A New Biomarker Copeptin in Determining Disease Severity in COVID-19
et al., Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, doi:10.36519/idcm.2024.324, Sep 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
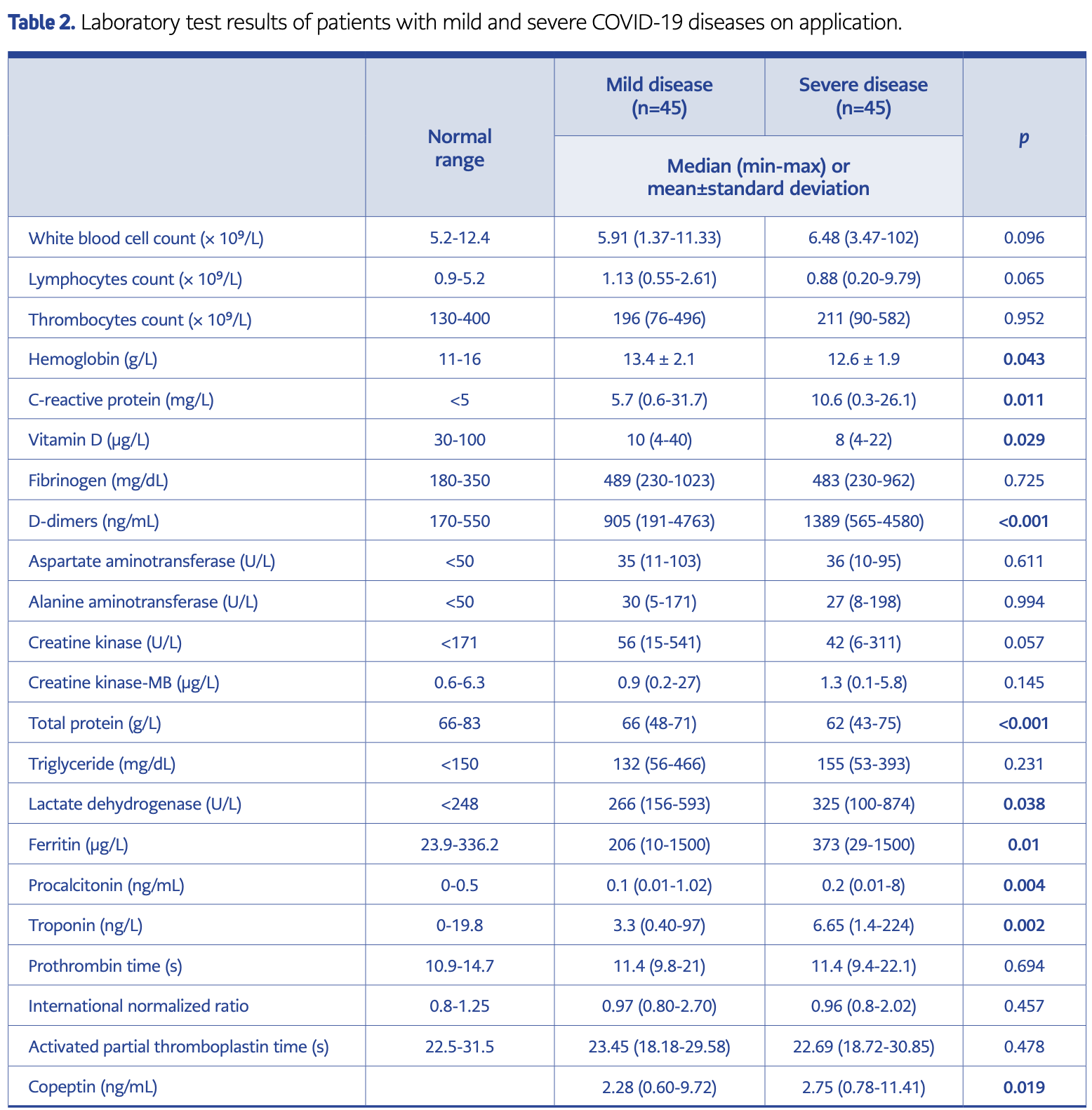
Prospective study of 90 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing that vitamin D levels were significantly lower in severe cases compared with mild/moderate cases. Hemoglobin and total protein were also lower in severe cases, while C-reactive protein, D-dimer, ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase, procalcitonin, troponin and copeptin levels were higher.
Korkmaz et al., 26 Sep 2024, Turkey, peer-reviewed, median age 64.0, 5 authors, study period 1 June, 2022 - 1 October, 2022.
Contact: drpinarkor@gmail.com.
A New Biomarker Copeptin in Determining Disease Severity in COVID-19
Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, doi:10.36519/idcm.2024.324
Objective: Copeptin is released from the posterior pituitary gland into systemic circulation in response to various stimuli, including stress. We aimed to evaluate the role of copeptin in determining the severity of the disease in patients with COVID-19.
