Neuropilin‐1 as a Neuroinflammatory Entry Factor for SARS‐CoV‐2 Is Attenuated in Vaccinated COVID‐19 Patients: A Case–Control Study
et al., Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.70630, Apr 2025
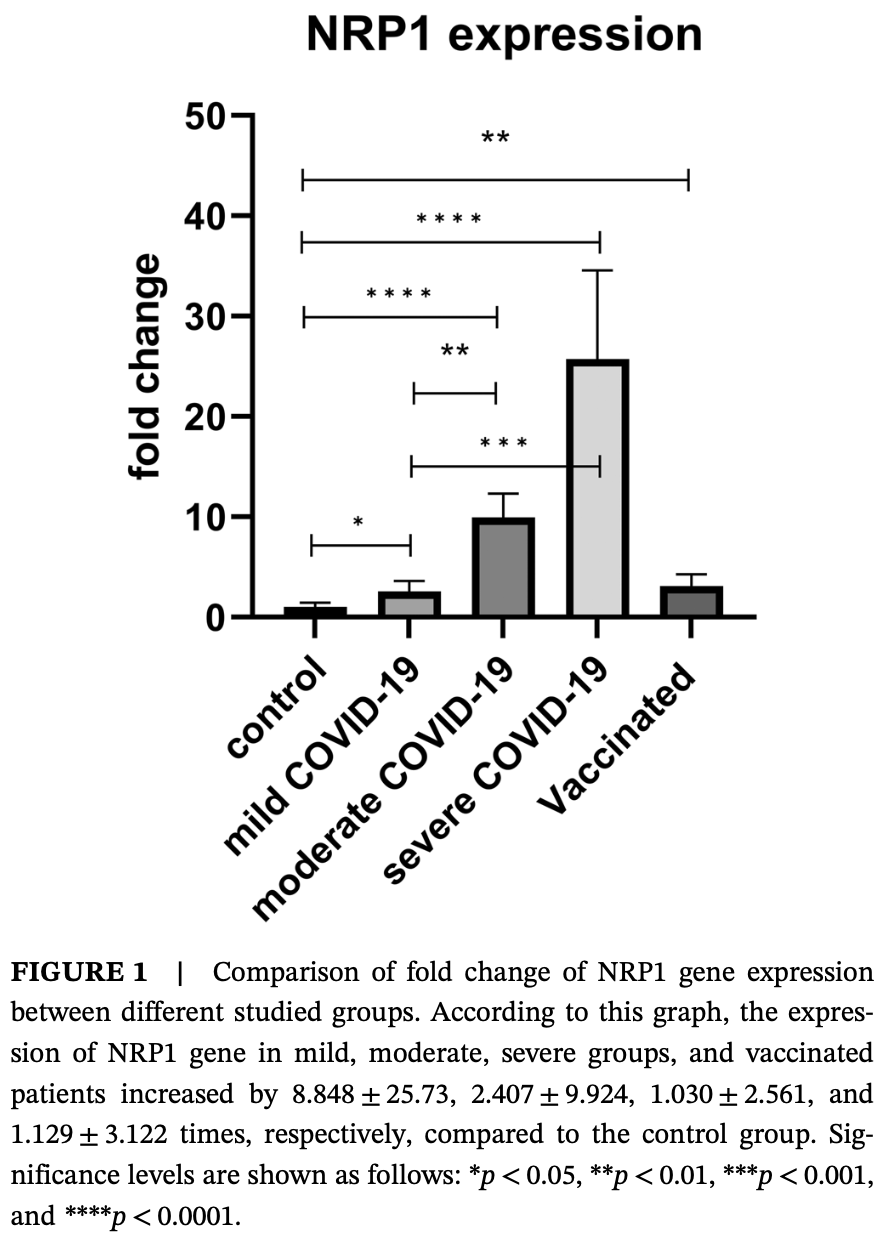
Case-control study of 80 COVID-19 patients and 30 healthy controls showing increased expression of Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and IL-6 genes in COVID-19 patients, with higher expression correlating with disease severity. Vaccinated COVID-19 patients had significantly lower IL-6 expression compared to unvaccinated patients with moderate and severe disease, and reduced NRP1 expression compared to other patient groups. Authors suggest NRP1 and IL-6 may serve as biomarkers of disease severity and potential therapeutic targets due to their role in inflammation and cytokine storm.
