Vitamin D Serum Levels and Its Association With COVID 19 Infection In Babylon Governorate, Iraq
et al., Natural Volatiles & Essential Oils, 8:4, Dec 2021
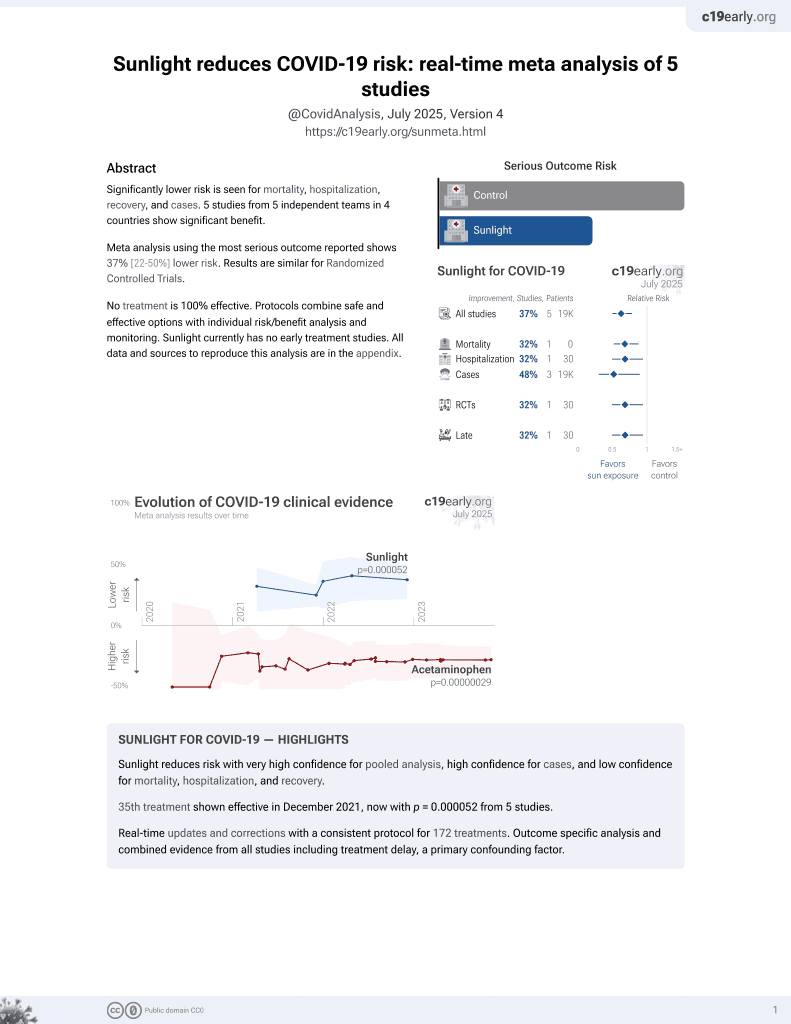
Sunlight for COVID-19
35th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
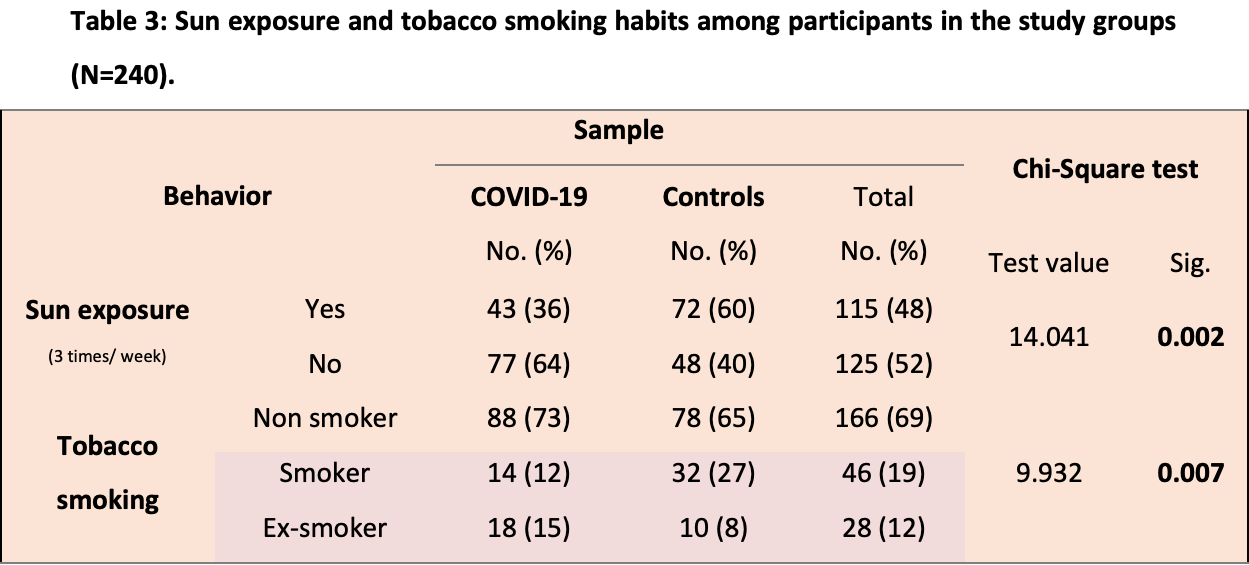
Analysis of 120 COVID-19 and 120 control patients in Iraq, showing lower risk of cases with regular sunlight exposure (3 times/week).
