol Ther
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Martinez-Vega, Mor-Marco, Herraiz-Ruiz, Raguer-Pardo, Cubells-Larrosa, Low molecular weight heparins in COVID-19 patients: beware of augmented renal clearance!, Crit Care
Mcauley, Laffey, Kane, Perkins, Mullan et al., Simvastatin in the acute respiratory distress syndrome, New England Journal of Medicine
Mccoy, Goren, Cadegiani, Vano-Galvan, Kovacevic et al., Proxalutamide reduces the rate of hospitalization for COVID-19 male outpatients: a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial, Front Med
Mccoy, Wambier, Herrera, Vano-Galvan, Gioia et al., Androgen receptor genetic variant predicts COVID-19 disease severity: a prospective longitudinal study of hospitalized COVID-19 male patients, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Meduri, Annane, Chrousos, Marik, Sinclair, Activation and regulation of systemic inflammation in ARDS: rationale for prolonged glucocorticoid therapy, Chest
Meduri, Bridges, Shih, Marik, Siemieniuk et al., Prolonged glucocorticoid treatment is associated with improved ARDS outcomes: analysis of individual patients' data from four randomized trials and trial-level meta-analysis of the updated literature, Intensive Care Med
Meduri, Tolley, Chrousos, Stentz, Prolonged methylprednisolone treatment suppresses systemic inflammation in patients with unresolving acute respiratory distress syndrome: evidence for inadequate endogenous glucocorticoid secretion and inflammation-induced immune cell resistance to glucocorticoids, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., Hlh Across Speciality Collaboration UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Menezes, Godin, Rodrigues, Coura, Melo et al., Thiamine and riboflavin inhibit production of cytokines and increase the anti-inflammatory activity of a corticosteroid in a chronic model of inflammation induced by complete Freund's adjuvant, Pharmacol Rep
Mertens, Lowes, Webster, Talib, Hall et al., Low zinc and selenium concentrations in sepsis are associated with oxidative damage and inflammation, Br J Anaesth
Meydani, Barnett, Dallal, Fine, Jacques et al., Serum zinc and pneumonia in nursing home elderly, Am J Clin Nutr
Middeldorp, Coppens, Van Haaps, Foppen, Vlaar et al., Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Mohammed, Fisher, Kraskauskas, Farkas, Brophy et al., Vitamin C: a novel regulator of neutrophil extracellular trap formation, Nutrients
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Rugge, Zorzi et al., Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532), Ann Oncol
Morath, Weigand, Zeier, Speer, Tiwari-Heckler, Plasma exchange in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Crit Care
Morichika, Takahashi, Iwagaki, Yoshino, Tamura et al., Histamine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in an intercellular adhesion molecule-1-and B7.1-dependent manner, J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Mortus, Manek, Brubaker, Loor, Cruz et al., Thromboelastographic results and hypercoagulability syndrome in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 who are critically ill, JAMA Netw Open
Moskowitz, Andersen, Huang, Berg, Grossestreuer et al., Ascorbic acid, corticosteroids, and thiamine in sepsis: a review of the biologic rationale and the present state of clinical evaluation, Crit Care
Moslemi, Khalili, Mohammadi, Mehrabi, Mohebbi, Thiamine for prevention of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery: a randomized clinical trial, J Res Pharm Pract
Mousavi, Heydari, Mehravaran, Saeedi, Alizadeh-Navaei et al., Melatonin effects on sleep quality and outcomes of COV-ID-19 patients: An open-label, randomized, controlled trial, J Med Virol
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Murthy, Siddalingappa, Suresh, Nicolau's syndrome following diclofenac administration: A report of two cases, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol
Nadkarni, Bagiella, Chang, Moreno, Pujadas et al., Anticoagulation, bleeding, mortality, and pathology in hospitalized patients with COV-ID-19, J Am Coll Cardiol
Nagge, Crowther, Hirsh, Is impaired renal function a contraindication to the use of low-molecular-weight heparin?, Arch Intern Med
Network, Ginde, Brower, Caterino, Finck et al., Early high-dose vitamin D3 for critically ill, vitamin D-deficient patients, N Engl J Med
New-Haven, Initial treatment algorithm for hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 respiratory failure, including mechanical ventilation and ECMO PLUS confirmed POSITIVE SARS-CoV-2 by PCR
Nicastri, Petrosillo, Bartoli, Lepore, Mondi et al., IRCCS. Recommendations for COVID-19 clinical management, Infect Dis Rep
Okamoto, Tanaka, Makino, Makino, Restoration of the glucocorticoid receptor function by the phosphodiester compound of vitamins C and E, EPC-K1 (L-ascorbic acid 2-[3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6 -yl hydrogen phosphate] potassium salt), via a redox-dependent mechanism, Biochem Pharmacol
Panigada, Bottino, Tagliabue, Grasselli, Novembrino et al., Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis, J Thromb Haemost