Hosseini et al., 7 Apr 2025, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: azadmehr2010@gmail.com, a.azadmehr@mubabol.ac.ir.
Neuropilin‐1 as a Neuroinflammatory Entry Factor for SARS‐CoV‐2 Is Attenuated in Vaccinated COVID‐19 Patients: A Case–Control Study
Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.70630
Background and Aim: COVID-19 is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) as a pandemic infectious disease. So far, it has been known that this virus uses several receptors to enter the host cell, one of which is neuropilin-1 (NRP1). Also, one of the main causes of clinical manifestations, severity of disease, and mortality of patients is cytokine storm syndrome, one of these cytokines being interleukin (IL)-6. Our aim was to study the level of expression of NRP1 and IL-6 genes in COVID-19 patients by using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Materials and Methods: Our study population included the test group (80 patients with COVID-19) and the control group (30 healthy individuals). Venous blood was taken from all subjects. After isolating PBMCs from blood using Ficoll, RNA was extracted. Then, cDNA synthesis, the expression level of NRP1 and IL-6 compared to GAPDH housekeeping gene was measured by real-time PCR. Results: The level of NRP1 gene expression was increased significantly in COVID-19 different groups compared to the control group. Surprisingly, it was observed that the amount of NRP1 gene decreased in the vaccinated group compared to nonvaccinated groups. IL-6 gene expression was also significantly increased in all groups except vaccinated patients compared to the control group. Also, the results indicated that there was a positive and statistically considerable relationship between IL-6 expression level and NRP1 expression level (p = 0.03).
Conclusion: The significant increase in the expression of NRP1 and IL-6 genes in COVID-19 patients, especially in moderate and severe cases, indicates their potential involvement in the progression of the disease, which may serve as biomarkers of disease severity. Also, since these genes play an important role in causing severe inflammation, cytokine storm, and immunopathological complications of COVID-19, further investigations maybe needed to achieve therapeutic goals to control COVID-19 and similar diseases.
Author Contributions Faezeh Hosseini: conceptualization, investigation, writingoriginal draft, writingreview and editing, visualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, data curation. Abbas Azadmehr: visualization, methodology, supervision, resources, project administration, funding acquisition, writingreview and editing, data curation, conceptualization, investigation. Kiarash Saleki: investigation, methodology, visualization, writingreview and editing, software, formal analysis, data curation. Mohamadreza Ahmadifard: methodology, investigation, visualization. Morteza Oladnabi: investigation, visualization, methodology. Moein Shirzad: methodology. Mostafa Javanian: visualization, investigation.
