Impact of Antidiabetic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
et al., Endocrinology and Metabolism, doi:10.3803/EnM.2024.1857, Jan 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
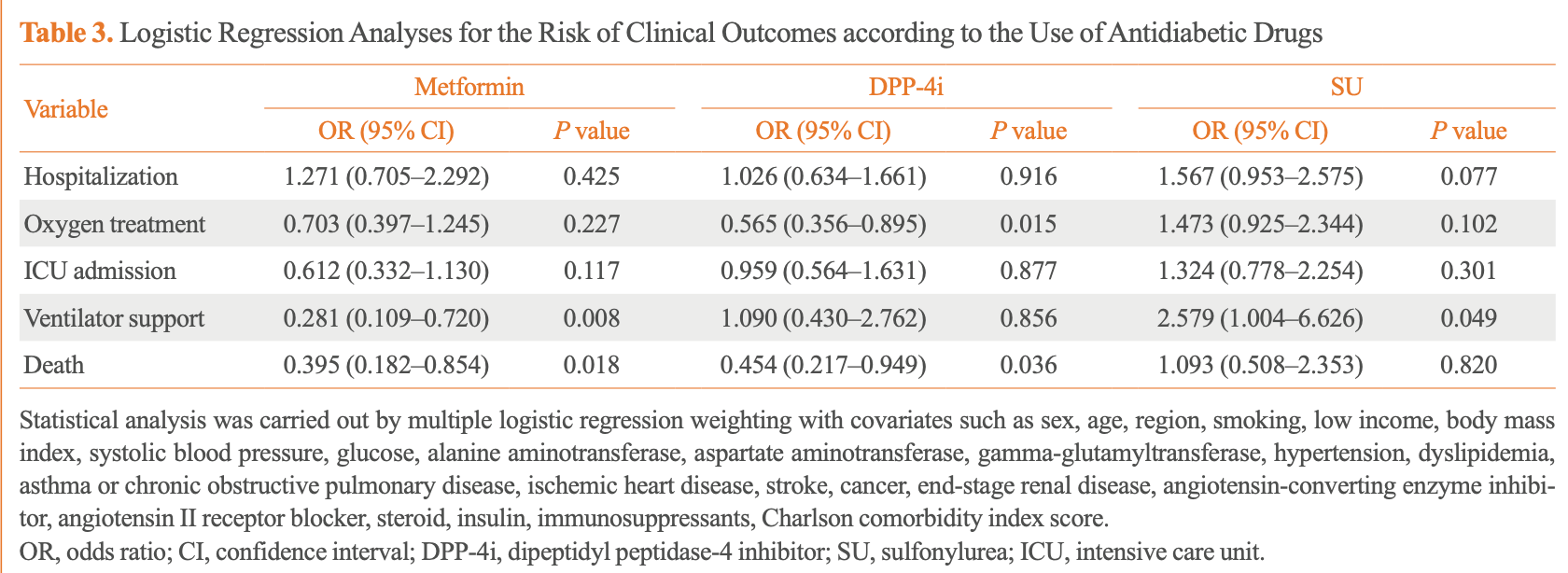
Retrospective 556 diabetic patients in South Korea with COVID-19 showing lower risk of mechanical ventilation and death with metformin, lower risks of oxygen treatment and death with DPP-4 inhibitors, and increased risk of mechanical ventilation with sulfonylureas. The study used nationwide data to analyze the impact of common antidiabetic medications on COVID-19 outcomes. Authors note that South Korea had a policy early in the pandemic of hospitalizing nearly all confirmed COVID-19 patients regardless of severity.
|
risk of death, 60.5% lower, OR 0.40, p = 0.02, treatment 461, control 95, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 71.9% lower, OR 0.28, p = 0.008, treatment 461, control 95, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 38.8% lower, OR 0.61, p = 0.12, treatment 461, control 95, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 29.7% lower, OR 0.70, p = 0.23, treatment 461, control 95, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 27.1% higher, OR 1.27, p = 0.42, treatment 461, control 95, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jang et al., 29 Jan 2024, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: hongsiri@hanmail.net.