Paranjpe, Fuster, Russak, Glicksberg, Levin et al., Association of treatment dose anticoagulation with in-hospital survival among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Am Coll Cardiol
Park, Lee, Re-analysis of single cell transcriptome reveals that the NR3C1-CXCL8-Neutrophil axis determines the severity of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Pastores, Annane, Rochwerg, Guideline, Task Force of S, Esicm. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI) in critically ill patients (Part II): Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) 2017, Intensive Care Med
Patel, Arachchillage, Ridge, Bianchi, Doyle et al., Pulmonary angiopathy in severe COVID-19: physiologic, imaging, and hematologic observations, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Patel, Zhong, Liaw, Tremblay, Tsao et al., Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?, Ann Oncol
Pertzov, Eliakim-Raz, Atamna, Trestioreanu, Yahav et al., Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) for the treatment of sepsis in adults -A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect
Putzu, Belletti, Cassina, Clivio, Monti et al., Vitamin D and outcomes in adult critically ill patients. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials, J Crit Care
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Hutter, Camargo, Association between preoperative 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and hospital-acquired infections following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, JAMA Surg
Ramanathan, Antognini, Combes, Paden, Zakhary et al., Planning and provision of ECMO services for severe ARDS during the COVID-19 pandemic and other outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases, Lancet Respir Med
Ramlall, Zucker, Tatonetti, Melatonin is significantly associated with survival of intubated COVID-19 patients
Rapkiewicz, Mai, Carsons, Pittaluga, Kleiner et al., Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series, EClinicalMedicine
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: a randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study), Postgrad Med J
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health
Reiter, Abreu-Gonzalez, Marik, Dominguez-Rodriguez, Therapeutic algorithm for use of melatonin in patients with COVID-19, Front Med
Reiter, Sharma, Ma, Dominquez-Rodriguez, Marik et al., Melatonin inhibits COVID-19-induced cytokine storm by reversing aerobic glycolysis in immune cells: a mechanistic analysis, Med Drug Discov
Ren, Zhang, Wang, Corrigendum to "Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment, Pharmacol. Res
Ren, Zhang, Wang, Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment, Pharmacol Res
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area, JAMA
Richmond, Schneider, Steffel, Sandor, Tarnutzer, Case report: new-onset retinal migraine after transseptal catheterization, Headache
Rodriguez-Nava, Garcia, Yanez-Bello, Chung, Garcia et al., Atorvastatin associated with decreased hazard for death in COVID-19 patients admitted to an ICU: a retrospective cohort study, Crit Care
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-care for common colds: the pivotal role of vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and echinacea in three main immune interactive clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) involved during an episode of common colds-practical advice on dosages and on the time to take these nutrients/ botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Rossi, Fanous, Colin, Viral strategies predisposing to respiratory bacterial superinfections, Pediatr Pulmonol
Salazar Arenas, Del Carpio-Toia, Galdos, Rodriguez-Morales, Alopecia and severity of COVID-19: a cross-sectional study in Peru, Infez Med
Salton, Confalonieri, Meduri, Santus, Harari et al., Prolonged low-dose methylpred-"MATH+" Treatment Protocol for COVID-19, J Clin Med Res
Salton, Confalonieri, Santus, Harari, Scala et al., Prolonged low-dose methylprednisolone in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia
Sang, Wang, Chen, Guo, Lu et al., Vitamin C inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by scavenging mitochondrial ROS, Inflammasome
Shah, Novel coronavirus-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation: a potential drug target in the treatment of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Sharifi, Vahedi, Nedjat, Rafiei, Hosseinzadeh-Attar, Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, APMIS
Shi, Xu, Duan, Yang, Wang, The pooled prevalence of pulmonary embolism in patients with COVID-19, Intensive Care Med
Shi, Zhou, He, Huang, Duan et al., Successful treatment with plasma exchange followed by intravenous immunoglobulin in a critically ill patient with COVID-19, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Shittu, Afolami, Improving the efficacy of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 may require Zinc additives -A better synergy for future COVID-19 clinical trials, Infez Med