Ethics Statement This work was approved by Ethics Committee of Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol, Iran (IR.MUBABOL.REC.1401.038). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Anfinrud, Stadnytskyi, Bax, Bax, Visualizing Speech-Generated Oral Fluid Droplets With Laser Light Scattering, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2007800
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Neuropilin-1 Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry and Infectivity, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd298
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Neuropilin-1 Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry and Provides a Possible Pathway Into the Central Nervous System
Chang, Bai, You, Associations Between Serum Interleukins (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10) and Disease Severity of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/2022/2755246
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging Coronaviruses: Genome Structure, Replication, and Pathogenesis, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.25681
Davies, Randeva, Chatha, Neuropilin-1 as a New Potential SARS-CoV2 Infection Mediator Implicated in the Neurologic Features and Central Nervous System Involvement of COVID-19, Molecular Medicine Reports, doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11510
Dey, Bishayi, Microglial Inflammatory Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Comprehensive Review, Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, doi:10.1155/2021/8874339
Diao, Wang, Tan, Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827
Dotan, Muller, Kanduc, David, Halpert et al., The SARS-CoV-2 as an Instrumental Trigger of Autoimmunity, Autoimmunity Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102792
El Kazafy, Fouad, Said, Correlations Between Cytokine Levels, Liver Function Markers, and Neuropilin-1 Expression in Patients With COVID-19, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10101636
Guo, Vander Kooi, Neuropilin Functions as an Essential Cell Surface Receptor, Journal of Biological Chemistry, doi:10.1074/jbc.R115.687327
Gutiérrez-Ortiz, Méndez-Guerrero, Rodrigo-Rey, Miller Fisher Syndrome and Polyneuritis Cranialis in COVID-19, Neurology, doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000009619
Hasan, Ali, Ali, Evaluation of Serum Neuropilin-1 Level as a Potential Marker of COVID-19 Severity in Iraqi Population, HIV Nursing
Heidarvand, Hosseini, Kazemi, Differentially Expressed Inflammatory Cell Death-Related Genes and the Serum Levels of IL-6 Are Determinants for Severity of Coronaviruses Diseases-2019 (COVID-19), Advanced Biomedical Research, doi:10.4103/abr.abr_232_22
Henderson, Canna, Schulert, On the Alert for Cytokine Storm: Immunopathology in COVID-19, Arthritis & Rheumatology, doi:10.1002/art.41285
Hu, Hu, Qin, Lin, Jiang, In Silico Analysis Identifies Neuropilin-1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for SARS-Cov-2 Infected Lung Cancer Patients, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.203159
Kang, Kishimoto, Interplay Between Interleukin-6 Signaling and the Vascular Endothelium in Cytokine Storms, Experimental & Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00649-0
Keshar, Kaddah, Selim, Study of Serum Level of Interleukin-6 in COVID 19 Patients: Prognostic Value and Its Relation to Disease Progression, European Chemical Bulletin
Lambert, Bouttier, Vassy, HTLV-1 Uses HSPG and Neuropilin-1 for Entry by Molecular Mimicry of VEGF165, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2008-04-150342
Lashin, Value of Interleukin 6 in Assessment of the Disease Severity in Patients With COVID-19 Infection Without Preexisting Comorbidities, Benha Medical Journal, doi:10.21608/bmfj.2023.185224.1738
Liu, Zhang, Yang, The Role of Interleukin-6 in Monitoring Severe Case of Coronavirus Disease 2019, EMBO Molecular Medicine, doi:10.15252/emmm.202012421
Malekpour, Khanmohammadi, Meybodi, COVID-19 as a Trigger of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Review of the Molecular Mechanism, Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.875
Mateu-Salat, Urgell, Chico, SARS-COV-2 as a Trigger for Autoimmune Disease: Report of Two Cases of Graves' Disease After COVID-19, Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01366-7
Mcconnell, Kawaguchi, Kondo, Liver Injury in COVID-19 and IL-6 Trans-Signaling-Induced Endotheliopathy, Journal of Hepatology, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.050
Mota, Fotinou, Rana, Architecture and Hydration of the Arginine-Binding Site of Neuropilin-1, FEBS Journal, doi:10.1111/febs.14405
Norouzi, Liaghat, Bakhtiyari, The Potential Role of COVID-19 in Progression, Chemo-Resistance, and Tumor Recurrence of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC), Oral Oncology, doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106483
Ohla, Veldhuizen, Green, Increasing Incidence of Parosmia and Phantosmia in Patients Recovering From COVID-19 Smell Loss, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.08.28.21262763
Oladnabi, Bagheri, Rezaei, Kanavi, Azadmehr et al., Extremely Low Frequency-Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Affect Proangiogenic-Related Gene Expression in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells, Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, doi:10.22038/ijbms.2018.25023.6214
Pradhan, Correlation Between Inflammatory Markers With Disease Severity of COVID 19 Infection, International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research
Prasad, Awasthi, Kag, Sethia, Interleukin-6 Evaluation as a Biomarker for Disease Severity and Mortality in Covid 19 Patients, Trends in Clinical and Medical Sciences
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical Predictors of Mortality due to COVID-19 Based on an Analysis of Data of 150 Patients From Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Medicine, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Saleki, Alijanizadeh, Azadmehr, Is neuropilin-1 the Neuroimmune Initiator of Multi-System Hyperinflammation in COVID-19?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115558
