Comparing Serum Levels of Vitamin D and Zinc in Novel Coronavirus–Infected Patients and Healthy Individuals in Northeastern Iran, 2020
et al., Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice, doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051, Aug 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
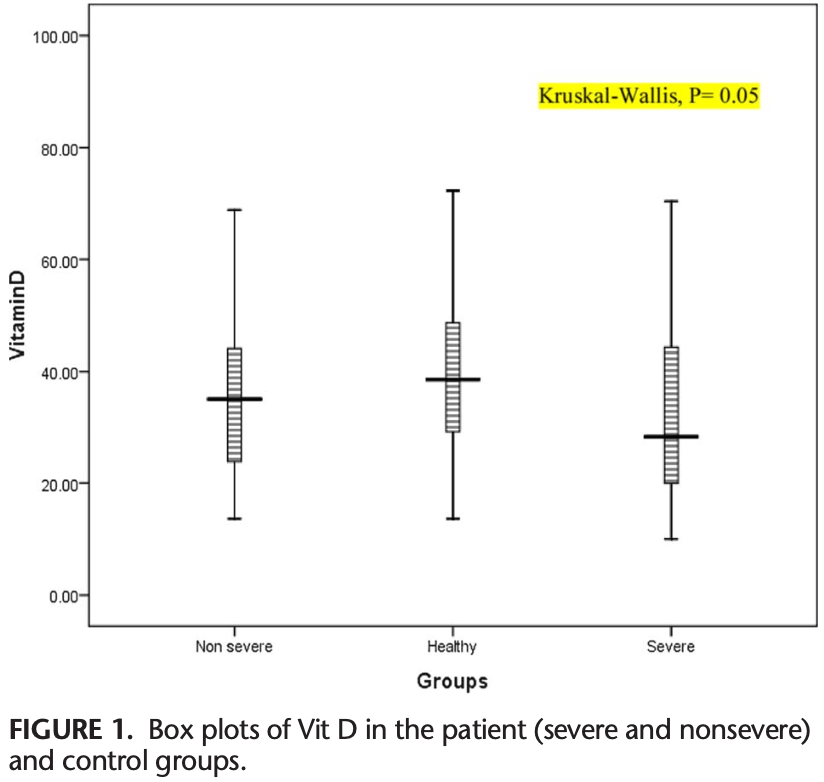
Analysis of 56 COVID-19 patients and 46 healthy control patients in Iran, showing that severe cases had lower levels of vitamin D compared with non-severe cases and healthy controls.
Study covers zinc and vitamin D.
Hosseini et al., 4 Aug 2021, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 24 March, 2020 - 5 May, 2020.
Contact: mahbobehfirooz@gmail.com.
Comparing Serum Levels of Vitamin D and Zinc in Novel Coronavirus-Infected Patients and Healthy Individuals in Northeastern Iran, 2020
Background: COVID-19 infection has recently become a pandemic disease around the world, and its risk factors have not fully evaluated. This study aimed to compare the serum vitamin D (Vit D) and zinc levels in patients infected with novel coronavirus and healthy volunteers (HVs). Methods: This was a single-center, cross-sectional study conducted on 56 patients (32 severe cases and 24 nonsevere) admitted to the COVID-19 ward and 46 HVs living in Esfarayen City, North Khorasan Province of Iran. Serum levels of Vit D and zinc in admitted patients to the COVID-19 ward and HVs were measured.
References
Ali, Nanji, A review on the role of vitamin D in asthma, Cureus
Beard, Bearden, Striker, Vitamin D and the anti-viral state, J Clin Virol
Bhat, Mudassir, Rather, Zinc levels in community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients; a case control study, Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc
Camini, Da, Caetano, Almeida, Implications of oxidative stress on viral pathogenesis, Arch Virol
Deng, Peng, Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China, J Clin Med
Finzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: a report on four patients, Int J Infect Dis
Ghoneim, Al-Azzawi, Elmasry, Association of vitamin D status in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc
Gilbert, Arum, Smith, Vitamin D deficiency and chronic lung disease, Can Respir J
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Griffin, Hewison, Hopkin, Vitamin D and COVID-19: evidence and recommendations for supplementation, Royal Soc Open Sci
Gruber-Bzura, Vitamin D and influenza-prevention or therapy, Int J Mol Sci
Hamidi Farahani, Gholami, Hazrati, Clinical features of ICU admitted and intubated novel corona virus-infected patients in Iran, Arch Clin Infect Dis
Hemilä, Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage, JRSM Open
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci Rep
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Scientific strabismus' or two related pandemics: COVID-19 & vitamin D deficiency, Br J Nutr
Karahan, Katkat, Impact of serum 25(OH) vitamin D level on mortality in patients with COVID-19 in Turkey, J Nutr Health Aging
Kaushik, Subramani, Anang, Zinc salts block hepatitis E virus replication by inhibiting the activity of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, J Virol
Kumar, Kubota, Chernov, Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, Med Hypotheses
Lodise, Tillotson, Managing bacterial infections in the era of COVID-19, Infect Dis Clin Pract
Luo, Liao, Shen, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 incidence and disease severity in Chinese people
Mamani, Muceli, Basir, Association between serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and community-acquired pneumonia: a case-control study, Int J Gen Med
Meehan, Penckofer, The role of vitamin D in the aging adult, J Aging Gerontol
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Network Open
Panagiotou, Tee, Ihsan, Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity, Clin Endocrinol (Oxf)
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Pletz, Terkamp, Schumacher, Vitamin D deficiency in community-acquired pneumonia: low levels of 1,25(OH)2 D are associated with disease severity, Respir Res
Reda, Abbas, Mohammed, The interplay between zinc, vitamin D and, IL-17 in patients with chronic hepatitis C liver disease, J Immunol Res
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Self-care for common colds: the pivotal role of vitamin D, vitamin C, zinc, and echinacea in three main immune interactive clusters (physical barriers, innate and adaptive immunity) involved during an episode of common colds-practical advice on dosages and on the time to take these nutrients/botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Shams, Afshari, Tajadini, The relationship of serum vitamin D and Zinc in a nationally representative sample of Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-III study, Med J Islam Repub Iran
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Zinc and respiratory tract infections: perspectives for COVID-19 (review), Int J Mol Med
Talat, Perry, Parsonnet, Vitamin d deficiency and tuberculosis progression, Emerg Infect Dis
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, She, Sims, Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wu, Wu, Zeng, Chest CT findings in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and its relationship with clinical features, Invest Radiol
Zhou, Du, Huang, Preventive effects of vitamin d on seasonal influenza A in infants: a multicenter, randomized, open, controlled clinical trial, Pediatric Infect Dis J
Zou, Chen, Zou, Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection, Front Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ipc.0000000000001051",
"ISSN": [
"1536-9943",
"1056-9103"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosseini",
"given": "Seyed Javad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moradi",
"given": "Bagher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marhemati",
"given": "Mahmood",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Firouzian",
"given": "Ali Asghar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ildarabadi",
"given": "Eshagh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abedi",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Firooz",
"given": "Mahbobeh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Clin Pract",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-04T17:03:18Z",
"timestamp": 1628096598000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-11T17:01:44Z",
"timestamp": 1636650104000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-25T13:52:09Z",
"timestamp": 1677333129347
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e390-e394",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2019722-e",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "bib2-20211111",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "bib3-20211111",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0",
"article-title": "Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "bib4-20211111",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical features of ICU admitted and intubated novel corona virus–infected patients in Iran",
"first-page": "e103295",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Arch Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "bib5-20211111",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/RLI.0000000000000670",
"article-title": "Chest CT findings in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and its relationship with clinical features",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Invest Radiol",
"key": "bib6-20211111",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/IPC.0000000000000894",