Singh, Das, Zinc for the common cold. Cochrane "MATH+" Treatment Protocol for COVID-19, J Clin Med Res
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID19
Smolinska, Groeger, Perez, Schiavi, Ferstl et al., Histamine receptor 2 is required to suppress innate immune responses to bacterial ligands in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Inflamm Bowel Dis
Sterne, Murthy, Diaz, Slutsky, Villar et al., Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA
Subramanian, Anand, Adderley, Okoth, Toulis et al., Increased COV-ID-19 infections in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a population-based study, Eur J Endocrinol
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: A Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol
Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Dossari, Alshahrani, Alharbi et al., Evaluation of thiamine as adjunctive therapy in COVID-19 critically ill "MATH+" Treatment Protocol for COVID-19, J Clin Med Res
Suna, Melahat, Murat, Figen, Ayperi, Effect of high-dose intravenous vitamin C on prognosis in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, Med Clin
Taccone, Gevenois, Peluso, Pletchette, Lheureux et al., Higher intensity thromboprophylaxis regimens and pulmonary embolism in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients, Crit Care Med
Tanaka, Matsuda, Miyagantani, Yukioka, Matsuda et al., Reduction of resuscitation fluid volumes in severely burned patients using ascorbic acid administration: a randomized, prospective study, Arch Surg
Tang, Bai, Chen, Gong, Li et al., Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J Thromb Haemost
Tang, Zhang, Wang, Zeng, Severe COVID-19 pneumonia: assessing inflammation burden with volume-rendered chest CT, Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging
Thomas, Varley, Johnston, Symington, Robinson et al., Thrombotic complications of patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom, Thromb Res
Tian, Sui, Tian, Zou, Xu et al., Case report: clinical treatment of the first critical patient with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Liaocheng, Shandong Province, Front Med
Tobin, Laghi, Jubran, Why COVID-19 Silent Hypoxemia Is Baffling to Physicians, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Tomazini, Maia, Cavalcanti, Berwanger, Rosa et al., Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the CoDEX randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Tyml, Vitamin C and microvascular dysfunction in systemic inflammation, Antioxidants
Vatsalya, Li, Frimodig, Gala, Srivastava et al., Therapeutic prospects for Th-17 cell immune storm syndrome and neurological symptoms in COVID-19: thiamine efficacy and safety, in-vitro evidence and pharmacokinetic profile
Velavan, Pallerla, Ruter, Kremsner, Krishna et al., Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity, EBioMedicine
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Venkatesh, Nair, Hypovitaminosis D and morbidity in critical illness: is there proof beyond reasonable doubt?, Critical Care
Villar, Confalonieri, Pastores, Meduri, Rationale for prolonged corticosteroid treatment in the acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by coronavirus disease 2019, Crit Care Explor
Villar, Confalonieri, Pastores, Meduri, Rationale for prolonged corticosteroid treatment in the acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by coronavirus disease 2019, Crit Care Explor
Wambier, Mccoy, Goren, Male balding as a major risk factor for severe COVID-19: A possible role for targeting androgens and transmembrane protease serine 2 to protect vulnerable individuals, J Am Acad Dermatol
Wambier, Vano-Galvan, Mccoy, Gomez-Zubiaur, Herrera et al., Androgenetic alopecia present in the majority of patients hospitalized with COVID-19: The "Gabrin sign, J Am Acad Dermatol
Wan, Sun, Kan, Guan, Zhang, Effect of statin therapy on mortality from infection and sepsis: a meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies, Crit Care
Wang, Mannan, Xiao, Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 and host entry factors distribution in a COVID-19 autopsy series, Commun Med
Waterer, Rello, Wunderink, COVID-19: first do no harm, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
White, Macdonald, Bull, Hayman, De Monteverde-Robb et al., Heparin resistance in COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Wichmann, Sperhake, Lutgehetmann, Steurer, Edler et al., Autopsy findings and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Wilson, Chotirmall, Bai, Rello, COVID-19: interim guidance on management pending empirical evidence
Wilson, Mechanism of action of vitamin C in sepsis: ascorbate modulates redox signaling in endothelium, Biofactors
Woolum, Abner, Kelly, Thompson Bastin, Morris et al., Effect of thiamine administration on lactate clearance and mortality in patients with septic shock, Crit Care Med
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
Wu, Hou, Du, Cai, Zheng et al., Corticosteroid therapy for coronavirus disease 2019-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a cohort study with propensity score analysis, Crit Care