Saleki, Aram, Alijanizadeh, Matrix Metalloproteinase/Fas Ligand (MMP/FasL) Interaction Dynamics in COVID-19: An In Silico Study and Neuroimmune Perspective, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30898
Saleki, Banazadeh, Miri, Azadmehr, Triangle of Cytokine Storm, Central Nervous System Involvement, and Viral Infection in COVID-19: The Role of sFasL and Neuropilin-1, Reviews in the Neurosciences, doi:10.1515/reneuro-2021-0047
Saleki, Shirzad, Javanian, Serum Soluble Fas Ligand Is a Severity and Mortality Prognostic Marker for COVID-19 Patients, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.947401
Setyo Nugroho, Marhana, Kusumastuti, Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Expression of Lung Tissue in COVID-19 Patient Severity Through Core Biopsy Post Mortem, Annals of Medicine and Surgery, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104648
Seyfi, Azadmehr, Ezoji, Mortality in ICU COVID-19 Patients Is Associated With Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR): Utility of NLR as a Promising Immunohematological Marker, Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1155/2023/9048749
Sherafat, Pfeiffer, Reiss, Wood, Nishiyama, Microglial Neuropilin-1 Promotes Oligodendrocyte Expansion During Development and Remyelination by Trans-Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22532-2
Szklarczyk, Kirsch, Koutrouli, The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest, Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac1000
Tanaka, Narazaki, Kishimoto, IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease, Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016295
Tanaka, Narazaki, Kishimoto, Therapeutic Targeting of the Interleukin-6 Receptor, Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134715
Toscano, Palmerini, Ravaglia, Guillain-Barré Syndrome Associated With Sars-Cov-2, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009191
Urazov, Chernov, Popov, Secretory Phospholipase A2 and Interleukin-6 Levels as Predictive Markers of the Severity and Outcome of Patients With COVID-19 Infections, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24065540
Van Doremalen, Bushmaker, Morris, Aerosol and Surface Stability of SARS-CoV-2 as Compared With SARS-CoV-1, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2004973
Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Neuropilin 1 Is an Entry Factor That Promotes EBV Infection of Nasopharyngeal Epithelial Cells, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/ncomms7240
Zalpoor, Akbari, Samei, The Roles of Eph Receptors, Neuropilin-1, P2X7, and CD147 in COVID-19-Associated Neurodegenerative Diseases: Inflammasome and JaK Inhibitors as Potential Promising Therapies, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-022-00311-1
Zamzami, Kabli, Alhothali, Post-COVID-19 Vaccine Parosmia: A Case Report, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.20292
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.70630",
"ISSN": [
"2398-8835",
"2398-8835"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.70630",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background and Aim</jats:title><jats:p>COVID‐19 is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus‐2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) as a pandemic infectious disease. So far, it has been known that this virus uses several receptors to enter the host cell, one of which is neuropilin‐1 (NRP1). Also, one of the main causes of clinical manifestations, severity of disease, and mortality of patients is cytokine storm syndrome, one of these cytokines being interleukin (IL)‐6. Our aim was to study the level of expression of NRP1 and IL‐6 genes in COVID‐19 patients by using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Materials and Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Our study population included the test group (80 patients with COVID‐19) and the control group (30 healthy individuals). Venous blood was taken from all subjects. After isolating PBMCs from blood using Ficoll, RNA was extracted. Then, cDNA synthesis, the expression level of NRP1 and IL‐6 compared to GAPDH housekeeping gene was measured by real‐time PCR.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The level of NRP1 gene expression was increased significantly in COVID‐19 different groups compared to the control group. Surprisingly, it was observed that the amount of NRP1 gene decreased in the vaccinated group compared to nonvaccinated groups. IL‐6 gene expression was also significantly increased in all groups except vaccinated patients compared to the control group. Also, the results indicated that there was a positive and statistically considerable relationship between IL‐6 expression level and NRP1 expression level (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The significant increase in the expression of NRP1 and IL‐6 genes in COVID‐19 patients, especially in moderate and severe cases, indicates their potential involvement in the progression of the disease, which may serve as biomarkers of disease severity. Also, since these genes play an important role in causing severe inflammation, cytokine storm, and immunopathological complications of COVID‐19, further investigations maybe needed to achieve therapeutic goals to control COVID‐19 and similar diseases.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/hsr2.70630"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-10-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-03-24"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-04-07"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
},
{
"name": "Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
}
],
"family": "Hosseini",
"given": "Faezeh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7698-9885",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Azadmehr",
