Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on symptoms after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in patients with primary biliary cholangitis and their family members
et al., Journal of Clinical Hepatology, doi:10.12449/JCH240714, Jul 2024
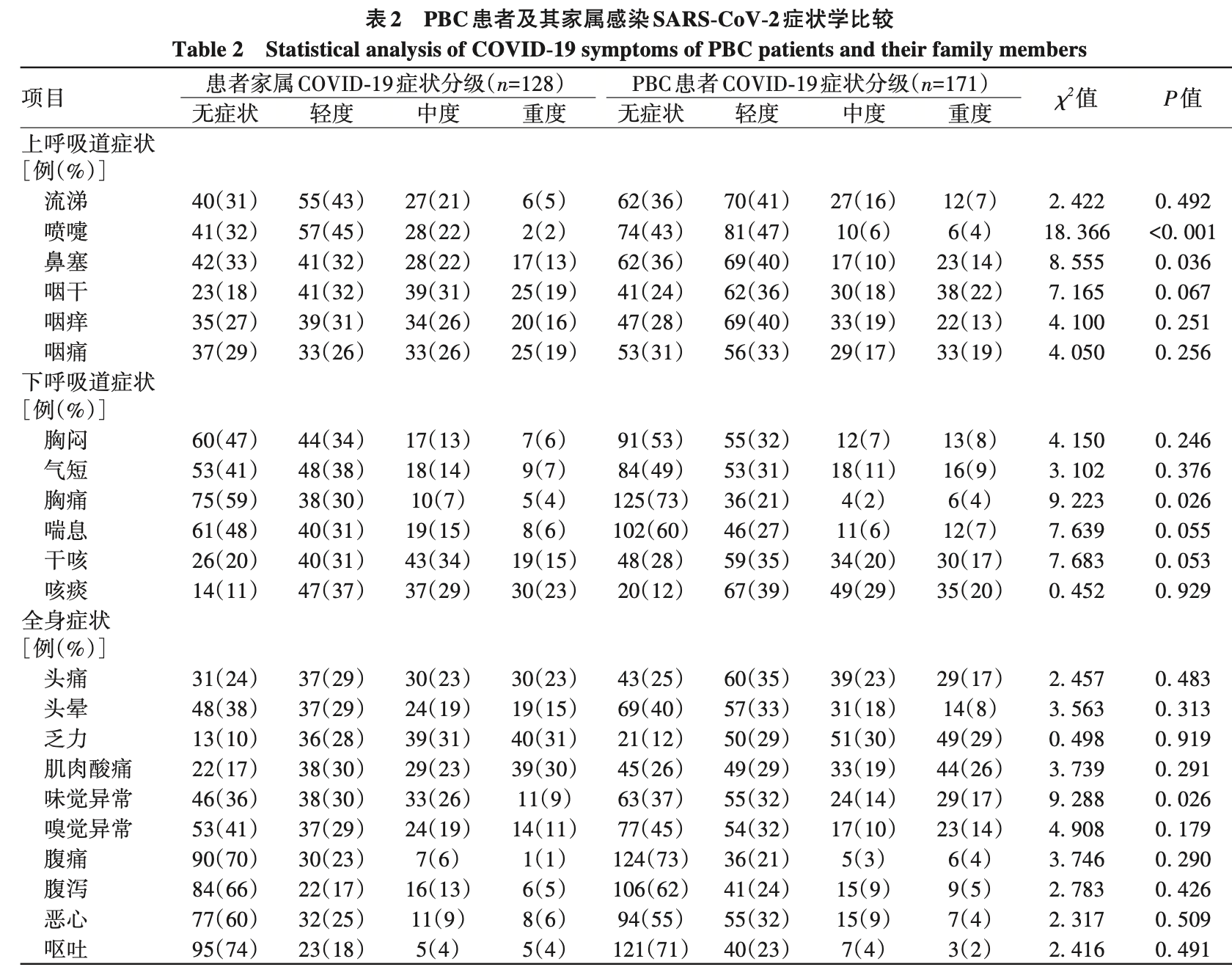
Retrospective 171 primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) patients taking ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and 128 family members, showing no reduction in SARS-CoV-2 infection rates but milder symptoms in PBC patients. All PBC patients and family members were infected with SARS-CoV-2. PBC patients reported significantly milder symptoms for nasal congestion, chest pain, sneezing, and taste abnormalities compared to family members.
Jia et al., 25 Jul 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on symptoms after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in patients with primary biliary cholangitis and their family members
doi:10.12449/JCH240714
摘要: 目的 探究熊去氧胆酸(UDCA)对原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)患者及其家属严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒 2(SARS-CoV-2)感染症状的影响。方法 通过问卷收集 2023 年 3 月 22 日之前就诊于空军军医大学第一附属医院的 PBC 患者(n=
References
Acosta, Global estimates of excess deaths from COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-022-04138-w
Albillos A, Lario, Cirrhosis-associated im• mune dysfunction: Distinctive features and clinical relevance[J], J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.010
Berlin Da, Gulick, Fj, Severe Covid-19[J], N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmcp2009575
Brevini, Maes, Gj, FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2[J], Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0
Cm, Xf, Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on symptoms after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in patients with primary biliary cholangitis and their family members[J], J Clin Hepatol
Cooper S, Tobar, Konen, Long COVID-19 liver mani• festation in children[J], J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, doi:10.1097/MPG.0000000000003521
Dennis A, Wamil, Alberts, Multiorgan impairment in low-risk individuals with post-COVID-19 syndrome: A prospective, community-based study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048391
Gaziano, Giambartolomei, Pereira Ac, Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repur• posing opportunities for COVID-19, J]. Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01310-z
Hu B, Guo, Zhou, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19[J], Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Ioannou Gn, Green, Risk factors for hospitaliza• tion, mechanical ventilation, or death among 10 131 US veterans with SARS-CoV-2 infection[J], JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22310
Khandker Ss, Godman, Mi, A systematic review on COVID-19 vaccine strategies, their effectiveness, and issues, J]. Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines9121387
Mathew, Sb, COVID-19 vaccine trig• gered autoimmune hepatitis: Case report, Eur J Hosp Pharm, doi:10.1136/ejhpharm-2022-003485
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, J]. Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Nc, Vitkovski, Post-COVID-19 cholangiopa• thy: A novel entity[J], Am J Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001154
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN Compr Clin Med, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4
Shahrani, Sooi, Hilmi, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) following coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccine-No longer exclusive to mRNA vaccine?, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/liv.15350
Study, Liver, EASL Clinical Prac• tice Guidelines: The diagnosis and management of patients with pri• mary biliary cholangitis[J], J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.022
Teijaro Jr, Dl, COVID-19 vaccines: Modes of immune activation and future challenges[J], Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00526-x
Tian Dd, Yh, Xu Hh, The emergence and epidemic characteristics of the highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant [J], J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27643
Wang, Han Y, Diagnosis and treatment of primary biliary cholangi• tis: Current status and challenges[J], J Clin Hepatol, doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.10.001
Wanner N, Molecular consequences of SARS-CoV-2 liver tropism[J], Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/s42255-022-00552-6
Williamson Ej, Aj, Bhaskaran, Factors asso• ciated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4
贾桂, 王秀芳, 熊去氧胆酸对原发性胆汁性胆管炎患 者及家属新型冠状病毒感染症状的影响