Impact of Antidiabetic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Endocrinology and Metabolism, doi:10.3803/enm.2024.1857
Background: Inconsistent results have been reported regarding the association between the use of antidiabetic drugs and the clinical outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 . This study aimed to investigate the effect of antidiabetic drugs on COVID-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes using data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) in South Korea. Methods: We analyzed the NHIS data of patients aged ≥20 years who tested positive for COVID-19 and were taking antidiabetic drugs between December 2019 and June 2020. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 based on the use of antidiabetic drugs. Results: A total of 556 patients taking antidiabetic drugs tested positive for COVID-19, including 271 male (48.7%), most of whom were in their sixties. Of all patients, 433 (77.9%) were hospitalized, 119 (21.4%) received oxygen treatment, 87 (15.6%) were admitted to the intensive care unit, 31 (5.6%) required mechanical ventilation, and 61 (11.0%) died. Metformin was significantly associated with the lower risks of mechanical ventilation (odds ratio [OR], 0.281; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.109 to 0.720; P=0.008), and death (OR, 0.395; 95% CI, 0.182 to 0.854; P=0.018). Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) were significantly associated with the lower risks of oxygen treatment (OR, 0.565; 95% CI, 0.356 to 0.895; P=0.015) and death (OR, 0.454; 95% CI, 0.217 to 0.949; P=0.036). Sulfonylurea was significantly associated with the higher risk of mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.579; 95% CI, 1.004 to 6.626; P=0.049).
Conclusion: In patients with diabetes and COVID-19, metformin exhibited reduced risks of mechanical ventilation and death, DPP-4i was linked with lower risks of oxygen treatment and death, while sulfonylurea was related to the increased risk of mechanical ventilation.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conception or design: E.J.R., W.Y.L. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: S.J.M., J.H.J., K.D.H. Drafting the work or revising: H.N.J., S.J.M., E.J.R., W.Y.L. Final approval of the manuscript: H.N.J., S.J.M., J.H.J., K.D.H., E.J.R., W.Y.L.
References
Abuhasira, Ayalon-Dangur, Zaslavsky, Koren, Keller et al., A randomized clinical trial of linagliptin vs. standard of care in patients hospitalized with diabetes and COVID-19, Front Endocrinol
Bae, Han, Ko, Yang, Choi et al., Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021, Diabetes Metab J
Baek, Lee, Kim, Choi, Sy, COVID-19-related outcomes in immunocompromised patients: a nationwide study in Korea, PLoS One
Bonora, Avogaro, Fadini, Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COV-ID-19: narrative review and meta-analysis, J Endocrinol In
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Broxmeyer, Capitano, Campbell, Hangoc, Cooper, Modulation of hematopoietic chemokine effects in vitro and in vivo by DPP-4/CD26, Stem Cells Dev
Cama, Marin-Prida, Acosta-Rivero, Acosta, Diaz et al., The microglial NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in human SARS-CoV-2 cerebral pathogenicity: a report of three post-mortem cases, J Neuroimmunol
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia
Chang, Hwang, Jeon, Kwak, Park et al., Fasting plasma glucose level independently predicts the mortality of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 infection: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study, Endocrinol Metab
Cheng, Liu, Li, Zhang, Lei et al., Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Chung, Lee, Ha, Yoon, Won et al., The risk of diabetes on clinical outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective cohort study, Diabetes Metab J
Dalan, Ang, Tan, Fong, Tay et al., The association of hypertension and diabetes pharmacotherapy with COVID-19 severity and immune signatures: an observational study, Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother
Esmaeili, Enayati, Abkenar, Ebrahimian, Salari, Glibenclamide mitigates cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuroinflammation in rats with type 2 diabetes and sporadic Alzheimer-like disease, Behav Brain Res
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COV-ID-19 patients: a review, Allergy
Gao, Liu, Zhong, Liu, Zhou et al., Risk of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes with COVID-19: a preliminary retrospective report, Clin Transl Sci
Glasheen, Cordier, Gumpina, Haugh, Davis, Charlson comorbidity index: ICD-9 update and ICD-10 translation, Am Health Drug Benefits
Guardado-Mendoza, Garcia-Magana, Martinez-Navarro, Macias-Cervantes, Aguilar-Guerrero et al., Effect of linagliptin plus insulin in comparison to insulin alone on metabolic control and prognosis in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Sci Rep
Guo, Shi, Zhang, Wang, Vale Moreira et al., Comorbid diabetes and the risk of disease severity or death among 8807 COVID-19 patients in China: a metaanalysis, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Han, Ma, Sun, Zhang, Qu et al., Association between anti-diabetic agents and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Med Res
Hughes, Smith-Mccain, Effects of sulfonylurea compounds on Pneumocystis carinii, J Infect Dis
Kawasaki, Htwe, Tatsumi, Dudek, DPP4 inhibition by sitagliptin attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in mice, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Kim, Han, Shin, Kim, Lee et al., Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: predisposing factors and outcome, Endocrinol Metab
Kim, Jeon, Kim, Moon, Cho et al., The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with moderate-to-severe coronavirus disease 2019 infection and diabetes in Daegu, South Korea, Diabetes Metab J
