Adverse events associated with monoclonal antibodies used for treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
et al., British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1002/bcp.70025, PROSPERO CRD42023447055, Mar 2025
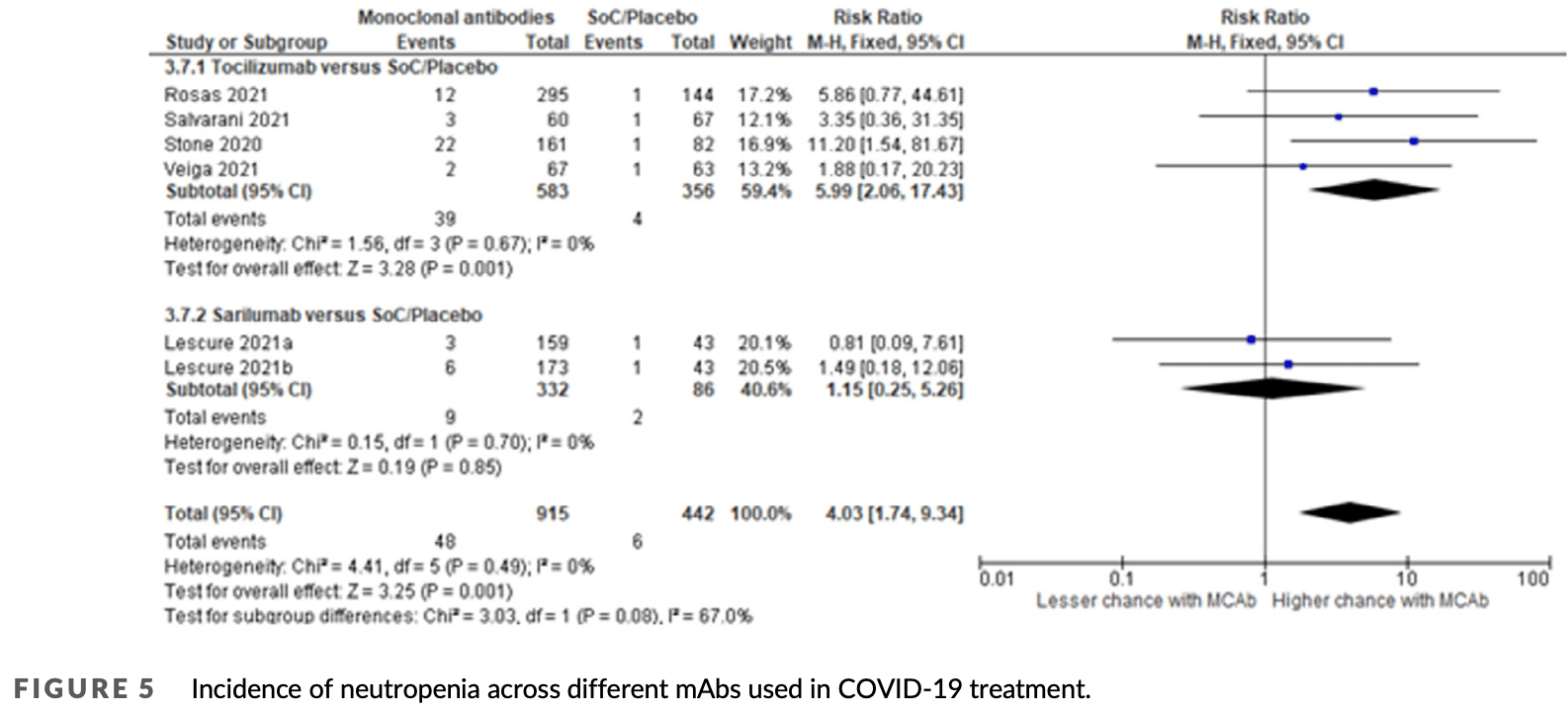
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 RCTs with 19,797 COVID-19 patients, showing a statistically significant increased risk of hepatotoxicity and neutropenia associated with monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments compared to standard of care or placebo. This elevated risk was reported with moderate certainty of evidence and appeared primarily linked to immunomodulatory mAbs targeting the IL-6 pathway, such as tocilizumab, which was the most frequently evaluated mAb in the included studies.
Study covers tocilizumab and sarilumab.
Htet et al., 6 Mar 2025, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period January 2020 - September 2023, trial PROSPERO CRD42023447055.
Contact: hhnoel@gmail.com.