"article-title": "Managing bacterial infections in the era of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "251",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Clin Pract",
"key": "bib7-20211111",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxaa332",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 incidence and disease severity in Chinese people [corrected]",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "98",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "bib9-20211111",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "‘Scientific strabismus’ or two related pandemics: COVID-19 & vitamin D deficiency",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "bib10-20211111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "bib11-20211111",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A review on the role of vitamin D in asthma",
"first-page": "e1288-e",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "bib12-20211111",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid1605.091693",
"article-title": "Vitamin d deficiency and tuberculosis progression",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "853",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "bib13-20211111",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082419",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and influenza-prevention or therapy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2419",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "bib14-20211111",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2010.12.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the anti-viral state",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "bib15-20211111",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Self-care for common colds: the pivotal role of vitamin D, vitamin C, zinc, and echinacea in three main immune interactive clusters (physical barriers, innate and adaptive immunity) involved during an episode of common colds-practical advice on dosages and on the time to take these nutrients/botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds",
"first-page": "5813095",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "bib16-20211111",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1001176-e",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "bib17-20211111",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc salts block hepatitis E virus replication by inhibiting the activity of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase",
"first-page": "e00754",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "bib18-20211111",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc lozenges and the common cold: a meta-analysis comparing zinc acetate and zinc gluconate, and the role of zinc dosage",
"first-page": "2054270417694291",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JRSM Open",
"key": "bib19-20211111",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-016-3187-y",
"article-title": "Implications of oxidative stress on viral pathogenesis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "907",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Virol",
"key": "bib20-20211111",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "The relationship of serum vitamin D and Zinc in a nationally representative sample of Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-III study",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Med J Islam Repub Iran",
"key": "bib21-20211111",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"article-title": "Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20191",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "bib23-20211111",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsos.201912",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19: evidence and recommendations for supplementation",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201912",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Royal Soc Open Sci",
"key": "bib24-20211111",
"volume": "7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1465-9921-15-53",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in community-acquired pneumonia: low levels of 1,25(OH)2 D are associated with disease severity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "bib25-20211111",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Preventive effects of vitamin d on seasonal influenza A in infants: a multicenter, randomized, open, controlled clinical trial",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Pediatric Infect Dis J",
"key": "bib26-20211111",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14276",
"article-title": "Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "508",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Endocrinol (Oxf)",
"key": "bib27-20211111",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S149049",
"article-title": "Association between serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and community-acquired pneumonia: a case-control study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "bib28-20211111",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12974/2309-6128.2014.02.02.1",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the aging adult",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "60",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Aging Gerontol",
"key": "bib29-20211111",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejcdt.2015.06.004",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc",
"key": "bib30-20211111",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2009/829130",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and chronic lung disease",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Can Respir J",
"key": "bib31-20211111",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejcdt.2015.12.020",
"article-title": "Zinc levels in community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients; a case control study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "485",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc",
"key": "bib32-20211111",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109848",
"article-title": "Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109848",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "bib33-20211111",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"article-title": "Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: a report on four patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "bib34-20211111",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The interplay between zinc, vitamin D and, IL-17 in patients with chronic hepatitis C liver disease",
"first-page": "846348",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "bib35-20211111",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc and respiratory tract infections: perspectives for COVID-19 (review)",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Med",
"key": "bib36-20211111",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-020-1479-0",
"article-title": "Impact of serum 25(OH) vitamin D level on mortality in patients with COVID-19 in Turkey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Health Aging",
"key": "bib37-20211111",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "bib38-20211111",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/IPC.0000000000001051"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Comparing Serum Levels of Vitamin D and Zinc in Novel Coronavirus–Infected Patients and Healthy Individuals in Northeastern Iran, 2020",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "29"
}