Wurtman, Age-related decreases in melatonin secretion-clinical consequences, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Xia, Fan, He, Zhu, Zheng, High-dose intravenous vitamin C attenuates hyperinflammation in severe coronavirus disease 2019, Nutrition
Xia, Qin, Ma, Zhu, Zheng, High-dose vitamin C ameliorates cardiac injury in COVID-19 pandemic: a retrospective cohort study, Aging
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med
Xu, Zhang, Pelayo, Monestier, Ammollo et al., Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis, Nat Med
Xue, Moyer, Peng, Wu, Hannafon et al., Chloroquine is a zinc ionophore, PLoS One
Yam, Lau, Lai, Shung, Chan et al., Corticosteroid treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong, J Infect
Yang, Tanner, Zheng, Watt, He et al., Bismuth complexes inhibit the SARS coronavirus, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
Ye, Rochwerg, Wang, Adhikari, Murthy et al., Treatment of patients with nonsevere and severe coronavirus disease 2019: an evidence-based guideline, CMAJ
Youssef, Ranasinghe, Grant, Peiris, Vitamin D's potential to reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections, Dermatoendocrinol
Zarehoseinzade, Allami, Ahmadi, Bijani, Mohammadi, Finasteride in hospitalized adult males with COVID-19: A risk factor for severity of the disease or an adjunct treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial, Med J Islam Repub Iran
Zhang, Jativa, Vitamin C supplementation in the critically ill: A systematic review and meta-analysis, SAGE Open Med
Zhang, Leung, Goleva, Anti-inflammatory and corticosteroid-enhancing actions of vitamin D in monocytes of patients with steroid-resistant and those with steroid-sensitive asthma, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Zhang, Leung, Goleva, Vitamin D enhances glucocorticoid action in human monocytes: involvement of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and mediator complex subunit 14, J Biol Chem
Zhang, Qin, Cheng, Shen, Zhao et al., In-hospital use of statins is associated with a reduced risk of mortality among individuals with COV-ID-19, Cell Metab
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann Intensive Care
Zhang, Wan, Sun, Kan, Wang, Association between vitamin D deficiency and mortality in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit Care
Zhang, Wang, Ni, Di, Ma et al., COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci
Zhang, Zhai, Ma, Chen, Gao, Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in severe COVID-19 patients, Br J Haematol
Zhao, Liu, Liu, Peng, Huang et al., High dose intravenous vitamin C for preventing the disease aggravation of moderate COVID-19 pneumonia. A retrospective propensity matched before-after study, Front Pharmacol
Zhou, Hou, Shen, Huang, Martin et al., Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2, Cell Discov
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zimerman, Fonseca, Correia, Barros, Onety et al., analysis of the Proxa-Rescue AndroCoV Trial
Zuo, Yalavarthi, Shi, Gockman, Zuo et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps in COV-ID-19, JCI Insight
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.14740/jocmr4658",
"ISSN": [
"1918-3003",
"1918-3011"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jocmr4658",
"alternative-id": [
"10.14740/jocmr4658"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kory",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meduri",
"given": "Ginfranco Umberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iglesias",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varon",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cadegiani",
"given": "Flavio Adsuara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marik",
"given": "Paul E.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Clinical Medicine Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.jocmr.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-24T09:20:38Z",
"timestamp": 1645694438000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-27T10:04:21Z",
"timestamp": 1645956261000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-27T10:40:23Z",
"timestamp": 1645958423555
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1918-3003"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1918-3011"
}
],
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2"
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643673600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.jocmr.org/index.php/JOCMR/article/download/4658/25893531",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "5784",
"original-title": [],
"page": "53-79",
"prefix": "10.14740",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elmer Press, Inc.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"J Clin Med Res"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"“MATH+” Multi-Modal Hospital Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 Infection: Clinical and Scientific Rationale"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/elmerpress-crossmark-policy",
"volume": "14"
}
kory5
