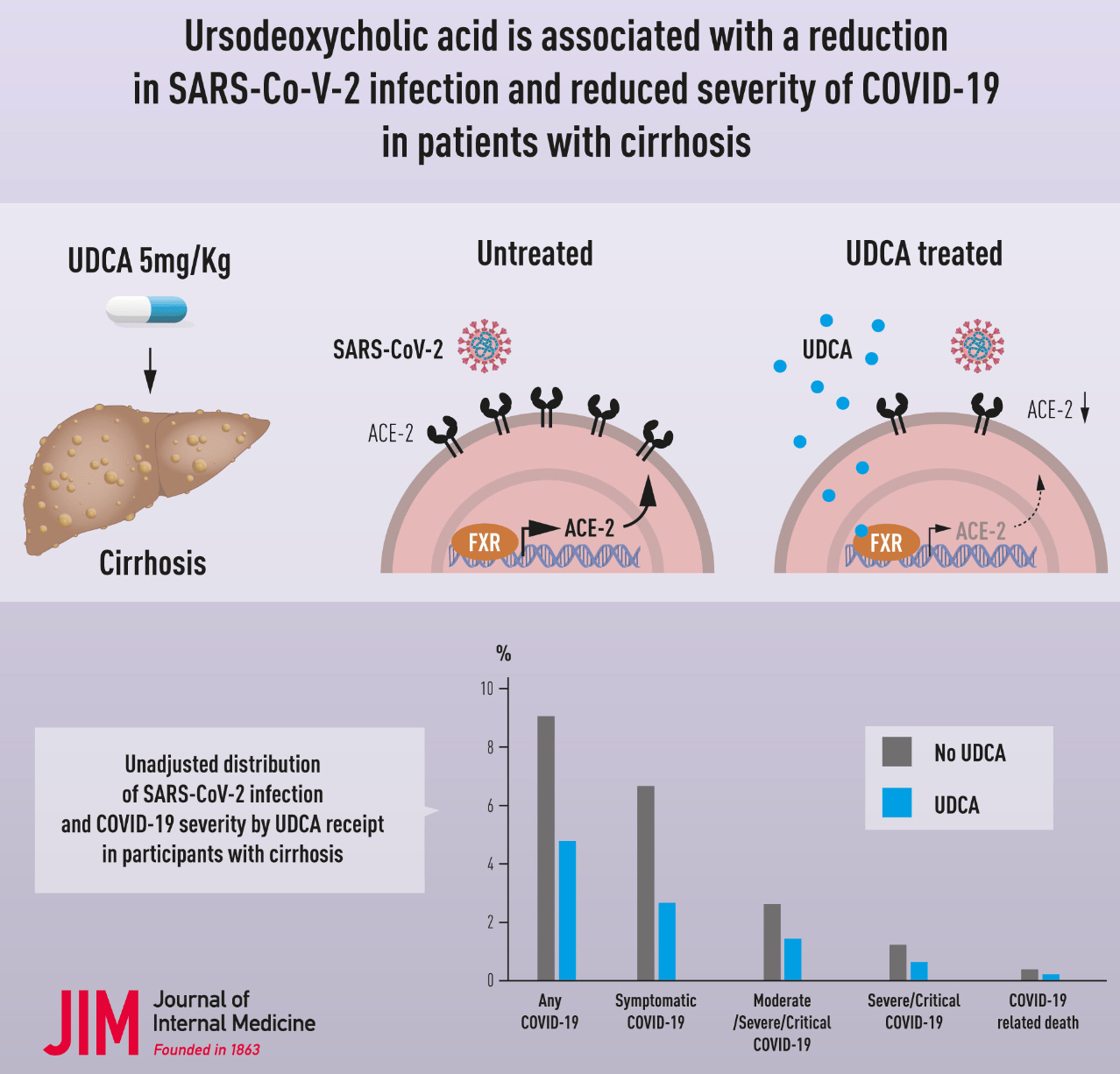
Ursodeoxycholic acid is associated with a reduction in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and reduced severity of COVID‐19 in patients with cirrhosis
et al., Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.1111/joim.13630, Apr 2023
Retrospective 3,214 veterans with cirrhosis comparing 1,607 participants taking ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) to 1,607 propensity score matched controls not taking UDCA. UDCA use was associated with significantly lower odds of SARS-CoV-2 infection, symptomatic COVID-19, moderate or worse COVID-19, and severe/critical COVID-19.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 42.0% lower, OR 0.58, p = 0.28, treatment 1,607, control 1,607, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 54.0% lower, OR 0.46, p = 0.03, treatment 1,607, control 1,607, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of moderate/severe case, 55.0% lower, OR 0.45, p = 0.002, treatment 1,607, control 1,607, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 50.0% lower, OR 0.50, p < 0.001, treatment 1,607, control 1,607, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 48.0% lower, OR 0.52, p < 0.001, treatment 1,607, control 1,607, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
John et al., 5 Apr 2023, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13630",
"ISSN": [
"0954-6820",
"1365-2796"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/joim.13630",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background and aims</jats:title><jats:p>Studies have demonstrated that reducing farnesoid X receptor activity with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) downregulates angiotensin‐converting enzyme in human lung, intestinal and cholangiocytes organoids in vitro, in human lungs and livers perfused ex situ, reducing internalization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) into the host cell. This offers a potential novel target against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19). The objective of our study was to compare the association between UDCA exposure and SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, as well as varying severities of COVID‐19, in a large national cohort of participants with cirrhosis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In this retrospective cohort study among participants with cirrhosis in the Veterans Outcomes and Costs Associated with Liver cohort, we compared participants with exposure to UDCA, with a propensity score (PS) matched group of participants without UDCA exposure, matched for clinical characteristics, and vaccination status. The outcomes included SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, symptomatic, at least moderate, severe, or critical COVID‐19, and COVID‐19‐related death.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>We compared 1607 participants with cirrhosis who were on UDCA, with 1607 PS‐matched controls. On multivariable logistic regression, UDCA exposure was associated with reduced odds of developing SARS‐CoV‐2 infection (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.41–0.71, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.0001). Among patients who developed COVID‐19, UDCA use was associated with reduced disease severity, including symptomatic COVID‐19 (aOR 0.54, 95% CI 0.39–0.73, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.0001), at least moderate COVID‐19 (aOR 0.51, 95% CI 0.32–0.81, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.005), and severe or critical COVID‐19 (aOR 0.48, 95% CI 0.25–0.94, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>In participants with cirrhosis, UDCA exposure was associated with both a decrease in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, and reduction in symptomatic, at least moderate, and severe/critical COVID‐19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/joim.13630"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-04-05"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Miami VA Medical System Miami Florida USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Digestive Health and Liver Diseases University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami Florida USA"
}
],
"family": "John",
"given": "Binu V.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Behavior and Policy Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond Virginia USA"
}
],
"family": "Bastaich",
"given": "Dustin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cambridge Liver Unit Cambridge University Hospital, NHS Foundation Trust Cambridge UK"
}
],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "Gwilym",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Wellcome—MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute Cambridge UK"
}
],
"family": "Brevini",
"given": "Teresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of North Carolina Chapel Hill North Carolina USA"
}
],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Miami VA Medical System Miami Florida USA"
}
],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Raphaella D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Herbert Wertheim Florida International University Miami Florida USA"
}