Adverse events associated with monoclonal antibodies used for treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1002/bcp.70025
Aims: This review aimed to synthesise the evidence related to the incidence of serious and non-serious adverse events with the use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) among COVID-19 patients. Methods: Databases were searched from January 2020 to September 2023 for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that used mAbs for the treatment of COVID-19 regardless of disease severity. Study screening, data extraction and data analysis were performed independently by two reviewers. The Cochrane risk of bias 1.0 tool was used for methodological quality assessment. Results: Sixteen studies were identified for analysis with 9682 participants in the intervention arm and 10 115 participants in the control arm. Seven trials reported hepatoxicity and there was a statistically significant increase in the chance of hepatoxicity among patients treated with mAbs compared to those given standard of care (SoC) or placebo with risk ratio (RR) = 1.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.29-2.24. Five trials reported for neutropenia and there was a statistically significant association of neutropenia with the use of mAbs compared to SoC or placebo with RR = 4.03, 95% CI 1.74-9.34. Ten trials reported any disease-related serious adverse events related to the disease and there was a reduction of risk compared to SoC/placebo, although this reduction was not statistically significant (RR = 0.88, 95% CI 0.70-1.11). Conclusions: The use of mAbs was found to be associated with an increased risk of hepatoxicity and neutropenia compared to SoC/placebo among COVID-19 patients with moderate certainty of evidence. Long-term observational studies are recommended to observe post-COVID adverse events related to the use of mAbs.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT There are no competing interests to declare.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
References
Alexander, Cidlowski, Kelly, The concise guide to pharmacology 2023/24: nuclear hormone receptors, Br J Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1111/bph.16179
Alexander, Fabbro, Kelly, The concise guide to pharmacology 2023/24: catalytic receptors, Br J Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1111/bph.16180
Alexander, Fabbro, Kelly, The concise guide to pharmacology 2023/24: enzymes, Br J Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1111/bph.16181
Alexander, Kelly, Mathie, The concise guide to pharmacology 2023/24: introduction and other protein targets, Br J Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1111/bph.16176
Aljuhani, Sulaiman, Korayem, The use of tocilizumab in COVID-19 critically ill patients with renal impairment: a multicenter, cohort study, Renal Fail, doi:info:doi/10.1080/0886022X.2023.2268213
Aygün, Kaya, Alhajj, Identifying side effects of commonly used drugs in the treatment of Covid 19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78697-1
Bernardo, Sesto, Giordano, Severe prolonged neutropenia following administration of tocilizumab in a patient affected by COVID-19: a case report and brief review of the literature, Drugs Ther Perspect, doi:info:doi/10.1111/aas.13795
Burmester, Choy, Kivitz, Low immunogenicity of tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016–210297
Campbell, Chen, Bhagat, Parker, Ostor, Risk of adverse events including serious infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab: a systematic literature review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials, Rheumatology, doi:info:doi/10.1093/rheumatology/keq343
Campochiaro, Della-Torre, Cavalli, Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19 patients: a single-Centre retrospective cohort study, Eur J Intern Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021
Cansever, Şahin, Dursun, Successful slow desensitization to tocilizumab in a 15-year-old patient, J Invest Allergol Clin Immunol, doi:info:doi/10.18176/jiaci.0314
Chai, Hu, Zhang, Specific ACE2 expression in cholangiocytes may cause liver damage after 2019-nCoV infection, bioRxiv, doi:info:doi/10.1101/2020.02.03.931766
Chiu, Bhardwaj, Sah, Safety profile of COVID-19 drugs in a real clinical setting, Eur J Clin Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s00228-021-03270-2
Corti, Purcell, Snell, Veesler, Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, Cell, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005
Deeks, Casirivimab/imdevimab: first approval, Drugs, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s40265-021-01620-z
Everds, Tarrant, Unexpected hematologic effects of biotherapeutics in nonclinical species and in humans, Oxicol Pathol, doi:info:doi/10.1177/0192623312467400
Farcy, Dalley, Miro, A comparison of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody therapies in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 disease at a single academic hospital, J Emerg Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.07.025
Fukuda, Sawa, Hoshino, Ohashi, Motoaki et al., Tocilizumab preserves renal function in rheumatoid arthritis with AA amyloidosis and end-stage kidney disease: two case reports, Clin Nephrol, doi:info:doi/10.5414/CN109971
Gao, Yin, Tan, Drug-induced liver injury following the use of tocilizumab or sarilumab in patients with coronavirus disease 2019, BMC Infect Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12879-022-07896-0
Gavriatopoulou, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Korompoki, Emerging treatment strategies for COVID-19 infection, Clin Exp Med, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s10238-020-00671-y
Giovanna, Immune-related adverse events of biological immunotherapies used in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:info:doi/10.3389/fphar.2022.973246
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Effect of sotrovimab on hospitalization or death among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:info:doi/10.1001/jama.2022.2832
Heo, Sotrovimab: first approval, Drugs, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s40265-022-01690-7
Hermine, Tharaux, Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:info:doi/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820
Htet, Kyung, Agarwal, Lezhitsa, Jaiprakash et al., A systematic review and meta-analysis of adverse events of WHOapproved COVID-19 treatment regimens, INPLASY Registration, doi:info:doi/10.37766/inplasy2023.8.0026
Htet, Kyung, Iezhitsa, A systematic review and metaanalysis of adverse events of WHO-approved COVID-19 treatment regimens, PROSPERO
