Investigating the Relationship between Food Intake and Severity of COVID-19 Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study
et al., Journal of Health System Research, doi:10.48305/jhsr.v21i1.1579, Mar 2025
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
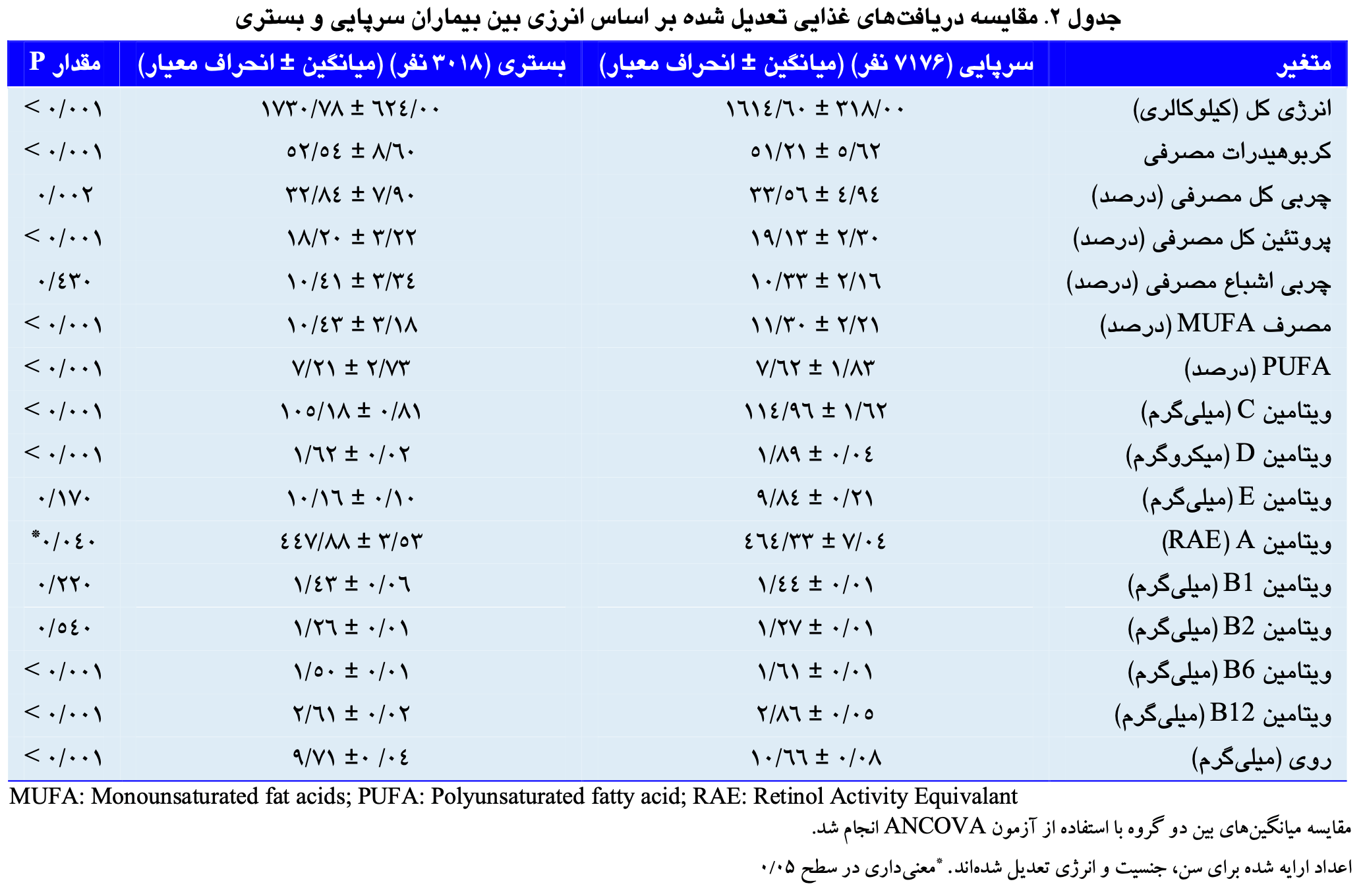
Cross-sectional study of 3,018 hospitalized (moderate and severe) and 717 outpatient (mild) COVID-19 patients showing differences in nutritional intake associated with disease severity. Patients requiring hospitalization had significantly lower consumption of MUFAs, PUFAs, vitamins C, D, A, B6, B12, and zinc compared to those with mild cases, and higher carbohydrate and energy intake. There was no significant difference for saturated fat, vitamins E, B1, and B2.
Kafeshani et al., 4 Mar 2025, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: kafeshani_nut@yahoo.com.