],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "Allison M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia Pennsylvania USA"
},
{
"name": "Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center Philadelphia Pennsylvania USA"
}
],
"family": "Kaplan",
"given": "David E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Digestive Diseases Yale School of Medicine New Haven Connecticut USA"
},
{
"name": "Section of Gastroenterology VA Connecticut Healthcare System West Haven Connecticut USA"
}
],
"family": "Taddei",
"given": "Tamar H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia Pennsylvania USA"
}
],
"family": "Serper",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia Pennsylvania USA"
}
],
"family": "Mahmud",
"given": "Nadim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Behavior and Policy Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond Virginia USA"
}
],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Yangyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Radiation Oncology Central Virginia Health System Richmond Virginia USA"
}
],
"family": "Chao",
"given": "Hann‐Hsiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Wellcome—MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute Cambridge UK"
},
{
"name": "Cambridge Liver Unit Cambridge University Hospital, NHS Foundation Trust Cambridge UK"
}
],
"family": "Sampaziotis",
"given": "Fotios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Behavior and Policy Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond Virginia USA"
}
],
"family": "Dahman",
"given": "Bassam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Internal Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Intern Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"pericles.pericles-gcp.literatumonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-05T16:54:11Z",
"timestamp": 1680713651000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-05T12:26:16Z",
"timestamp": 1693916776000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-03T01:17:42Z",
"timestamp": 1698974262032
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 9,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680652800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/joim.13630",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "636-647",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"author": "COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines Panel",
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1",
"volume-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) treatment guidelines"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1",
"volume-title": "Centers for disease control and prevention COVID‐19 data tracker"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.32337",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4325",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2022.05.038",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-022-07644-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12072‐020‐10077‐3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2022.09.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1",
"unstructured": "Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for PAXLOVIDTM.https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download. Acccessed 11/30/22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05053-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1",
"unstructured": "The COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines Panel's Statement on Omicron Subvariants.Pre‐exposure prophylaxis and therapeutic management of non‐hospitalized patients with COVID‐19.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/statement‐on‐omicron‐subvariants/Accessed 11/30/22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1",
"unstructured": "AchufusiTGO SafadiAO MahabadiN.Ursodeoxycholic acid. [Updated 2022 Jan 30]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545303/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001280",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31776",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0000000000003615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.11.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.32619",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00009-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00341-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7010e4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18332/tid/119324",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_33_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_34_1",
"unstructured": "COVID data tracker‐variant proportions.https://covid.cdc.gov/covid‐data‐tracker/#variant‐proportions. Accessed 11/30/2022"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_35_1",
"unstructured": "Frequently asked questions about COVID‐19 vaccination.https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019‐ncov/vaccines/faq.html. Accessed 1/24/23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_36_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joim.13630"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid is associated with a reduction in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and reduced severity of COVID‐19 in patients with cirrhosis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "293"
}