Hwang, Lu, Su, Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 therapy and SARS-CoV-2 detection, J Biomed Sci, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s12929-021-00784-w
Karampitsakos, Papaioannou, Tsiri, Tocilizumab versus baricitinib in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: an open label, randomized controlled trial, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmi.2022.10.015
Keske, Akyol, Tanrıöver, Effectiveness of tocilizumab in non-intubated cases with COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Infection, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s15010-023-02047-2
Kili C, Iki C L, Mayer, Artukovi C M, Radonči C Km, Safe and efficient use of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a case report, Medicina, doi:info:doi/10.3390/medicina59091517
Kim, Ahn, Oh, Clinical significance of tocilizumabrelated neutropenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Joint Bone Spine, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jbspin.2022.105510
Kim, Ahn, Oh, Retrospective analysis of tocilizumabinduced neutropenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Arthritis Rheumatol
Koike, Harigai, Inokuma, Postmarketing surveillance of tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: interim analysis of 3881 patients, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1136/ard.2011.151092
Laurence, Farahi, Juss, Effects of tocilizumab on neutrophil function and kinetics, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:info:doi/10.1111/eci.12799
Lescure, Honda, Fowler, Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099–0
Li, Sempowski, Saunders, Acharya, Haynes, Sars-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for COVID-19 prevention and treatment, Annu Rev Med, doi:info:doi/10.1146/annurev-med-042420-113838
Mahroum, Watad, Bridgewood, Systematic review and meta-analysis of tocilizumab therapy versus standard of care in over 15,000 COVID-19 pneumonia patients during the first eight months of the pandemic, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:info:doi/10.3390/ijerph18179149
Mahroum, Watad, Bridgewood, Systematic review and meta-analysis of tocilizumab therapy versus standard of care in over 15,000 COVID-19 pneumonia patients during the first eight months of the pandemic, Int. J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18179149
Maláska, Stašek, Duška, Effect of dexamethasone in patients with ARDS and COVID-19 (REMED trial)-study protocol for a prospective, multi-centre, open-label, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial, Trials, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s13063-021-05963-6
Mazzitelli, Arrighi, Serapide, Use of subcutaneous tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, J Med Virol, doi:info:doi/10.1002/jmv.26016
Mccreary, Lemon, Megli, Monoclonal antibodies for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy, medRxiv, doi:info:doi/10.1101/2022.04.20.22274090
Mori, Yoshitama, Hidaka, Hirakata, Ueki, Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab therapy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and renal insufficiency: a real-life registry study in Japan (the ACTRA-RI study), Ann Rheum Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014–206695
Muhovi C, Bojovi C, Bulatovi C A, First case of drug-induced liver injury associated with the use of tocilizumab in a patient with COVID-19, Liver Int, doi:info:doi/10.1111/liv.14516
Munch, Granholm, Myatra, Higher vs. lower doses of dexamethasone in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxia (COVID STEROID 2) trial: protocol and statistical analysis plan, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, doi:info:doi/10.1111/aas.13795
Nishimoto, Ito, Takagi, Safety and efficacy profiles of tocilizumab monotherapy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analysis of six initial trials and five long-term extensions, Mod Rheumatol, doi:info:doi/10.3109/s10165-010-0279-5
Ochani, Asad, Yasmin, COVID-19 pandemic: from origins to outcomes. A comprehensive review of viral pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, and management, Infez Med
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:info:doi/10.1136/bmj.n71
Peng, She, Mei, Association between tocilizumab treatment and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Aging, doi:info:doi/10.18632/aging.203834
Piscoya, Del Parra Riego, Cerna-Viacava, Efficacy and harms of tocilizumab for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS ONE, doi:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0269368
Rocchi, Puxeddu, Cataldo, Hypersensitivity reactions to tocilizumab: role of skin tests in diagnosis, Rheumatol, doi:info:doi/10.1093/rheumatology/keu181
Rosas, Bräu, Waters, Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2028700
Rubio-Rivas, Forero, Mora-Luján, Beneficial and harmful outcomes of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pharmacotherapy, doi:info:doi/10.1002/phar.2627
Salama, Han, Yau, Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2030340
Salvarani, Dolci, Massari, Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med, doi:info:doi/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615
Serviddio, Villani, Stallone, Scioscia, Foschino-Barbaro et al., Tocilizumab and liver injury in patients with COVID-19, Therap Adv Gastroenterol, doi:info:doi/10.1177/1756284820959183
Shovman, Shoenfeld, Langevitz, Tocilizumab-induced neutropenia in rheumatoid arthritis patients with previous history of neutropenia: case series and review of literature, Immunol Res, doi:info:doi/10.1007/s12026-014-8590-4
Sieper, Porter-Brown, Thompson, Harari, Dougados, Assessment of short-term symptomatic efficacy of tocilizumab in ankylosing spondylitis: results of randomised, placebo-controlled trials, Ann Rheum Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013–203559
Soin, Kumar, Choudhary, Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00081–3
Somersan-Karakaya, Mylonakis, Menon, Casirivimab and imdevimab for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Infect Dis, doi:info:doi/10.1093/infdis/jiac320
Stone, Frigault, Nj, Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2028836
Tleyjeh, Kashour, Damlaj, Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in COVID-19 patients: a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.036
Trøseid, Hentzien, Ader, Immunocompromised patients have been neglected in COVID-19 trials: a call for action, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.cmi.2022.05.005
Veiga, Prats, Farias, Effect of tocilizumab on clinical outcomes at 15 days in patients with severe or critical coronavirus disease 2019: randomised controlled trial, BMJ, doi:info:doi/10.1136/bmj.n84