Investigating the Relationship between Food Intake and Severity of COVID-19 Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study
doi:10.48305/jhsr.v21i1.1579
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an emerging infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SASR-CoV-2) with pandemic potential in humans. Recent findings emphasize the importance of nutrition in preventing and controlling this virus. Given that no study has been conducted on the comparison of food intake with the severity of COVID-19 disease, this study was intended to compare food intake with the severity of COVID-19 disease in adults. Methods: In this cross-sectional-analytical study, the dietary patterns of 3018 inpatients (moderate and severe group) and 717 outpatients (mild group) were determined by using the food frequency questionnaire (FFQ). A paired t-test was used to compare quantitative variables, and the chi-square test was used to compare qualitative variables. The comparison of food intake was done using the analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) test. Findings: Between the two outpatient and inpatient groups, a significant difference was observed in the consumption of carbohydrates, protein, fat, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), vitamins C, D, A, B6, B12, and zinc after adjusting for the effect of energy (P < 0.001). No difference was observed between consumption of saturated fat (P = 0.430), vitamins E (P = 0.170), B1 (P = 0.210), and B2 (P = 0.530).
Conclusion: The consumption of total fat, MUFA and PUFA, vitamins C, D, A, B12, B6, and zinc was related to the severity of COVID-19.
References
Alpert, The Role of Vitamins and Minerals on the Immune System, Home Health Care Manag Pract
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr Opin Pharmacol
Basiri, Theory about treatments and morbidity prevention of corona virus disease (Covid-19), J Pharm Pharmacol
Calder, Nutrition, immunity and COVID-19, BMJ Nutr Prev Health
Carella, Angelo, Angelo, Valeria, Marinelli, Vitamin supplements in the Era of SARS-Cov2 pandemic, GSC biol pharm sci
Castelo-Branco, Soveral, The immune system and aging: a review, Gynecol Endocrinol
Chandra, Nutrition, immunity and infection: from basic knowledge of dietary manipulation of immune responses to practical application of ameliorating suffering and improving survival, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Craig, Marshall, Sjöström, Bauman, Booth et al., International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity, Med Sci Sports Exerc
Farnoosh, Alishiri, Zijoud, Dorostkar, Farahani, Understanding the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Based on Available Evidence -A Narrative Review, J Mil Med
Gachkar, Heidari, Forooshani, Gholipour, Farahani et al., Effect of Jujube Tea on Peripheral Blood Count of Patients With COVID-19, J Mod Fam Med
Ginter, Simko, Panakova, Antioxidants in health and disease, Bratisl Lek Listy
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients
Kamali, Hoseinzadeh-Chahkandak, The Role of Vitamins in the Prevention and/or Treatment of COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Mod Care J
Kandeel, Al-Nazawi, Virtual screening and repurposing of FDA approved drugs against COVID-19 main protease, Life Sci
Khan, Naushad, Effects of Corona Virus on the World Community, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3532001
Kumrungsee, Zhang, Chartkul, Yanaka, Kato, Potential Role of Vitamin B6 in Ameliorating the Severity of COVID-19 and Its Complications, Front Nutr
Mattioli, Farinetti, Comment on "Western Dietary Pattern Antioxidant Intakes and Oxidative Stress: Importance during the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Pandemic, Adv Nutr
Merino, Joshi, Nguyen, Leeming, Mazidi et al., Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Gut
Mohammadifard, Sajjadi, Maghroun, Alikhasi, Nilforoushzadeh et al., Validation of a simplified food frequency questionnaire for the assessment of dietary habits in Iranian adults: Isfahan Healthy Heart Program, Iran, ARYA Atheroscler
Mora, Iwata, Von Andrian, Vitamin effects on the immune system: vitamins A and D take centre stage, Nat Rev Immunol
Nueangnong, Subih, Hm, The 2020's world deadliest pandemic: corona virus (COVID-19) and International Medical Law (IML), Cogent Soc Sci
Organization, Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected. Interim guidance, Pediatr Med Rodz
Pasaoglu, Sancak, Bukan, Lipid peroxidation and resistance to oxidation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Tohoku J Exp Med
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Perez-Araluce, Martinez-Gonzalez, Fernandez-Lazaro, Bes-Rastrollo, Gea et al., Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the 'Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra' cohort, Clin Nutr
Scudiero, Lombardo, Brancaccio, Mennitti, Cesaro et al., Exercise, Immune System, Nutrition, Respiratory and Cardiovascular Diseases during COVID-19: A Complex Combination, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Shahbaz, Fatima, Basharat, Yu, Hussain, Role of vitamin C in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, AIMS Microbiol
Yang, Peng, Wang, Guan, Jiang et al., The deadly coronaviruses: The 2003 SARS pandemic and the 2020 novel coronavirus epidemic in China, J Autoimmun
Zhang, Liu, Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review, J Med Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.48305/jhsr.v21i1.1579",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.48305/jhsr.v21i1.1579",
"author": [
{
"family": "Kafeshani",
"given": "Marzieh"
},
{
"family": "Ansaralhosieni",
"given": "Hanieh"
},
{
"family": "Mohamadifard",
"given": "Noushin"
},
{
"family": "Taheri",
"given": "Marzieh"
},
{
"family": "Najafian",
"given": "Jamshid"
},
{
"family": "Sarrafzadegan",
"given": "Nizal"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Health System Research",
"container-title-short": "J Health Syst Res",
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
},
"journalAbbreviation": "J Health Syst Res",
"language": "eng",
"publisher": "Isfahan University of Medical Sciences",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Investigating the Relationship between Food Intake and Severity of COVID-19 Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "21"
}
kafeshani