"given": "Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
},
{
"name": "USERN Office Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of E‐Learning in Medical Sciences Faculty of Medical Education and Learning Technologies, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Saleki",
"given": "Kiarash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ahmadifard",
"given": "Mohamadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ischemic Disorders Research Center, Golestan University of Medical Sciences Gorgan Iran"
}
],
"family": "Oladnabi",
"given": "Morteza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
}
],
"family": "Shirzad",
"given": "Moein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine Research Center, Health Research Institute, Babol University of Medical Sciences Babol Iran"
}
],
"family": "Javanian",
"given": "Mostafa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Health Science Reports",
"container-title-short": "Health Science Reports",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T08:41:02Z",
"timestamp": 1744015262000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T08:41:19Z",
"timestamp": 1744015279000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T09:10:10Z",
"timestamp": 1744017010572,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 6,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743984000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/hsr2.70630",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2007800",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2004973",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd298",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.R115.687327",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2008-04-150342",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.14405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms7240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s11658-022-00311-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22532-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.41285",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134715",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a016295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/8874339",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-021-00649-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2023/9048749",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/reneuro-2021-0047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115558",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.947401",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22038/ijbms.2018.25023.6214",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac1000",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.07.137802",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_12_24_1",
"unstructured": "L.Cantuti‐Castelvetri R.Ojha L. D.Pedro et al. “Neuropilin‐1 Facilitates SARS‐CoV‐2 Cell Entry and Provides a Possible Pathway Into the Central Nervous System ” preprint BioRxiv 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2020.11510",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101636",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_26_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of Serum Neuropilin‐1 Level as a Potential Marker of COVID‐19 Severity in Iraqi Population",
"author": "Hasan M. S. S.",
"first-page": "1311",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "HIV Nursing",
"key": "e_1_2_12_27_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.20292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.08.28.21262763",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_12_29_1",
"unstructured": "K.Ohla M. G.Veldhuizen T.Green et al. “Increasing Incidence of Parosmia and Phantosmia in Patients Recovering From COVID‐19 Smell Loss ” preprint MedRxiv 2021 https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.28.21262763."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.203159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106483",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25681",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/abr.abr_232_22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21608/bmfj.2023.185224.1738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012421",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_35_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Correlation Between Inflammatory Markers With Disease Severity of COVID 19 Infection",
"author": "Pradhan A. K.",
"first-page": "653",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research",
"key": "e_1_2_12_36_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Interleukin‐6 Evaluation as a Biomarker for Disease Severity and Mortality in Covid 19 Patients",
"author": "Prasad R.",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Trends in Clinical and Medical Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_12_37_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24065540",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/2755246",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_40_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Study of Serum Level of Interleukin‐6 in COVID 19 Patients: Prognostic Value and Its Relation to Disease Progression",
"author": "Keshar N.",
"first-page": "3722",
"journal-title": "European Chemical Bulletin",
"key": "e_1_2_12_41_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102792",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2009191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01366-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0000000000009619",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_49_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hsr2.70630"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Neuropilin‐1 as a Neuroinflammatory Entry Factor for SARS‐CoV‐2 Is Attenuated in Vaccinated COVID‐19 Patients: A Case–Control Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "8"
}