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted prospectively in two centers between June 1, 2022, and October 1, 2022. Severe and mild-moderate COVID-19 patients were compared in terms of clinical, laboratory and imaging findings, and serum copeptin levels at hospitalization. Results: A total of 90 patients were included in the study; 45 patients were in severe disease groups. Dyspnea, loss of appetite, and loss of smell were significantly more common in the severe disease group (p<0.001, p=0.025, and p<0.001, respectively). Among the tomography findings, the consolidation frequency was similar in both groups (p=0.259). C-reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer, ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), procalcitonin, troponin and copeptin levels were higher in the severe group (p<0.05); hemoglobin, total protein and vitamin D levels were lower (p=0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) values for severe disease were 0.643 for copeptin (p=0.019), 0.656 for CRP (p=0.011), 0.684 for procalcitonin (p=0.004), 0.657 for ferritin (p=0.01), 0.72 for D-dimer (p=0), 0.688 for troponin (p=0.002), and 0.672 for age (p=0.005).
Conclusion: In our study, copeptin was identified as a new prognostic biomarker indicating the severity of the disease in patients with COVID-19.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Financial Disclosure: The authors declared that this study has received no financial support.
References
Christ-Crain, Fenske, Copeptin in the diagnosis of vasopressin-dependent disorders of fluid homeostasis, Nat Rev Endocrinol
Christ-Crain, Fenske, Copeptin in the differential diagnosis of hypotonic polyuria, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-019-01087-6
Christ-Crain, Vasopressin and copeptin in health and disease, Rev Endocr Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-019-09509-9
Demerdash, Omar, Arida, Evaluation of copeptin and psychological stress among healthcare providers during COVID-19 pandemic, Egyptian J Anaes, doi:10.1080/11101849.2021.1925442
Dobsa, Edozien, Copeptin and its potential role in diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases, Biochem Med, doi:10.11613/bm.2013.021
Elshafei, Khidr, El-Husseiny, Gomaa, RAAS, ACE2 and COVID-19; a mechanistic review, Saudi J Biol Sci
Gregoriano, Molitor, Haag, Kutz, Koch et al., Activation of vasopressin system during COVID-19 is associated with adverse clinical outcomes: an observational study, J Endocr Soc, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvab045
Hammad, Elshafei, Khidr, El-Husseiny, Gomaa et al., Copeptin: a neuroendocrine biomarker of COVID-19 severity, Biomark Med, doi:10.2217/bmm-2021-1100
Indirli, Bandera, Valenti, Ceriotti, Modugno et al., COVID-19 Network Working Group. Prognostic value of copeptin and mid-regional proadrenomedullin in COVID-19-hospitalized patients, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:10.1111/eci.13753
Katan, Morgenthaler, Widmer, Puder, König et al., Copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the vasopressin precursor, correlates with the individual stress level, Neuro Endocrinol Lett
Kaufmann, Ahmed, Kassem, Freynhofer, Jäger et al., Improvement of outcome prediction of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 by a dual marker strategy using high-sensitive cardiac troponin I and copeptin, Clin Res Cardiol
Koch, Yagmur, Hoss, Buendgens, Herbers et al., Clinical relevance of copeptin plasma levels as a biomarker of disease severity and mortality in critically ill patients, J Clin Lab Anal, doi:10.1002/jcla.22614
Kuluöztürk, İn, Telo, Karabulut, Geçkil, Efficacy of copeptin in distinguishing COVID-19 pneumonia from community-acquired pneumonia, J Med Virol
Lone, Ahmad, COVID-19 pandemic -an African perspective, Emerg Microbes Infect
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Muthyala, Sasidharan, John, Lal, Mishra, Utility of cardiac bioenzymes in predicting cardiovascular outcomes in SARS-CoV-2, World J Virol, doi:10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.375
Müller, Morgenthaler, Stolz, Schuetz, Müller et al., Circulating levels of copeptin, a novel biomarker, in lower respiratory tract infections, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2007.01762.x
Pal, Berhanu, Desalegn, Kandi, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update, Cureus
Ruzzenenti, Maloberti, Giani, Biolcati, Leidi et al., Covid-19 Niguarda Working Group. Covid and cardiovascular diseases: direct and indirect damages and future perspective, High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev, doi:10.1007/s40292-021-00464-8
Seligman, Papassotiriou, Morgenthaler, Meisner, Teixeira, Copeptin, a novel prognostic biomarker in ventilator-associated pneumonia, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc6780
Yousaf, Sd, Al-Soub, Mohamed, COVID-19-associated SIADH: a clue in the times of pandemic!, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00178.2020
Zhang, Dong, Zhao, Wang, Li, Prognostic significance of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones in early sepsis: a study performed in the emergency department, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-014-3468-4
İn, Kuluöztürk, Telo, Toraman, Karabulut, Can copeptin predict the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 infection?, Rev Assoc Med Bras
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.36519/idcm.2024.324",
"ISSN": [
"2667-646X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36519/idcm.2024.324",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5035-5895",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Korkmaz",
"given": "Pınar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0005-192X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mıstanoglu-Özatag",
"given": "Duru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1794-4473",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Keskin",
"given": "Havva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7147-0179",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kocak",
"given": "Havva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2326-5565",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ucar",
"given": "Selcen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Clin Microbiol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-02T08:36:51Z",
"timestamp": 1727858211000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-02T08:36:52Z",
"timestamp": 1727858212000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-02T09:40:28Z",
"timestamp": 1727862028098
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
26
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"member": "22401",
"original-title": [],
"page": "225-232",
"prefix": "10.36519",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Doc Design and Informatics Co. Ltd.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.idcmjournal.org/copeptin-in-covid-19"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A New Biomarker Copeptin in Determining Disease Severity in \nCOVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "6"
}