Wei, Lin, Wei, Tocilizumab treatment for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:info:doi/10.1186/s40249-021-00857-w
Zadeh, Asl, Forouharnejad, Mechanism and adverse effects of COVID-19 drugs: a basic review, Int J Physiol Pathophys Pharmacol
Zhao, Zhu, Zhang, Tocilizumab combined with favipiravir in the treatment of COVID-19: a multicenter trial in a small sample size, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110825
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bcp.70025",
"ISSN": [
"0306-5251",
"1365-2125"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bcp.70025",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Aims</jats:title><jats:p>This review aimed to synthesise the evidence related to the incidence of serious and non‐serious adverse events with the use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) among COVID‐19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Databases were searched from January 2020 to September 2023 for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that used mAbs for the treatment of COVID‐19 regardless of disease severity. Study screening, data extraction and data analysis were performed independently by two reviewers. The Cochrane risk of bias 1.0 tool was used for methodological quality assessment.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Sixteen studies were identified for analysis with 9682 participants in the intervention arm and 10 115 participants in the control arm. Seven trials reported hepatoxicity and there was a statistically significant increase in the chance of hepatoxicity among patients treated with mAbs compared to those given standard of care (SoC) or placebo with risk ratio (RR) = 1.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.29–2.24. Five trials reported for neutropenia and there was a statistically significant association of neutropenia with the use of mAbs compared to SoC or placebo with RR = 4.03, 95% CI 1.74–9.34. Ten trials reported any disease‐related serious adverse events related to the disease and there was a reduction of risk compared to SoC/placebo, although this reduction was not statistically significant (RR = 0.88, 95% CI 0.70–1.11).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>The use of mAbs was found to be associated with an increased risk of hepatoxicity and neutropenia compared to SoC/placebo among COVID‐19 patients with moderate certainty of evidence. Long‐term observational studies are recommended to observe post‐COVID adverse events related to the use of mAbs.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/bcp.70025"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2143-8629",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Htet",
"given": "Htet",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0005-8428-6177",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kyung",
"given": "Han You",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0326-424X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Burud",
"given": "Ismail Abdul Sattar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9948-4428",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jaiprakash",
"given": "Heethal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7073-8092",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Subramaniam",
"given": "Thiruselvi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2852-8486",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Iezhitsa",
"given": "Igor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3050-7449",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine IMU University Kuala Lumpur Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Agarwal",
"given": "Renu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Brit J Clinical Pharma",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-10T06:51:32Z",
"timestamp": 1741589492000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-28T07:16:31Z",
"timestamp": 1745824591000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009381",
"award": [
"BMS I‐2022 (15)"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100009381",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "International Medical University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-29T04:01:16Z",
"timestamp": 1745899276904,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1741219200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/bcp.70025",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1306-1321",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "COVID‐19 pandemic: from origins to outcomes. A comprehensive review of viral pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, and management",
"author": "Ochani R",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infez Med",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1",
"unstructured": "COVID‐19 cases| WHO COVID‐19 dashboard. datadot.https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwub‐HBhCyARIsAPctr7wt4KGje6JUmyWQljSMQWGhr8jvXTZSdsSZR5ay9OAp2p1uOWMFJb0aAmAXEALw_wcB. Published March 3 2024. Accessed March 23 2024."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID‐19.www.who.int.https://www.who.int/teams/health-care-readiness/covid-19/therapeutics. Accessed March 23 2024."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1",
"unstructured": "Clinical management of COVID‐19: living guideline 18 August 2023. www.who.int World Health Organization 13 Jan. 2023 www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2023.2. Accessed March 13 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265‐021‐01620‐z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1",
"unstructured": "COVID‐19 Treatment Guidelines Panel.Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed August 4 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265‐022‐01690‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879‐022‐07896‐0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.973246",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-78697-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Mechanism and adverse effects of COVID‐19 drugs: a basic review",
"author": "Zadeh MN",
"first-page": "102",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int J Physiol Pathophys Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228‐021‐03270‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18179149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010‐023‐02047‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/phar.2627",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249‐021‐00857‐w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1",