Meyerholz, Lambertz, Mccray, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 distribution in the human respiratory tract: implications for the middle east respiratory syndrome, Am J Pathol
Moon, Rhee, Jung, Han, Kim et al., Independent impact of diabetes on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in 5,307 patients in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study, Diabetes Metab J
Nafakhi, Alareedh, Al-Buthabhak, Shaghee, Nafakhi et al., Predictors of adverse in-hospital outcome and recovery in patients with diabetes mellitus and COV-ID-19 pneumonia in Iraq, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Nguyen, Ho, Nguyen, Ho, Li et al., Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis, Metabolism
Ou, Zhu, Li, Zhong, Li, Risk factors of severe cases with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Epidemiol Infect
Pedrosa, Martins, Rizzo, Silva-Nunes, Metformin in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a hidden path. From altered inflammation to reduced mortality. A review from the literature, J Diabetes Complications
Postler, Peng, Bhatt, Ghosh, Metformin selectively dampens the acute inflammatory response through an AMPK-dependent mechanism, Sci Rep
Quianzon, Cheikh, History of current non-insulin medications for diabetes mellitus, J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect
Reis, Santos, Silva, Silva, Thabane et al., Effect of early treatment with metformin on risk of emergency care and hospitalization among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETH-ER randomized platform clinical trial, Lancet Reg Health Am
Schaller, Sharma, Dupee, Nguyen, Uruena et al., Ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung reveals heterogeneous host defense and therapeutic responses, JCI Insight
Shi, Zhang, Jiang, Zhang, Hu et al., Clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality of CO-VID-19 patients with diabetes in Wuhan, China: a two-center, retrospective study, Diabetes Care
Singh, Singh, Saboo, Misra, Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: a critical appraisal of literature, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Soare, Gyorfi, Matei, Dees, Rauber et al., Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 as a marker of activated fibroblasts and a potential target for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis, Arthritis Rheumatol
Ventura-Lopez, Cervantes-Luevano, Flores-Caballero, Alvarez-Delgado, Bernaldez-Sarabia, Treatment with metformin glycinate reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load: an in vitro model and randomized, double-blind, phase IIb clinical trial, Biomed Pharmacother
Viollet, Guigas, Garcia, Leclerc, Foretz et al., Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview, Clin Sci (Lond)
Xian, Liu, Nilsson, Gatchalian, Crother et al., Metformin inhibition of mitochondrial ATP and DNA synthesis abrogates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pulmonary inflammation, Immunity
Xin, Wei, Ji, Zheng, Gu et al., Metformin uniquely prevents thrombosis by inhibiting platelet activation and mtDNA release, Sci Rep
Yang, Wang, Jia, Neuroprotection of glibenclamide against brain injury after cardiac arrest via modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome, Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc
Zhang, Dong, Liu, Gao, Risk and protective factors for COVID-19 morbidity, severity, and mortality, Clin Rev Allergy Immunol
Zhang, Li, Zhang, Cao, Zhao et al., The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and secondary hyperglycaemia with coronavirus disease 2019: a single-centre, retrospective, observational study in Wuhan, Diabetes Obes Metab
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3803/enm.2024.1857",
"ISSN": [
"2093-596X",
"2093-5978"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1857",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-10-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-01-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published online",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-01-29"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6186-2937",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Jang",
"given": "Han Na",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6286-7254",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Moon",
"given": "Sun Joon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jung",
"given": "Jin Hyung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Kyung-Do",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6108-7758",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Rhee",
"given": "Eun-Jung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1082-7592",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Won-Young",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Endocrinology and Metabolism",
"container-title-short": "Endocrinol Metab",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.e-enm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T07:37:43Z",
"timestamp": 1706513863000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T07:37:44Z",
"timestamp": 1706513864000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T00:24:12Z",
"timestamp": 1706574252836
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.e-enm.org/upload/pdf/enm-2024-1857.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2119",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3803",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Korean Endocrine Society",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.e-enm.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.3803/EnM.2024.1857"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of Antidiabetic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Nationwide Population-Based Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/crossmark_policy"
}
