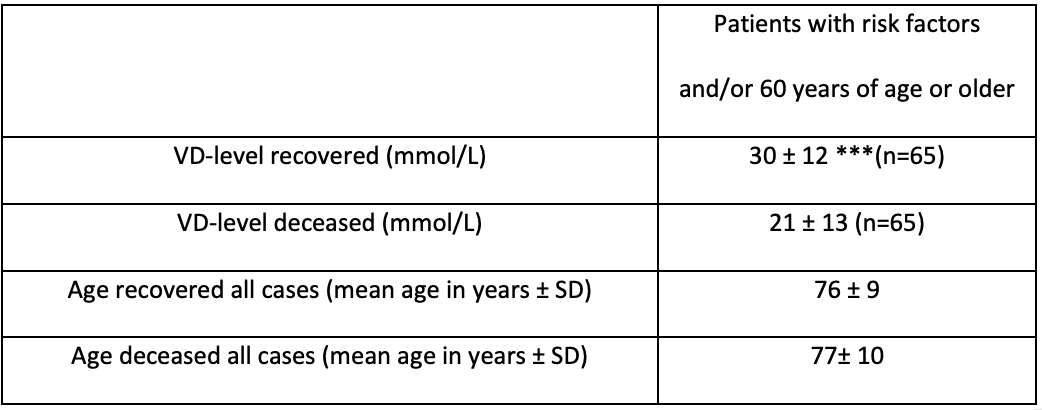
COVID-19 mortality is associated with low Vitamin D levels in patients with risk factors and/or advanced age
et al., Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.11.025, Nov 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 257 hospitalized patients in Hungary, showing mortality associated with lower vitamin D levels for all patients, for patients >60, and for age-matched patients with risk factors or age >60. The non-age-matched analyses are confounded by age, with elderly patients more likely to have lower vitamin D levels.
Jenei et al., 24 Nov 2021, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
COVID-19 mortality is associated with low vitamin D levels in patients with risk factors and/or advanced age
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.11.025
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of interest statement The authors do not declare any conflicts of interest
Author contributions
References
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., None
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and metaanalysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Jolliffe, Stefanidis, Wang, Kermani, Dimitrov et al., Vitamin D Metabolism Is Dysregulated in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J
Patchen, Clark, Gaddis, Hancock, Cassano, Genetically predicted serum vitamin D and COVID-19: a Mendelian randomisation study, BMJ Nutr Prev Health
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Szeto, Zucker, Lasota, Rubin, Walker et al., Vitamin D Status and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients, Endocr Res
Vimaleswaran, Forouhi, Khunti, Vitamin D and covid-19, BMJ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.11.025",
"ISSN": [
"2405-4577"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.11.025",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405457721011293"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5963-1817",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jenei",
"given": "Tímea",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenei",
"given": "Sándor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tamás",
"given": "László T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Putics",
"given": "Ákos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knausz",
"given": "Márta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hegedüs",
"given": "Irén",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dinnyés",
"given": "Imre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7012-2060",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Szalai",
"given": "Zsuzsanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molnár",
"given": "Tamás F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Büki",
"given": "Béla",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Clinical Nutrition ESPEN"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-24T02:04:02Z",
"timestamp": 1637719442000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-27T10:33:58Z",
"timestamp": 1638009238000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-28T06:48:35Z",
"timestamp": 1638082115134
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2405-4577"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721011293?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721011293?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Clinical Nutrition ESPEN"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"COVID-19 mortality is associated with low Vitamin D levels in patients with risk factors and/or advanced age"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