"unstructured": "HtetH KyungHY IezhitsaI et al.A systematic review and meta‐analysis of adverse events of WHO‐approved COVID‐19 treatment regimens. PROSPERO 2023 CRD42023447055.https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023447055"
},
{
"DOI": "10.37766/inplasy2023.8.0026",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1",
"unstructured": "HtetH KyungHY AgarwalR LezhitsaIN JaiprakashH BurudIAS.A systematic review and meta‐analysis of adverse events of WHO‐approved COVID‐19 treatment regimens. INPLASY Registration number: (2023) INPLASY202380026. doi:10.37766/inplasy2023.8.0026."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1",
"volume-title": "Covidence systematic review software"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1",
"unstructured": "International Council for Harmonisation.Clinical safety data management: definitions and standards for expedited reporting E2A. In the International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use 1994 Oct."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1",
"unstructured": "The Cochrane Collaboration.Review Manager (RevMan) (v 2020).www.revman.cochrane.org"
},
{
"author": "McMaster University and Evidence Prime",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1",
"volume-title": "GRADEpro GDT: gradepro guideline development tool [software]",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.16180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.16181",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.16179",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.16176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028836",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6820",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213‐2600(21)00099–0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(21)00676–0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2030340",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213‐2600(21)00081–3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n84",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110825",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(22)00163–5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.07.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac320",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.10.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238‐020‐00671‐y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev‐med‐042420‐113838",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12929‐021‐00784‐w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18179149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.05.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.14516",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_53_1"
},
{
"author": "National Library of Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_10_54_1",
"volume-title": "Tocilizumab [internet]. PubMed",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbspin.2022.105510",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_55_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.12799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_56_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.03.931766",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_57_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1756284820959183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_58_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aas.13795",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_59_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063‐021‐05963‐6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_60_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0192623312467400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_61_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0269368",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_62_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12026‐014‐8590‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_63_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/s10165‐010‐0279‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_64_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aas.13795",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_65_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Retrospective analysis of tocilizumab‐induced neutropenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [abstract]",
"author": "Kim Y",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_66_1",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/keq343",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_67_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis‐2013–203559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_68_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18176/jiaci.0314",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_69_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_70_1",
"unstructured": "Actemra (tocilizumab)—risk of fatal anaphylaxis—for health professionals: health Canada endorsed important safety information on Actemra (tocilizumab).http://healthycanadians.gc.ca/recall-alert-rappel-avis/hc-sc/2010/14586a-eng.php"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis‐2016–210297",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_71_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/keu181",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_72_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard.2011.151092",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_73_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis‐2014–206695",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_74_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5414/CN109971",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_75_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina59091517",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_76_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/0886022X.2023.2268213",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_77_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.04.20.22274090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_78_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_79_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.203834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_80_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.05.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_81_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 80,
"references-count": 80,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bcp.70025"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Adverse events associated with monoclonal antibodies used for treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "91"
}
htet