Study covers sunlight and vitamin D.
|
risk of case, 62.8% lower, OR 0.37, p < 0.001, higher sunlight exposure 43 of 120 (35.8%) cases,
72 of 120 (60.0%) controls, NNT 4.1, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jabbar et al., 31 Dec 2021, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Vitamin D Serum Levels and Its Association With COVID 19 Infection In Babylon Governorate, Iraq
Considering the role of the data that indicate the importance of Vitamin D adequacy in protecting human being againstdifferent pathogens in patients exposed to infectious agents, the role of this Vitamin in Covid-19 patients is a matter of debate. Objectives: to identify the association between vitamin D level and infection with SARS-COV-2 of adult patients attending or admitted to Merjan Teaching Hospital , Babylon , Iraq .Methodology: this was a cross sectional comparison study of 240 participants, the total sample mean ±SD age was 46.9±15.4 years, 120confirmed diagnosed cases and admitted to coronavirus unit and 120 negative cases (comparison group). The study carried out from January to June 2021 in Merjan Teaching Hospital, Babylon, Iraq. A pretested questionnaire used to interview patients after obtaining their verbal consents. Serum 25(OH) vitamin D measured to both groups of participants using immunoassay method (maglumi instrument) and body mass index (BMI) measured. The questionnaire included demographicinformation, clinical symptoms, unhealthy habits, and underlying health conditions, (comorbidities related to each participant elicited and recorded). Results: This study showed that vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency were positively and significantly associated with SARS-COV-2 infection, COVID-19-cnfirmed patients had significantly lower serum vitamin D levels than comparison group (p = 0.01). In addition, the results revealed that the COVID-19 cases with Vitamin D inadequacy were significantly associated with low educational level, low socioeconomic status, and much lowest among female patients (p<0.05). Conclusions: Vitamin D inadequacy was significantly associated with COVID 19 infection.
Conflict of interests The researchers declare that no conflict of interests.
Funding Source There is no fund for this study.
References
Abdollahia, Sarvestani, Ghaderkhani, Mahmoudi-Aliabadim, Jafarzadeh et al., The association between the level of serum 25(OH) vitamin D, obesity, and underlying diseases with the risk of developing COVID-19 infection: A case-control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran, J Med Virol
Al-Dabhani, Tsilidis, Murphy, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and association with metabolic syndrome in a Qatari population, Nutr& Diabetes
Alvarez-Rodriguez, Lopez-Hoyos, Garcia-Unzueta, Amado, Cacho et al., Age and low levels of circulating vitamin D are associated with impaired innate immune function, J Leukoc Biol
Ben-Eltriki, Hopefl, Wright, Association between Vitamin D Status and Risk of Developing Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, J Am CollNutr
Das, Samad, Ahinkorahbo, Hagan, Peprah et al., Effect of Vitamin D Deficiency on COVID-19 Status: A Systematic Review, COVID
El Sammakmy, Wossaibi, Howeisha, Alsaeed, High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the sunny Eastern region of Saudi Arabia: a hospital-based study, EMHJ -Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal
He, Hao, The effect of vitamin D3 on blood pressure in people with vitamin D deficiency: A system review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Hernández, Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, J ClinEndocrinolMetab
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging ClinExp Res
Jawad, Baiee, Prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency and its correlates with overweight and obesity in community-dwelling old adults, Med J Babylon
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, Br Med J
Mendes, Santos, Borges, Afonso, Moreira et al., Vitamin D status and functional parameters: A cross-sectional study in an older population, PLoS One
Moon, Kong, Kim, Effect of Secondhand Smoking, Determined by Urinary Cotinine Level on Bone Health, International journal of preventive medicine
Nakashima, Yokoyama, Yokoo, Urashima, Role of Vitamin D in diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, World J Diabetes
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, ClinEndocrinol (Oxf)
Reis, Fernandes, Sales, Santos, Santos et al., Influence of vitamin D status on hospital length of stay and prognosis in hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a multicenter prospective cohort study, Am J ClinNutr
Santos, Amaral, Guerra, Vitamin D status and associated factors among Portuguese older adults: results from the Nutrition UP 65 cross-sectional study, BMJ Open
Snijder, Lips, Seidell, Visser, Deeg et al., None
Ye, Tang, Liao, Shaw, Deng et al., Does Serum Vitamin D Level Affect COVID-19 Infection and Its Severity?-A Case-Control Study, J Am CollNutr
Yisak235-Yisak, Ewunetei, Kefale, Mamuye, Teshome et al., Effects of Vitamin D on COVID-19 Infection and Prognosis: A Systematic Review, Risk ManagHealthc Policy
jabbar